The document discusses features and concepts related to .NET, including:
- .NET supports object oriented programming and dynamic web pages. It provides efficient data access, code sharing capabilities, and improved security.
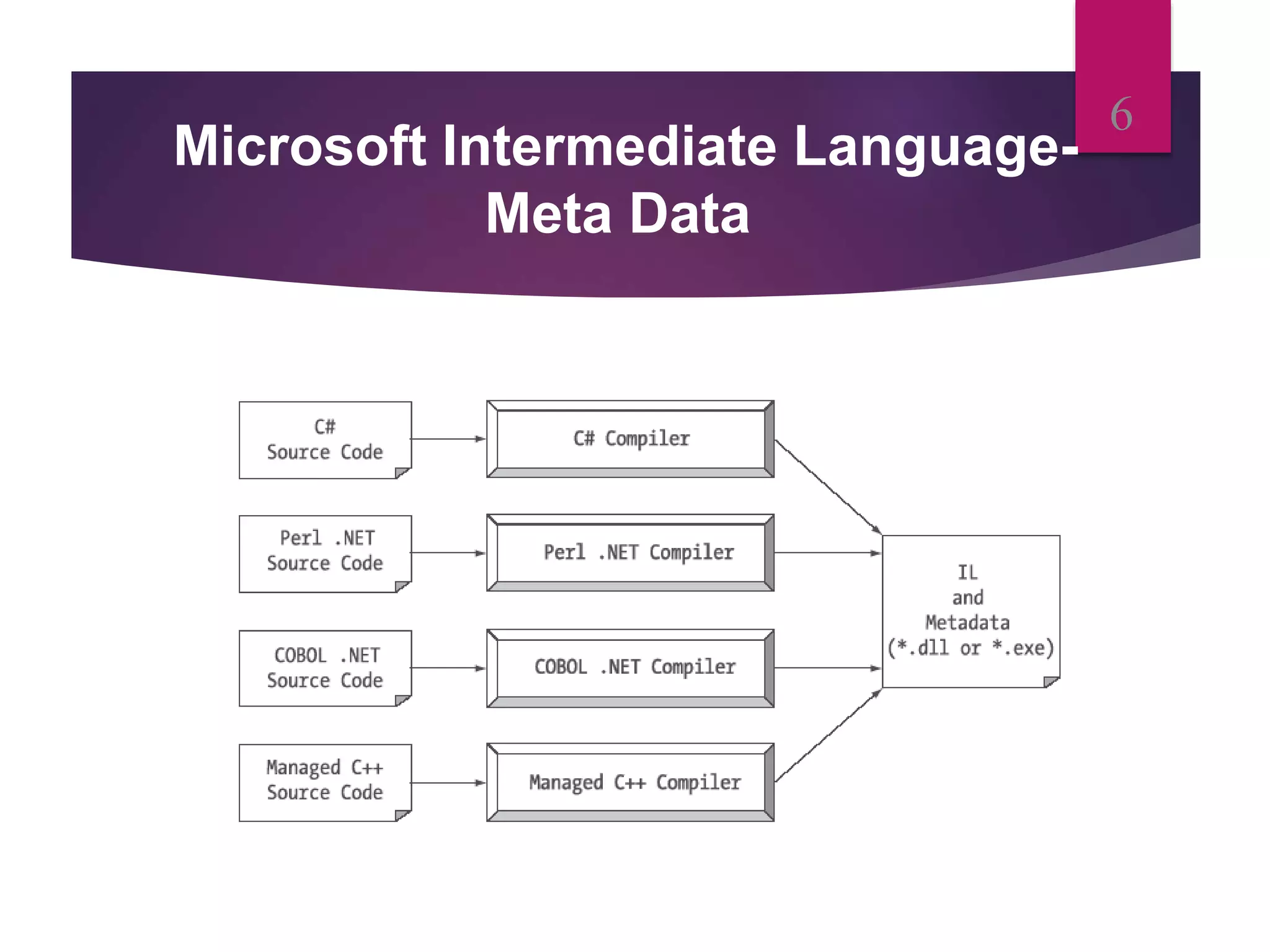
- Source code in any .NET language is compiled to Microsoft Intermediate Language (MSIL) code. At runtime, MSIL is converted to machine code by the Just-In-Time compiler.
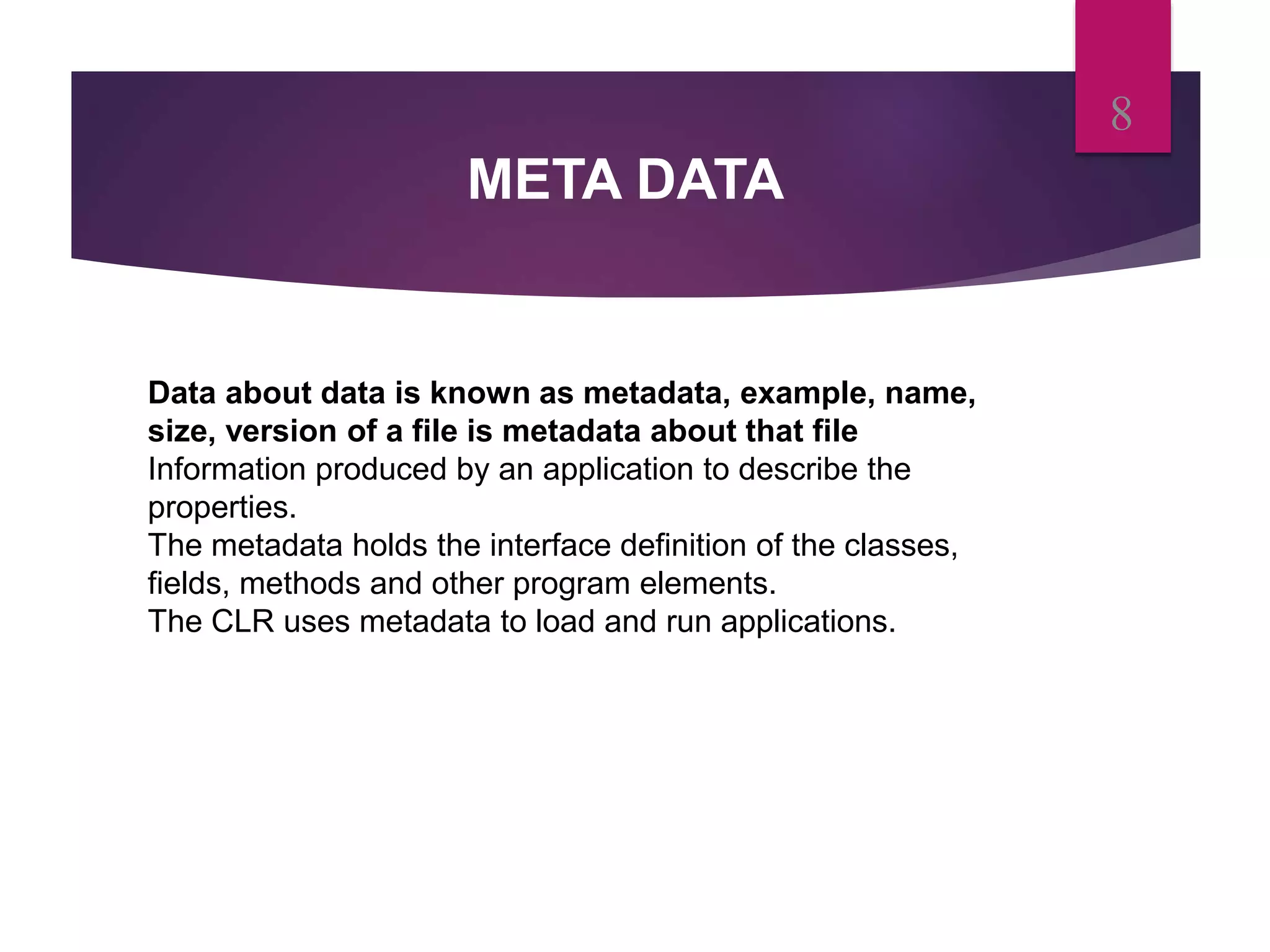
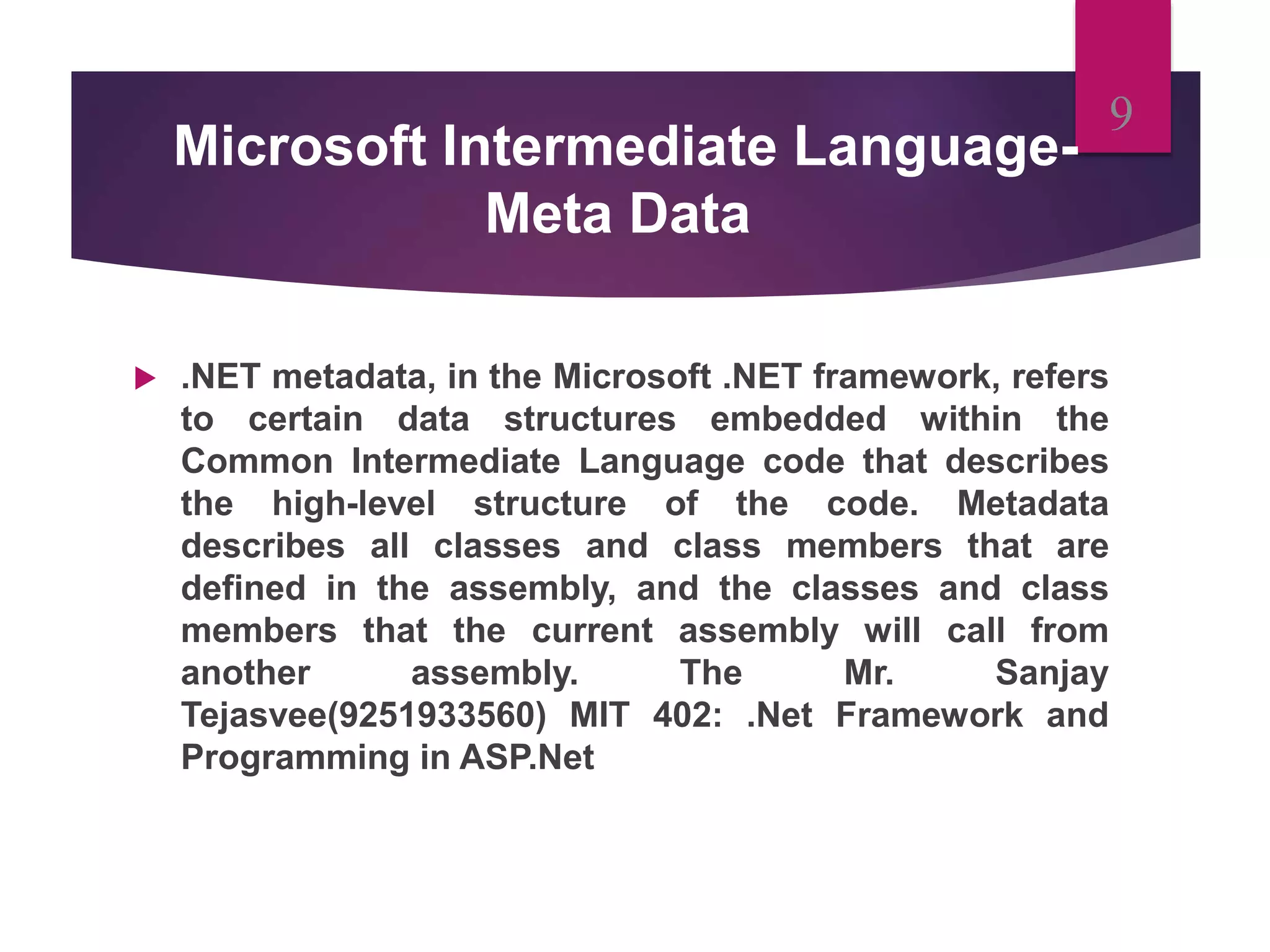
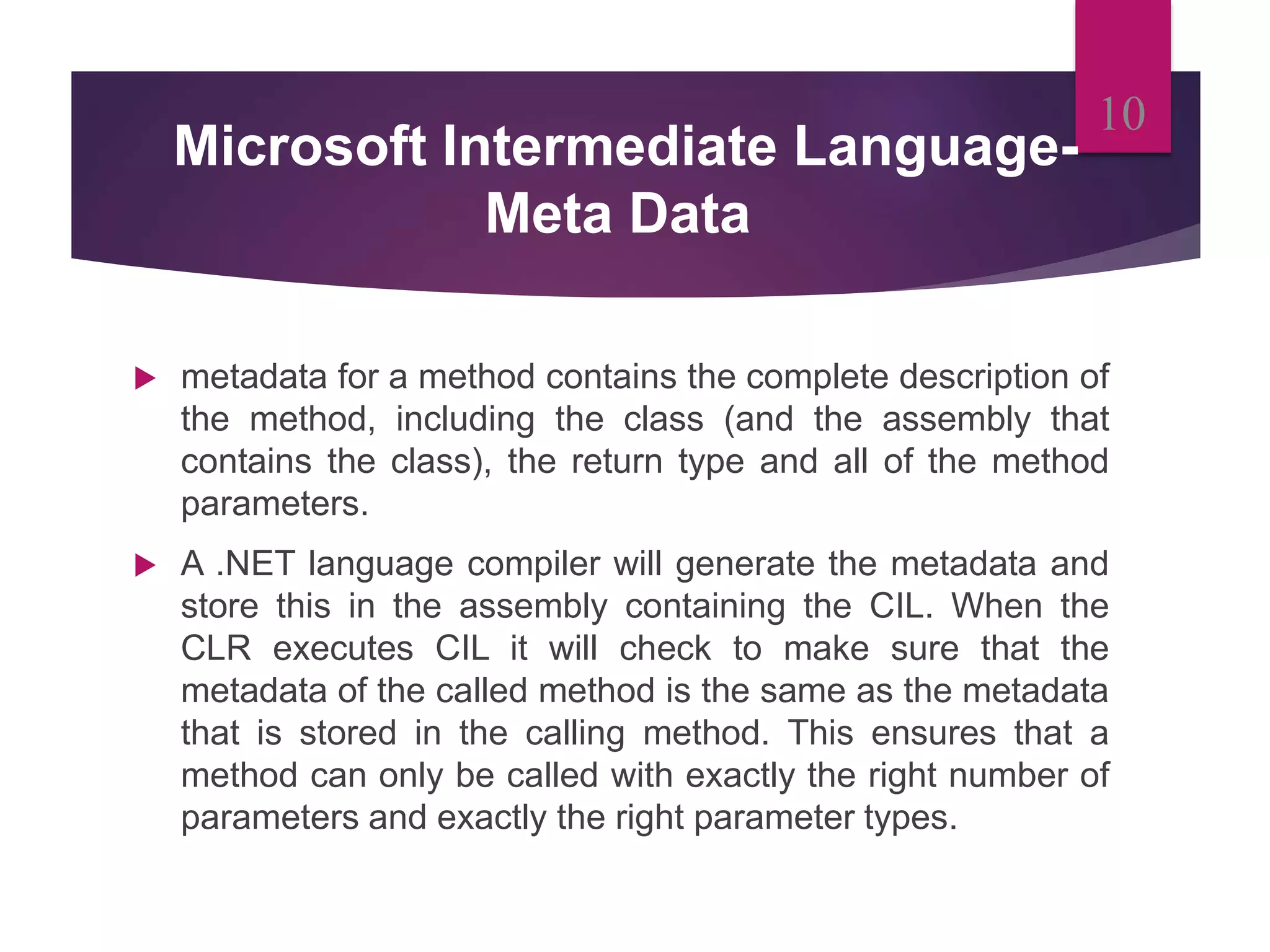
- Metadata contains data describing classes, methods, and other elements in .NET applications. The common language runtime uses metadata to load and execute applications.