karyotype.pptx
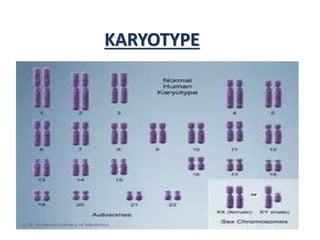
- 1. KARYOTYPE
- 2. • The general morphology i.e., the size of chromosome, the position of centromere, the presence of secondary constrictions and the size of satellite bodies of the somatic chromosome complement of an individual constitutes its karyotype. • The karyotype of a normal somatic cell of a normal individual represents the karyotype of the concerned species.
- 3. • A perfectly symmetrical karyotype has all metacentric chromosomes of the same size. • Karyotype showing a deviation from this state are called asymmetrical • Species showing a greater asymmetry in their karyotype are considered more advanced than those showing less asymmetry.
- 4. IDIOTYPE • The karyotype of a species may be repeated diagrammatically showing all the morphological features of the chromosomes. • Gives same amount of the information as the concerned karyotype.
- 5. APPLICATION OF KARYOTYPING • To detect and study structural and numerical chromosomal change. • The karyotypes of different group compared and similarities in karyotype are considered to represent evolutionary relationship. • It also suggests primitive or advanced feature of an organism.
- 7. • Band is a part of chromosome which is clearly distinguishable from its adjacent segments by appearing darker or lighter with various banding methods. • The artificial production of such bands by treatment with specific dyes is referred to as chromosome banding. • Banding techniques are based on identification of chromosome segment that consist that consist of either AT & GC rich region or of constitutive hetrochromatin.
- 8. • The pattern of chromosome banding is highly specific in each chromosome of a species. • Depending upon the pre treatment of the chromosome and the used dyes or fluorochromes, most common type of banding techniques are: i. Q-banding ii. C-banding iii. G-banding iv. R-banding
- 9. Q /Fluorescent Banding • First banding technique used by Caspersson, Zech and Johannson(1970). • Quinacrine mustard or quinacrine dihydrochloride produces bright and dull flourescent bands known as Q-Bands. • Bright bands are composed of DNA that was rich in the bases A&T due to formation of AT-quinacrin complex fluorescens.
- 10. C-Banding • Stains constitutive heterochromatin usually lies near centromere. • Heterochromatin binds a lot of the dye(Giemsa), while the rest of the chromosomes absorb only little of it. Denaturation Renaturation Staining • Well suited for the characterization of plant chromosomes
- 11. G-Banding • Uses geimsa dye. - Giemsa stain, named after Gustav Giemsa, - It is a mixture of methylene blue and eosin. • No pretreatment before staining else resembles the C Banding. • G-Band visualizes the sulphur rich regions of chromosome. • Well suited for animal cells.
- 12. R-Banding • Stains regions rich in GC that are typical for euchromatin. • Helpful in staining the distal ends of chromosome. • Patterns reverse of G Bands. • Helpful in staining the distal ends of chromosomes therefore used to detect deletions and translocation that involves telomeres of chromosomes • Stained used- acridine orange dyes.
- 14. • in situ hybridization technique is to locate physical position of a known DNA sequences on the chromosome, thus helps in the physical mapping of genes or repeated DNA sequences. • DNA is denatured then incubated in a solution of labelled DNA, whose position on a chromosome, we are interested in knowing • Therefore repeated or unique DNA sequences can be utilized as radioactive labelled or biotinylated probes for the study of the location of these sequences on the chromosomes
- 15. General steps with minor variation 1. Label the probe (e.g. biotinylated UTP) 2. Preheat the slides and denaturate chromosomal DNA 3. Denature the probe and prepare hybridization mix 4. Place labelled probe and place the cover slip and seal and incubate 4-14 hrs at 40°C 5. Remove cover slip and wash off hybridization mix. 6. Drain the slides but do not dry. 7. Subject to detection procedure(staining and visulization)
- 16. Fluorescencence in situ hybridization • Used to detect the presence and absence of known DNA sequence on chromosome. • FISH involves the depositing a fluorescent molecule at the site of in situ hybridization • Fluorescence visualized under fluorescent microscope. • Probes can be genome or chromosome specific DNA or single copy sequence
- 17. STEPS INVOLVED IN FISH Melting of DNA ( both in nucleus and in probe ) Labelling of probe with fluorescent molecule eg.Biotin Hybridization with the probe Incubation in immuno fluorescent reagent Fluorescent microscopy
- 18. ADVANTAGES • High resolution • High sensitivity and speed • Variety of probe labelling schemes • Hybridization of repeated sequence can be supressed by prehybridization • Both metaphase cells spread or interphase nuclei can be fixed on slides.
- 19. GENOMIC IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION • Total genomic DNA derived from alien species is used as a probe, for in situ hybridization to identify the presence of whole chromosome or chromosome segment from the corresponding alien species in a crop background. • The probe is used together with excess amount of unlabelled blocking DNA from the species being probed, (also called genome blocking ).
- 20. • This excess DNA blocks the genome of species being probed so that the labelled alien genomic DNA may not hybridize with it, thus permitting the detection of presence of the alien chromatin.
- 21. Multi color FISH • Used to detect the presence of introgressed alien chromatin in a crop species. • Uses mixtures of differently colored probes. • Each chromosome identified by a characteristic color using whole chromosome probe mixtures and variety of ratios of colors. • Indirect method for mcFISH uses biotin or antibodies as fluorescent molecules • Direct method uses fluorochrome-labelled nucleotide for probe labelling. Hence no need for immunocytochemical detection.
- 22. Application Of in situ Hybridization • Chromosome mapping - utilized in many plants to identify chromosome accurately using species specific probes, ribosomal genes and even unique sequence. • Genome analysis – GISH permits characterization of the genome and chromosome of hybrid plants,allopolyploid and recombinant inbred lines.
- 23. • Phylogenetic relationship – GISH offers new opportunities in phylogenetic and taxonomic studies for determining and testing genomic relationship of wild and cultivated plant species giving unique information about similarities between DNA from related species. • Analysis of somaclonal variation – useful in identifying the type of genomic changes that might occur during in vitro culture. • Detection of alien chromatid – not only can be identified but can also be counted in wide hybrids and amphidiploids.
- 24. • Detection of chromosomal abberations : it permits the identification of small chromosome aberrations, which are not readily detected by standard high resolution banding technique. • Chromosome organization at interphase nuclei : useful for investigating chromosome organized in the interphase nucleus, orientation of telomeres and centromeres, special location of individual chromosome and the relationship between chromatin decondensation and gene expression.
- 25. CHROMOSOME PAINTING • Refers to the hybridization of fluorescently labeled chromosome specific, composite probe pools to cytological preparations • The simultaneous hybridization of multiple chromosome painting probes, each attached with a specific fluorochrome combination of multiple chromosome painting probe, each tagged with a specific fluorochrome resulting in differential color display of individual chromosomes i.e., color karyotyping
- 26. APPLICATION OF CHROMOSOME PAINTING • Marker chromosome classification. • Detection of small translocation which are cytogenetically similar in appearance. • To study complex chromosomal aberrations.
- 27. References • Singh BD. 2009. Genetics. Kalyani Publications • Devi J, Ko JM and Seo BB. 2005. FISH and GISH modern cytogenetic techniques. Indian journal of biotechnology. 4 • Gupta PK. 2007. Cytogenetics. Rastogi publications