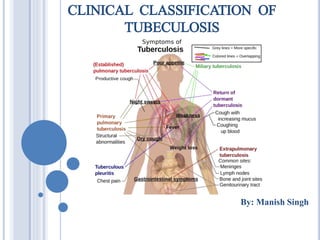
CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION OF TUBECULOSIS
- 1. CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION OF TUBECULOSIS By: Manish Singh
- 2. TUBERCULOSIS: INTRODUCTION Tuberculosis (TB), is one of the oldest diseases known to affect humans and is likely to have existed in prehominids, is a major cause of death worldwide. This disease is caused by bacteria of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and usually affects the lungs, although other organs are involved in up to one-third of cases. If properly treated, TB caused by drug-susceptible strains is curable in virtually all cases. If untreated, the disease may be fatal within 5 years in 50–65% of cases. Transmission usually takes place through the airborne spread of droplet nuclei produced by patients with infectious pulmonary TB.
- 3. EPIDEMIOLOGY Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis(MTB), which is part of a complex of organisms including M. bovis (reservoir cattle) and M. africanum (reservoir human). Recent figures suggest a decline in the incidence of TB, but its impact on world health remains significant. In 2010, an estimated 8.8 million incident cases occurred and TB was estimated to account for nearly 1.5 million deaths, making it the second most common cause of death due to an infective disease. Furthermore, it is estimated that around one-third of the world’s population has latent TB.
- 4. CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS TB is classified mainly in Two groups Pulmonary TB Primary Pulmonary Disease Post-Primary pulmonary Disease (Adult-Type) Miliary TB Extra-Pulmonary TB Lymph Node TB (Lymphadenitis) Pleural TB TB of Upper Airways Genitourinary TB Skeletal TB Tuberculous Meningitis & Tuberculoma Gastrointestinal TB Pericardial TB (Tuberculous Pericarditis) HIV-Associated TB Less Common Extra-Pulmonary Forms
- 6. Pulmonary TB Primary Pulmonary Disease: Primary TB refers to the infection of a previously uninfected (tuberculin-negative) individual. A few patients develop a self- limiting febrile illness but clinical disease only occurs if there is a hypersensitivity reaction or progressive infection. Progressive primary disease may appear during the course of the initial illness or after a latent period of weeks or months.
- 7. FEATURES OF PRIMARY TB Infection (4–8 wks) Influenza-like illness Primary complex Skin test conversion Disease Lymphadenopathy: hilar (often unilateral), paratracheal or mediastinal Collapse (especially right middle lobe) Consolidation (especially right middle lobe) Obstructive emphysema Cavitation (rare) Pleural effusion Miliary Meningitis Pericarditis Hypersensitivity Erythema nodosum Phlyctenular conjunctivitis Dactylitis
- 8. POST-PRIMARY PULMONARY DISEASE (ADULT-TYPE) Also referred adult type TB, refers to exogenous (‘new’ infection) or endogenous (reactivation of a dormant primary lesion) infection in a person who has been sensitised by earlier exposure. It is most frequently pulmonary and characteristically occurs in the apex of an upper lobe, where the oxygen tension favours survival of the strictly aerobic organism. The onset is usually insidious, developing slowly over several weeks. Systemic symptoms include fever, night sweats, malaise, and loss of appetite and weight, and are accompanied by progressive pulmonary symptoms. In extensive disease, collapse may be marked and results in significant displacement of the trachea and mediastinum. Occasionally, a caseous lymph node may drain into an adjoining bronchus, leading to tuberculous pneumonia.
- 9. Chest X-ray: major manifestations and differential diagnosis of pulmonary TB
- 10. Miliary TB Blood-borne dissemination gives rise to miliary TB, which may present acutely but more frequently is characterised by 2–3 weeks of fever, night sweats, anorexia, weight loss and a dry cough. Hepatosplenomegaly may develop and the presence of a headache may indicate coexistent tuberculous meningitis. Auscultation of the chest is frequently normal, but in more advanced disease, widespread crackles are evident. Fundoscopy may show choroidal tubercles. The classical appearances on chest X-ray are of fine 1–2 mm lesions (‘millet seed’) distributed throughout the lung fields, although occasionally the appearances are coarser. Anaemia and leucopenia reflect bone marrow involvement. ‘Cryptic’ miliary TB is an unusual presentation sometimes seen in old age.
- 11. KEY POINT FOR CRYPTIC MILIARY TB Age over 60 yrs Intermittent low-grade pyrexia of unknown origin Unexplained weight loss, general debility (hepatosplenomegaly in 25–50%) Normal chest X-ray Blood dyscrasias; leukaemoid reaction, pancytopenia Negative tuberculin skin test Confirmation by biopsy with granulomas and/or acid-fast bacilli in liver or bone marrow
- 12. EXTRA-PULMONARY TB Extrapulmonary sites most commonly involved in TB are the lymph nodes, pleura, genitourinary tract, bones and joints, meninges, peritoneum, and pericardium. However, virtually all organ systems may be affected. As a result of hematogenous dissemination in HIV- infected individuals, extrapulmonary TB is seen more commonly today than in the past. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis accounts for about 20% of cases in those who are HIV-negative but is more common in HIV-positive individuals.
- 13. SYSTEMIC PRESENTATIONS OF EXTRAPULMONARY TB
- 14. Lymph Node TB (Lymphadenitis) Once caused mainly by M. bovis, tuberculous lymphadenitis is today due largely to M. tuberculosis. Lymph nodes are the most common extrapulmonary site of disease. Cervical and mediastinal glands are affected most frequently, followed by axillary and inguinal, and more than one region may be involved. Disease may represent primary infection, spread from contiguous sites, or reactivation. Supraclavicular lymphadenopathy is often the result of spread from mediastinal disease. The nodes are usually painless and initially mobile but become matted together with time. When caseation and liquefaction occur, the swelling becomes fluctuant and may discharge through the skin with the formation of a ‘collar-stud’ abscess and sinus formation. The tuberculin test is usually strongly positive. During or after treatment, paradoxical enlargement, development of new nodes and suppuration may all occur but without evidence of continued infection; surgical excision is rarely necessary.
- 15. Pleural TB Involvement of the pleura accounts for 20% of extrapulmonary cases. Isolated pleural effusion usually reflects recent primary infection, and the collection of fluid in the pleural space represents a hypersensitivity response to mycobacterial antigens. Pleural disease may also result from contiguous parenchymal spread, as in many cases of pleurisy accompanying postprimary disease. Depending on the extent of reactivity, the effusion may be small, remain unnoticed, and resolve spontaneously or may be sufficiently large to cause symptoms such as fever, pleuritic chest pain, and dyspnea. Physical findings are those of pleural effusion: dullness to percussion and absence of breath sounds. A chest radiograph reveals the effusion and, in up to one-third of cases, also shows a parenchymal lesion. The pleural fluid is purulent and thick and contains large numbers of lymphocytes. Acid-fast smears and mycobacterial cultures are often positive. Surgical drainage is usually required as an adjunct to chemotherapy. Tuberculous empyema may result in severe pleural fibrosis and restrictive lung disease. Removal of the thickened visceral pleura (decortication) is occasionally necessary to improve lung function.
- 16. TB of Upper Airways TB of the upper airways may involve the larynx, pharynx, and epiglottis. Symptoms include hoarseness, dysphonia, and dysphagia in addition to chronic productive cough. Findings depend on the site of involvement, and ulcerations may be seen on laryngoscopy. Acid-fast smear of the sputum is often positive, but biopsy may be necessary in some cases to establish the diagnosis. Note:- Carcinoma of the larynx may have similar features but is usually painless.
- 17. Genitourinary TB Genitourinary TB, which accounts for 10–15% of all extrapulmonary cases, may involve any portion of the genitourinary tract. Local symptoms predominate, Fever and night sweats are rare with renal tract TB and patients are often only mildly symptomatic for many years. Haematuria, frequency and dysuria are often present, with sterile pyuria found on urine microscopy and culture. Genital TB is diagnosed more commonly in female than in male patients. In women, infertility from endometritis, or pelvic pain and swelling from salpingitis or a tubo-ovarian abscess occurs occasionally. In men, genitourinary TB may present as epididymitis or prostatitis. Genitourinary TB responds well to chemotherapy
- 18. MRI of culture-confirmed renal tuberculosis. T2-weighted coronary plane: coronal sections showing several renal lesions in both the cortical and the medullary tissues of the right kidney
- 19. Skeletal TB TB of the bones and joints is responsible for 10% of extrapulmonary cases. The spine is the most common site for bony TB (Pott’s disease), which usually presents with chronic back pain and typically involves the lower thoracic and lumbar spine . The infection starts as a discitis and then spreads along the spinal ligaments to involve the adjacent anterior vertebral bodies, causing angulation of the vertebrae with subsequent kyphosis. Paravertebral and psoas abscess formation is common and the disease may present with a large (cold) abscess in the inguinal region. The major differential diagnosis is malignancy, which tends to affect the vertebral body and leave the disc intact. Important complications include spinal instability or cord compression. TB can affect any joint but most frequently involves the hip or knee. Presentation is usually insidious, with pain and swelling; fever and night sweats are uncommon. Radiological changes are often non-specific but, as disease progresses, reduction in joint space and erosions appear. Poncet’s arthropathy is an immunologically mediated polyarthritis that usually resolves within 2 months of starting treatment.
- 20. CT scan demonstrating destruction of the right pedicle of T10 due to Pott's disease. The patient, a 70-year-old Asian woman, presented with back pain and weight loss and had biopsy-proven tuberculosis.
- 21. Tuberculous Meningitis & Tuberculoma TB of the central nervous system accounts for 5% of extrapulmonary cases. It is seen most often in young children but also develops in adults, especially those infected with HIV. Tuberculous meningitis results from the hematogenous spread of primary or postprimary pulmonary TB or from the rupture of a subependymal tubercle into the subarachnoid space. The disease often presents subtly as headache and slight mental changes after a prodrome of weeks of low-grade fever, malaise, anorexia, and irritability. Typically, the disease evolves over 1–2 weeks, a course longer than that of bacterial meningitis. Since meningeal involvement is pronounced at the base of the brain, paresis of cranial nerves (ocular nerves in particular) is a frequent finding, and the involvement of cerebral arteries may produce focal ischemia. The ultimate evolution is toward coma, with hydrocephalus and intracranial hypertension. Tuberculoma, an uncommon manifestation of central nervous system TB, presents as one or more space-occupying lesions and usually causes seizures and focal signs.
- 22. Gastrointestinal TB Gastrointestinal TB is uncommon, making up 3.5% of extrapulmonary cases. TB can affect any part of the bowel and patients may present with a wide range of symptoms and signs Various pathogenetic mechanisms are involved: swallowing of sputum with direct seeding, hematogenous spread, ingestion of milk from cows affected by bovine TB. Although any portion of the gastrointestinal tract may be affected, the terminal ileum and the cecum are the sites most commonly involved. Fever, night sweats, anorexia and weight loss are usually prominent and a right iliac fossa mass may be palpable. Ultrasound or CT may reveal thickened bowel wall, abdominal lymphadenopathy, mesenteric thickening or ascites. Barium enema and small bowel enema reveal narrowing, shortening and distortion of the bowel, with caecal involvement predominating. Diagnosis rests on obtaining histology by either colonoscopy or mini- laparotomy. The main differential diagnosis is Crohn’s disease.
- 23. Pericardial TB (Tuberculous Pericarditis) Due either to direct extension from adjacent mediastinal or hilar lymph nodes or to hematogenous spread,pericardial TB has often been a disease of the elderly. Disease occurs in two pericardial effusion and constrictive pericarditis. Fever and night sweats are rarely prominent and the presentation is usually insidious, with breathlessness and abdominal swelling. Coexistent pulmonary disease is very rare, with the exception of pleural effusion. Pulsus paradoxus, hepatomegaly, prominent ascites and peripheral oedema are common to both types. Pericardial effusion is associated with increased pericardial dullness and a globular enlarged heart on chest X-ray, and pericardial calcification occurs in around 25% of cases. Constriction is associated with an early third heart sound and, occasionally, atrial fibrillation. Diagnosis is based on the clinical, radiological and echocardiographic. The effusion is frequently blood-stained. Open pericardial biopsy can be performed where there is diagnostic uncertainty. The addition of corticosteroids to antituberculosis treatment has been shown to help both forms of pericardial disease.
- 24. HIV-Associated TB TB can appear at any stage of HIV infection, and its presentation varies with the stage. When CMI is only partially compromised, pulmonary TB presents in a typical manner with upper-lobe infiltrates and cavitation and without significant lymphadenopathy or pleural effusion. In late stages of HIV infection, a primary TB–like pattern, with diffuse interstitial or miliary infiltrates, little or no cavitation, and intrathoracic lymphadenopathy, is more common. Extrapulmonary TB is common among HIV-infected patients. The most common forms are lymphatic, disseminated,pleural, and pericardial. Mycobacteremia and meningitis are also frequent, particularly in advanced HIV disease.
- 25. Less Common Extra-Pulmonary Forms Tuberculous otitis is rare and presents as hearing loss, otorrhea, and tympanic membrane perforation. In the nasopharynx, TB may simulate granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener's). Cutaneous manifestations of TB include primary infection due to direct inoculation, abscesses and chronic ulcers, scrofuloderma, lupus vulgaris (a smoldering disease with nodules, plaques, and fissures), miliary lesions, and erythema nodosum. Tuberculous mastitis results from retrograde lymphatic spread, often from the axillary lymph nodes. Adrenal TB is a manifestation of disseminated disease presenting rarely as adrenal insufficiency. Congenital TB results from transplacental spread of tubercle bacilli to the fetus or from ingestion of contaminated amniotic fluid. This rare disease affects the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and various other organs.
