Unit 2.2 thm
- 1. Simple Rankine cycle 06/10/17 JIT 1
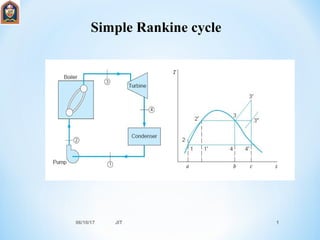
- 2. The main components of steam power plant are i. BOILER ii. TURBINE iii. CONDENSER iv. COOLING TOWER v. PUMP . 06/10/17 JIT 2
- 3. From graph 1-2 = isentropic process 2-3 = isobaric process 3-4 = isentropic process 4-1 = isobaric process . 06/10/17 JIT 3
- 4. Boiler :- Boiler is used to produce steam . Heat energy produced by coal is used to produce steam. Water is allowed to heat until it becomes into vapor state. Vapor is sent into turbine. TURBINE :- Turbine produces the work. Work produced is used to run the generator. The enthalpies at the enter and exit of the turbine are different. Then Vapor is sent into the condenser. CONDENSER :- The vapor is condensed to water in the condenser and sent into the pump. PUMP :- Pump send the water again into the Boiler and the cycle repeats again. 06/10/17 JIT 4
- 5. By considering the devices as steady flow devices and by applying the energy balance we get Steam turbine : W turbine = h1 - h2 Condenser :- Q rejected = h2 – h3 Pump :- W pump = h4 – h3 Boiler :- Q added = h1 – h4 06/10/17 JIT 5
- 6. Turbine produces the more work if the water is heated to super heated region. If the water is heated to super heated then the turbine will produce the more work . 06/10/17 JIT 6
- 7. But there is a problem if water is heated to super heated i.e. when it is condensed the vapor is not converted into water completely . It remains still as a mixture. It is difficult for the pump to handle both liquid and water which leads to CAVITATION . 06/10/17 JIT 7
- 8. INTRODUCTION What is IC Engine? An internal combustion engine is a thermal system (power plant) that converts heat obtained from chemical energy sources (gasoline, natural gas) into mechanical work. Where are IC Engines Used? IC engines are used as the propulsion systems for land transport vehicles such as automobiles (cars, etc.), marine vehicles (boats, etc.) and small airplanes. IC engines are also used in portable electrical generators and as prime mover in grass cutting machine, etc. 06/10/17 JIT 8
- 9. 06/10/17 JIT 9 Basic Components of IC Engines • Cylinder, piston, inlet valve and exhaust valve. • Piston moves from the top dead center (TDC) to the bottom dead center (BDC). • Clearance volume, Vc is a spacing between the top of the piston and the valve’s heads when the piston is at the end of the delivery stroke. • Swept volume or displacement volume, Vs is the volume between TDC and BDC.
- 10. Classifications: Internal Combustion Engines (IC Engines) External Combustion Engines (EC Engines) Internal Combustion Engines (IC Engines): IC Engines are those in which combustion of fuels take places inside engine cylinder (Example: Petrol, Diesel, GAS) External Combustion Engines (EC Engines): EC Engines are those in which combustion of fuels take places outside engine cylinder (Example: Steam Engine, Steam turbine) 06/10/17 JIT 10
- 11. Classification of IC Engines: a. According to the cycle of operation Spark ignition engines(Petrol or Constant volume or Otto cycle) Compression ignition engines(Diesel or Constant Pressure) b. According to the type of fuel used Petrol, Diesel, Gas Engine. c. According to the method of fuel SI & CI d. According to the Process of combustion Otto cycle, Diesel cycle, Dual combustion cycle06/10/17 JIT 11
- 12. About Petrol Engine: A petrol engine (also known as a gasoline engine in North America) is an internal combustion engine with spark-ignition, designed to run on petrol (gasoline). 06/10/17 JIT 12
- 13. Working Cycles Four Stroke Petrol Engine: It is also known as Otto cycle or constant volume cycle. Cycle of operation is completed in 4-strokes of the piston or 2 revolutions of the crankshaft. Each stroke consists of 180°, of crankshaft rotation and hence a cycle consists of 720°of crankshaft rotation. 2-stroke: 1 power stroke per 1 crankshaft rev 4-stroke: 1 power stroke per 2 crankshaft rev 06/10/17 JIT 13
- 14. Principle of Operation: The series of operations of an ideal four-stroke SI engine are as follows Suction Stroke or charging stroke Compression Stroke Expansion or Power Stroke or working stroke Exhaust Stroke 06/10/17 JIT 14
- 15. Principle of Operation 06/10/17 JIT 15
- 16. Principle of Operation: Stroke Valve Position Suction Stroke Suction Valve open Exhaust Valve closed Compression Stroke Both Valves closed Expansion or Power Stroke Both Valves closed Exhaust Stroke Exhaust Valve open Suction Valve closed 06/10/17 JIT 16
- 17. Working Principles of Four Stroke Diesel Engine: Increased pressure of combustion gases acts on piston -> converted to rotary motion Can be 2 or 4 stroke engines 2-stroke: 1 power stroke per 1 crankshaft rev 4-stroke: 1 power stroke per 2 crankshaft rev Engine stroke: A stroke is a single traverse of the cylinder by the piston (from TDC to BDC) 1 revolution of crankshaft = 2 strokes of piston 06/10/17 JIT 17
- 18. Exhaust Suction Compression Ign.-Combn. Expansion Exhaust 06/10/17 JIT 18
- 19. Working Principles Of Four Stroke Diesel Engine: Intake stroke Intake valve open, exhaust valve shut Piston travels from TDC to BDC Air drawn in Compression stroke Intake and exhaust valves shut Piston travels from BDC to TDC Temperature and pressure of air increase 06/10/17 JIT 19
- 20. Working Principles Of Four Stroke Diesel Engine: Power stroke Intake and exhaust valves shut Fuel injected into cylinder and ignites Piston forced from TDC to BDC Exhaust stroke Intake valve shut, exhaust valve open Piston moves from BDC to TDC Combustion gases expelled06/10/17 JIT 20
- 21. 06/10/17 JIT 21
- 22. 06/10/17 JIT 22 Two Stroke Cycle Petrol Engine Construction : •A piston reciprocates inside the cylinder •It is connected to the crankshaft by means of connecting rod and crank •There are no valves in two stroke engines, instead of valves ports are cut on the cylinder walls. •There are three ports, namely inlet, exhaust and transfer ports. •The closing and opening of the ports are obtained by the movement of piston. The crown of piston is made in to a shape to perform this. •A spark plug is also provided.
- 23. 06/10/17 JIT 23 Two stroke cycle Petrol Engines - Working • The piston moves up from Bottom Dead Centre (BDC) to Top Dead Centre (TDC) • Both transfer and exhaust ports are covered by the piston. • Air fuel mixture which is transferred already into the engine cylinder is compressed by moving piston. • The pressure and temperature increases • at the end of compression.
- 24. 06/10/17 JIT 24 Two stroke cycle Petrol Engines - Working First Stroke : (b) Ignition and Inductance: • Piston almost reaches the top dead centre •The air fuel mixture inside the cylinder is ignited by means of an electric spark produced by a spark plug •At the same time, the inlet port is uncovered by the plane. •Fresh air fuel mixture enters the crankcase through the inlet port
- 25. 06/10/17 JIT 25 Two stroke cycle Petrol Engines - Working (c)Expansion and Crankcase compression •The burning gases expand in the cylinder •The burning gases force the piston to move down. Thus useful work is obtained. •When the piston moves down, the air fuel mixture in the crankcase is partially compressed. This compression is known as Crank case compression.
- 26. 06/10/17 JIT 26 Two stroke cycle Petrol Engines - Working (d) Exhaust and transfer: •At the end of expansion, exhaust port is uncovered. •Burnt gases escape to the atmosphere. •Transfer port is also opened. The partially compressed air fuel mixture enters the cylinder through the transfer port. •The crown of the piston is made of a deflected shape. So the fresh charge entering the cylinder is deflected upwards in the cylinder. •Thus the escape of fresh charge along with the exhaust gases is reduced
- 27. Compression Intake and exhaust valves shut Piston travels from BDC to TDC Temperature and pressure of air increase Power stroke Intake and exhaust valves shut Fuel injected into cylinder and ignites Piston forced from TDC to BDC Working Principles Of Two Stroke Diesel Engine 06/10/17 JIT 27
- 28. Application Of Four stroke Cycle Engine Used in heavy vehicles Buses, Lorries, Trucks etc., Application Of Two stroke Cycle Engine Used in light vehicles Bikes, Scooters, Mopeds Ship propulsion 06/10/17 JIT 28
- 29. Application Of Four stroke Petrol Engine Buses ,Trucks Mobile electric generating sets. Small pumping sets with side cars Application Of Four stroke Diesel Engine 30kw-Tractors 40to 100kw – jeeps, buses and trucks 200 to 400kw-Earthmoving m/c 100 to 35000kw-Marine application 06/10/17 JIT 29
- 30. 06/10/17 JIT 30 I.C ENGINE TERMINOLGY
- 31. 06/10/17 JIT 31 standard terms used in I.C Engines are 1. Bore: Inside diameter of the cylinder is termed as Bore and it is designated by the letter d and is usually expressed in millimeter (mm) 2. Top Dead Center (TDC): The extreme position reached by the piston at the top of the cylinder in the vertical engine is called Top Dead center. It is also called the Inner dead centre (IDC). 3. Bottom Dead Center (BDC): The extreme position reached by the piston at the Bottom of the cylinder in the vertical engine is called Bottom Dead center. It is also called the Outer dead centre (ODC).
- 32. 06/10/17 JIT 32 5. Compression ratio (r): It is the ratio of Maximum cylinder volume to the Clearance volume. 6. Cylinder volume (v): It is the sum of swept volume and the Clearance volume. V = Vs + Vc 7. Displacement (or)Swept volume (Vs): It is the volume of space generated by the movement of piston from one dead center to another dead center. It is expressed in terms of cubic centimeter (cc) and given by VS = A * L = π * d2 * L / 4 8. Clearance Volume( Vc): It is the space in the cylinder, when the piston is at Top Dead Center It is designated as VC and expressed in cubic centimeter (cc).
- 33. 06/10/17 JIT 33 Petrol Engines * A petrol engine draws a mixture of petrol and air during suction stroke. * The carburetor is employed to mix air and petrol in the required proportion and to supply it to the engine during suction stroke. * Pressure at the end of compression is about 10 bar. * The charge (i.e. petrol and air mixture) is ignited with the help of spark plug. Diesel Engines * A diesel engine draws only air during suction stroke. *The injector or atomizer is employed to inject the fuel at the end of combustion stroke. *Pressure at the end of compression is about 35 bar. *The fuel is injected in the form of fine spray. The temperature of the compressed air is sufficiently high to ignite the fuel.
- 34. 06/10/17 JIT 34 *The maintenance cost is less. *The thermal efficiency is about 26%. *Overheating trouble is more due to low thermal efficiency. *These are high speed engines. *The petrol engines are generally employed in light duty vehicle such as scooters, motorcycles and cars. These are also used in aeroplanes. * The maintenance cost is more. * The thermal efficiency is about 40%. * Overheating trouble is less due to high thermal efficiency. * These are relatively low speed engines. * The diesel engines are generally employed in heavy duty vehicles like buses, trucks, and earth moving machines.