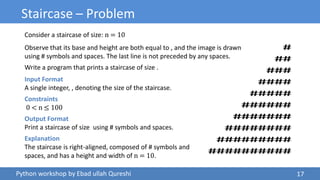
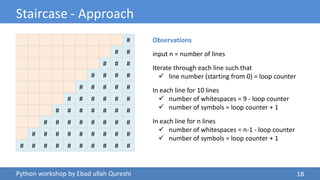
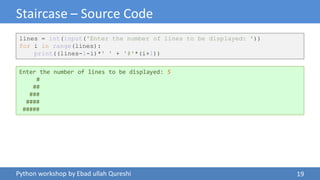
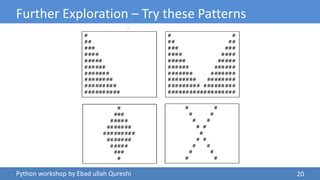
The document details a Python workshop led by Ebad Ullah Qureshi, focusing on control structures, loops, and conditional statements. It covers key concepts such as algorithms, input handling, decision-making statements, and loops, along with practical examples like a discount price calculator and a staircase pattern generator. The workshop aims to enhance programming skills by introducing fundamental Python programming constructs and their applications.