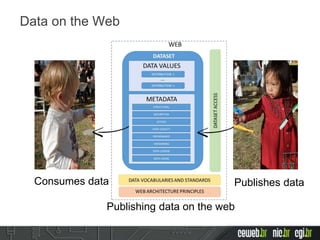
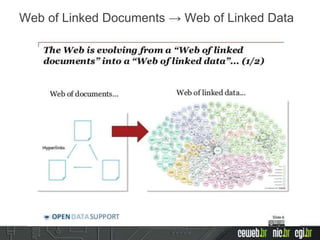
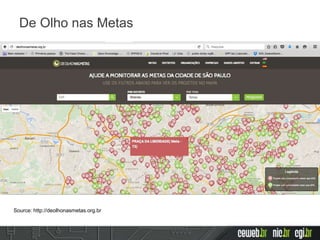
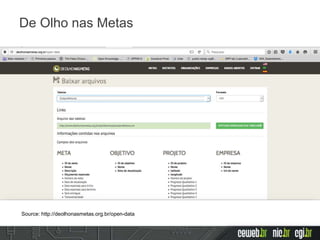
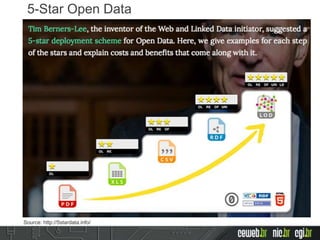
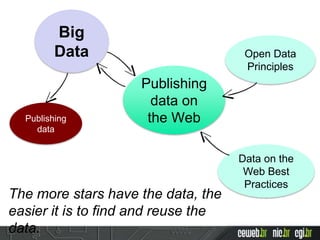
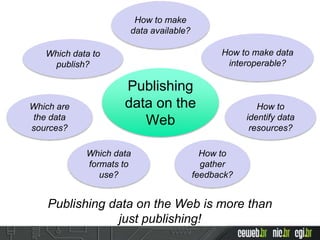
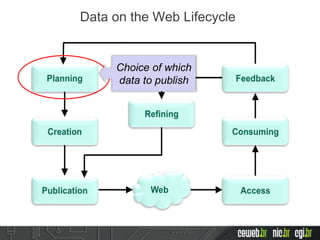
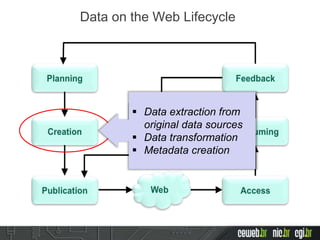
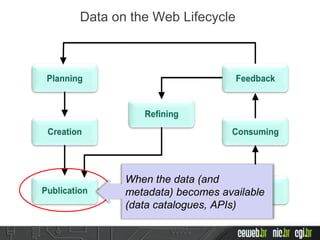
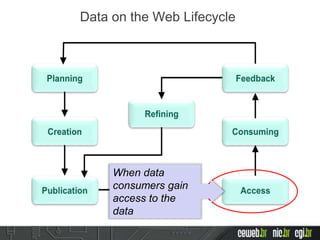
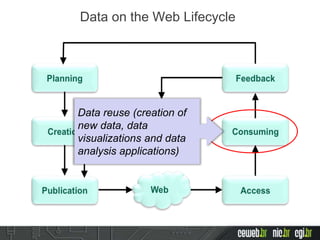
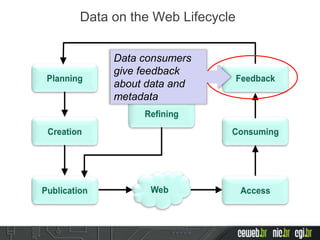
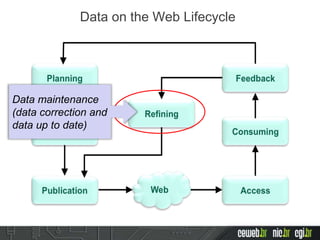
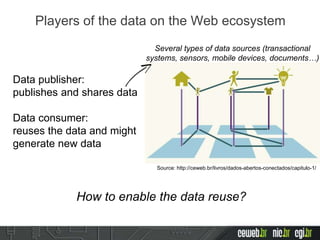
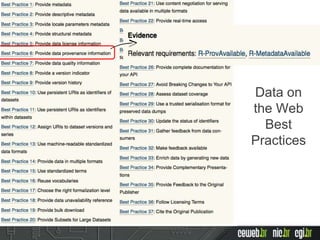
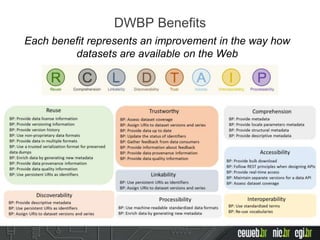
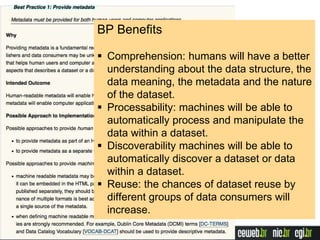
The document discusses the publishing of data on the web, covering concepts like linked data, open data, and the data lifecycle. It details best practices to improve data management and promote reusability, addressing challenges such as metadata, data quality, and privacy concerns. Additionally, it outlines the goals of the Data on the Web Best Practices Working Group and emphasizes the importance of collaboration between data publishers and consumers.