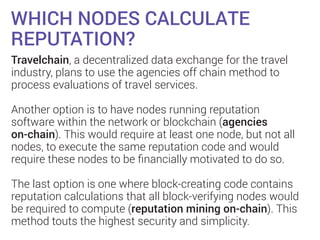
BitBay offers a decentralized marketplace leveraging blockchain technology and aims to address the global demand for legal identification through digital ID systems. The document discusses the architecture of blockchain reputation management, including data storage options, the frequency of reputation calculations, and mechanisms for ensuring reliable reputation metrics. BitBay employs an off-chain method for reputation storage to enhance transaction speeds, alongside a double deposit escrow system to deter cheating.