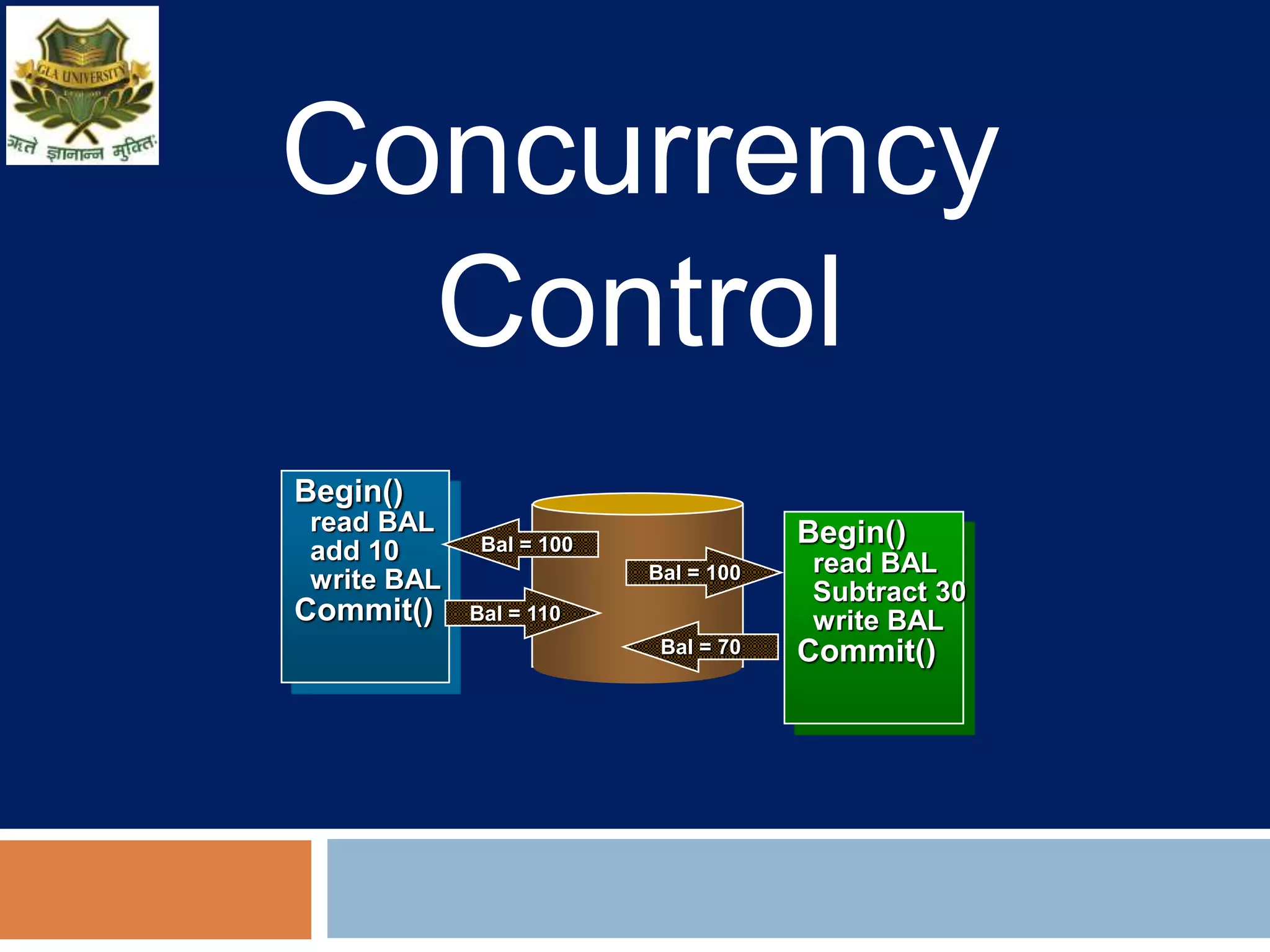
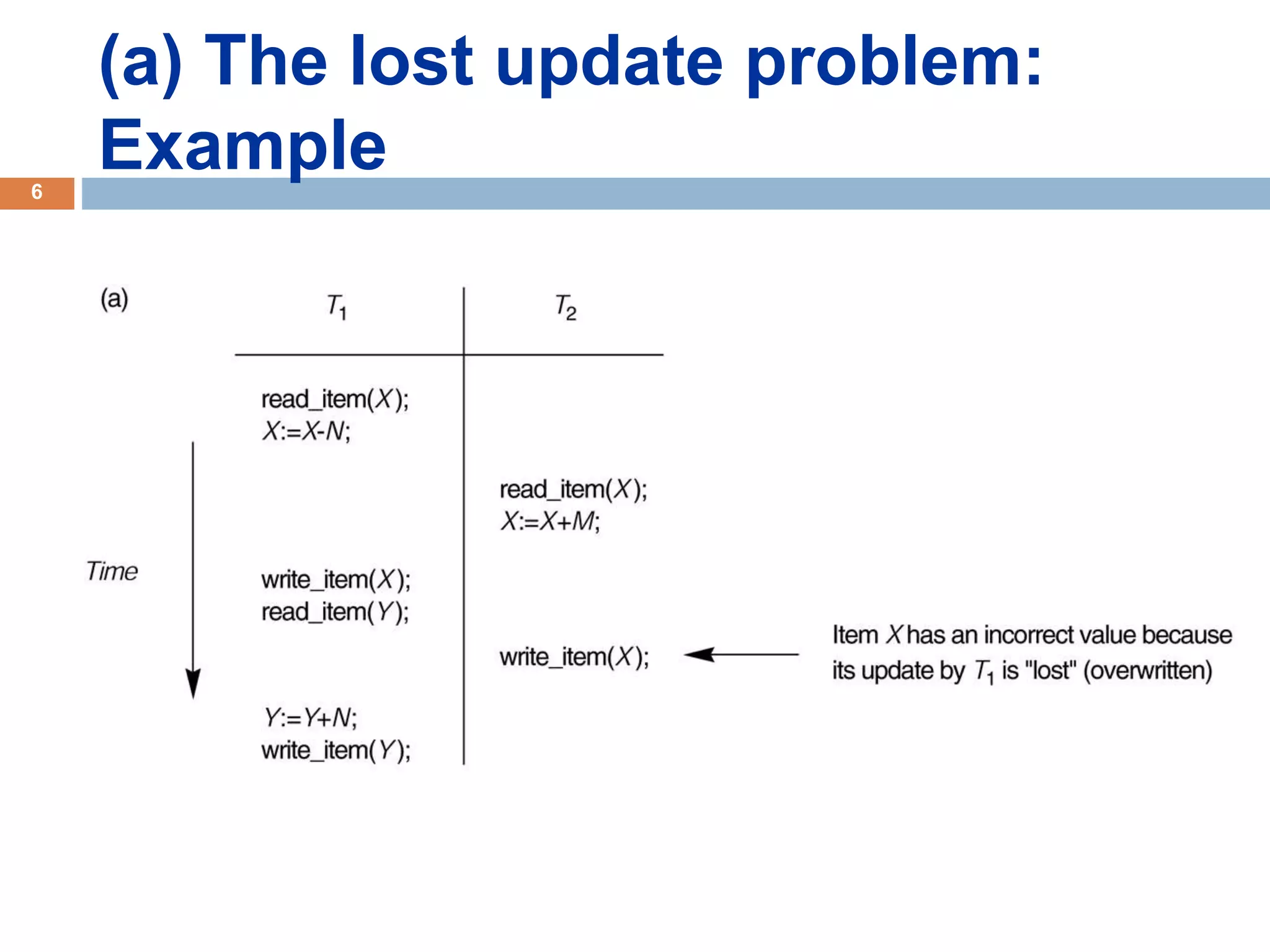
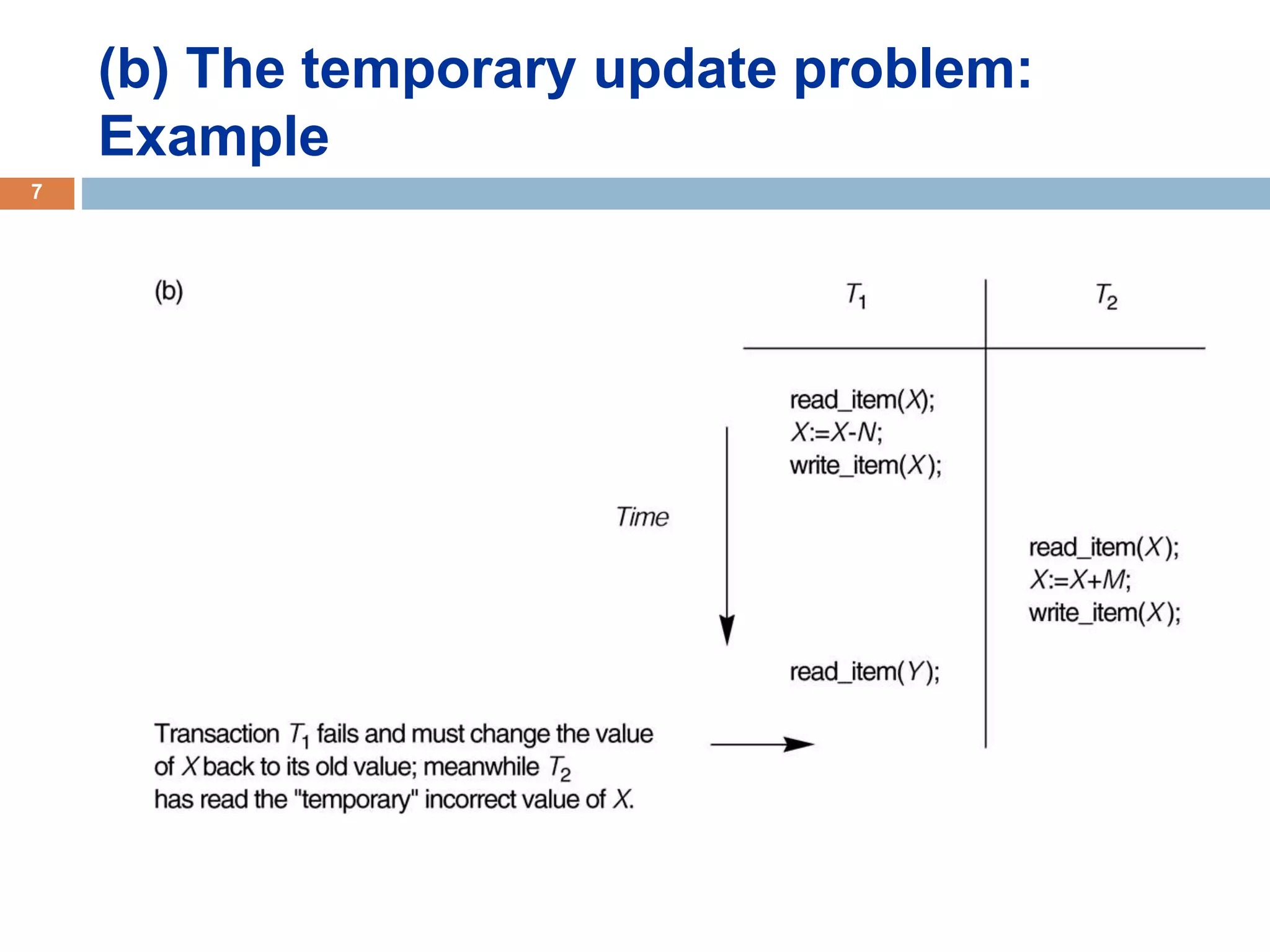
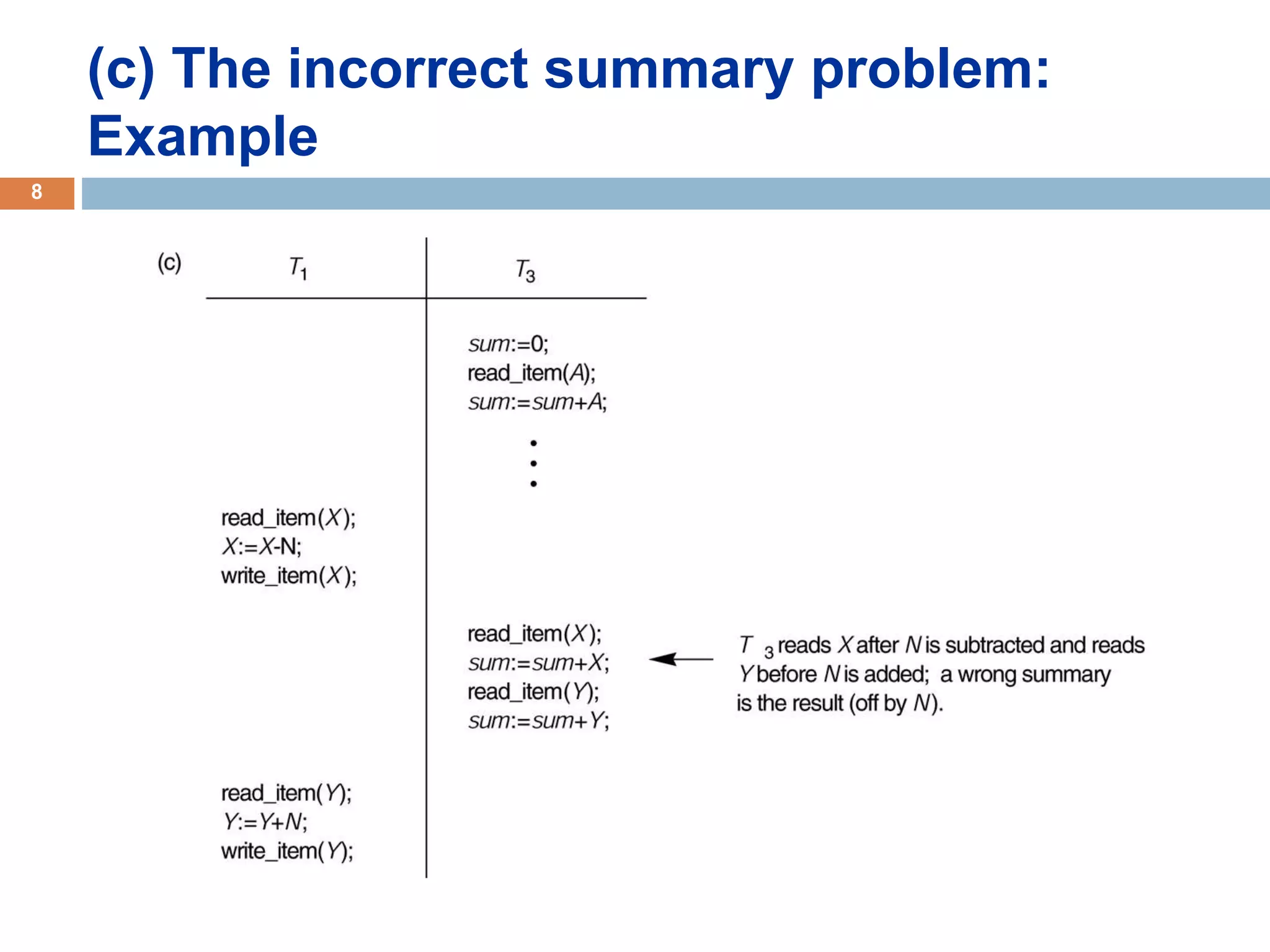
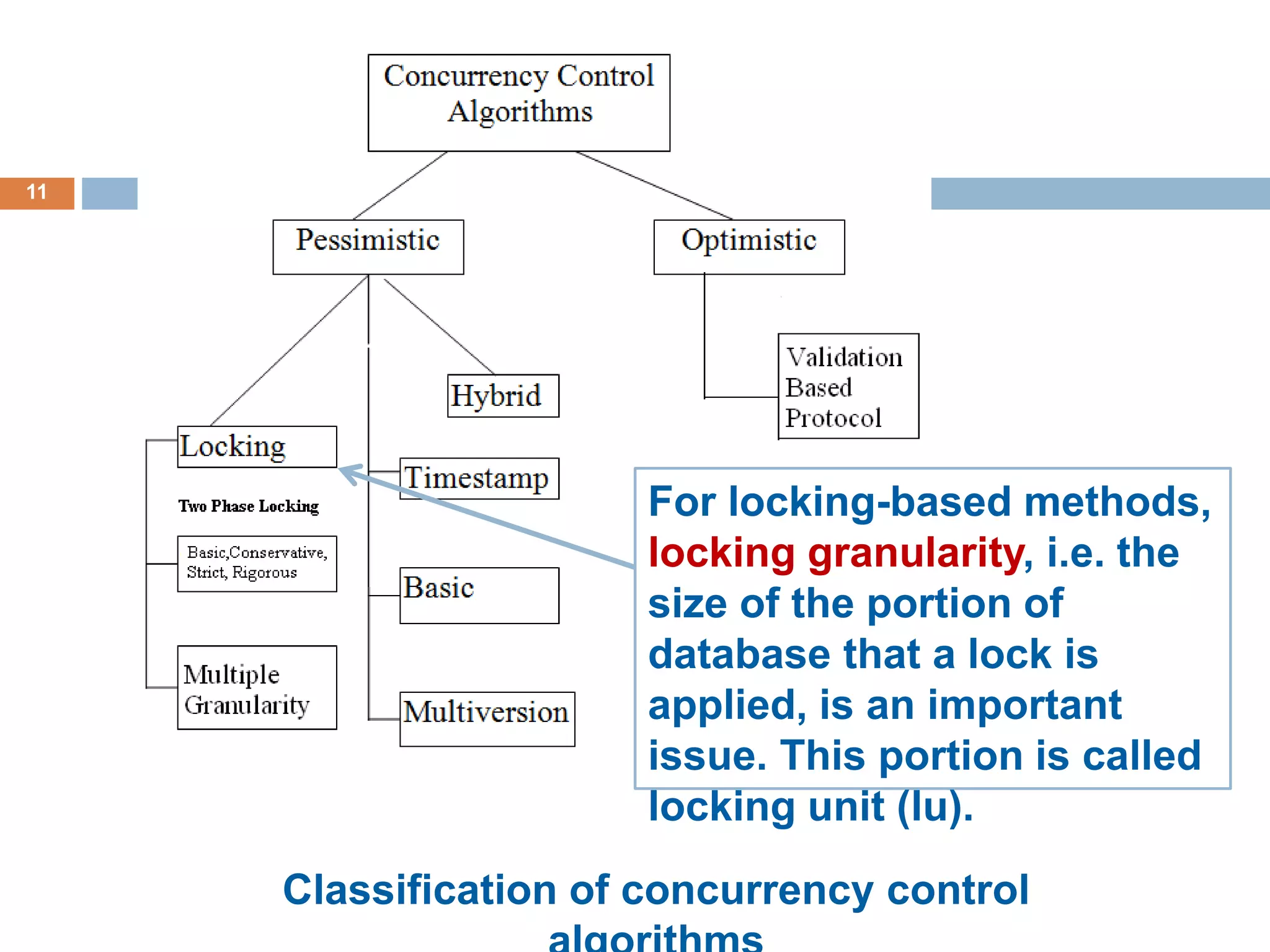
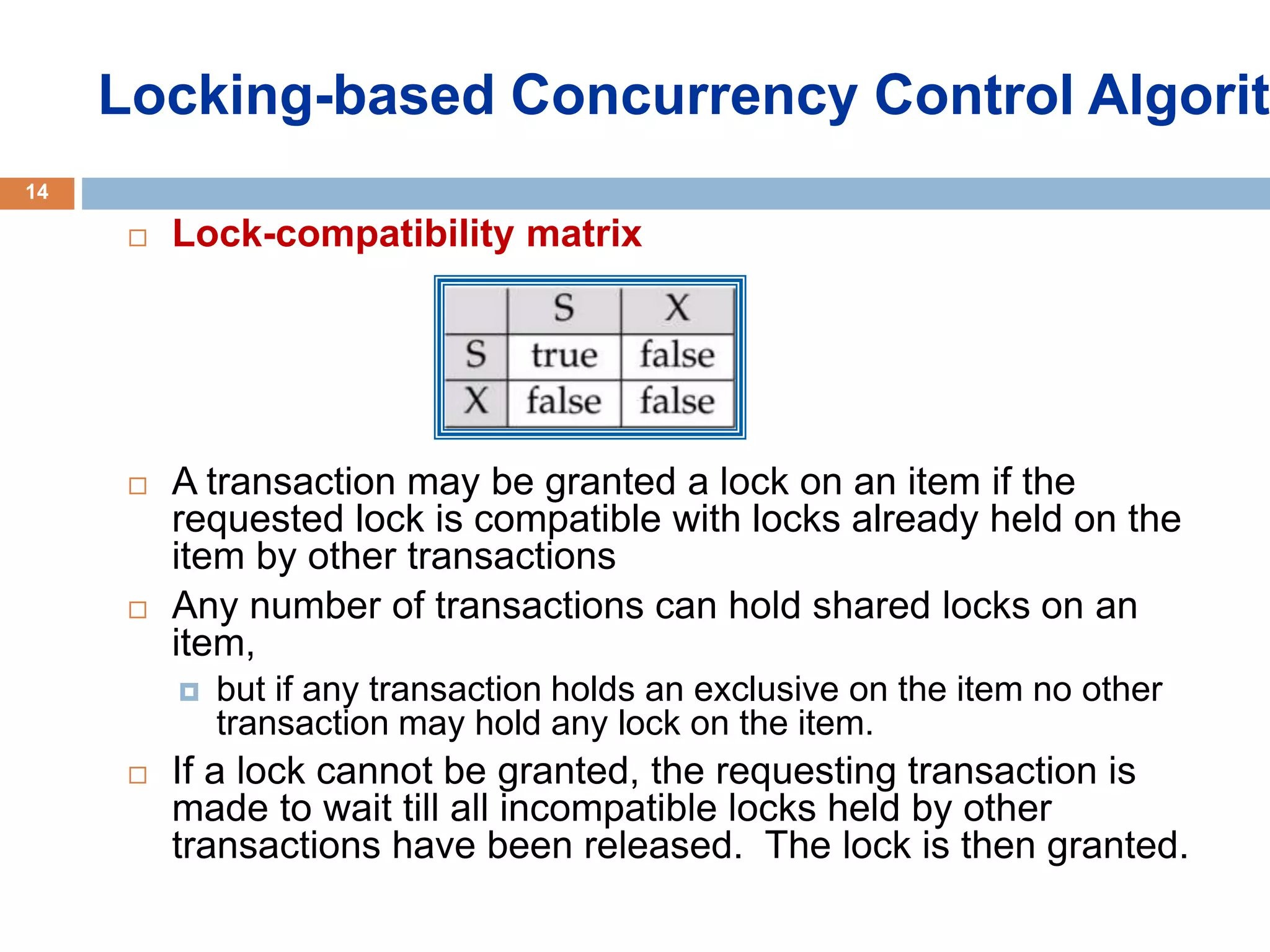
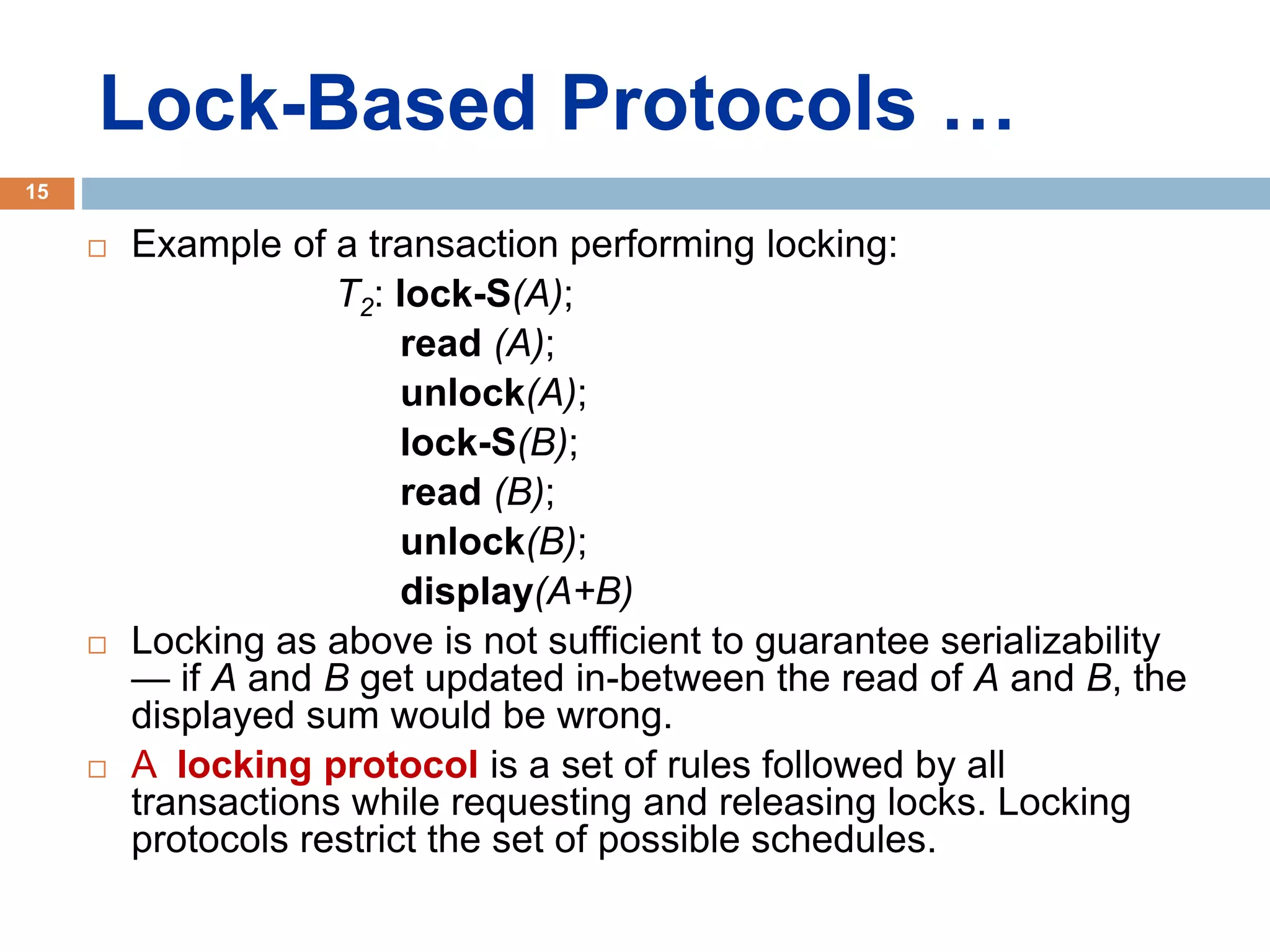
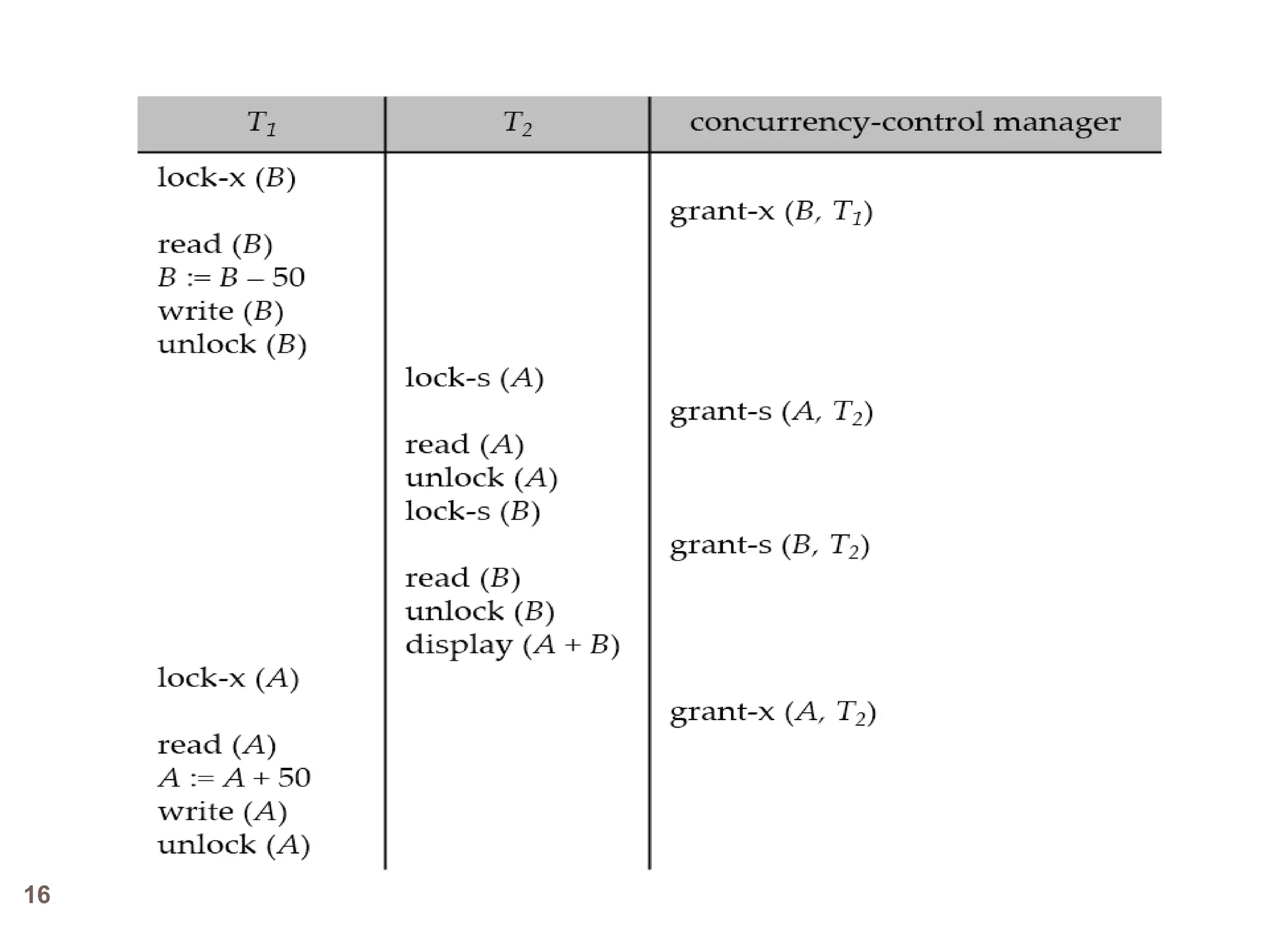
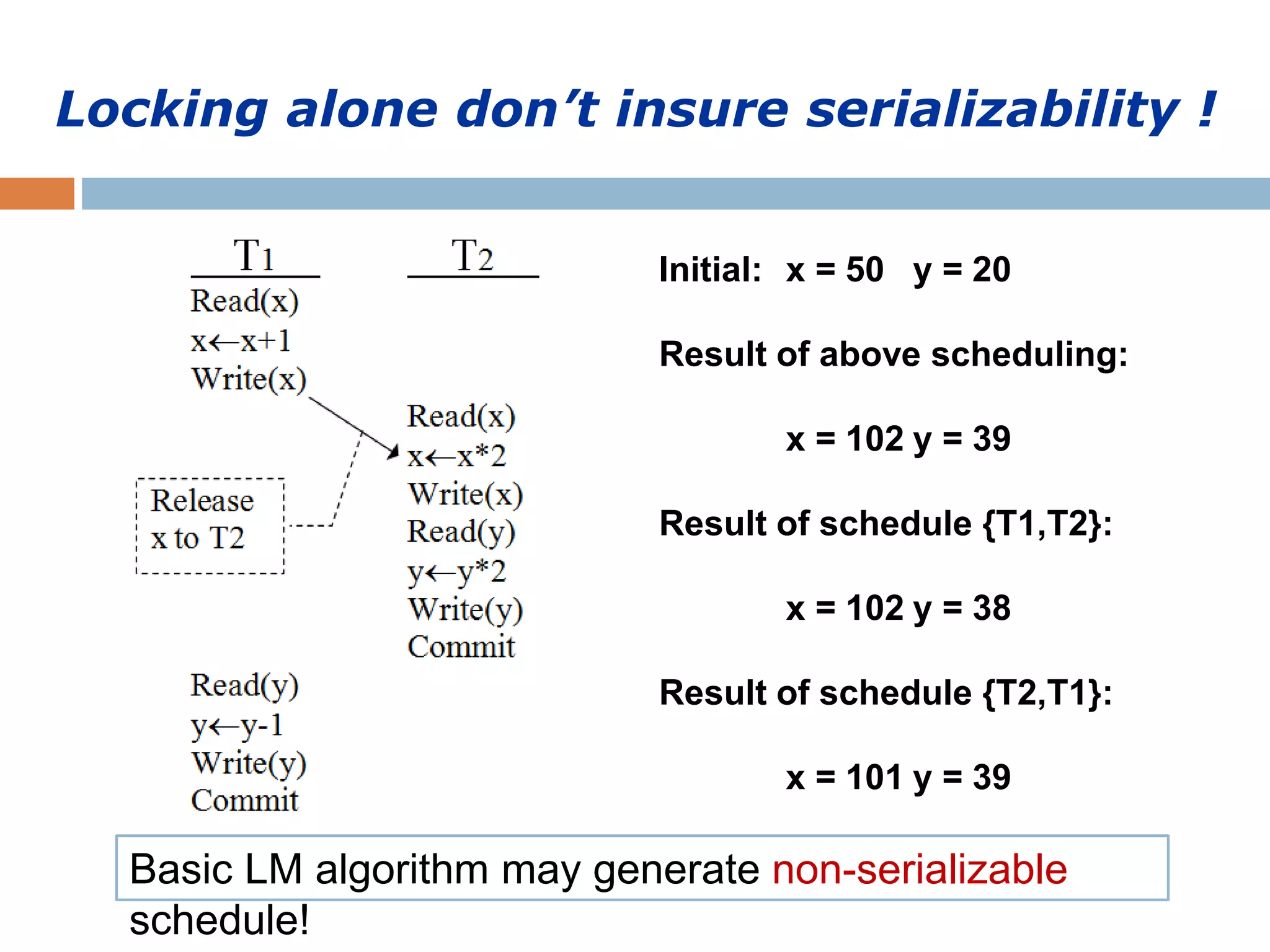
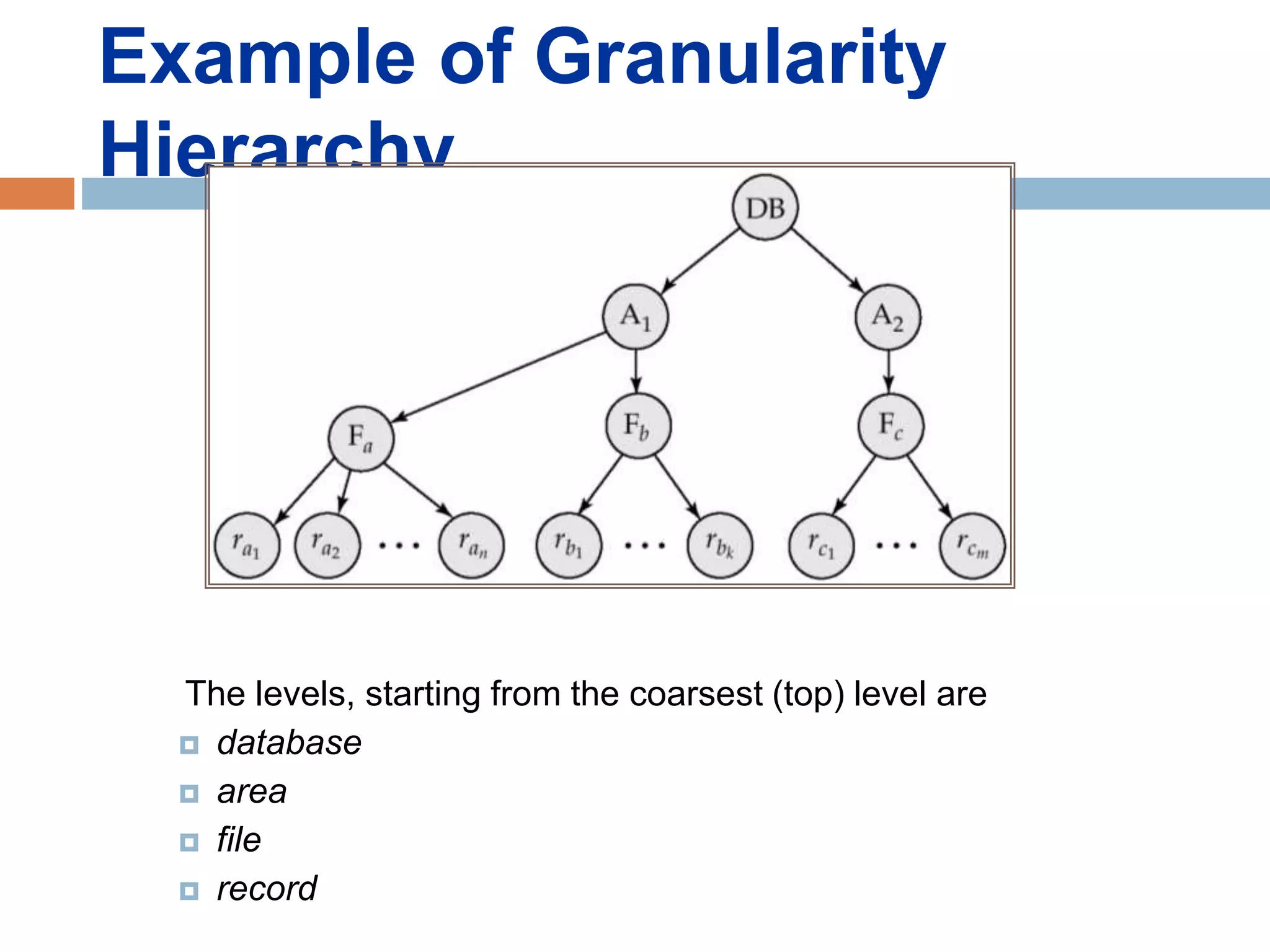
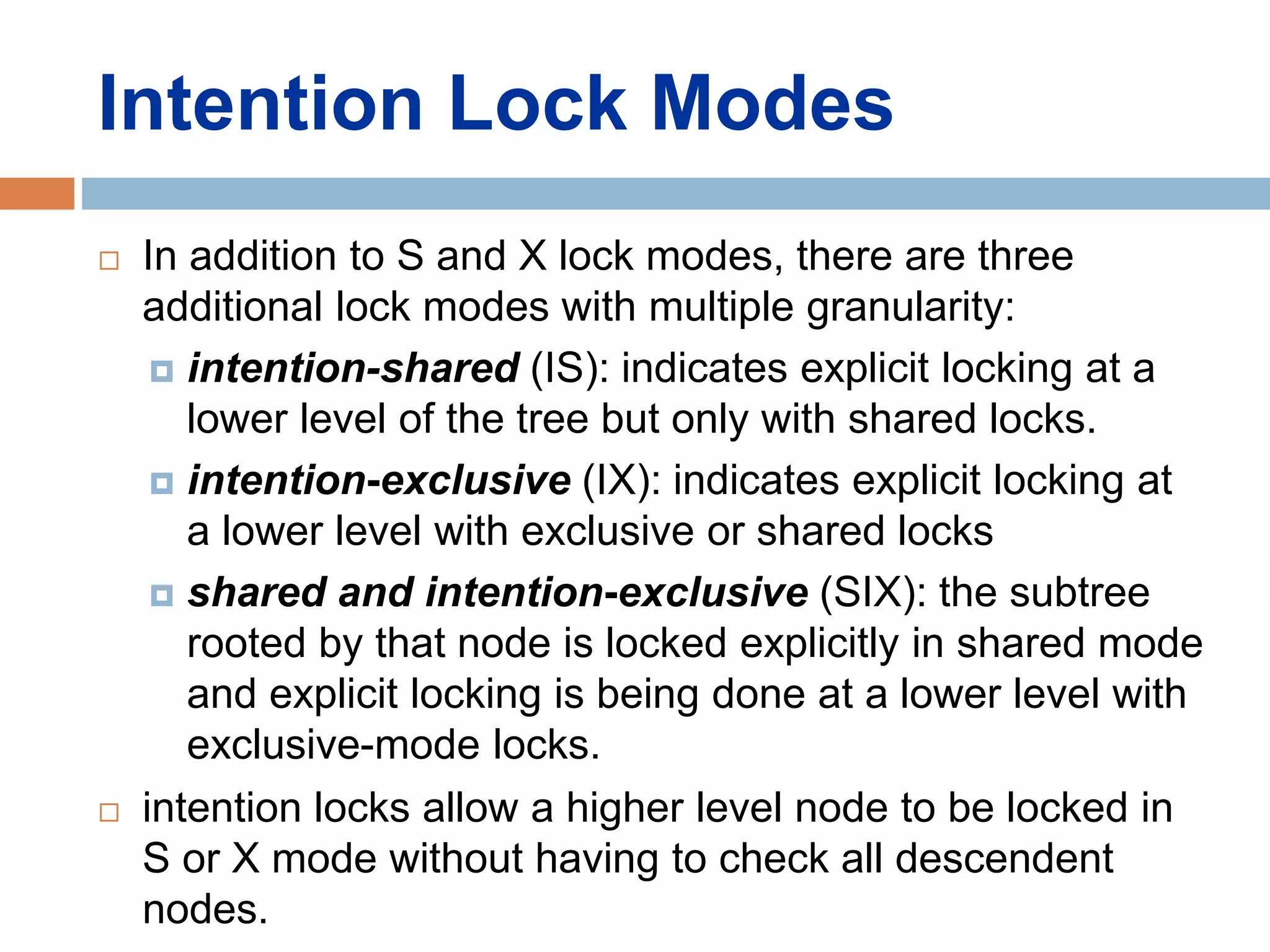
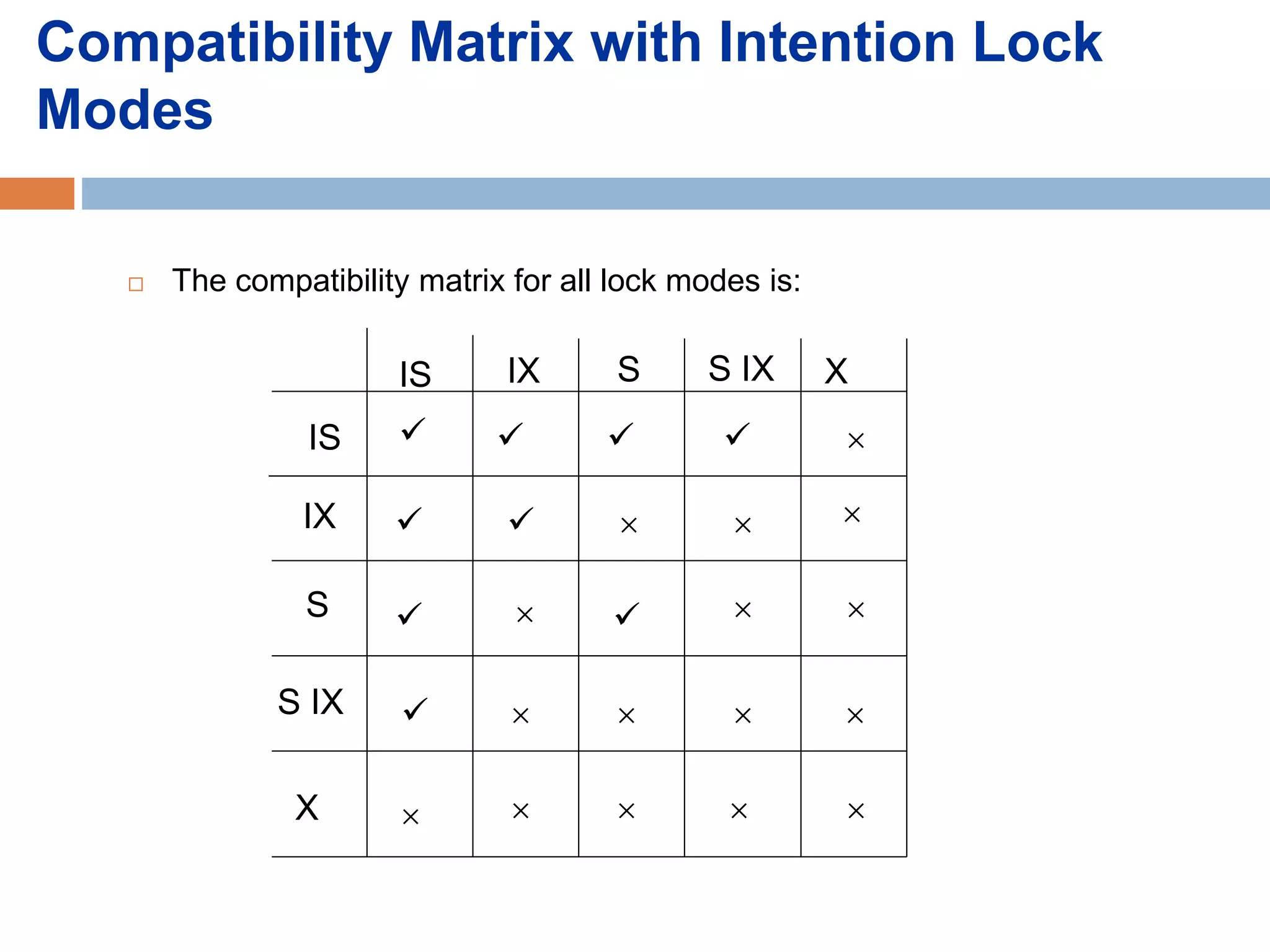
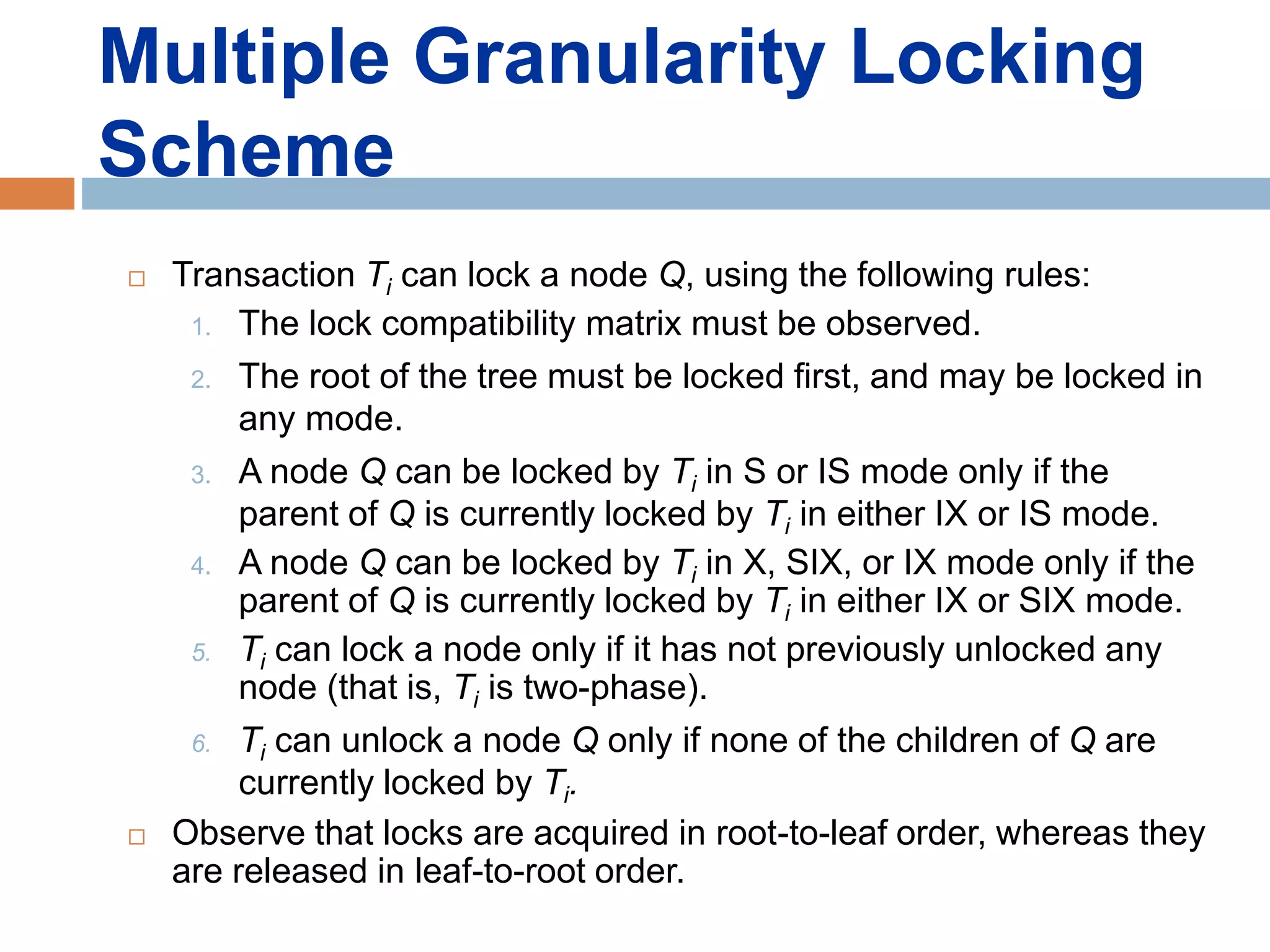
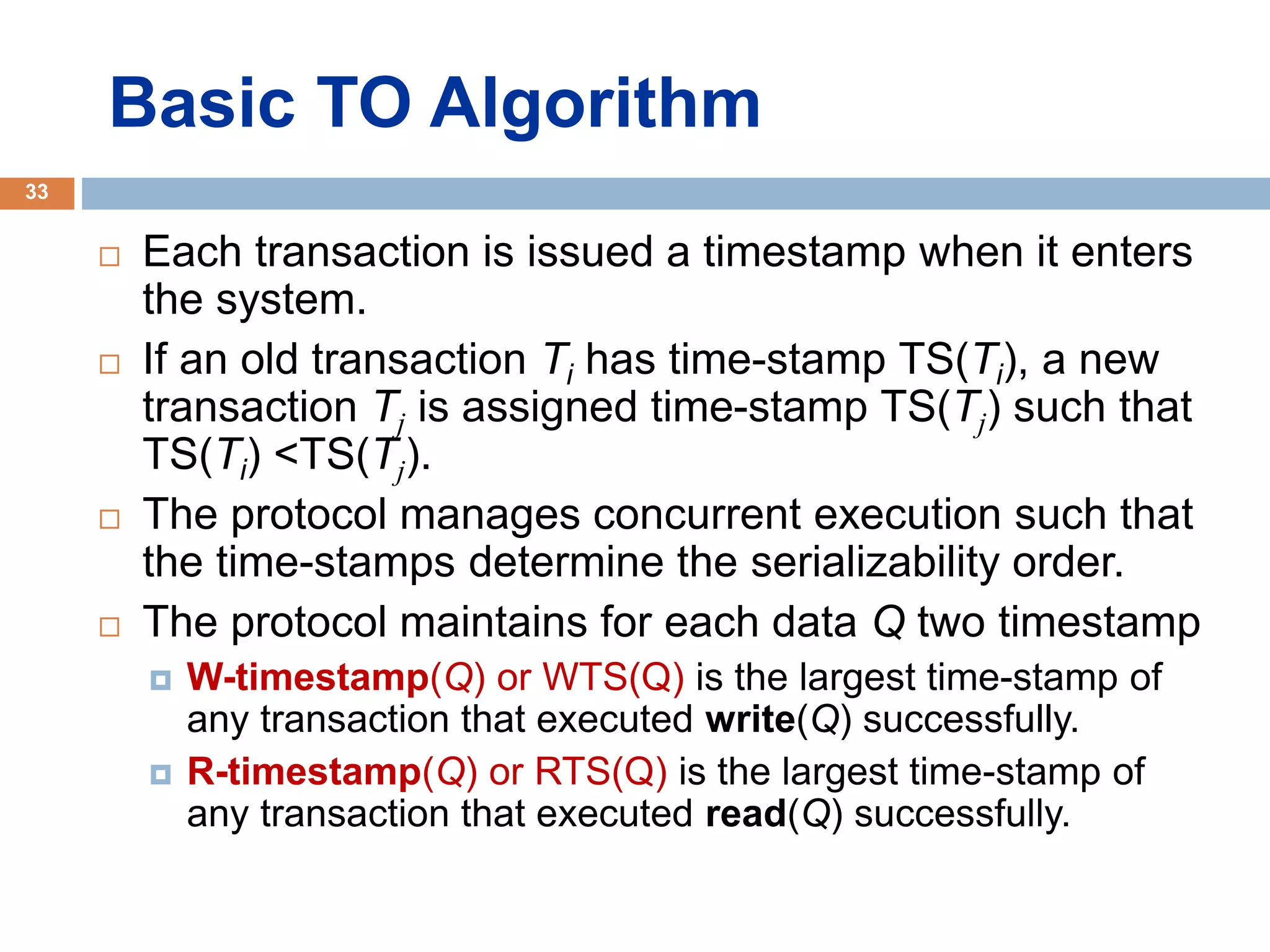
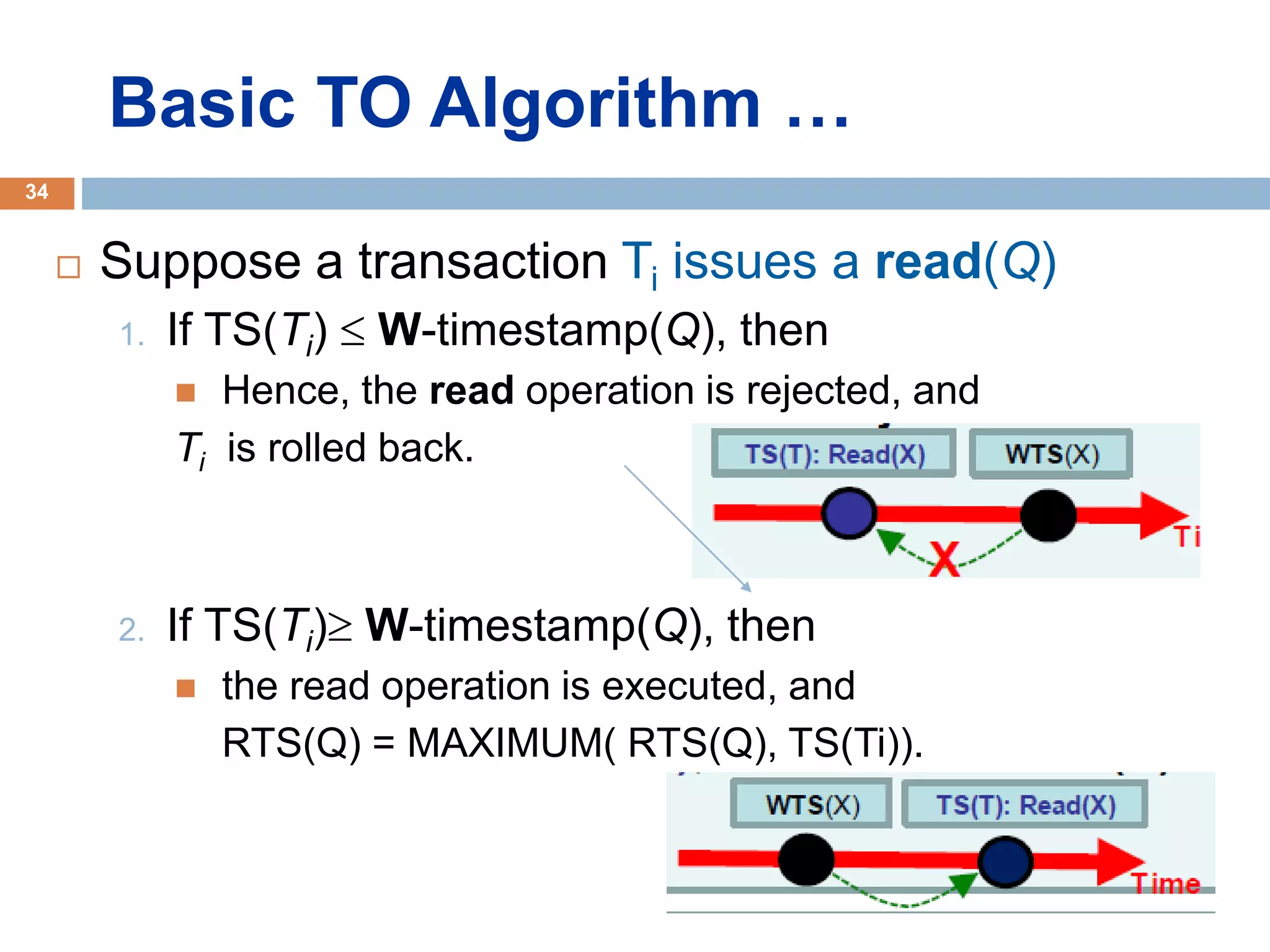
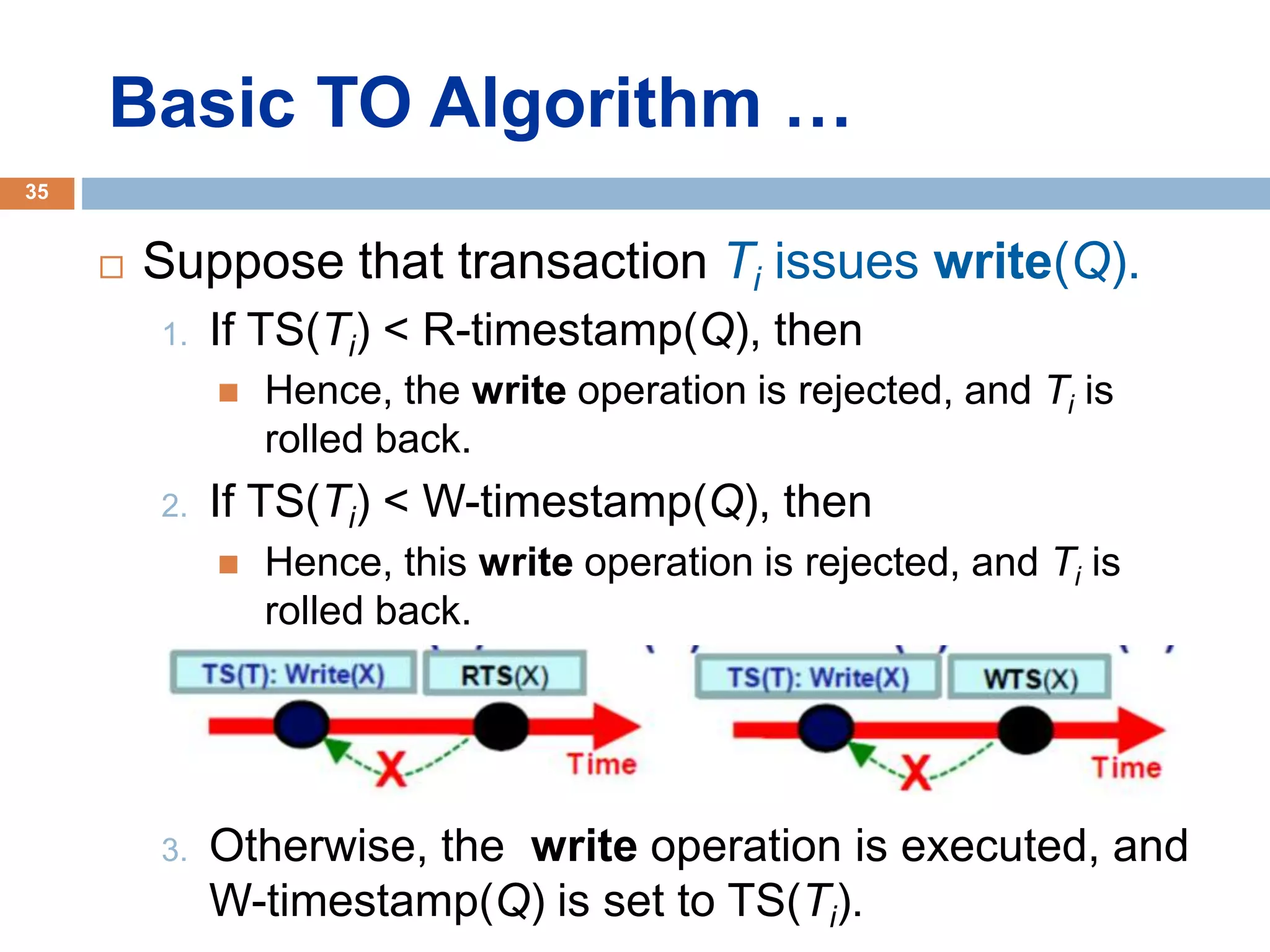
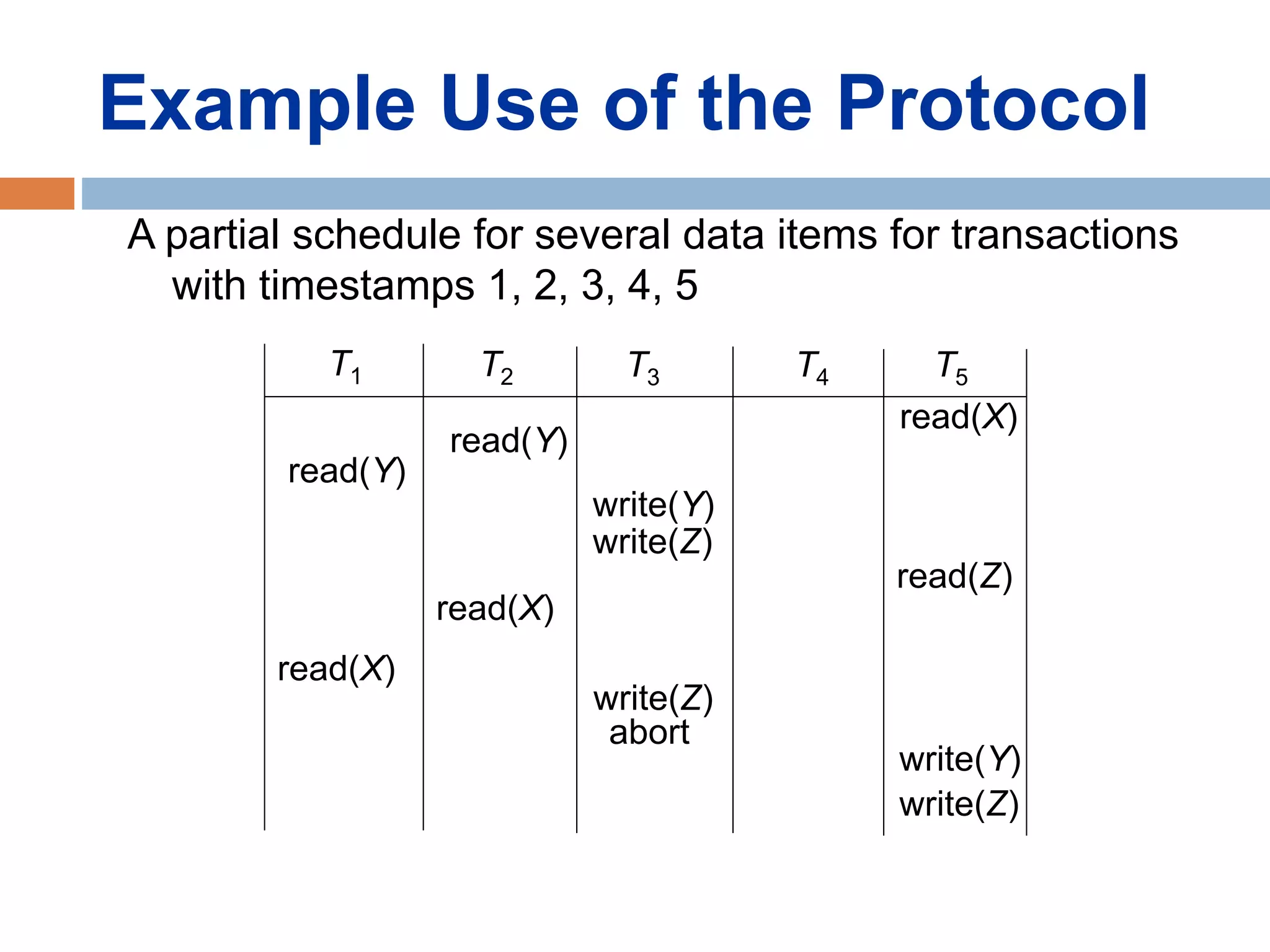
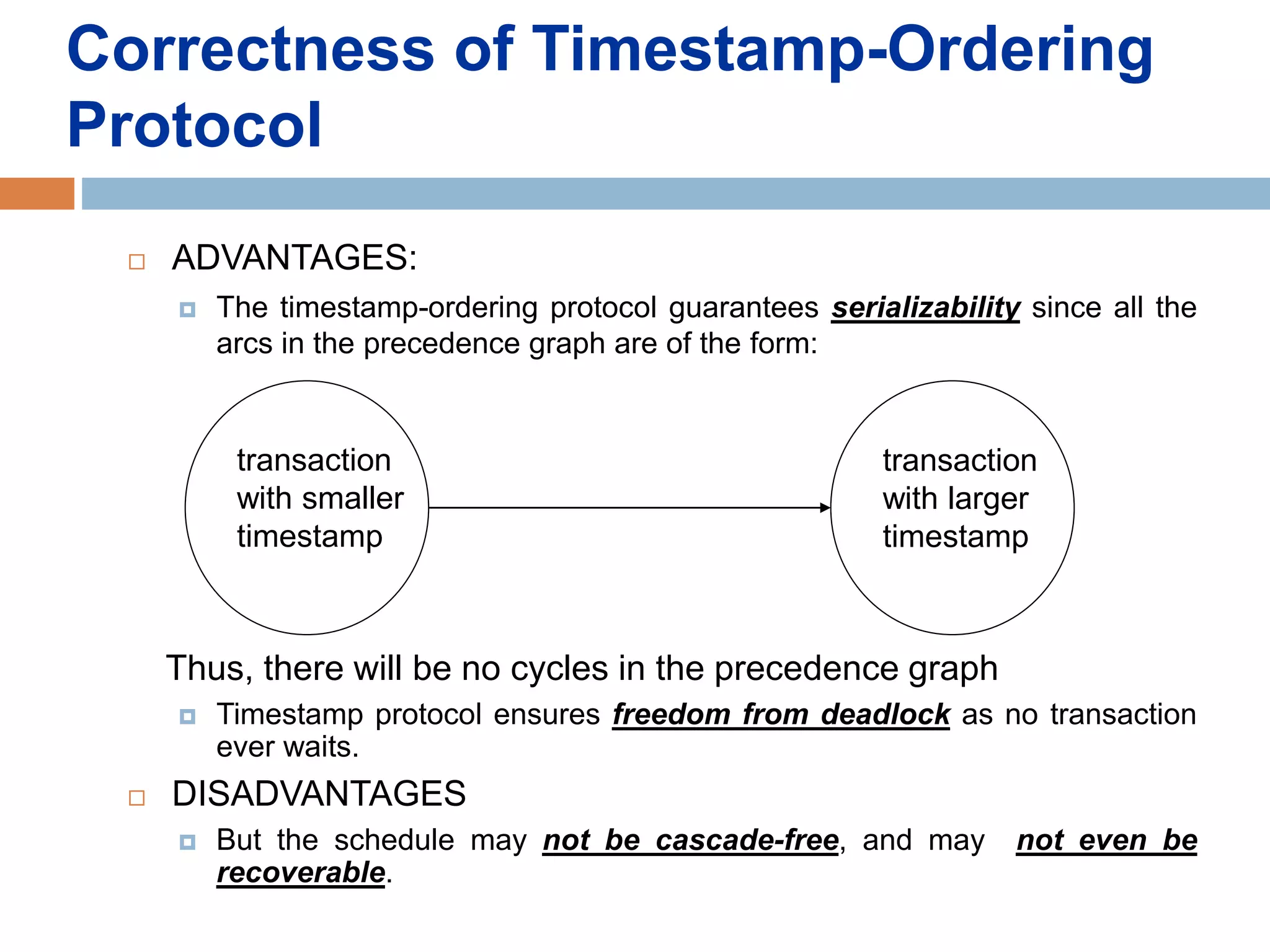
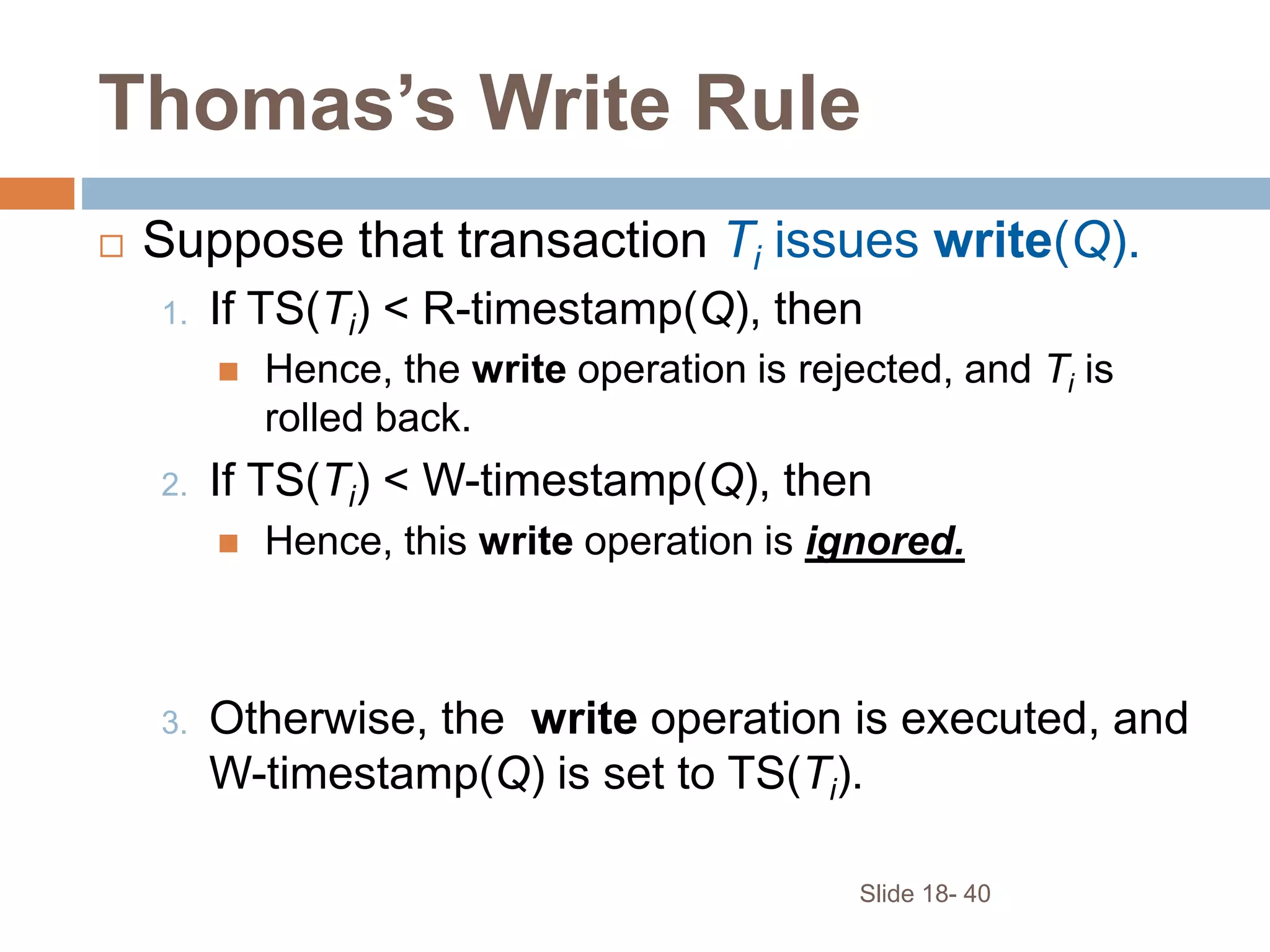
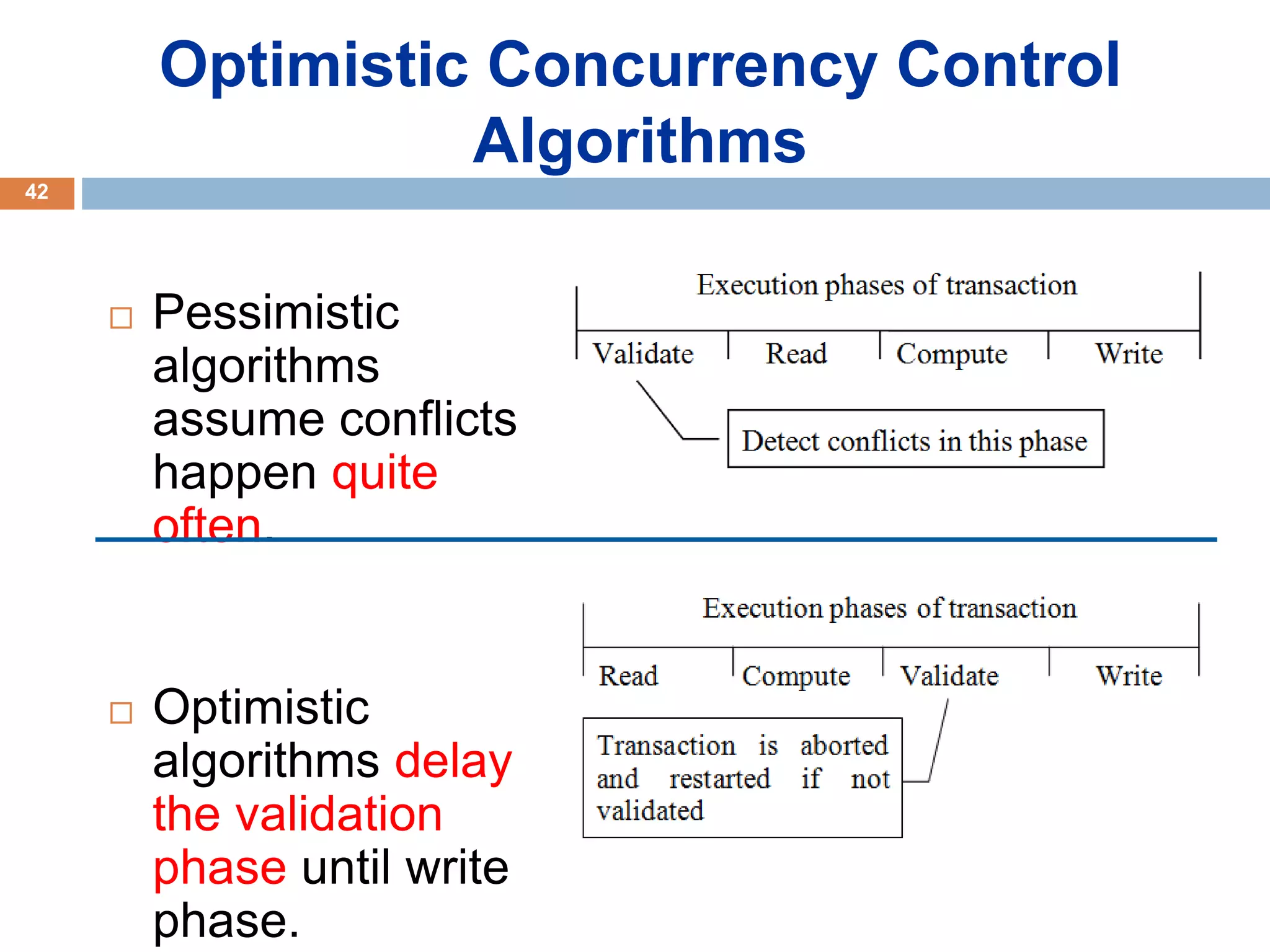
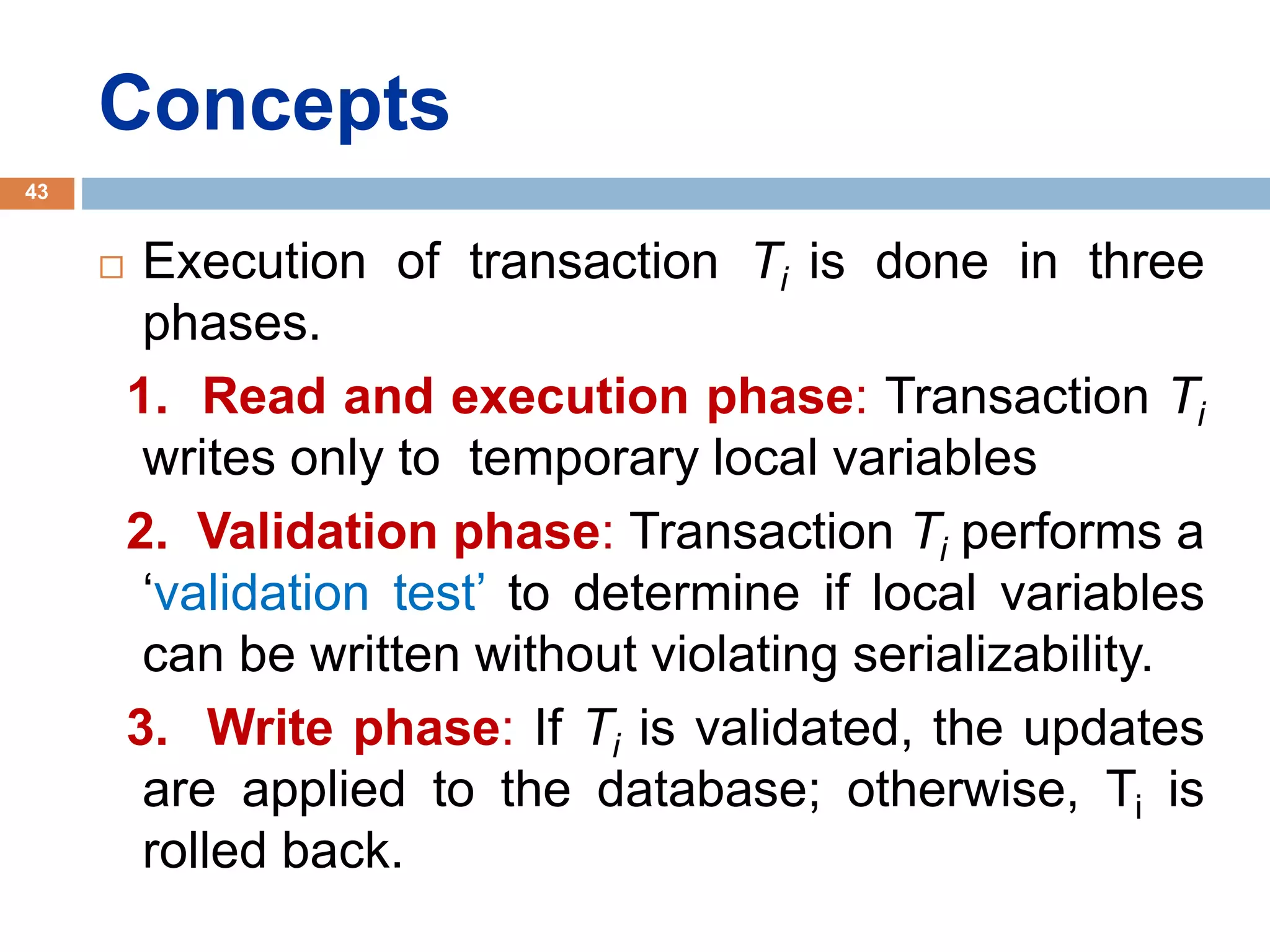
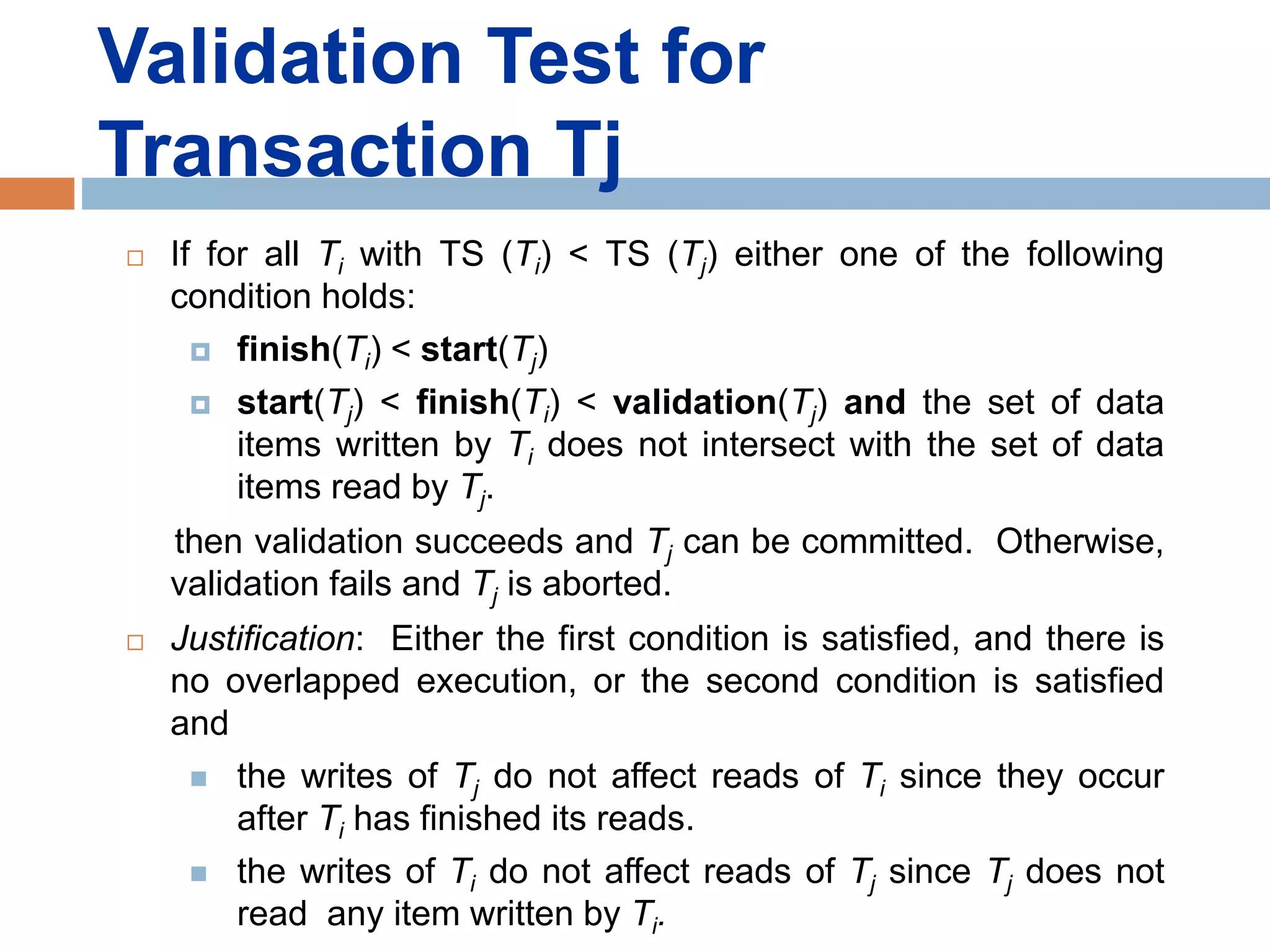
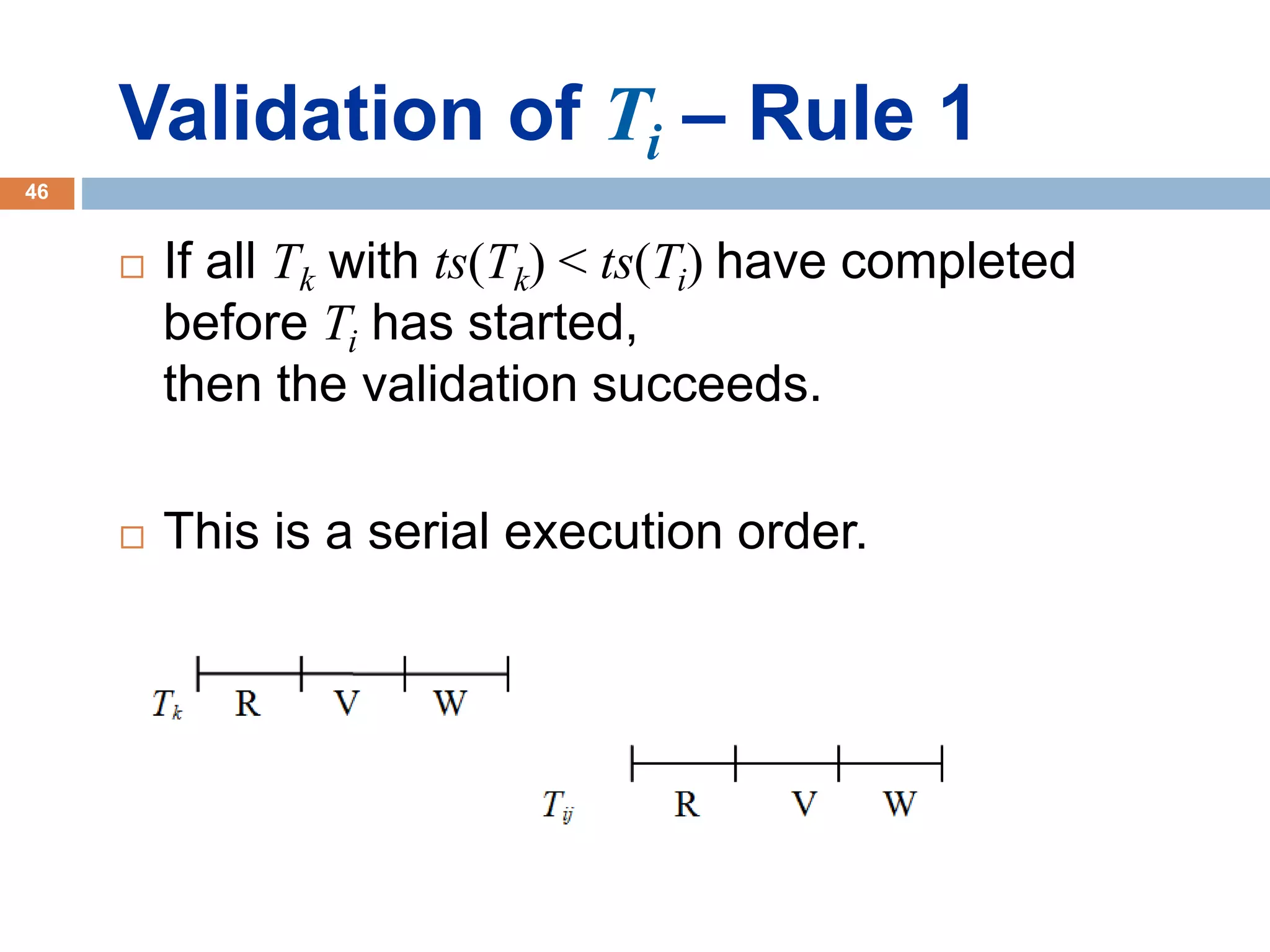
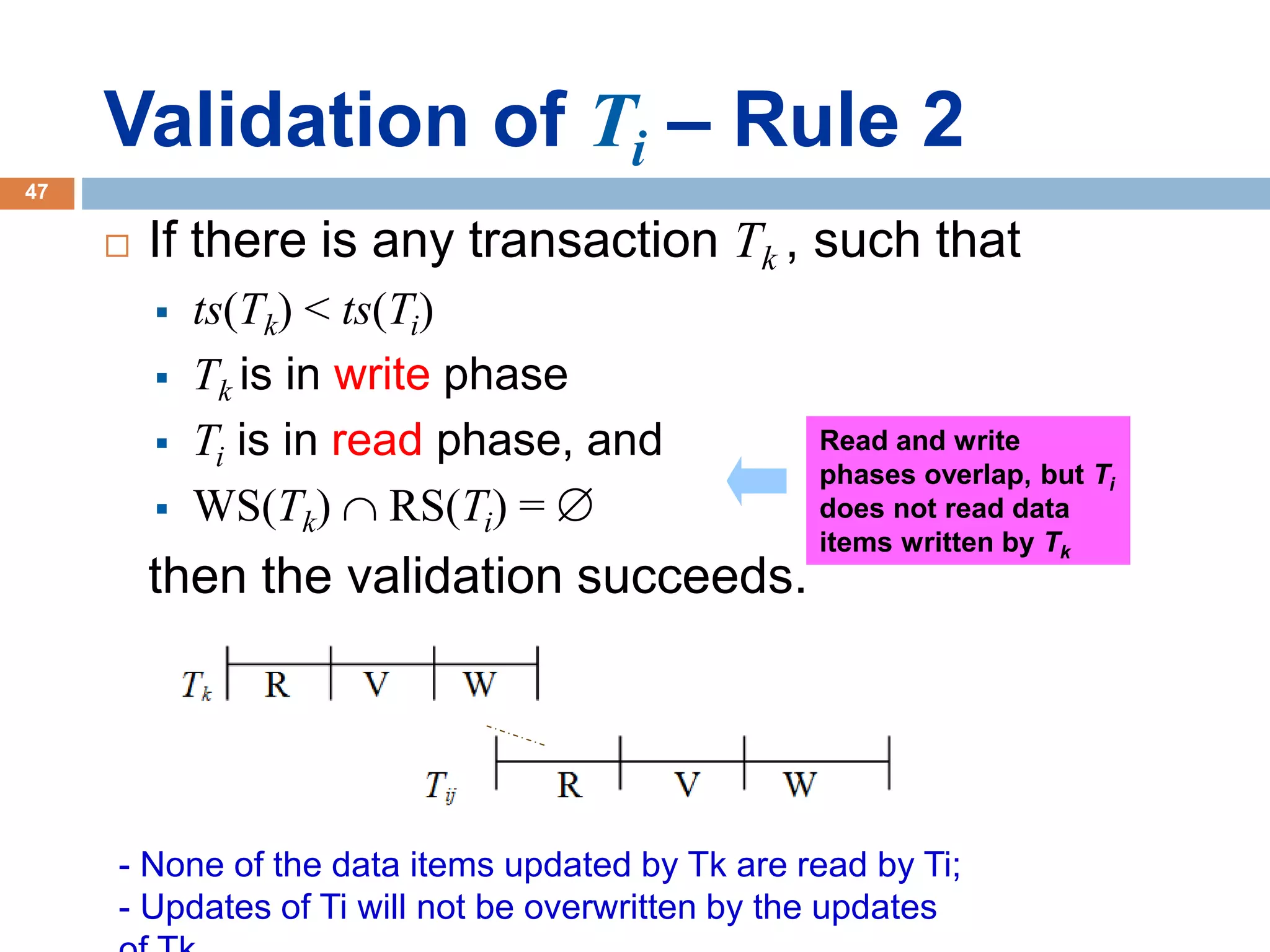
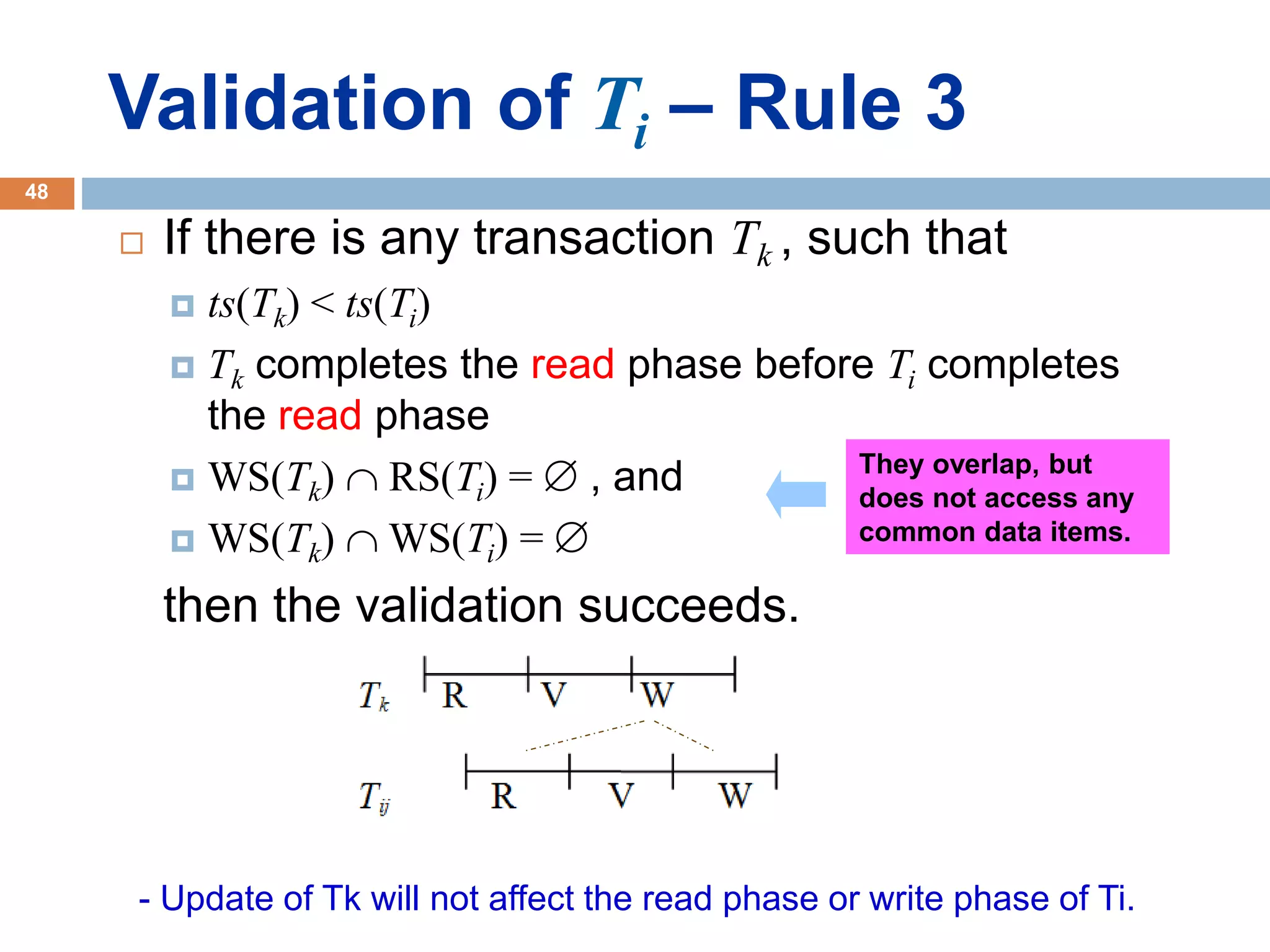
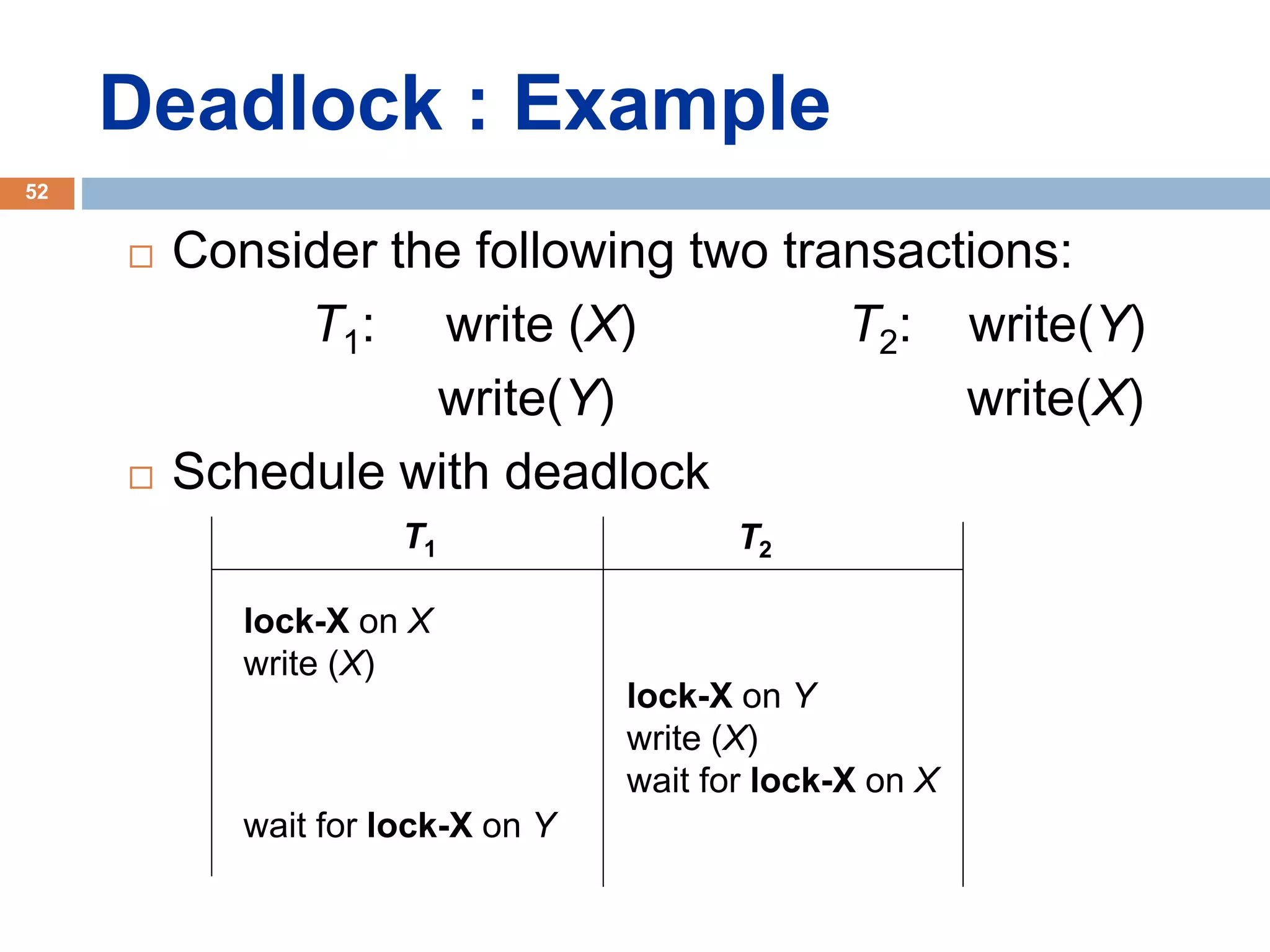
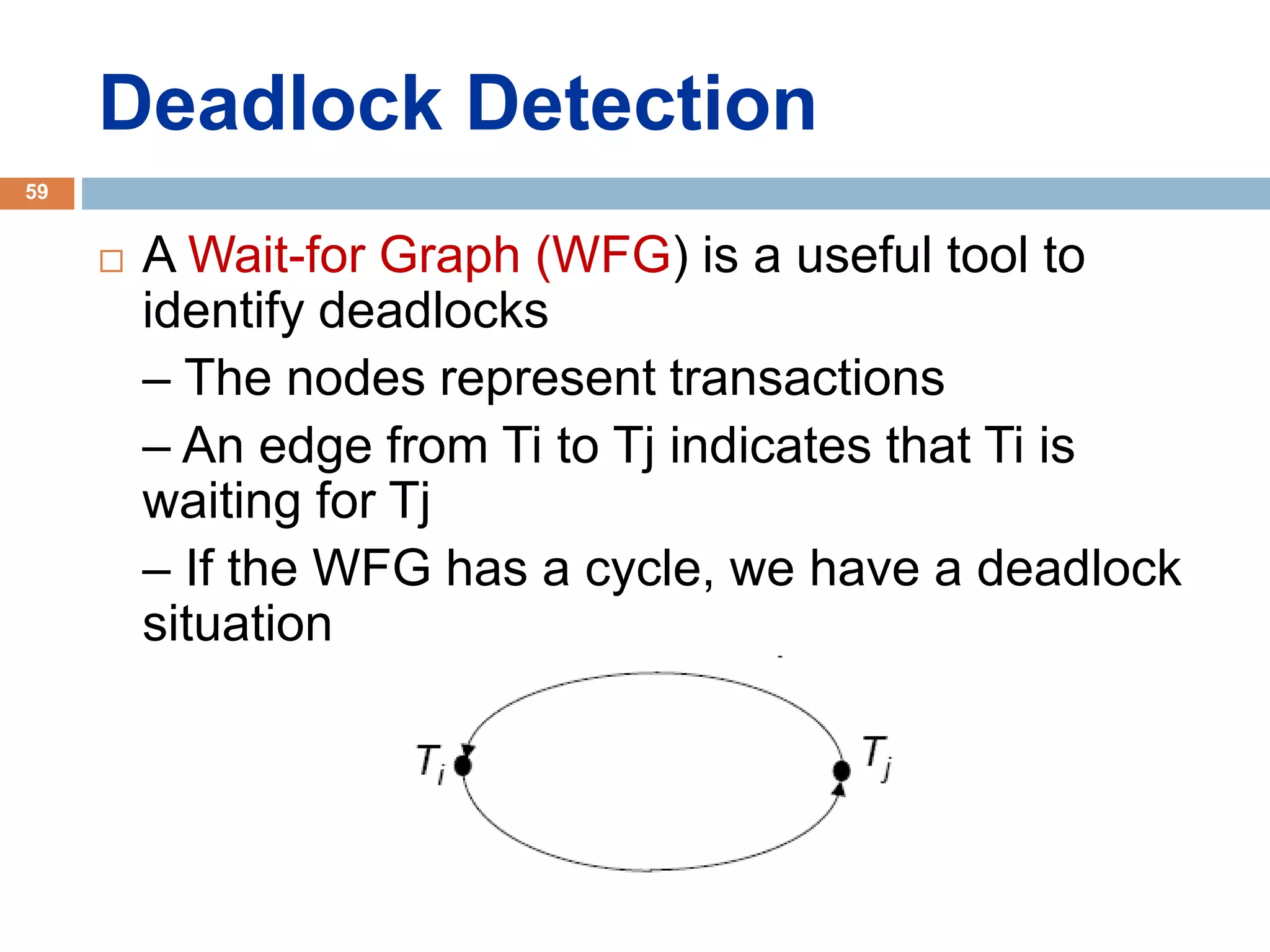
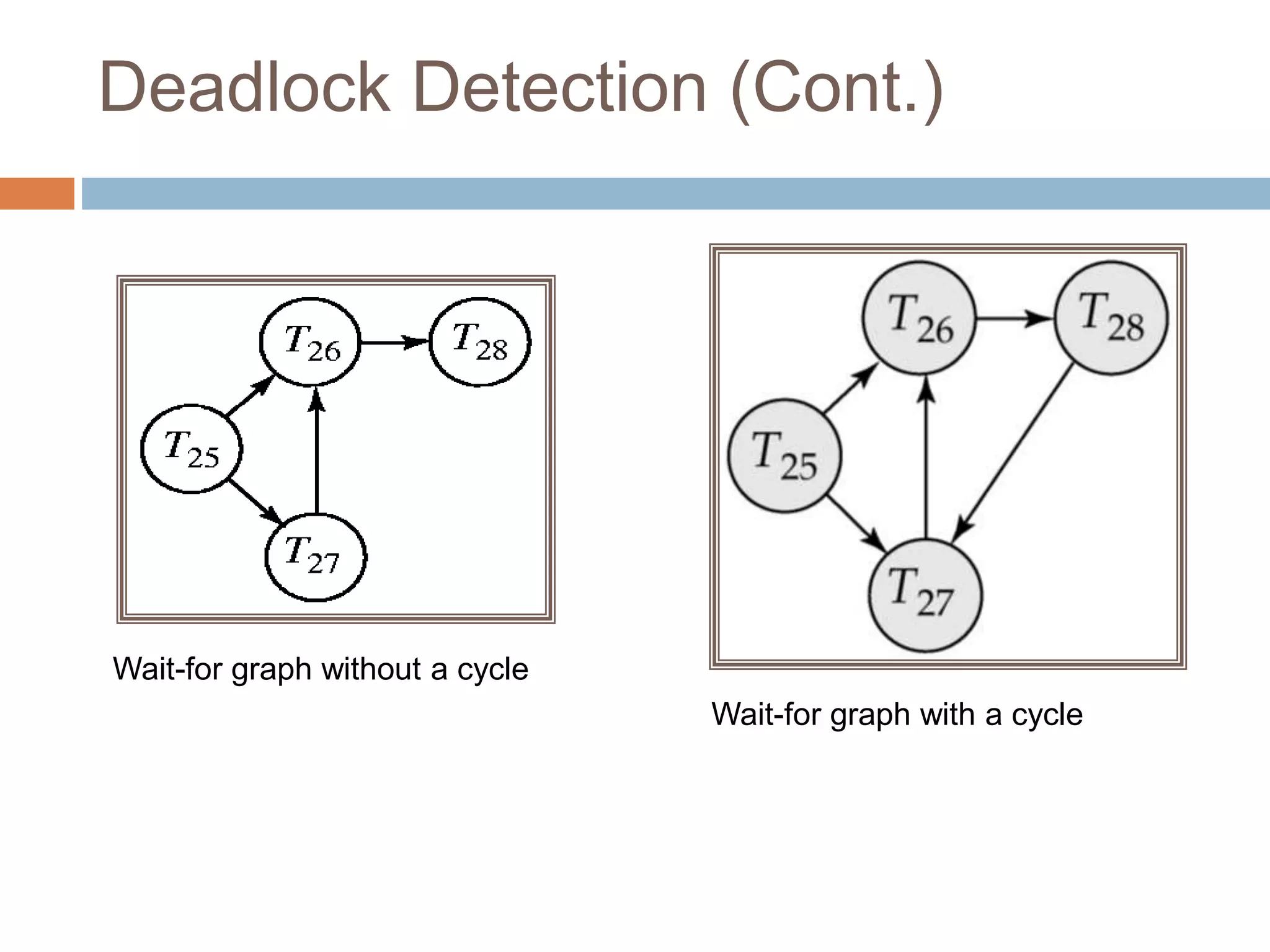
Concurrency control techniques ensure consistency and reliability of concurrent transactions in a database. They synchronize transaction operations to maintain consistency while allowing maximum concurrency. Three main techniques are locking-based protocols, timestamp ordering, and optimistic concurrency control. Locking-based protocols like two-phase locking use locks to control access to shared data and guarantee serializability. Timestamp ordering assigns timestamps to transactions and validates reads and writes based on timestamp order. Optimistic concurrency control allows transactions to read and write tentatively without locking, and validates at the end to commit only if no conflicts occurred.