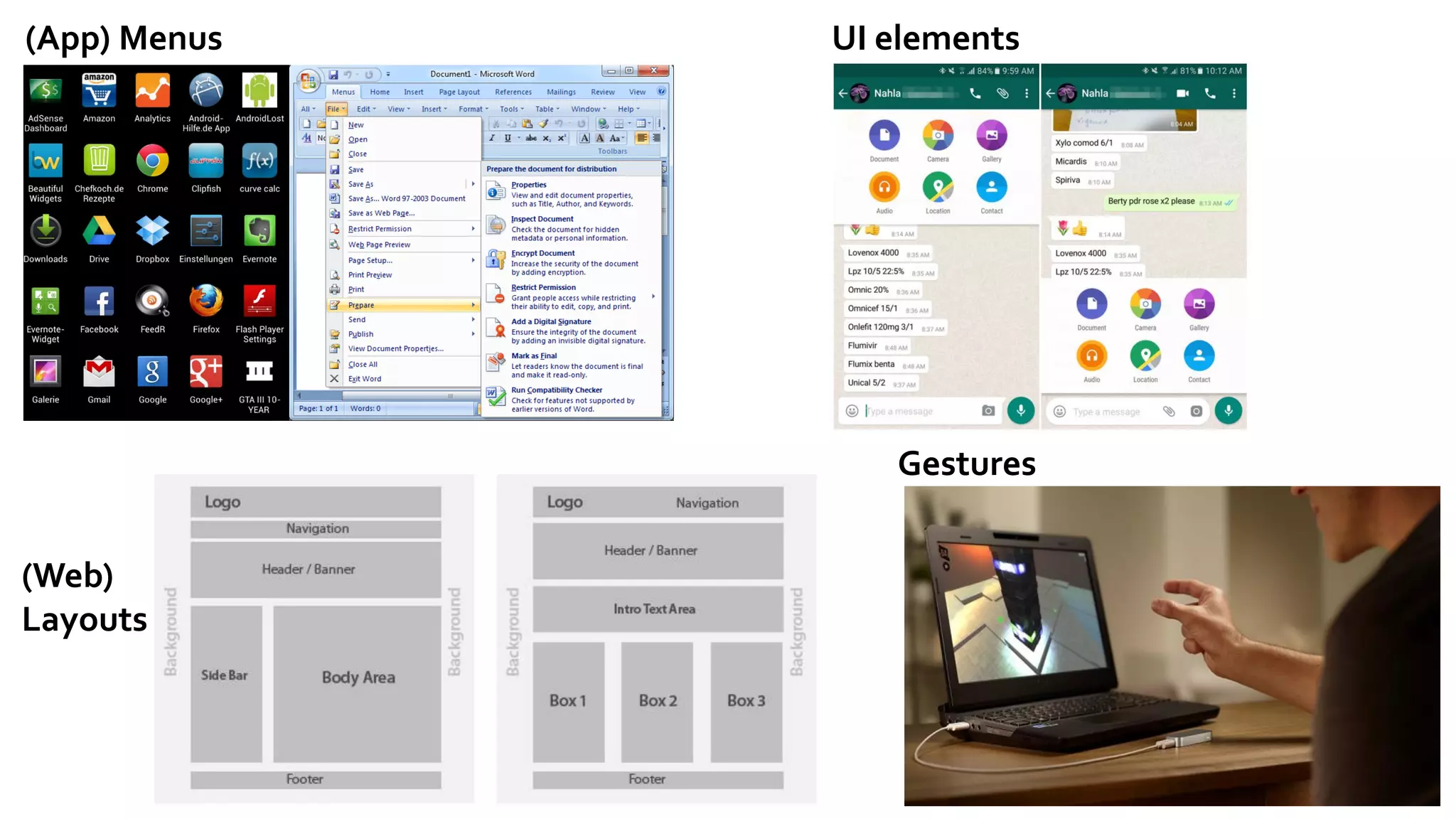
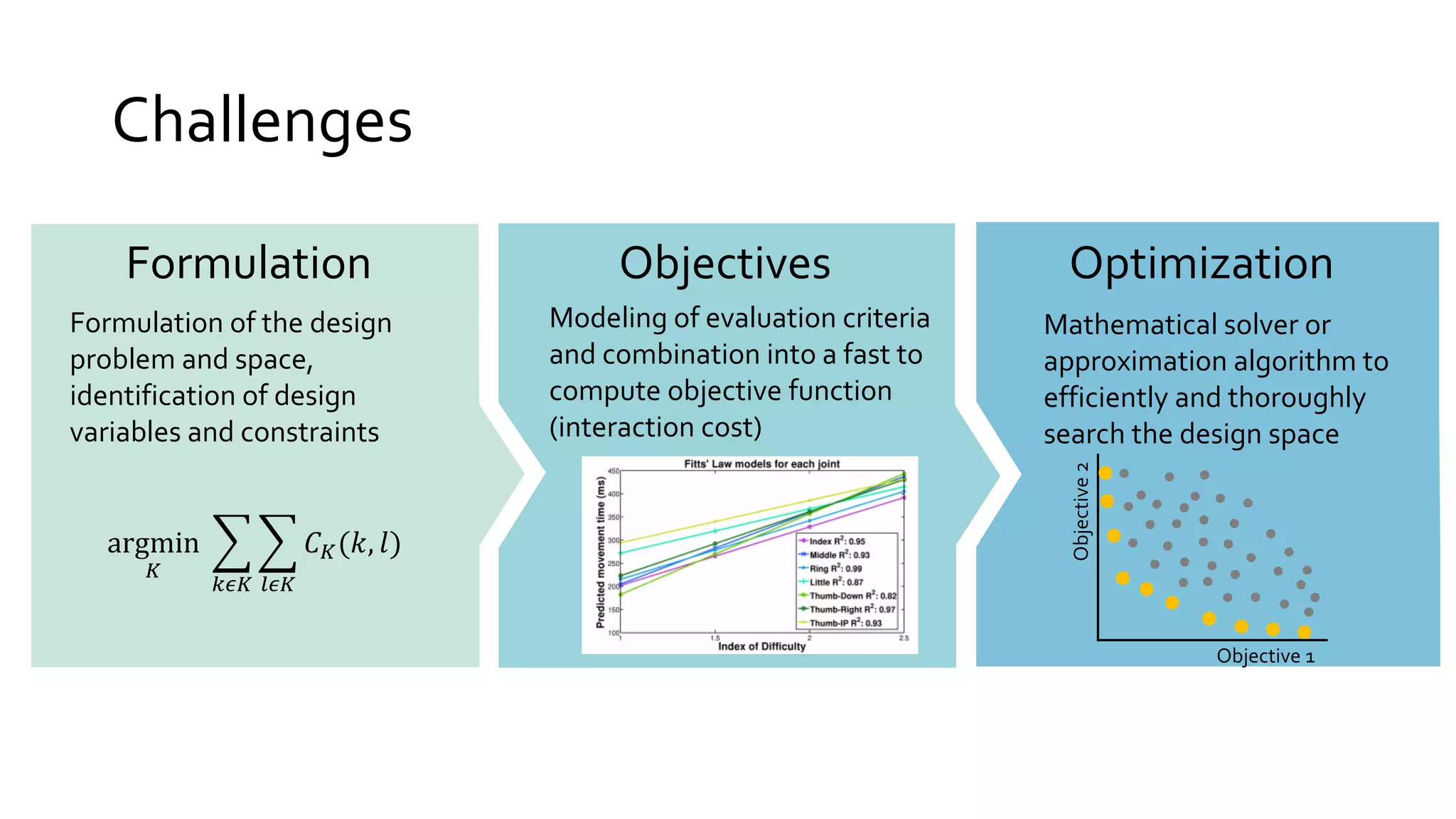
The document discusses the optimization of text input using mid-air hand gestures, exploring the challenges of assigning letters to gestures and evaluating design effectiveness. It emphasizes mathematical methods for efficient design space exploration, utilizing techniques like integer programming and heuristic algorithms to balance multiple objectives in text entry performance. The research aims to enhance user experience by integrating ergonomic and cognitive factors while accommodating diverse typing tasks.


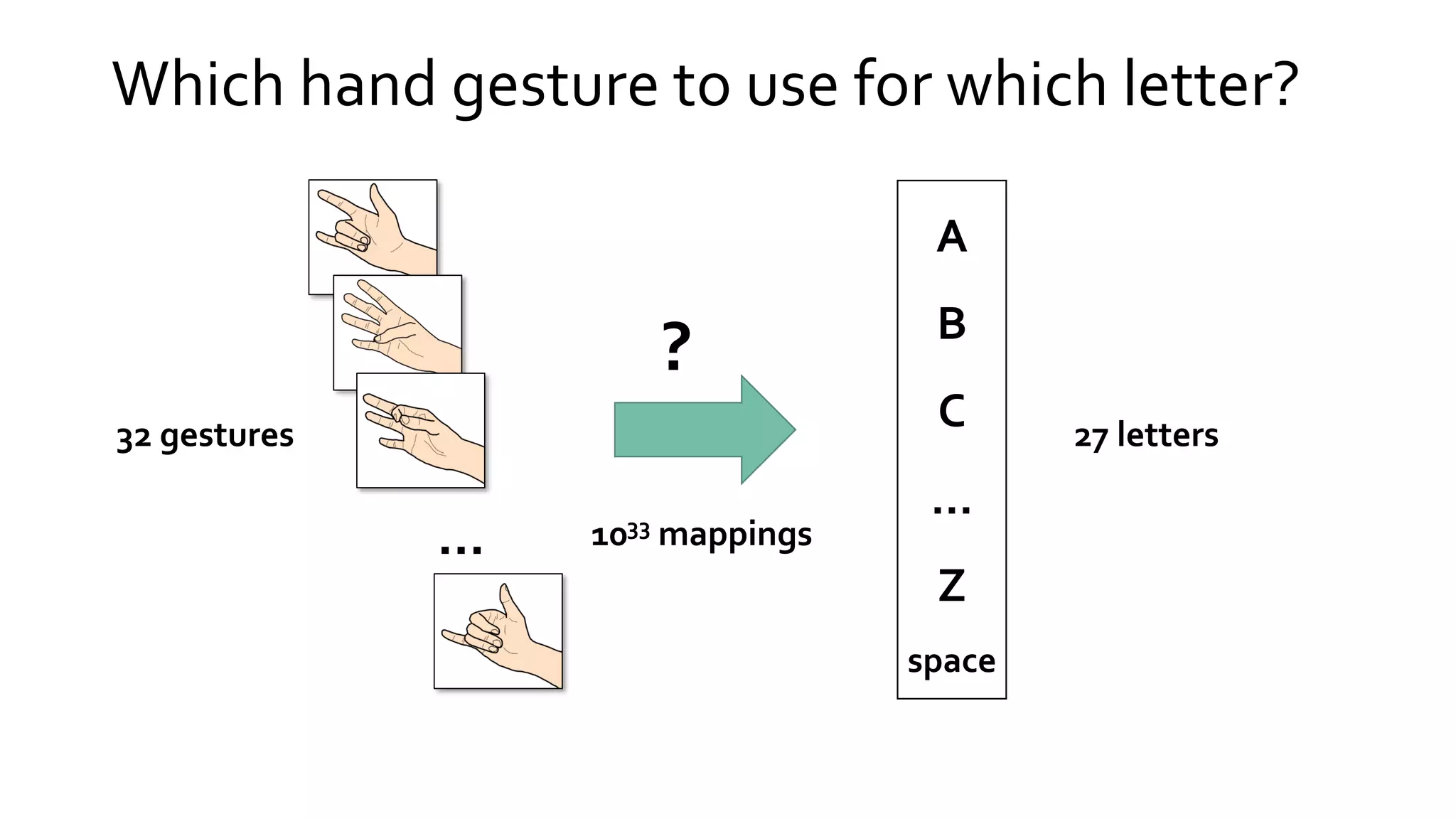
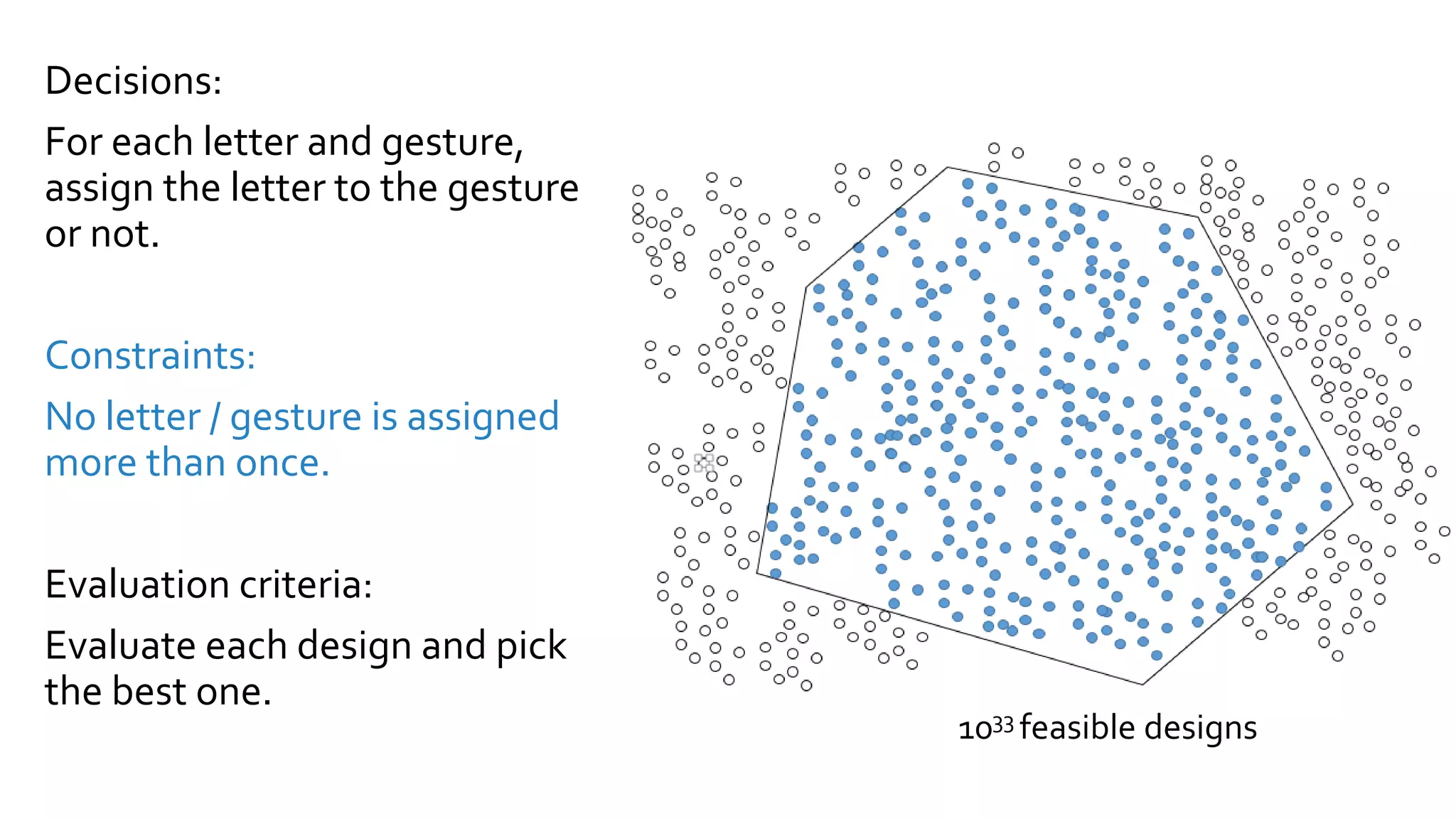

![The (quadratic) letter assignment problem
Given: n letters – 𝑖, 𝑗 𝜖 𝛴
m gestures – 𝑘, 𝑙 𝜖 𝐺
Let: 𝑥𝑖𝑘 = 1 if letter 𝑖 is assigned to gesture 𝑘, 𝑥𝑖𝑘 = 0 otherwise
𝐗 = {𝑥𝑖𝑘 | ∀ 𝑖 𝜖 𝛴, 𝑘 𝜖 𝐺, 𝑥𝑖𝑘 𝜖 0,1 } characterises the full design space
[Burkhard, 1977]
Formulation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-8-2048.jpg)
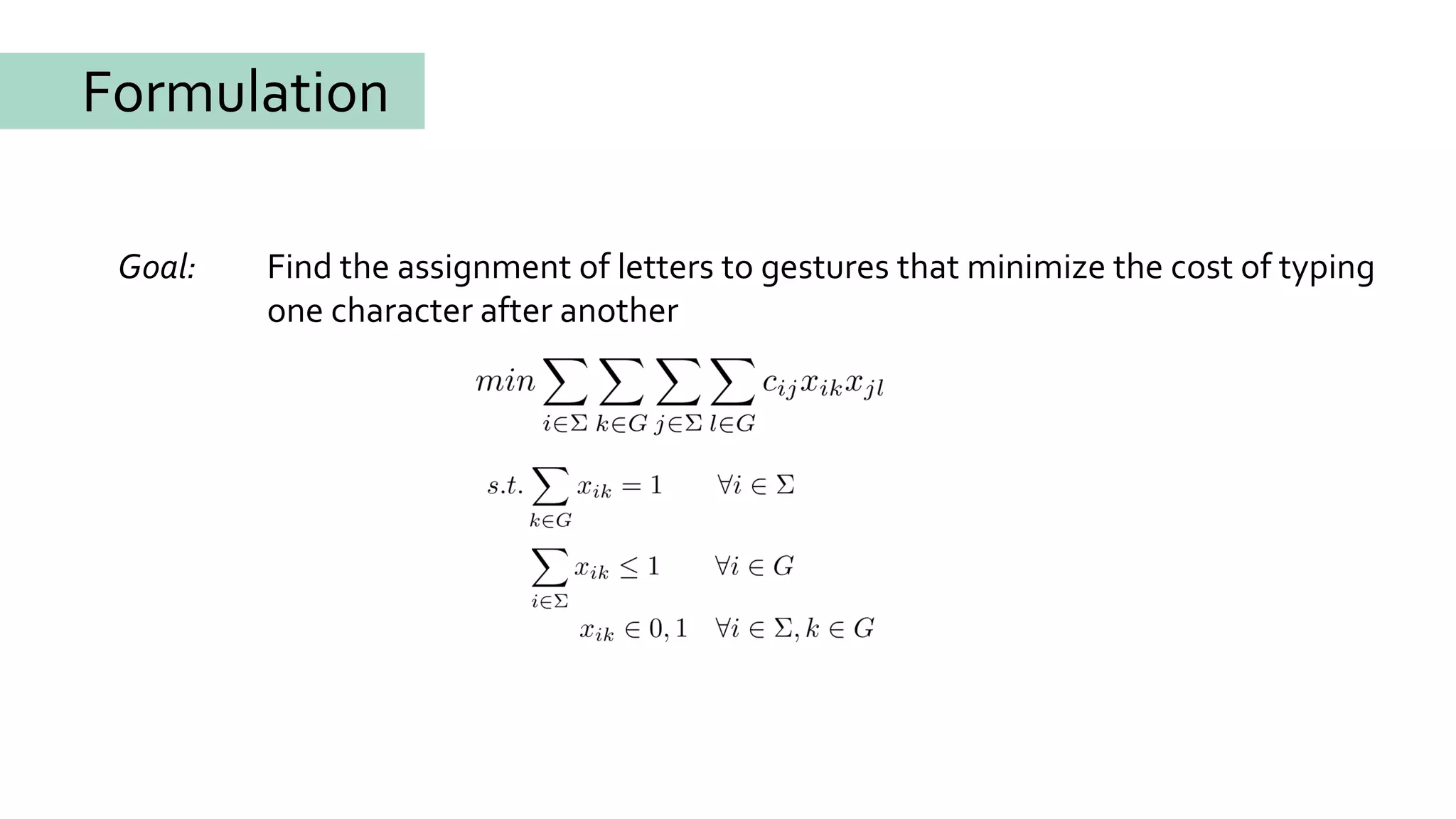
![[Zhai, Hunter & Smith, 2000]
[Light & Anderson, 1993]
Formulation
[Oulasvirta & Karrenbauer, 2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-10-2048.jpg)
![” It is almost impossible to write correctly French
with a keyboard marketed in France”
French Ministry of Culture and Communications
[Feit, Nancel,Weir, John, Bailly,
Karrenbauer, Oulasvirta, upcoming]
Formulation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-11-2048.jpg)
![[Feit, Nancel,Weir, John, Bailly,
Karrenbauer, Oulasvirta, upcoming]
Formulation
é è à ù ê Ê É È À ç Ç æ Æ œ Œ ß ẞ þ Þ ð Ð ŋ Ŋ ij IJ ə Ə ʒ Ʒ & θ ı İ @ ™ ® ©
ſ º ª · ´ ˋ ˆ ¨ ˉ ̲ ˘ ̑ ˇ ˜ ˙ ̣ ̊ ˝ ˵ ¸ ˛ ̦ ̵ ̷ + < > = ± × ÷ ≤ ≥ ≃ % ‰ √ ∞ ¼ ½ ¾
# / | . , ; : ! ? ¡ ¿ … - - — – _ * † ‡ § ( ) [ ] { } “ ” ‘ ’ « » ‚ „ ‹ › € $ £ ¢ ¤ ¥ ₩
?? ?
> 𝟏𝟎 𝟐𝟏𝟑
𝒂𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒈𝒏𝒎𝒆𝒏𝒕𝒔](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-12-2048.jpg)
![[Feit, Nancel,Weir, John, Bailly,
Karrenbauer, Oulasvirta, upcoming]
Formulation
è](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-13-2048.jpg)
![Objectives
• Performance – Fitts’ law weighted by letter pair frequency
• QWERTY similarity [Dunlop & Levine 2012]
• Word or gesture clarity [Dunlop & Levine 2012, Smith, Bi & Zhai 2015]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-14-2048.jpg)

![Objectives
[How we type,
Feit, Weir, Oulasvirta, CHI 2016]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-16-2048.jpg)
![Objectives
…
|C6| = 0.38
Middle vs. Ring, participant 2046
Non-instructed:Ring
Instructed: Middle
Gesture performance models
based on Fitts’ law and theories
of motor control
Anatomical comfort:
Individuation index for each
finger
[Investigating the Dexterity of Multi-Finger Input for Mid-AirText Entry,
Sridhar, Feit,Theobalt, Oulasvirta, CHI 2015]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-17-2048.jpg)
![Objectives
[Feit, Nancel,Weir, John, Bailly,
Karrenbauer, Oulasvirta, upcoming]
Standardization committee:
”The new keyboard should facilitate typing of correct french, should be easy to learn and intuitive to use”
• Performance and ergonomics of typing a
special character before or after a letter
• Intuitive and easy to learn:
• Grouping similar characters
• Position similar to QWERTY
• Language statistics take into account different
typing tasks, e.g. programming, social media
usage, formal writing, etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-18-2048.jpg)
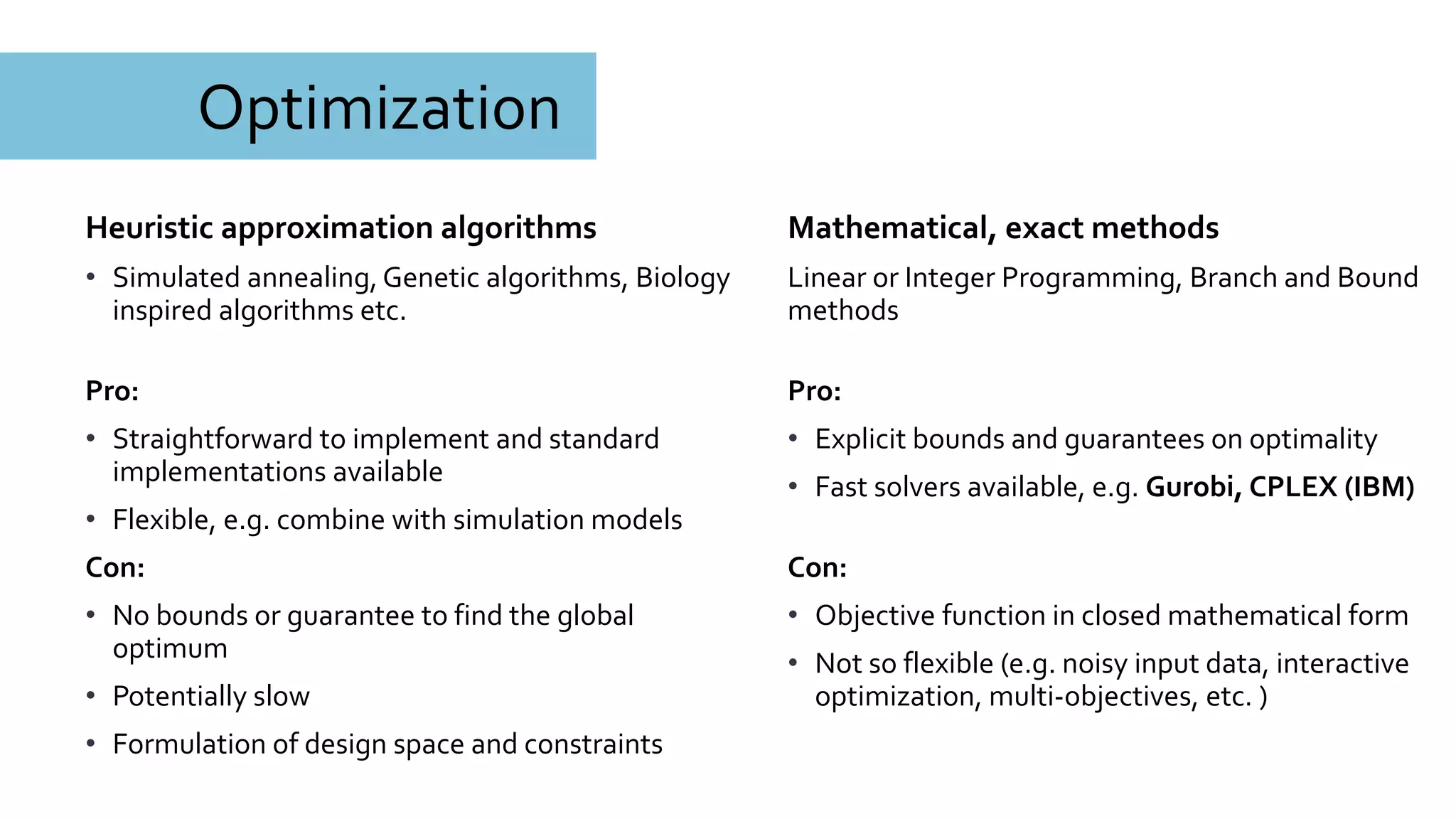
![Optimization
[Feit, Nancel,Weir, John, Bailly,
Karrenbauer, Oulasvirta, upcoming]
Mathematical solver: Gurobi
• Guarantees to cover the full
design space
• Gives explicit bounds
• Nevertheless: cannot solve to
the global optimum
Challenge: integrate
optimization with stakeholders’
opinions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dagstuhloptimizationoftextinput-180122154639/75/Optimization-of-Text-Input-20-2048.jpg)