OCT
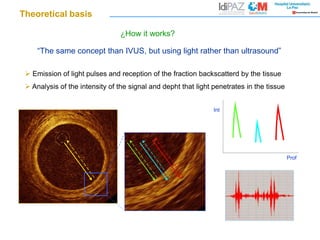
- 1. “The same concept than IVUS, but using light rather than ultrasound” Emission of light pulses and reception of the fraction backscatterd by the tissue Analysis of the intensity of the signal and depht that light penetrates in the tissue Int Prof ¿How it works? Theoretical basis
- 2. Introduction What are the optical properties that we use to characterize tissues? “Reflectivity”: Bright, signal intensity Attenuation: determines the depth of light into the tissue
- 3. Image acquisition Blood is a non-transparent media. For this reason it´s neccesary to displace blood from the lumen during image acquisition. Techniques: Occlusive: Inflation of low compliant occlussion balloon proximal to the target lesion and injection of saline through the lumen of the balloon. Non occlussive: Injection of dye through the guiding catheter. Brezinski ME et al. Intern J Cardiol 2006;107:154-65 Tomlins PH et al. J. Phys D: Appl Phys 2005;38:2519-35 Pinto TL et al. J Intervent Cardiol 2006;19:566-73 Yamaguchi T et al. Am J Cardiol 2008;101:562-67 Tanigawa J et al. Eurointerv 2007;3:128-36 Prati F et al. Eurointerv 2007;3:365-70 Blood
- 4. Axial resolution 15-20 microns (0.015-0.02 mm) Main advantage: HIGH RESOLUTION Introduction OCT is near of celular range resolution Ten folds higher resolution than IVUS
- 5. Advantage: Highly detailed imaging of intraluminal structures, interface plaque-lumen and superficial portions of vessel wall Introduction
- 6. ¿Where is the external vessel border? Disadvantages: Limited penetration (1.5 - 2 mm). Poor definition of deep regions, specially in lipid-rich plaques, positive remodeling Interference with blood: Need of “flushing” Introducción
- 7. Jang IK et al. JACC 2002;39:604-9 Rieber J et al. Coron Art Dis 2006;17:425-30 Stamper D et al. JACC 2006;47:C69-79 Kawasaki M et al. JACC 2006;48:81-8 Fibrotic plaque: Hiperintense, homogeneous, low atenuation Lipid-rich plaque (necrotic core): Hipointense, high atenuation, diffuse borders Calcified plaque: Hipointense, mid atenuation, sharp borders Coronary lesions OCT morphology of coronary plaques
- 8. Fibrotic plaques Coronary lesions Hiperintense, homogeneous, low attenuation (high penetration)
- 9. Calcified plaques Hipointense, mid attenuation, well-defined, sharp borders Coronary lesions
- 10. Coronary lesions Calcified plaques Hipointense, mid attenuation, well-defined, sharp borders
- 11. Hipointense, high atenuation (low penetration), diffuse borders Lipid-rich plaques/necrotic core Coronary lesions
- 12. Thin-cap fibroatheroma OCT is the unique technique available in daily practice that allows accurate measurement of fibrous cap thickness. Previous pathological studies have identified 65 microns thickness as the threshold of high risk for plaque rupture Coronary lesions