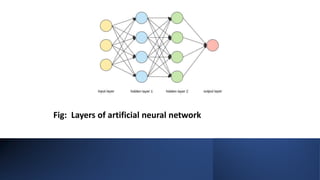
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are a machine learning approach modeled after the human brain. ANNs consist of artificial neurons that are connected in a network similar to biological neurons. Each neuron receives inputs, applies an activation function, and outputs a value. ANNs are specified by their neuron model, architecture including connections between neurons with weights, and a learning algorithm to train the network by modifying weights. ANNs have advantages like storing information on the entire network, working with incomplete knowledge, fault tolerance, and parallel processing. However, they also have disadvantages such as hardware dependence, unexplained behavior, difficulty determining network structure, and unknown optimal training duration.