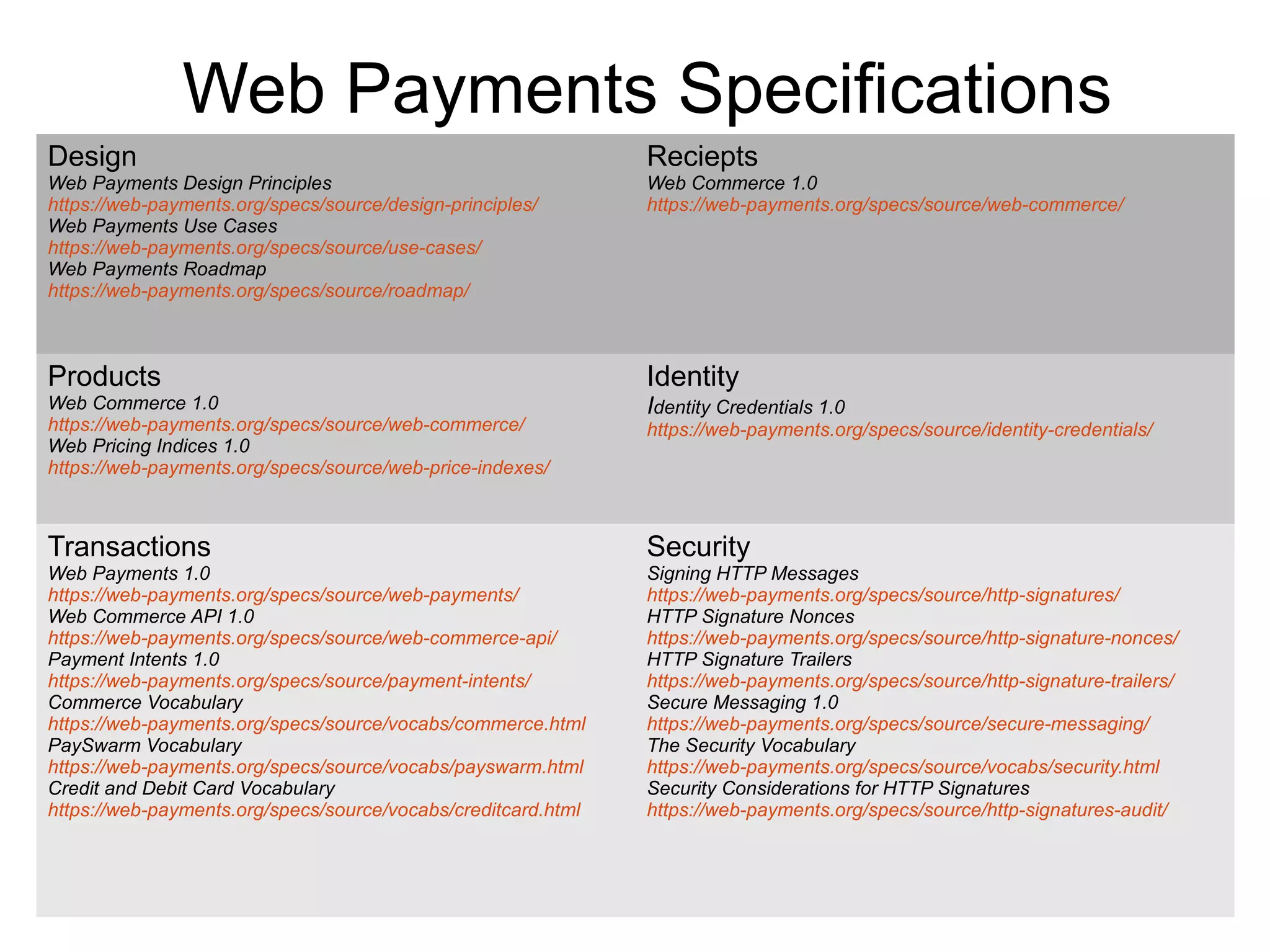
The document provides an overview of linked data and its application in web payments, emphasizing various levels of complexity from linked document networks to semantic linked open data. It outlines the design principles for web payments, which need to be decentralized, secure, extensible, and capable of supporting multiple currencies, including virtual ones. The specifications and practical implementations are also discussed, highlighting the importance of using standards like RDF and JSON-LD in the web payments ecosystem.



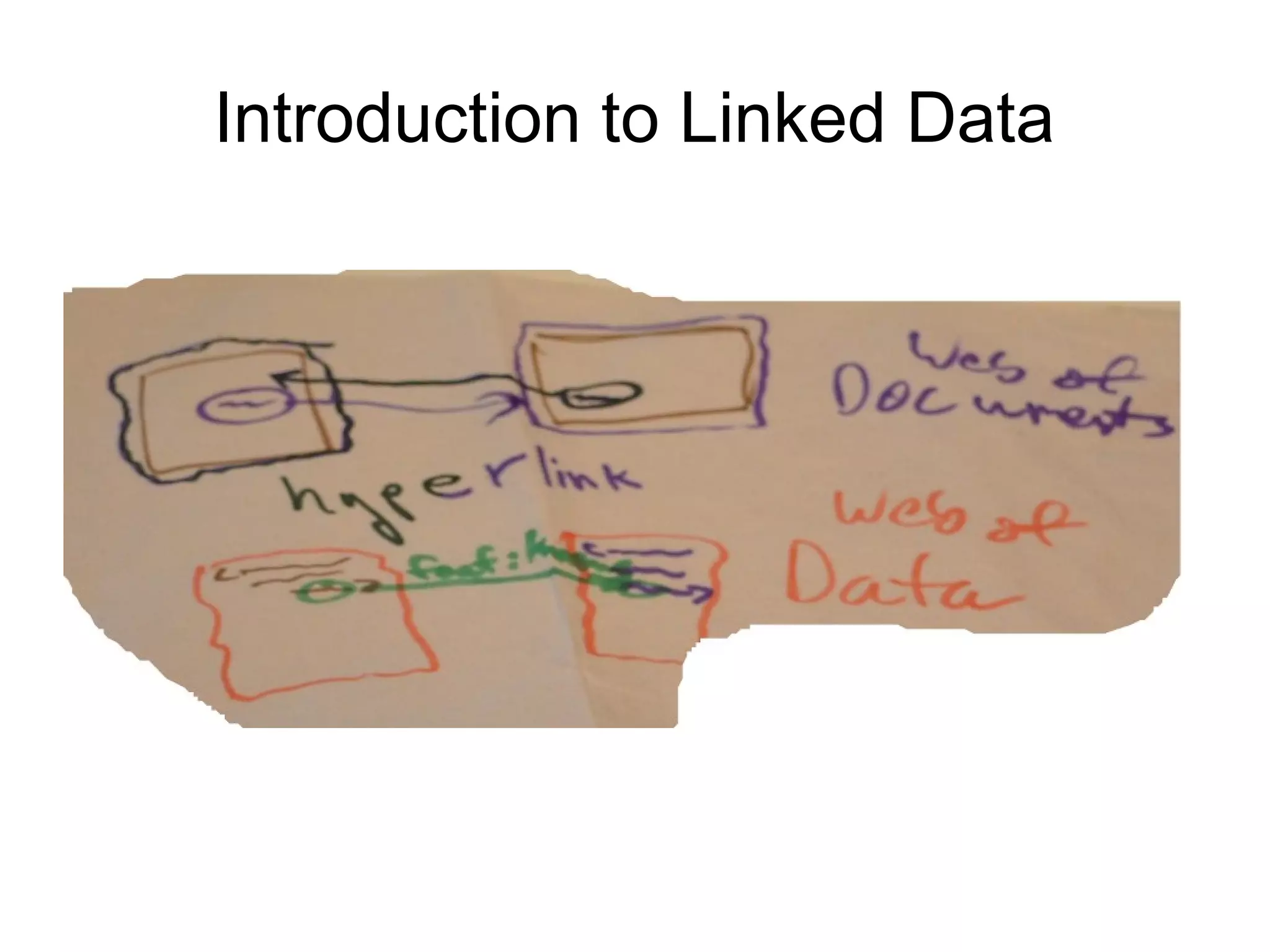
![Different Levels of the Web
[Web] to address the following (levels of complexity?)
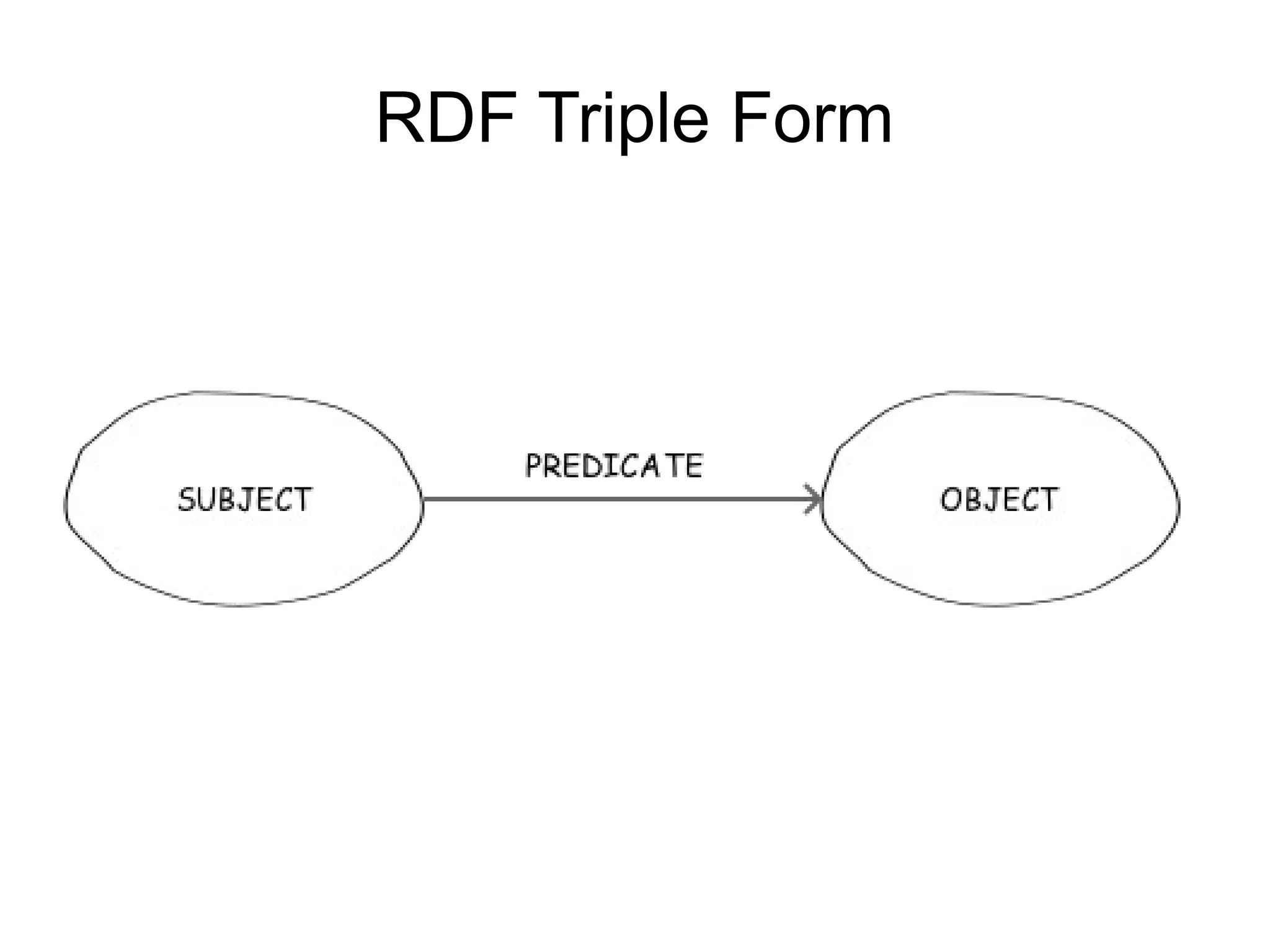
1. Linked Document Network
“every hyperlink denotes a document
location”
2. Linked Data Network
“hyperlinks denote entities”
3. Linked Open Data
“hyperlinks denote entities … resolving to
human and machine readable entity description
documents”
4. Semantic Linked Open Data
“all of the above with the addition of human and machine
readable and comprehensible relation semantics”
Source: http://kidehen.blogspot.com/2014/03/world-wide-
web-25-years-later.html
Kingsley Idehen
CC BY 3.0 AT
http://creativecommons.org/
licenses/by/3.0/at/deed.en
By http://creativecommons.
org/licenses/by/3.0/at/
deed.en](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introlinkeddataandwebpaymentsunfinisheded-141025214945-conversion-gate01/75/Introduction-to-Linked-Data-and-Web-Payments-6-2048.jpg)



![JSON-LD Syntax
● Example 24:
<http://www.w3.org/TR/json-ld/>
{
"@context":
{
"xsd": "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#",
"name": "http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/name",
"age":
{
"@id": "http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/age",
"@type": "xsd:integer"
},
"homepage":
{
"@id": "http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1/homepage",
"@type": "@id"
}
},
"@id": "http://example.com/people#john",
"name": "John Smith",
"age": "41",
"homepage":
[
"http://personal.example.org/",
"http://work.example.com/jsmith/"
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introlinkeddataandwebpaymentsunfinisheded-141025214945-conversion-gate01/75/Introduction-to-Linked-Data-and-Web-Payments-13-2048.jpg)