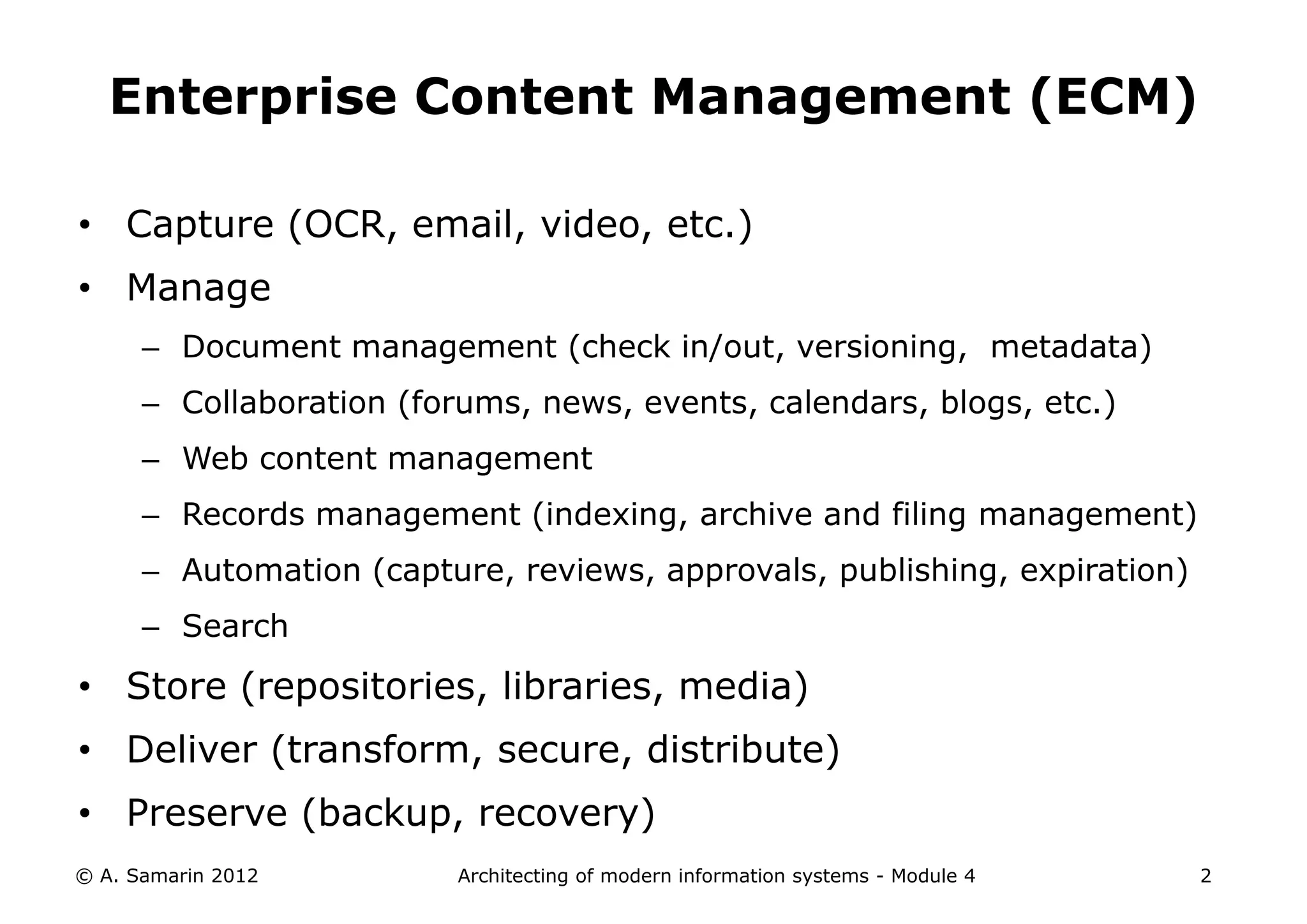
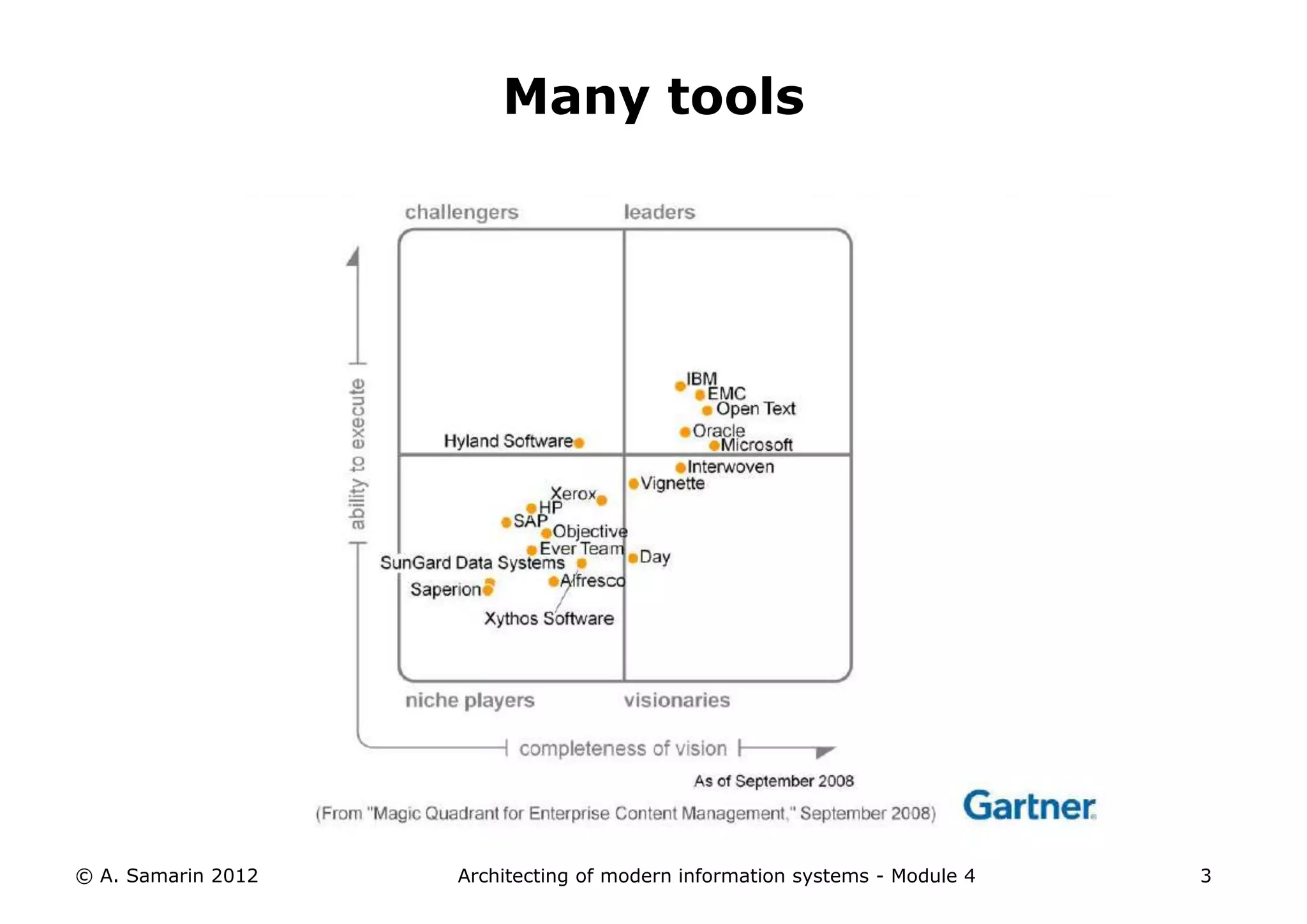
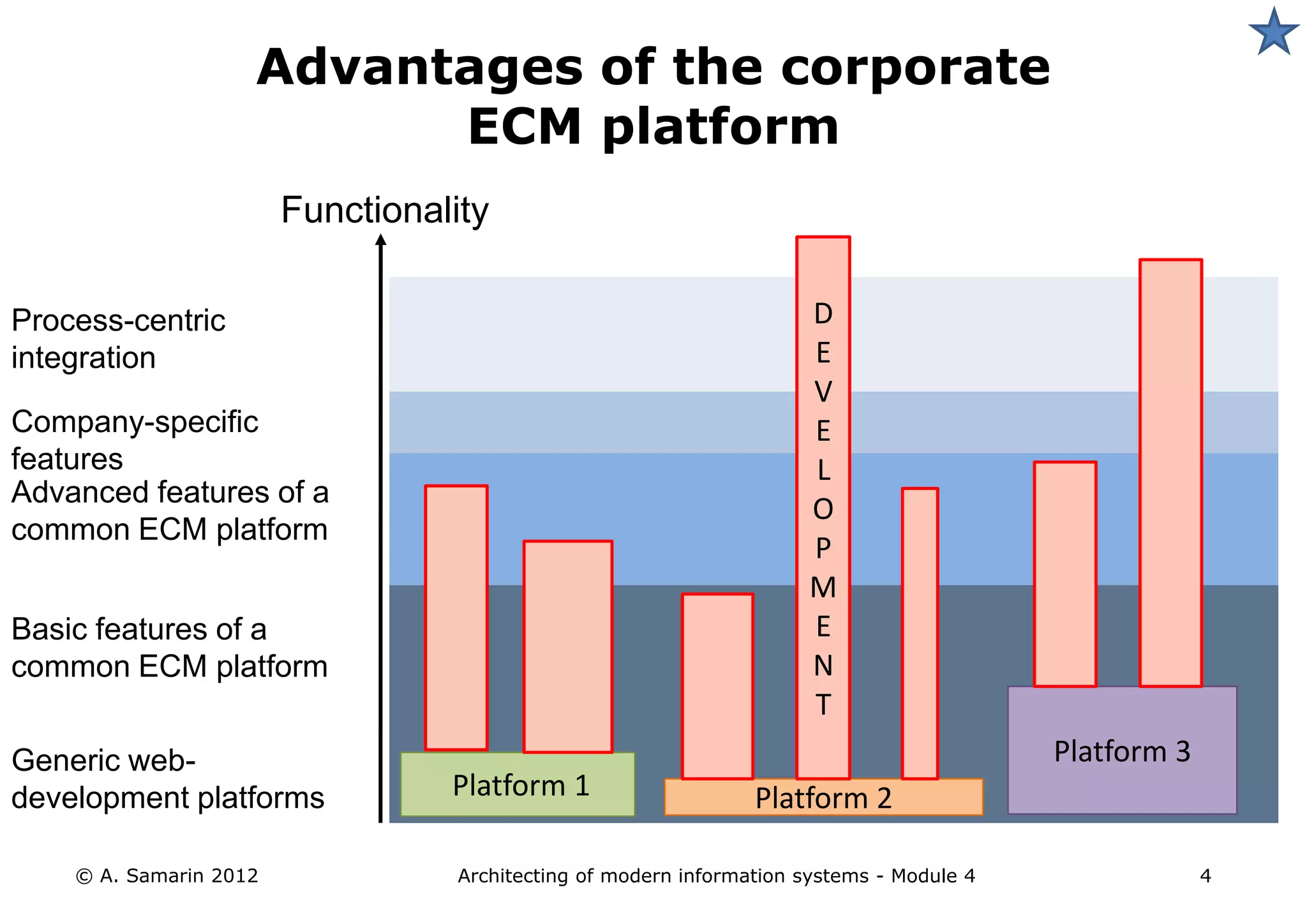
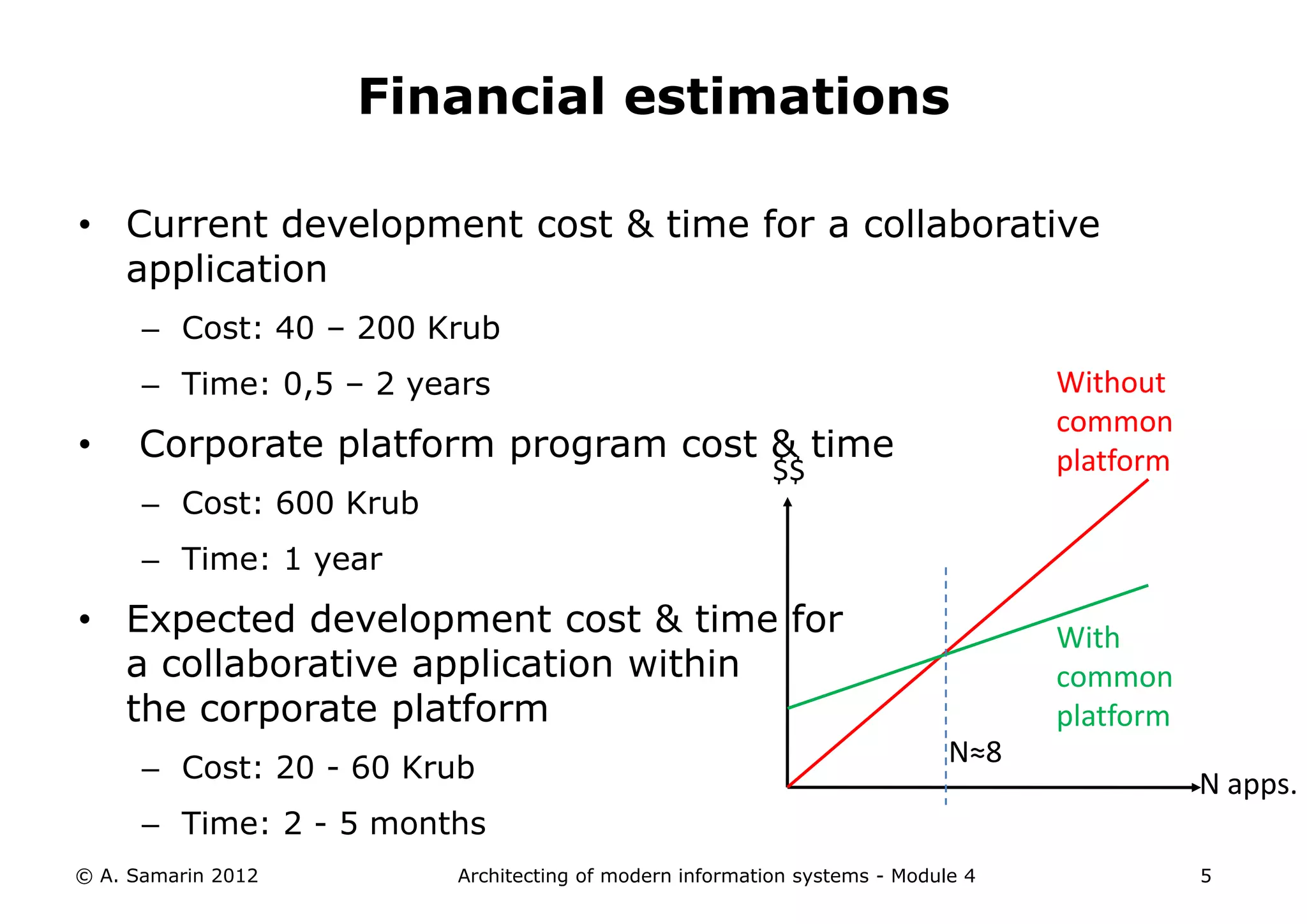
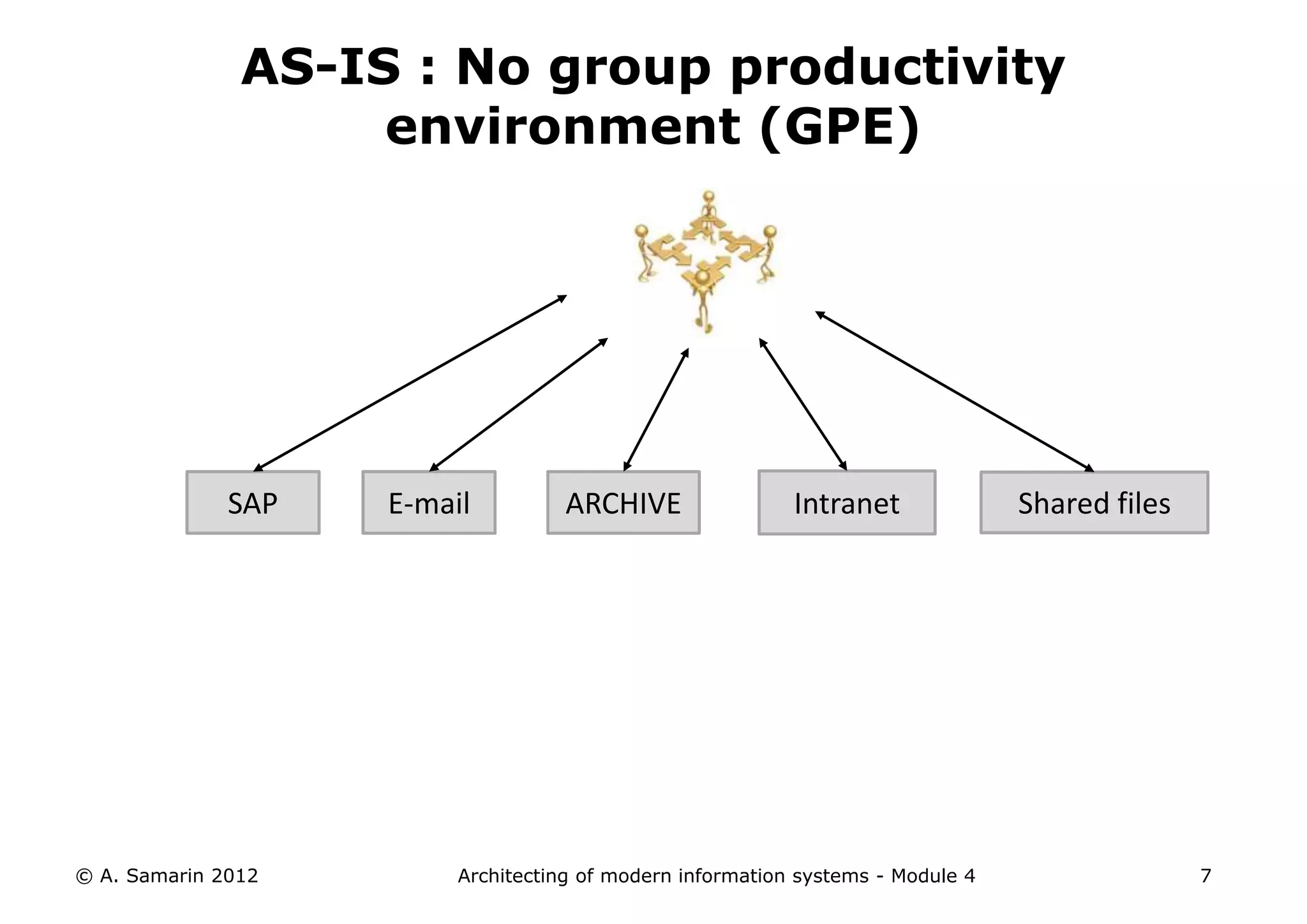
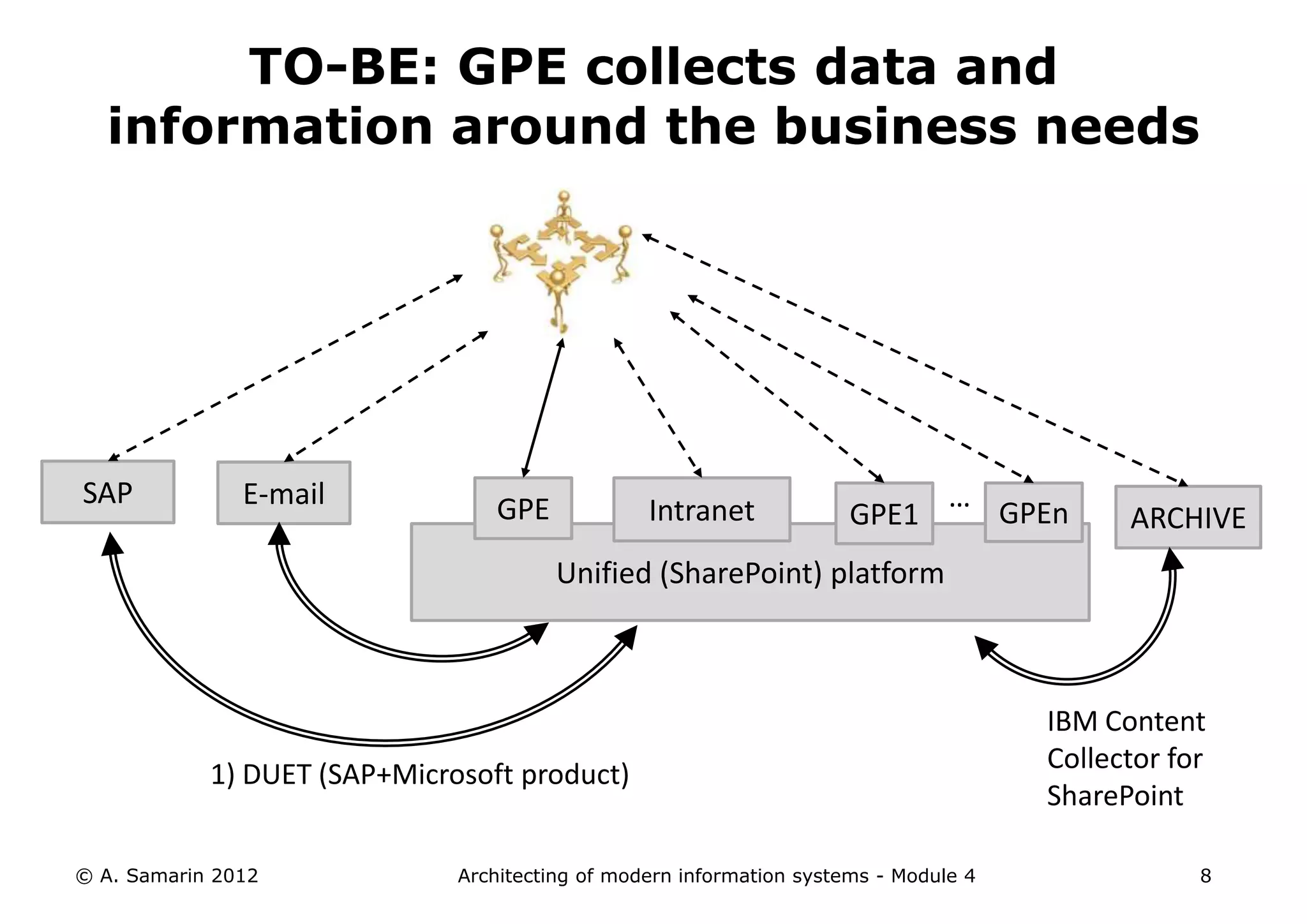
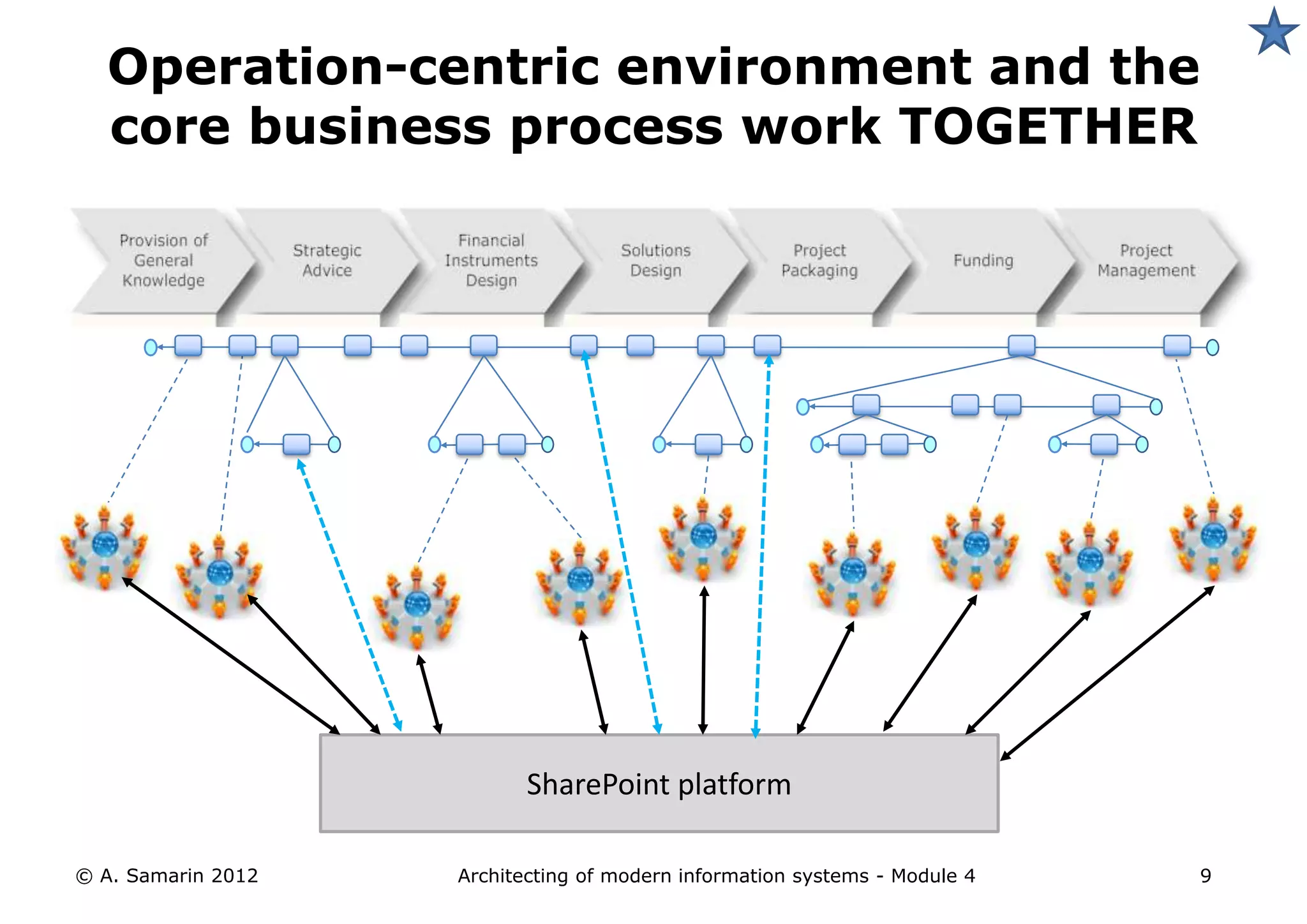
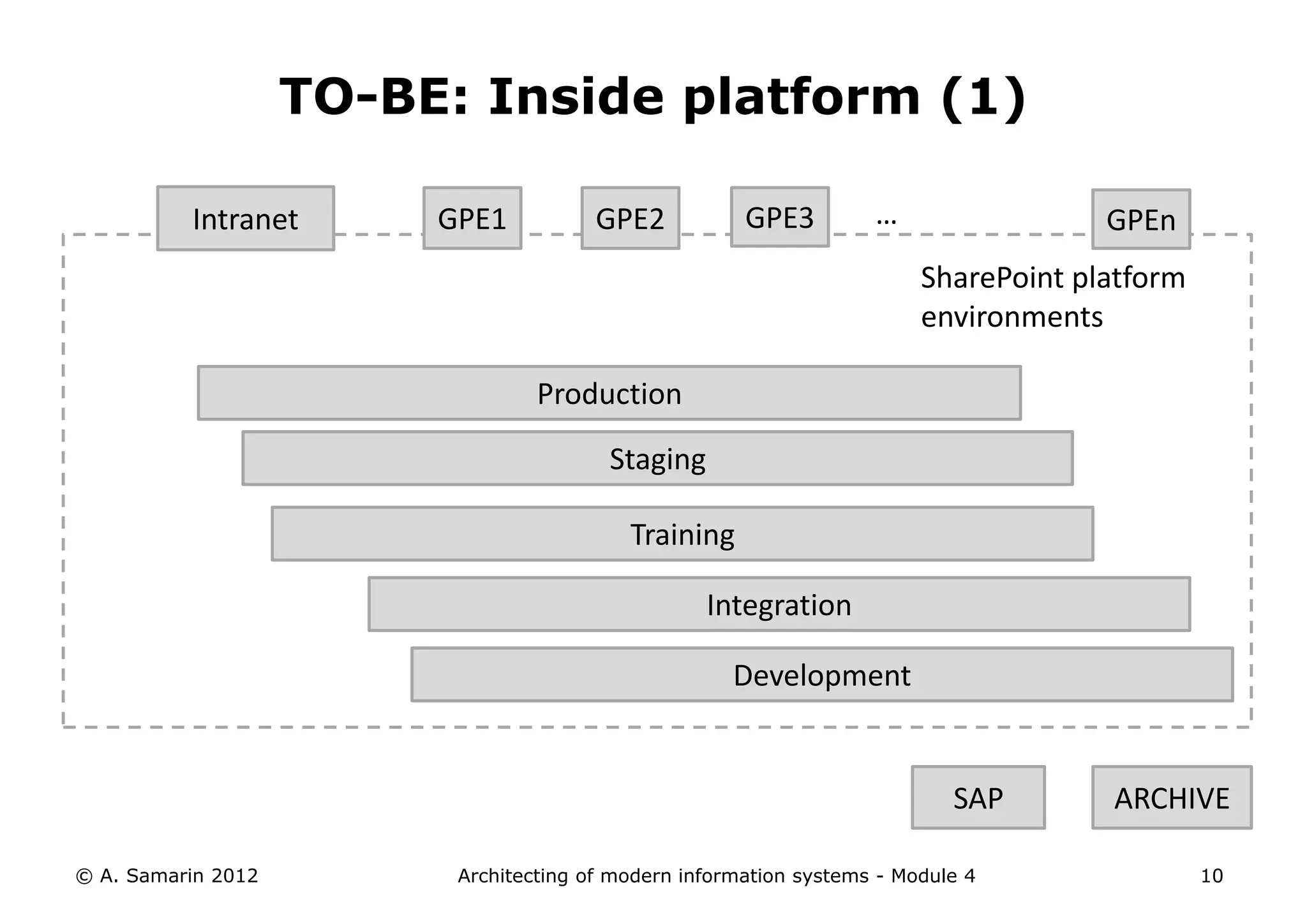
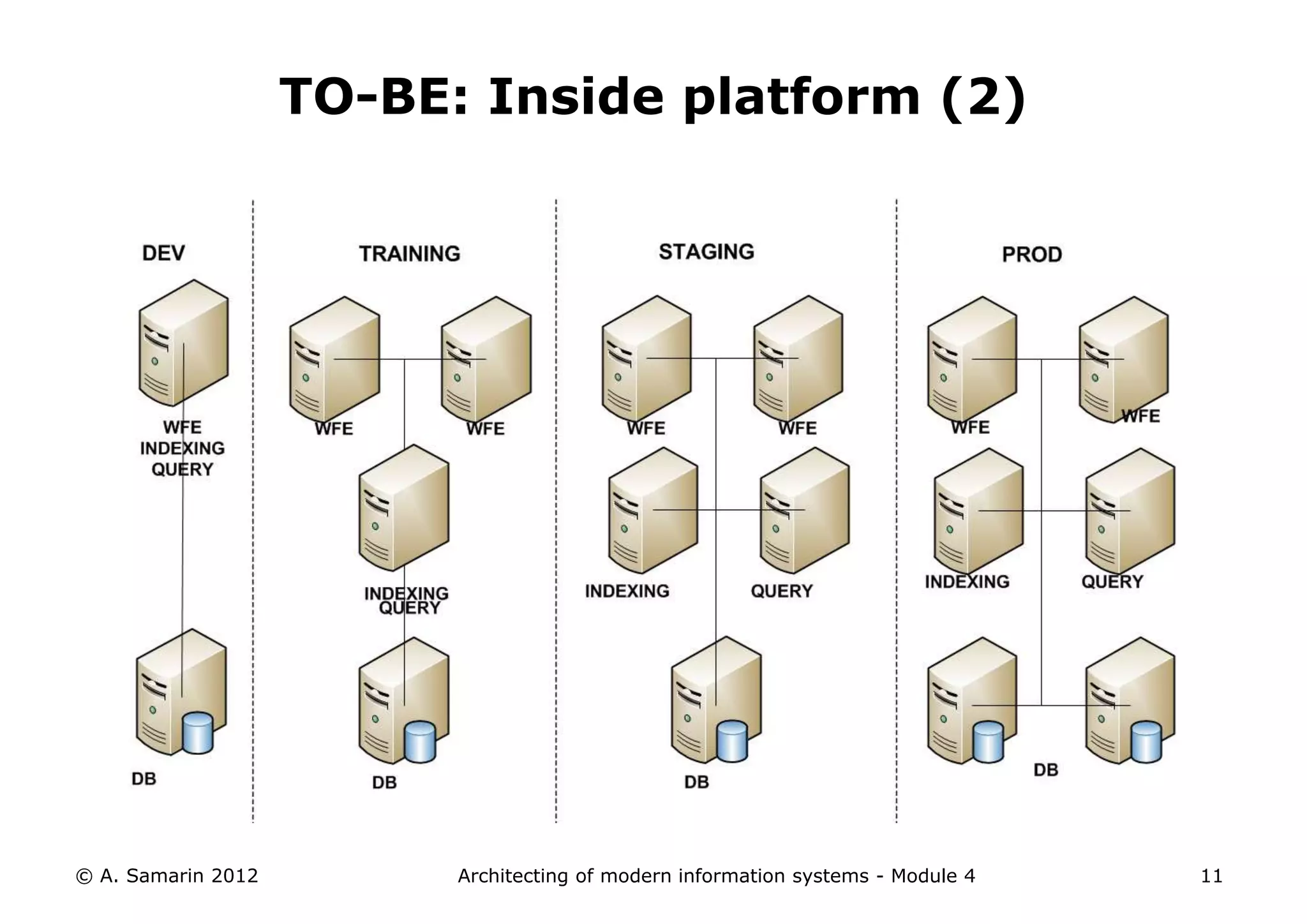
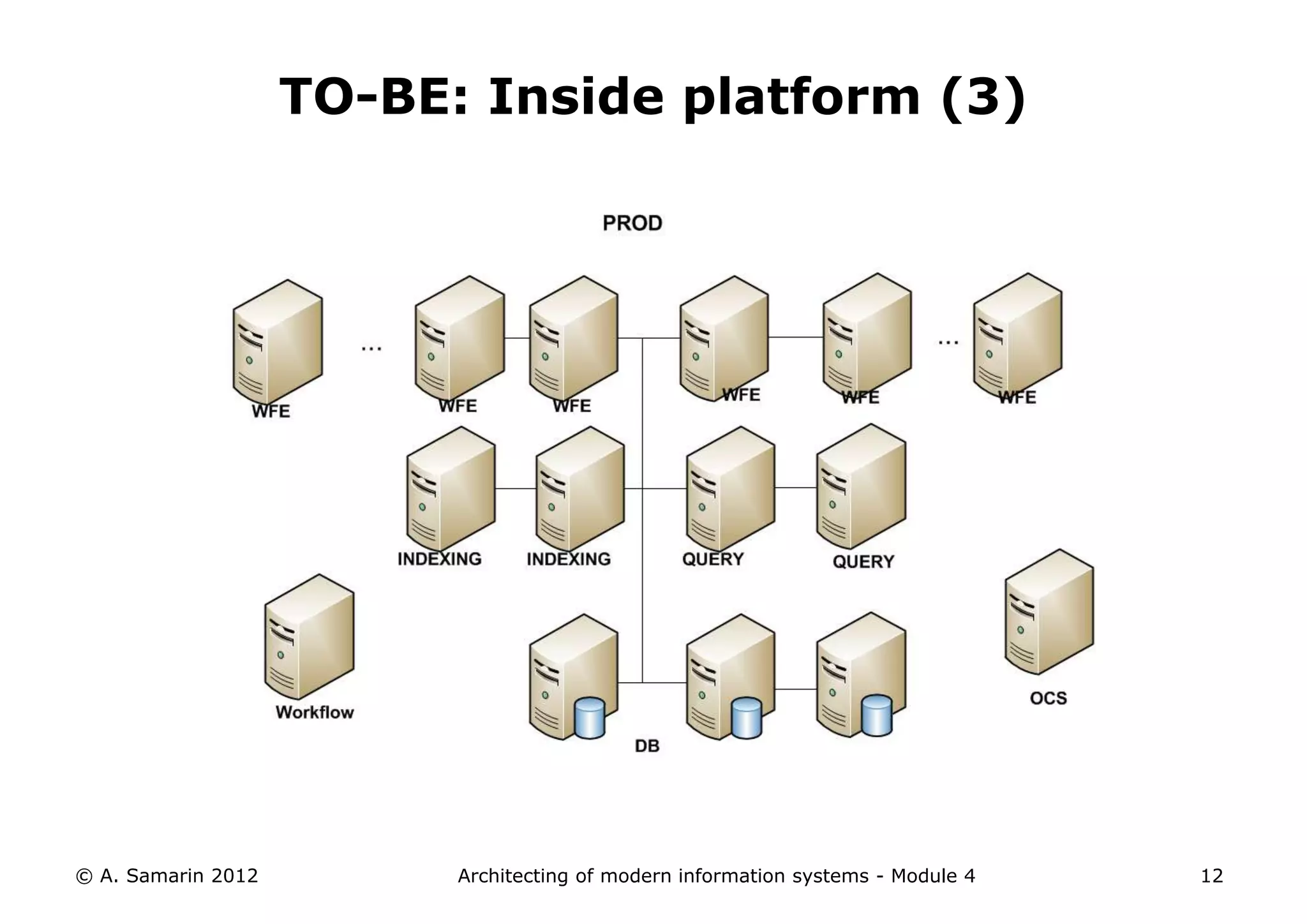
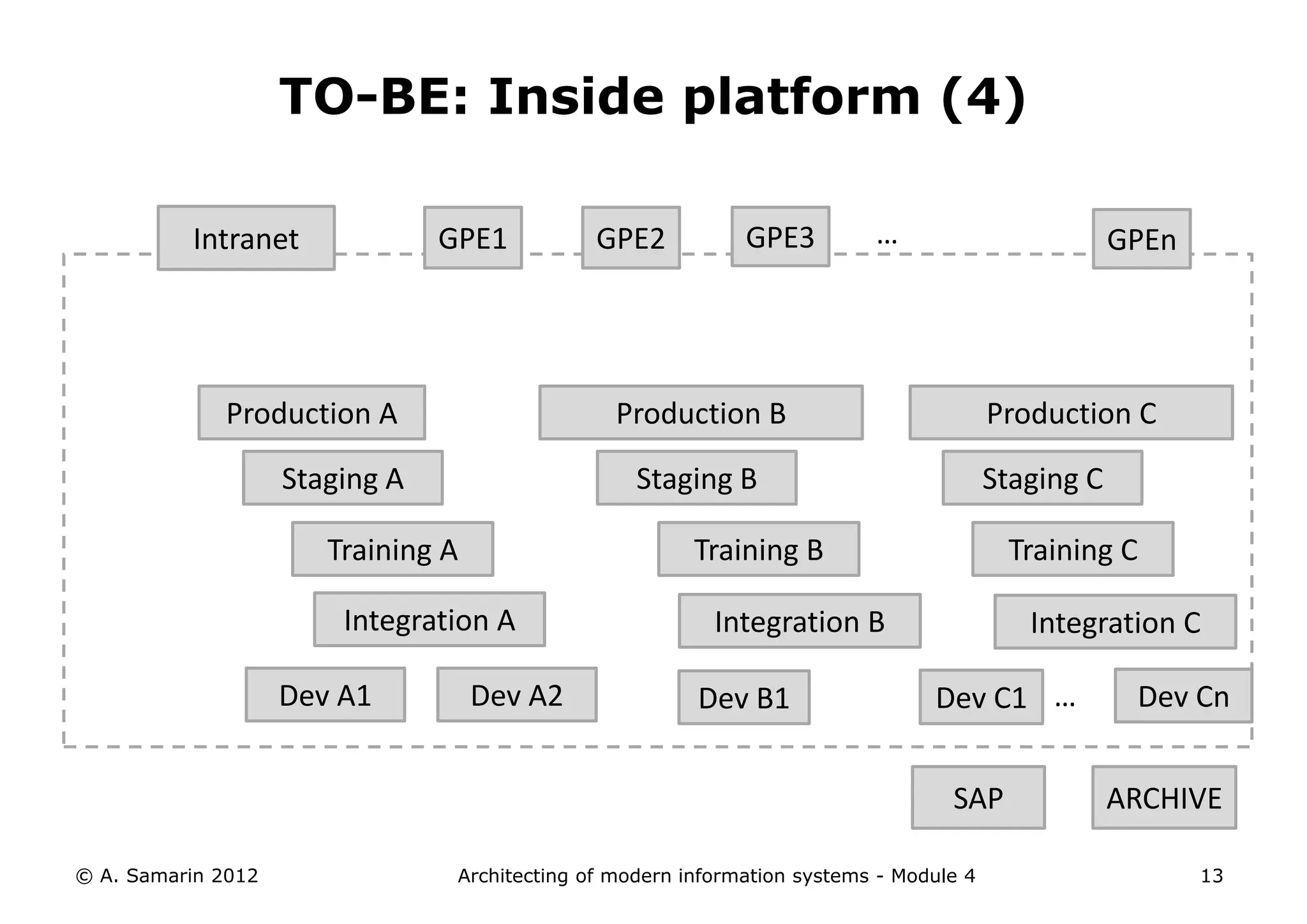
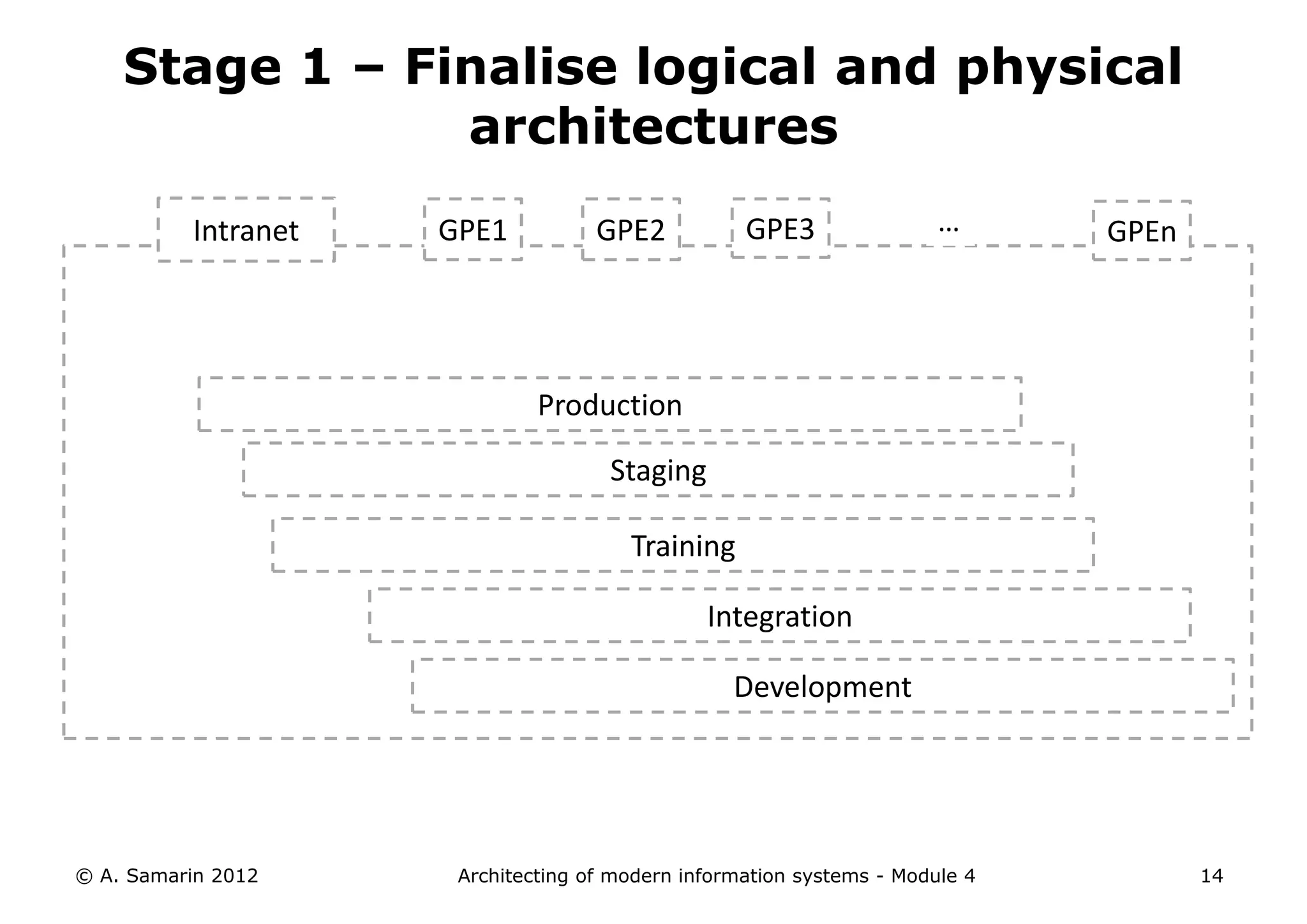
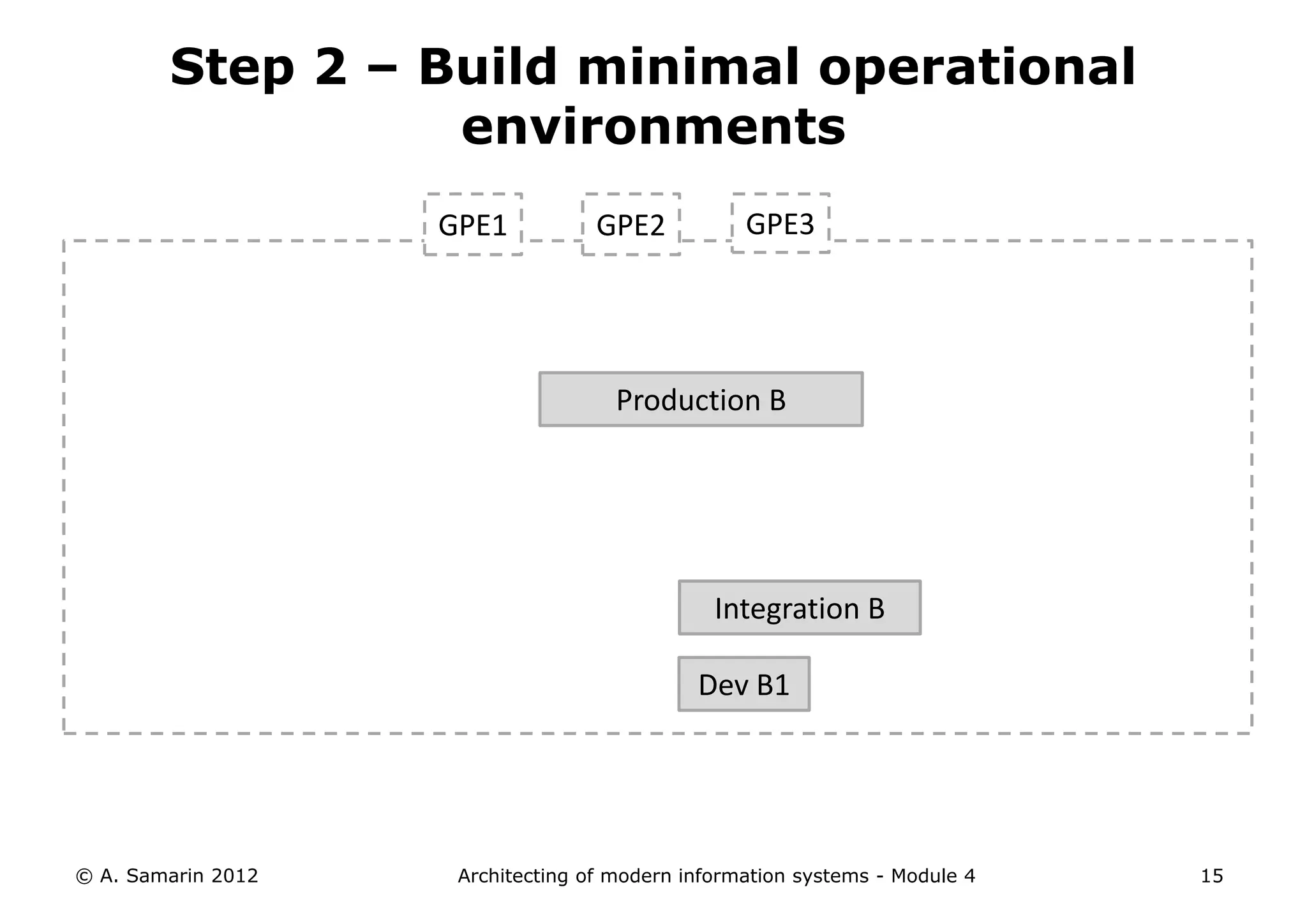
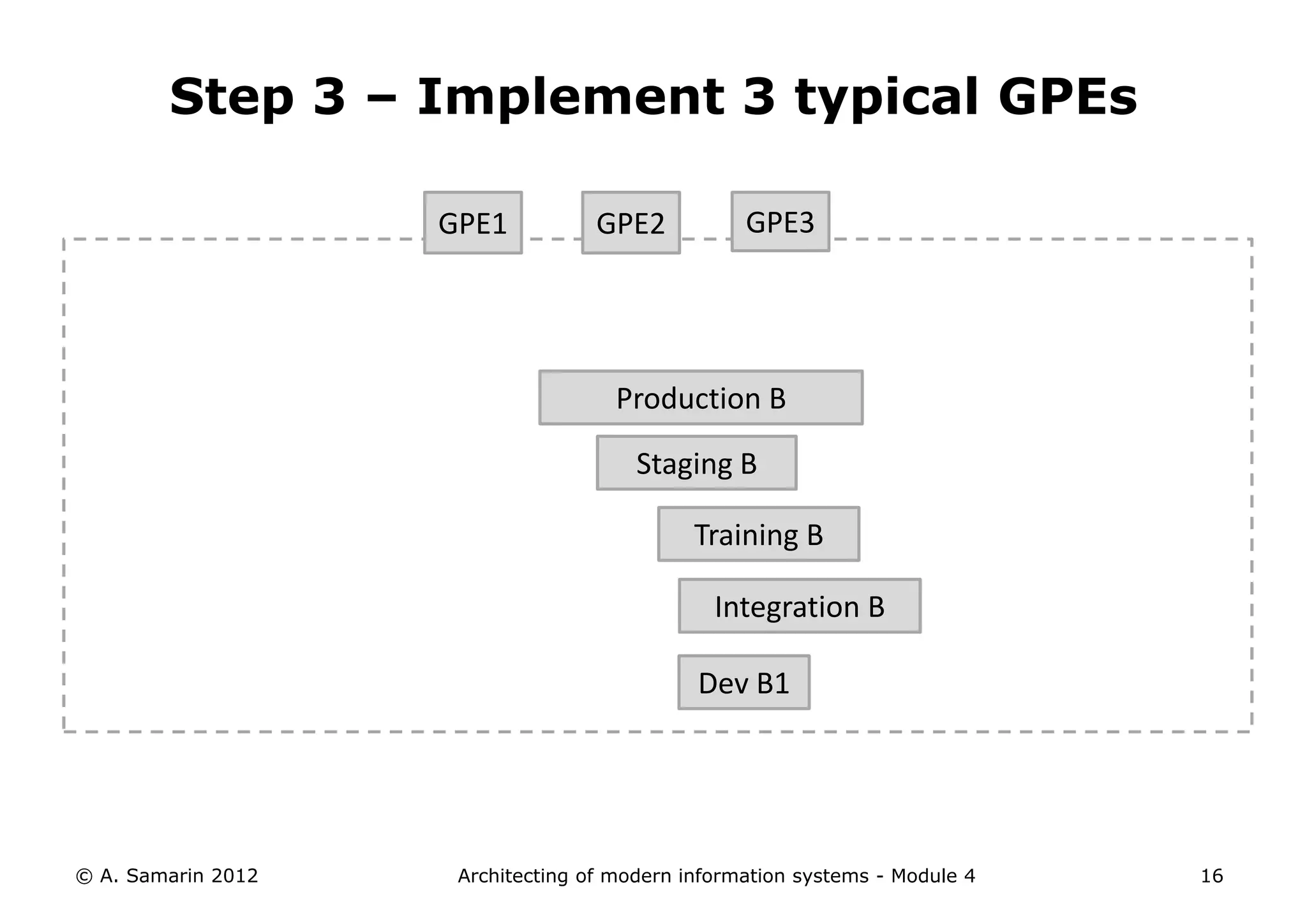
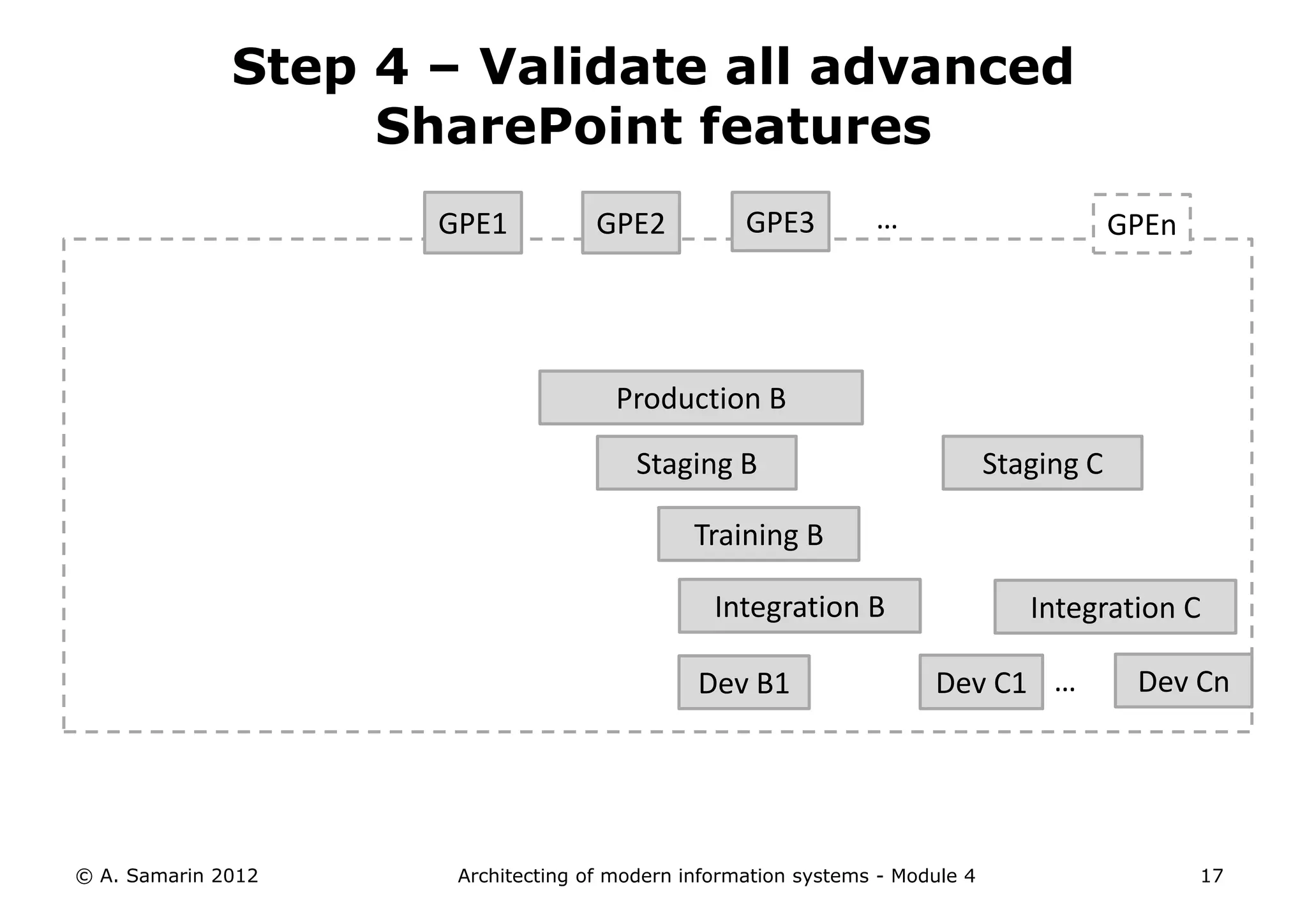
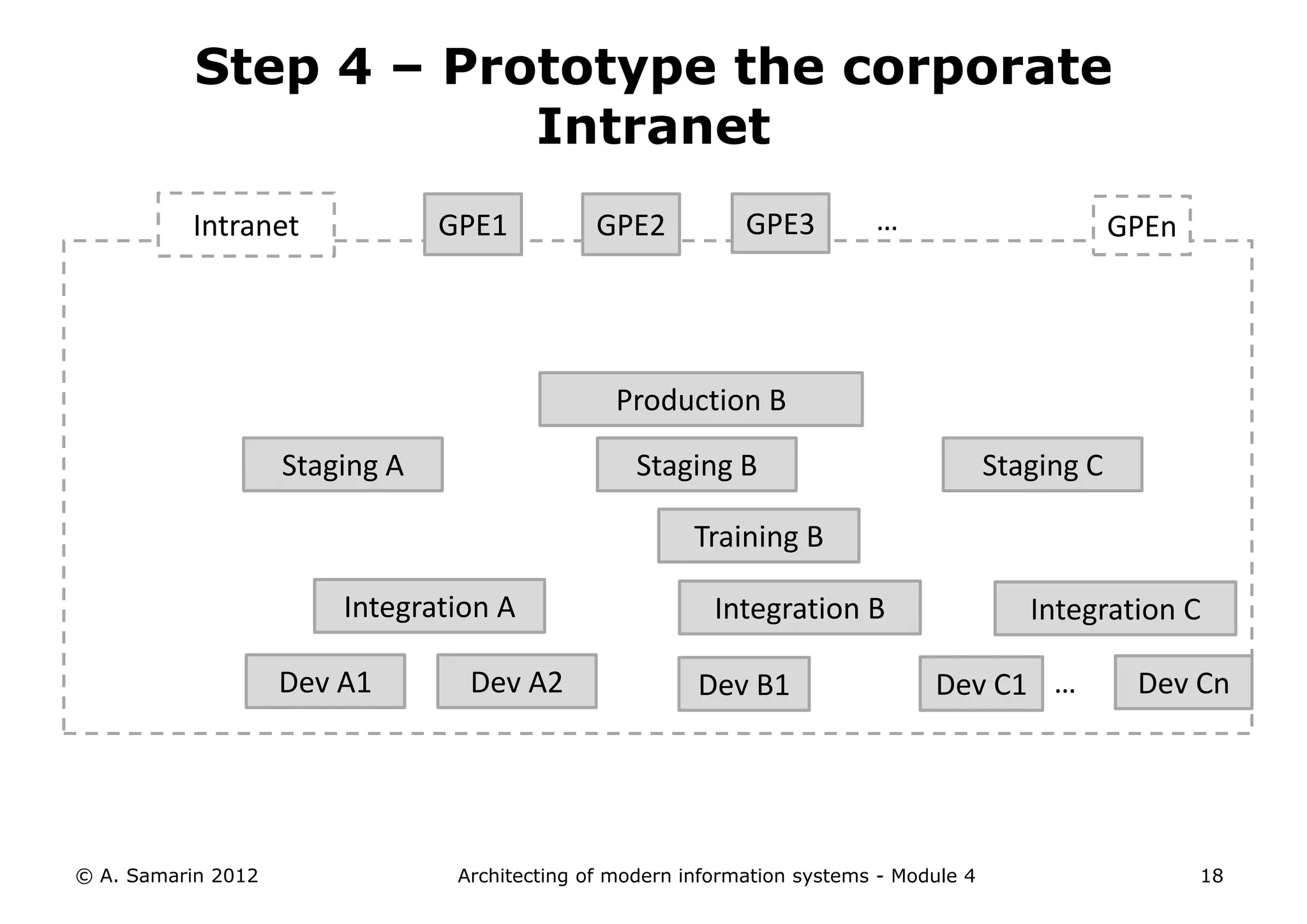
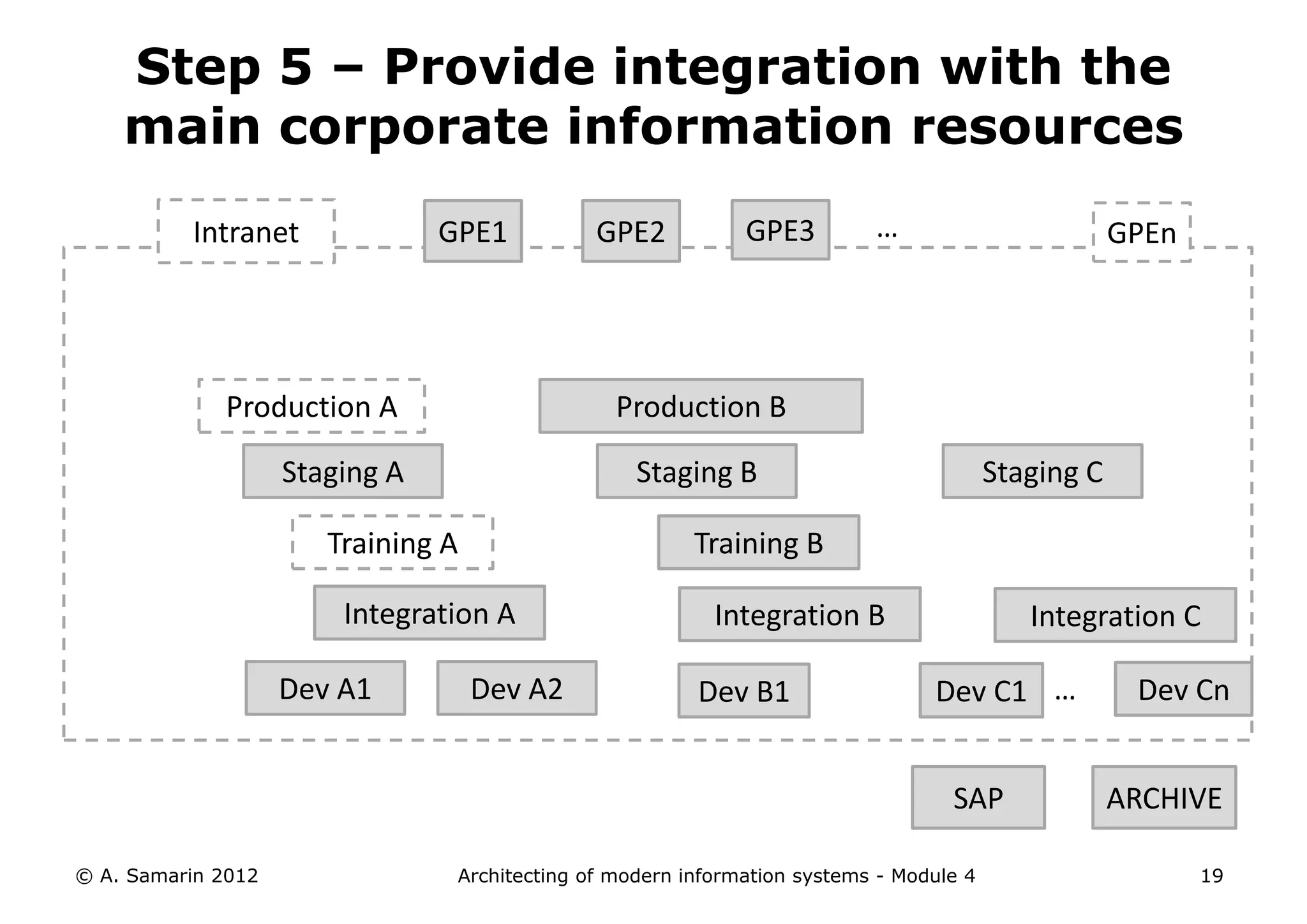
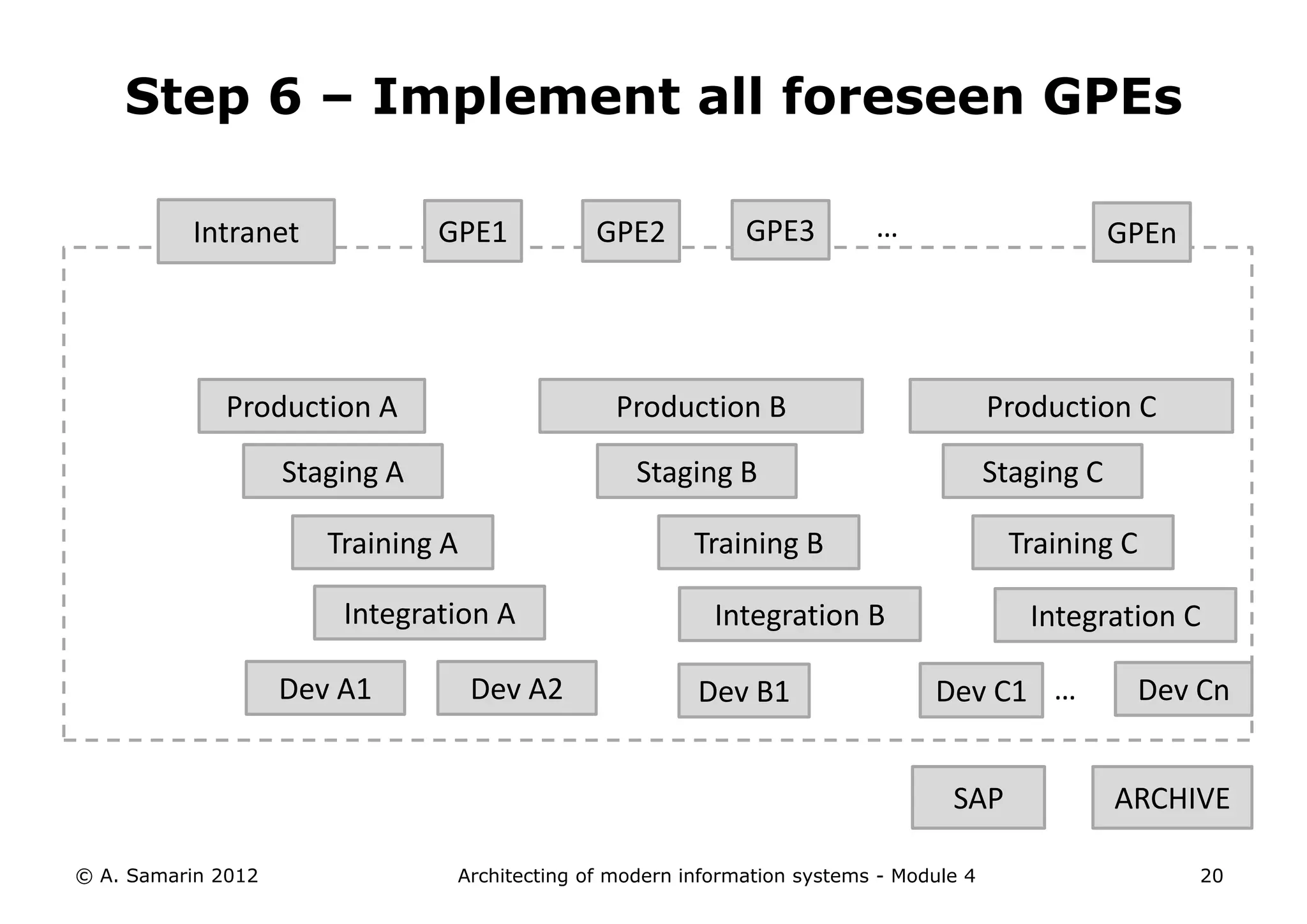
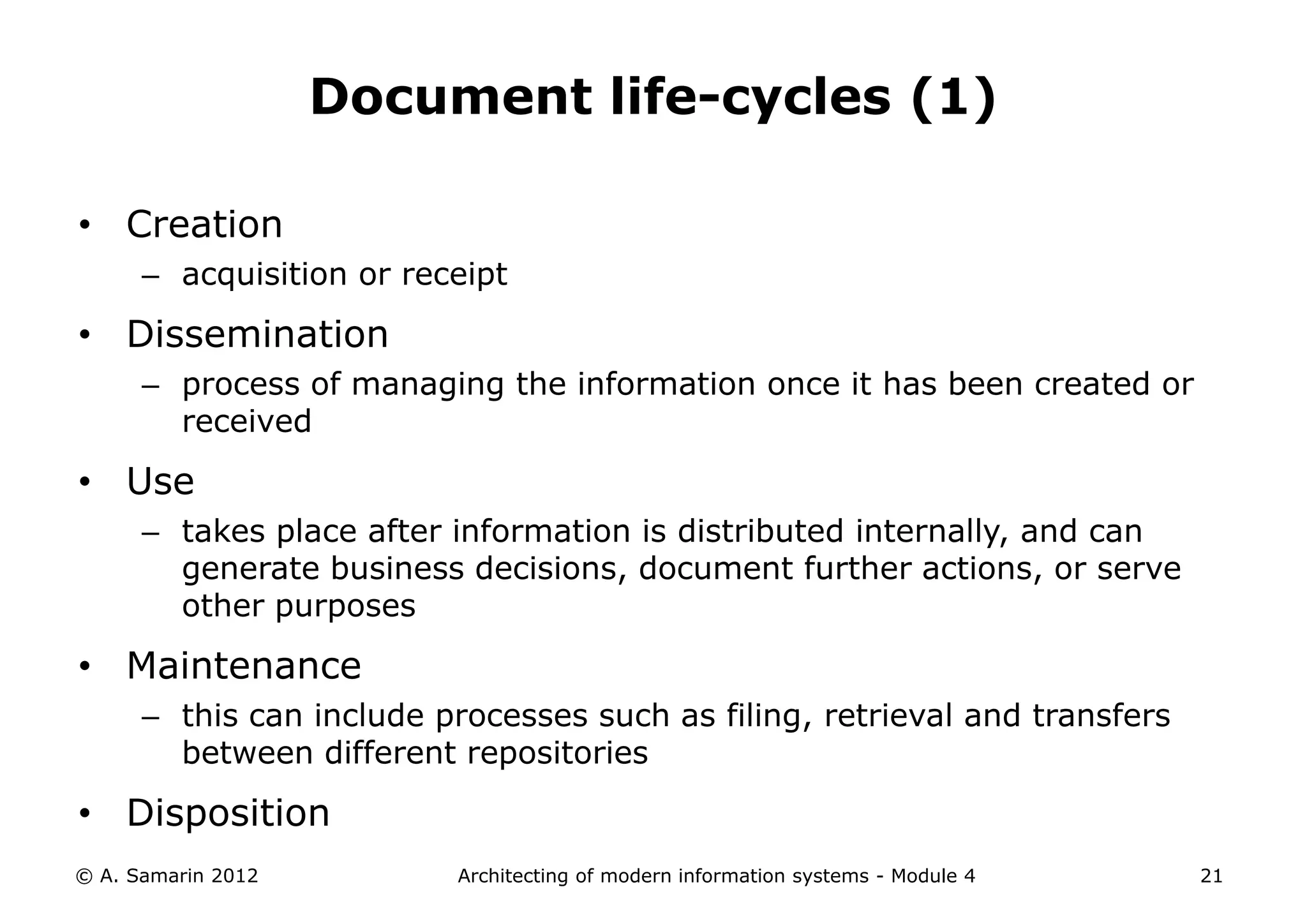
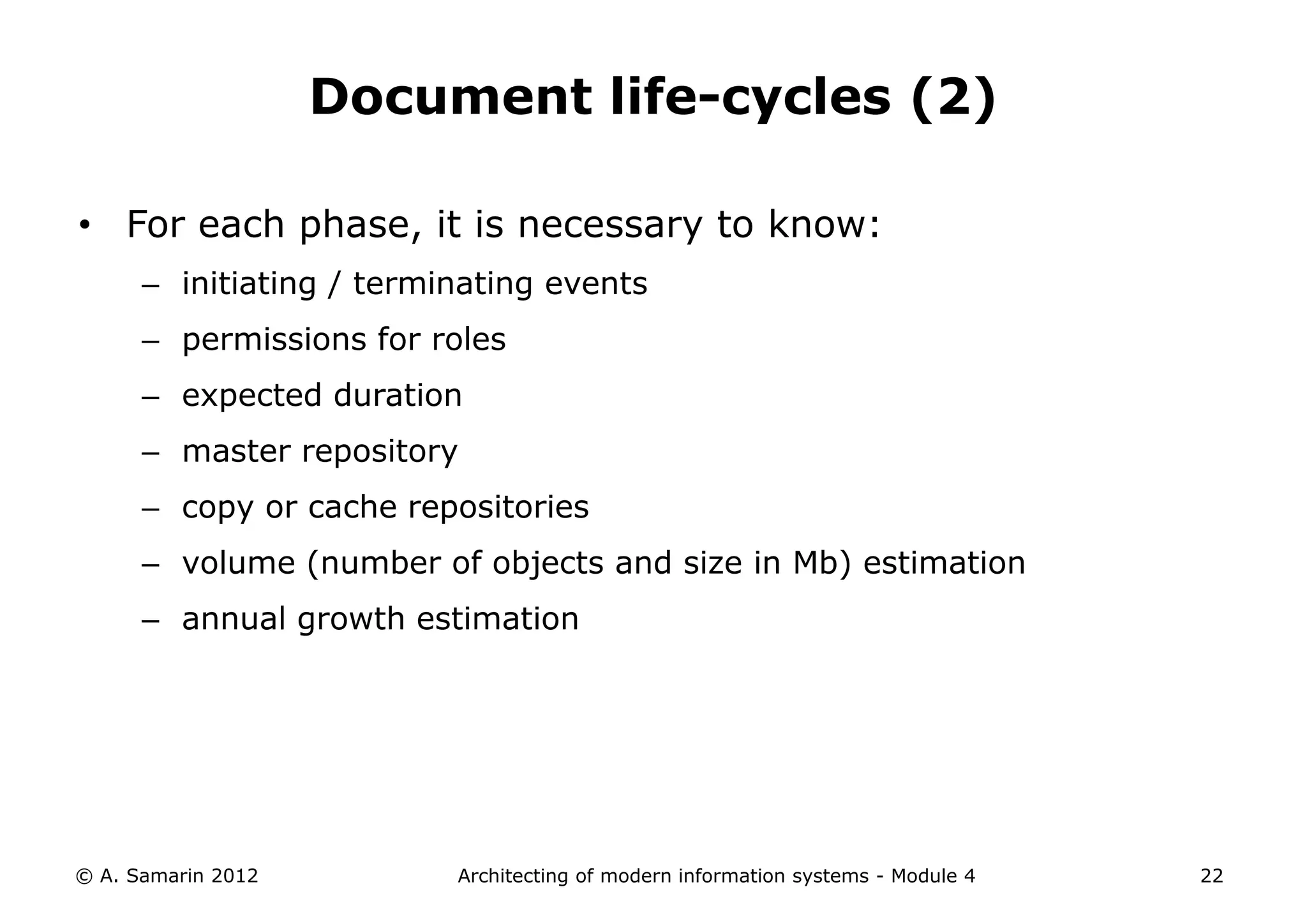
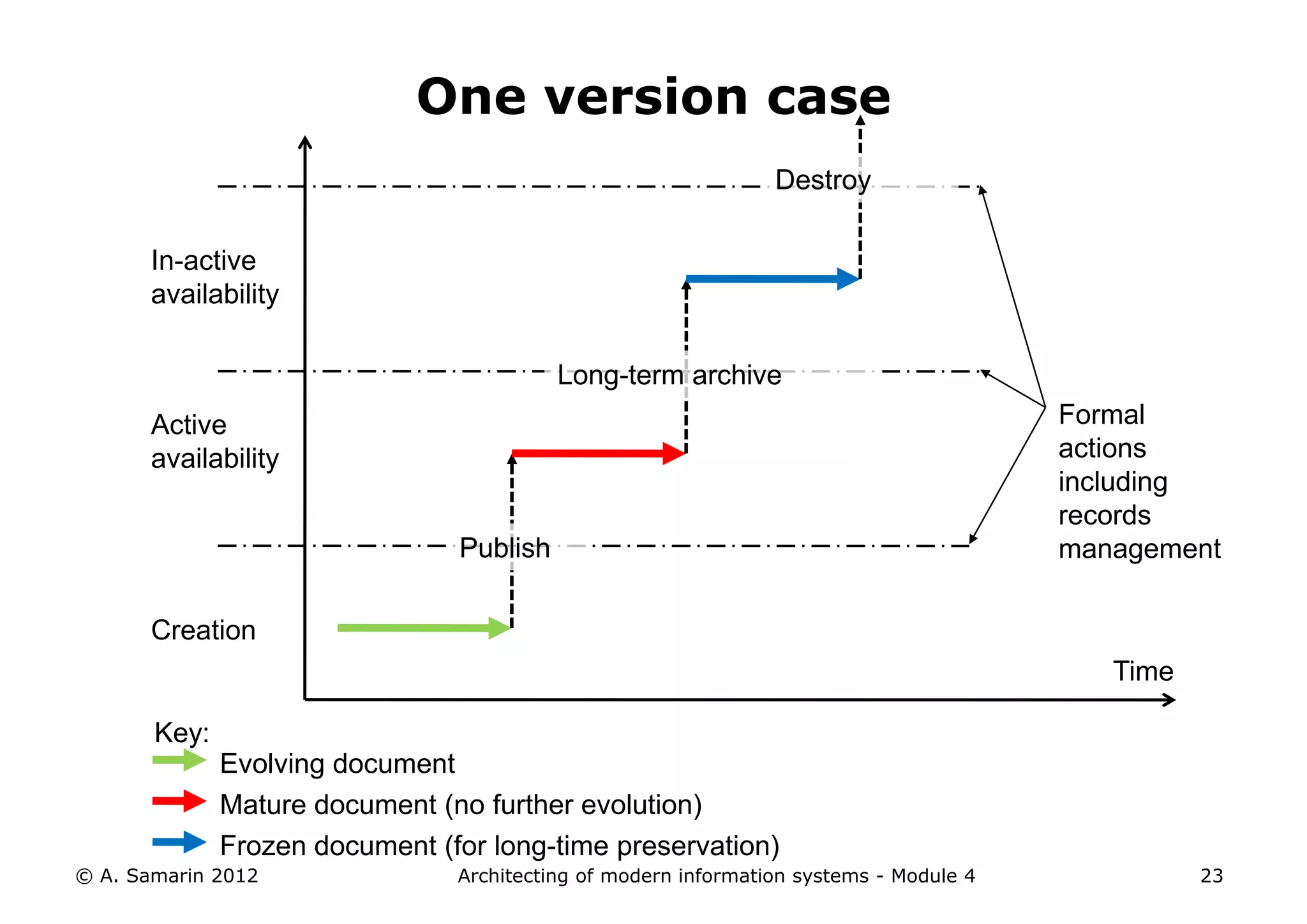
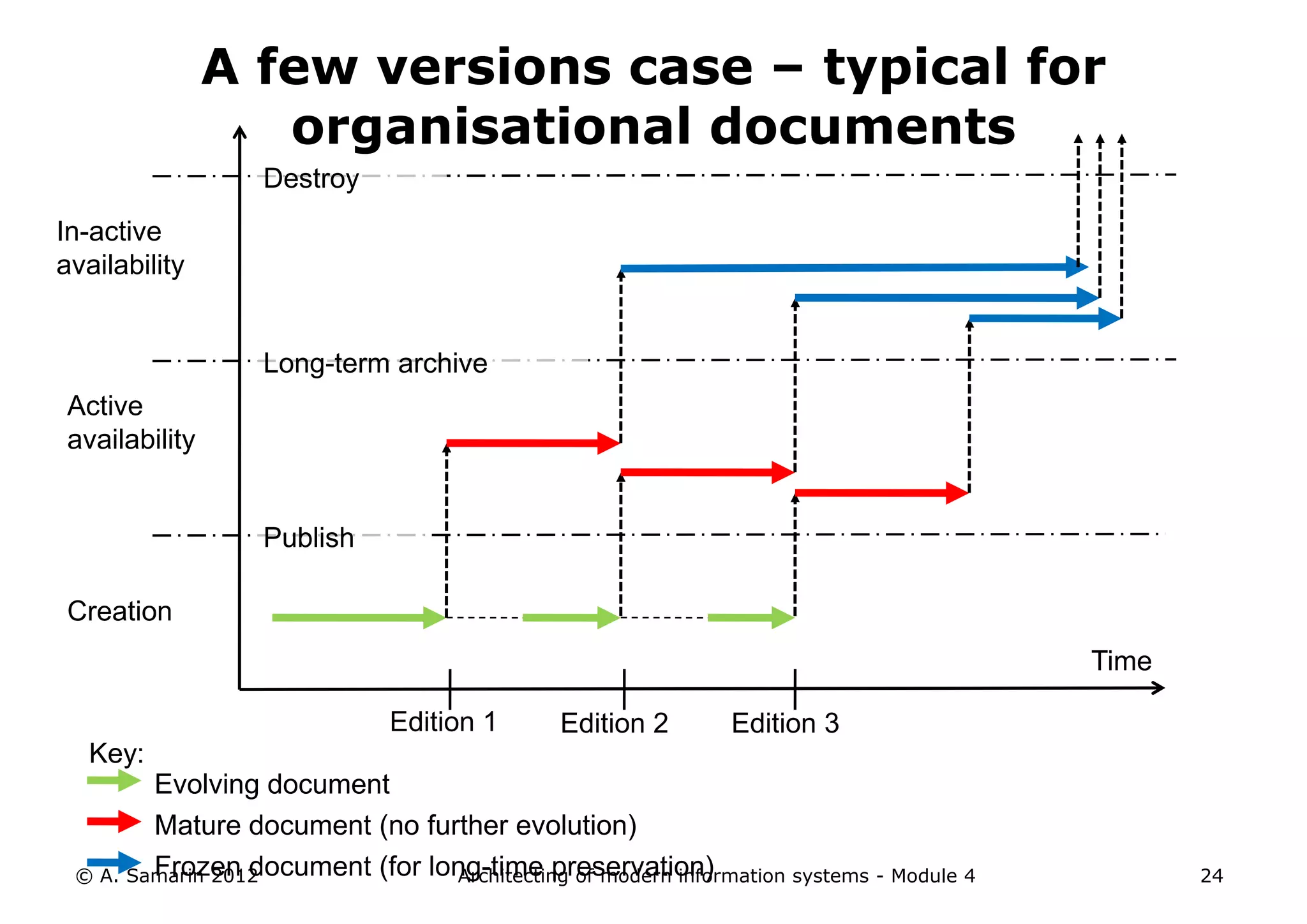
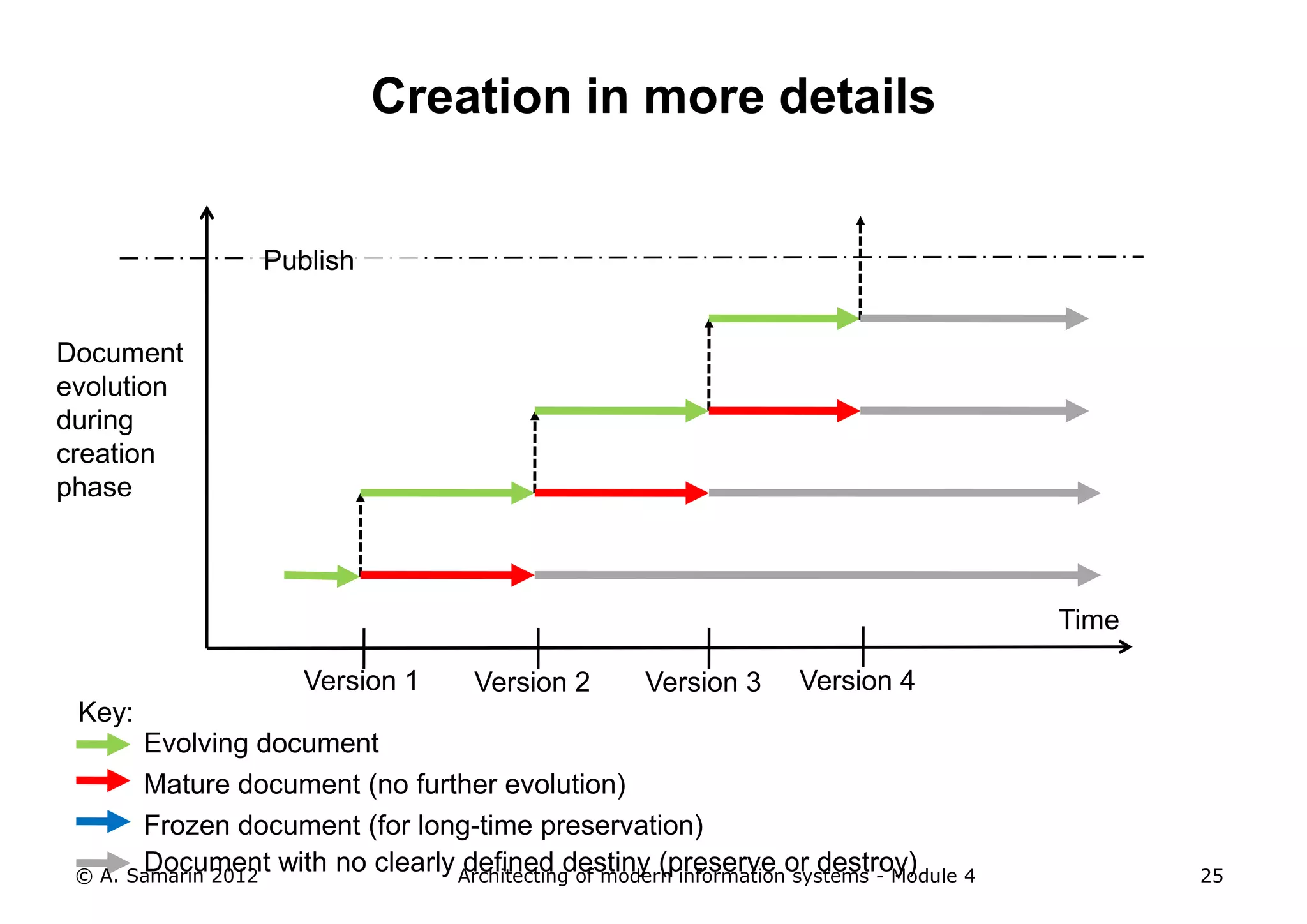
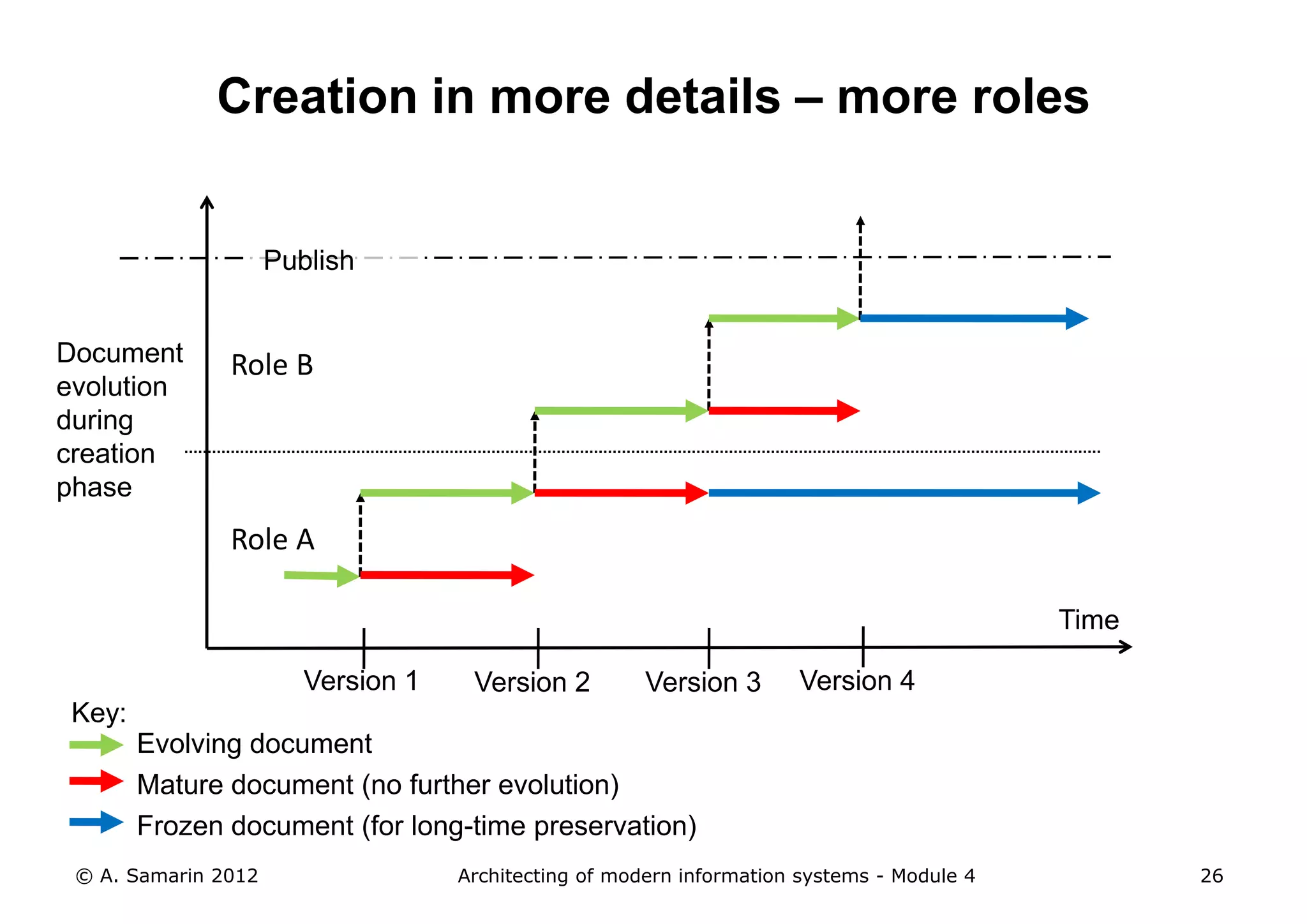
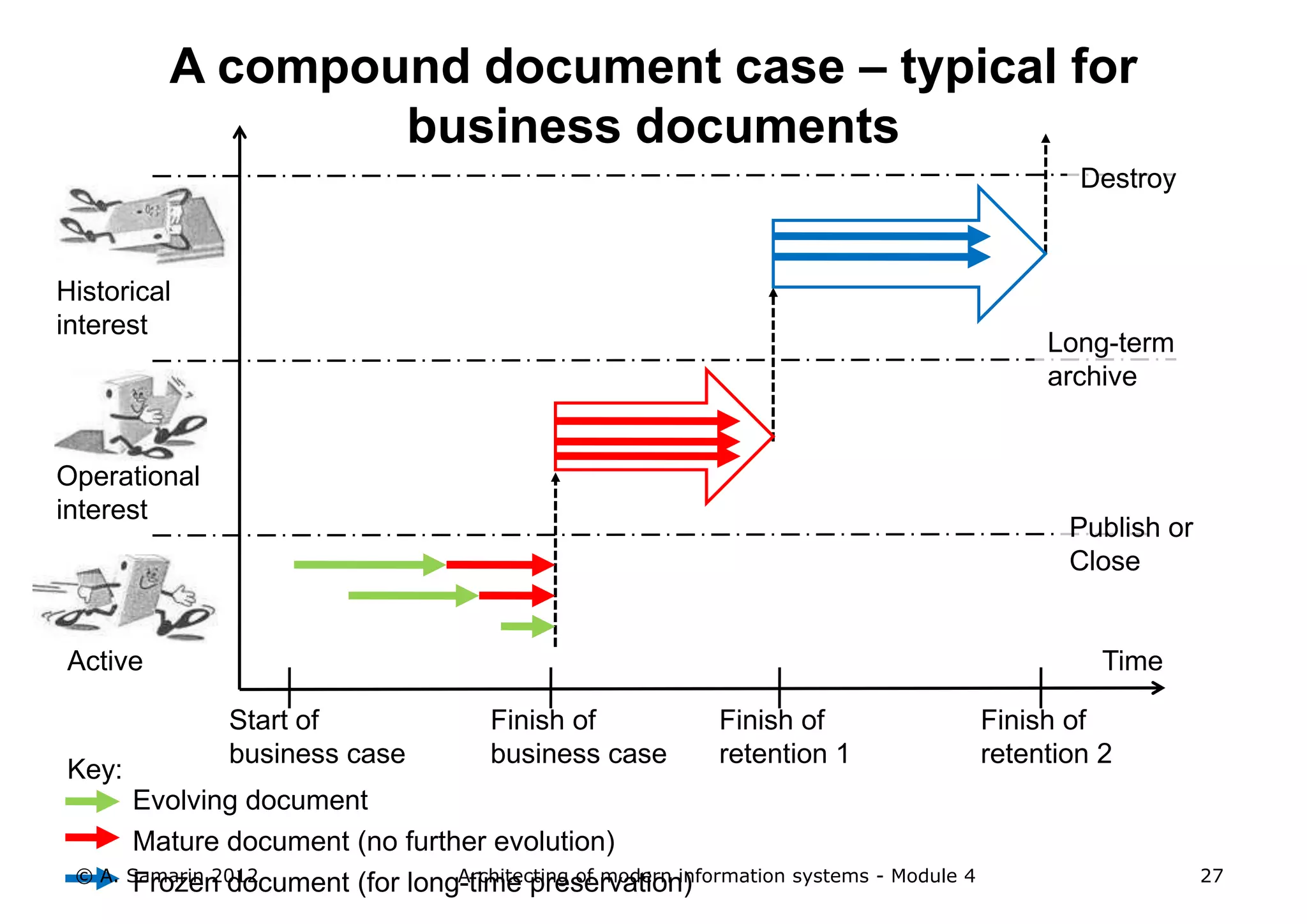
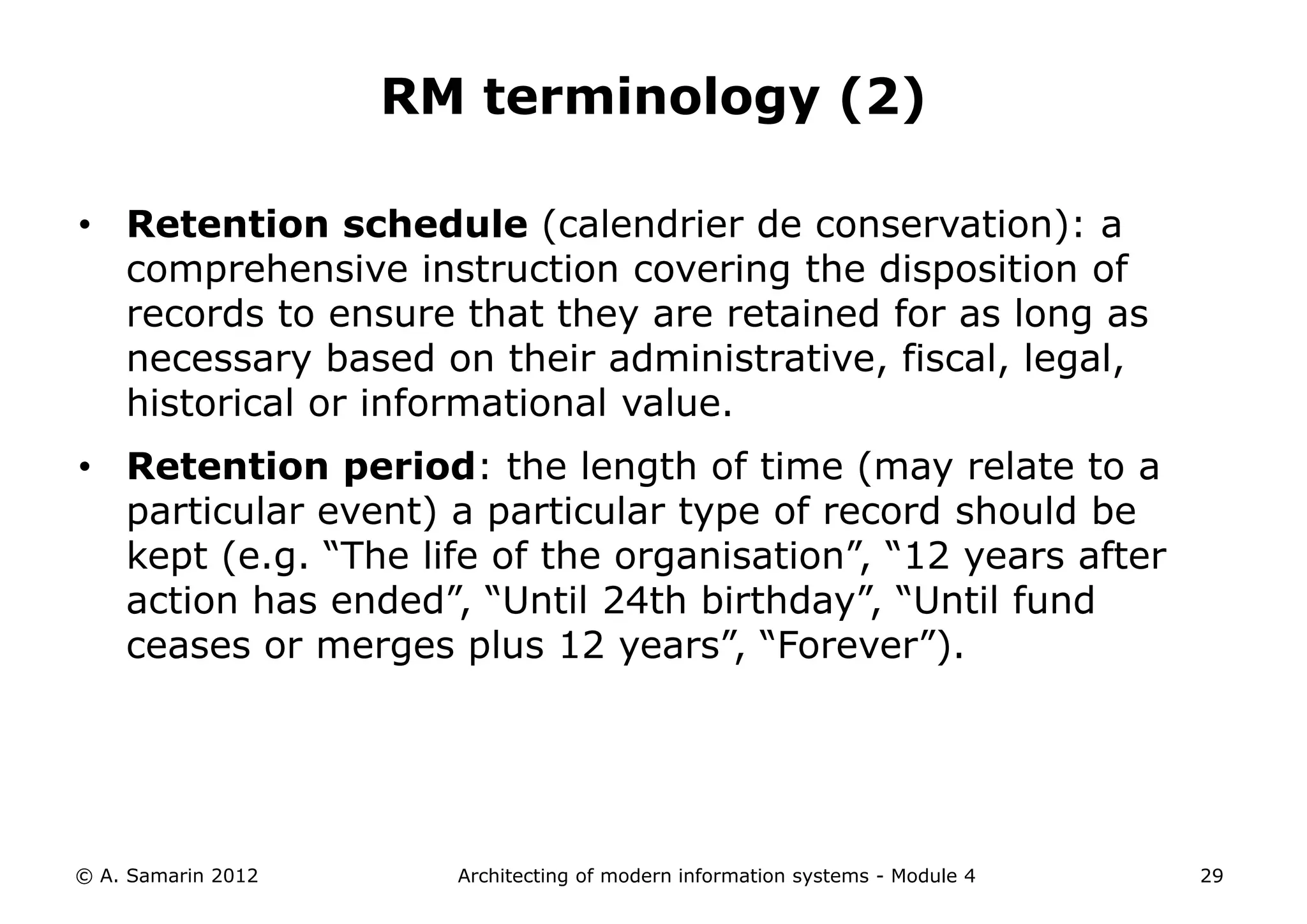
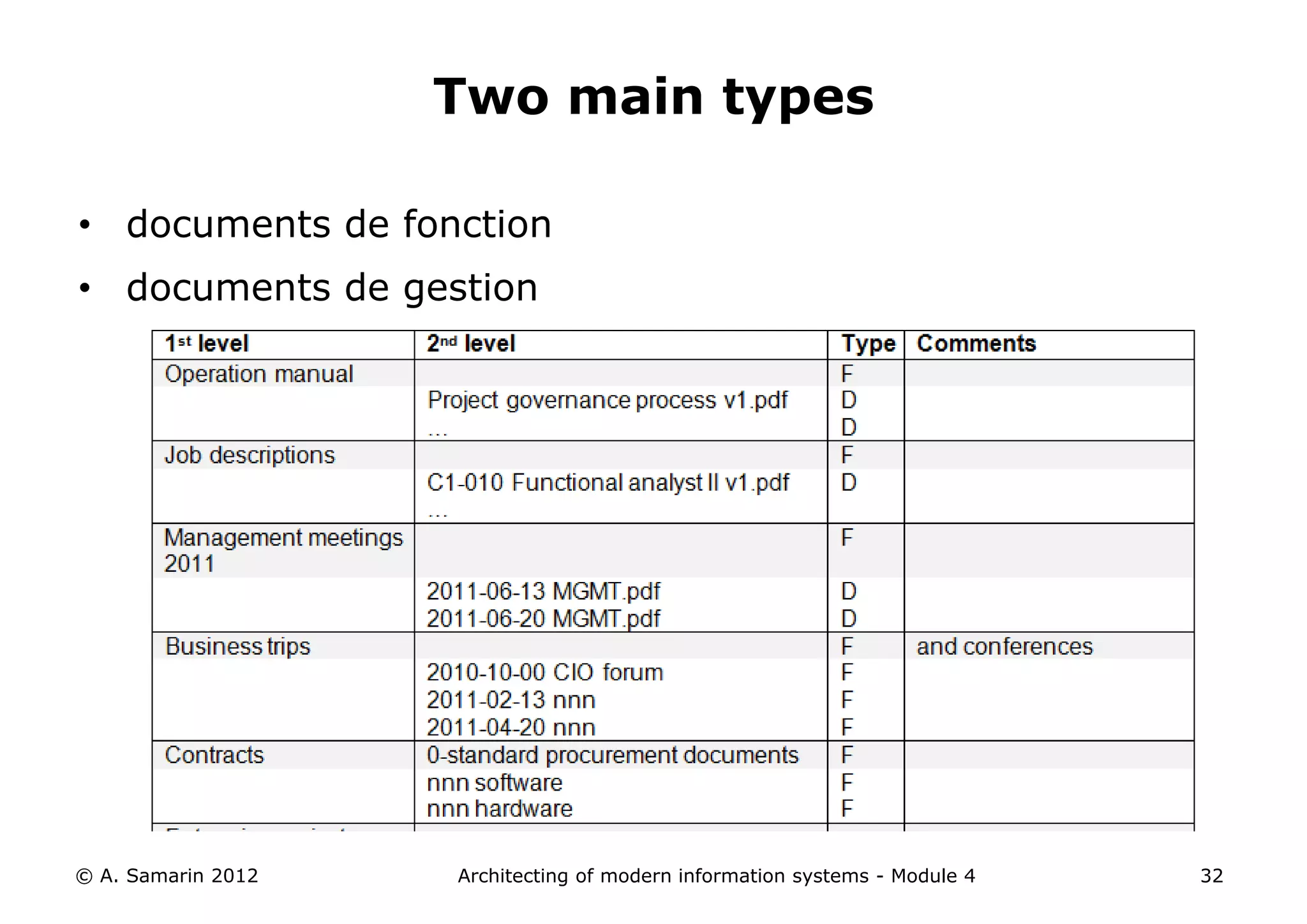
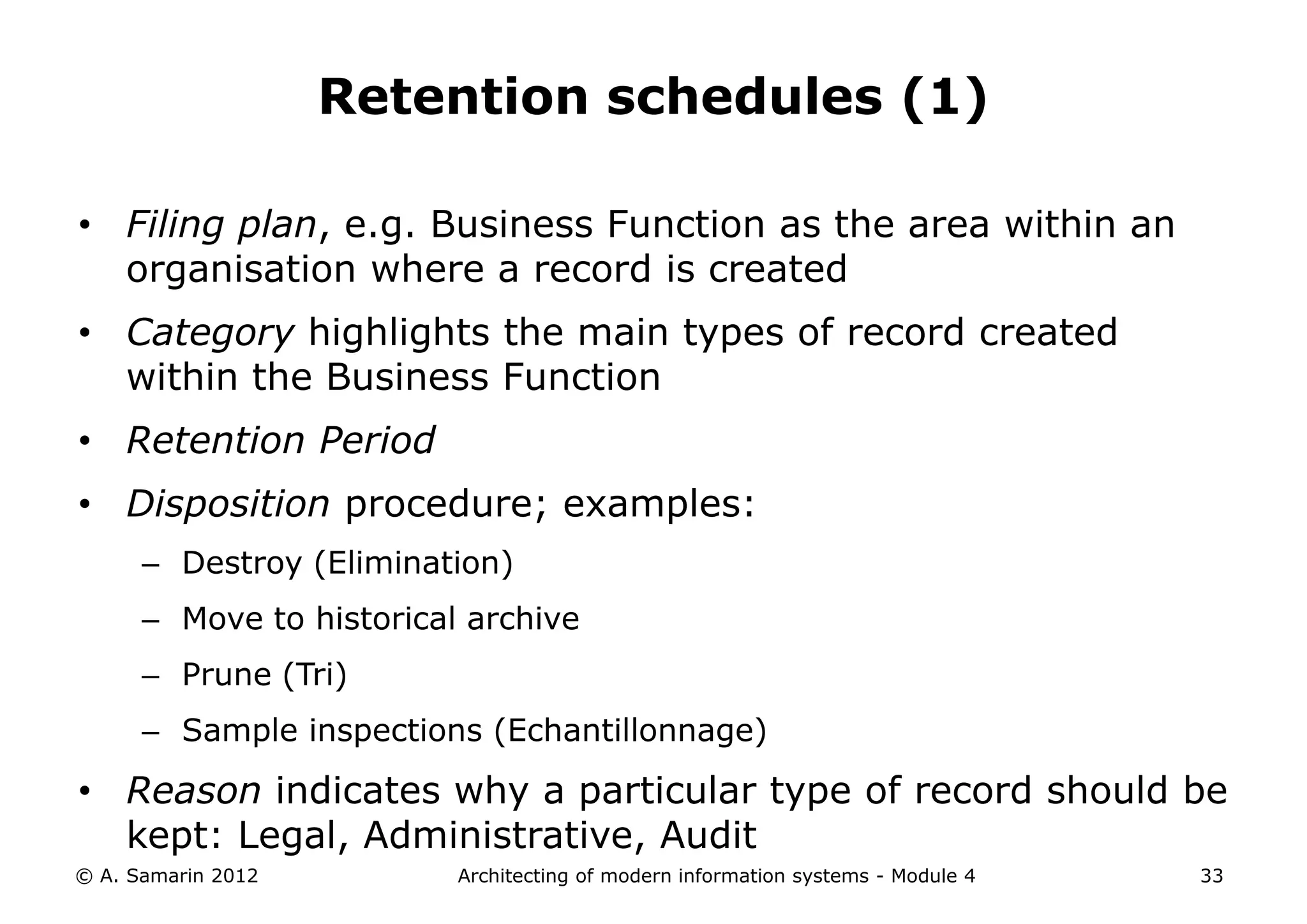
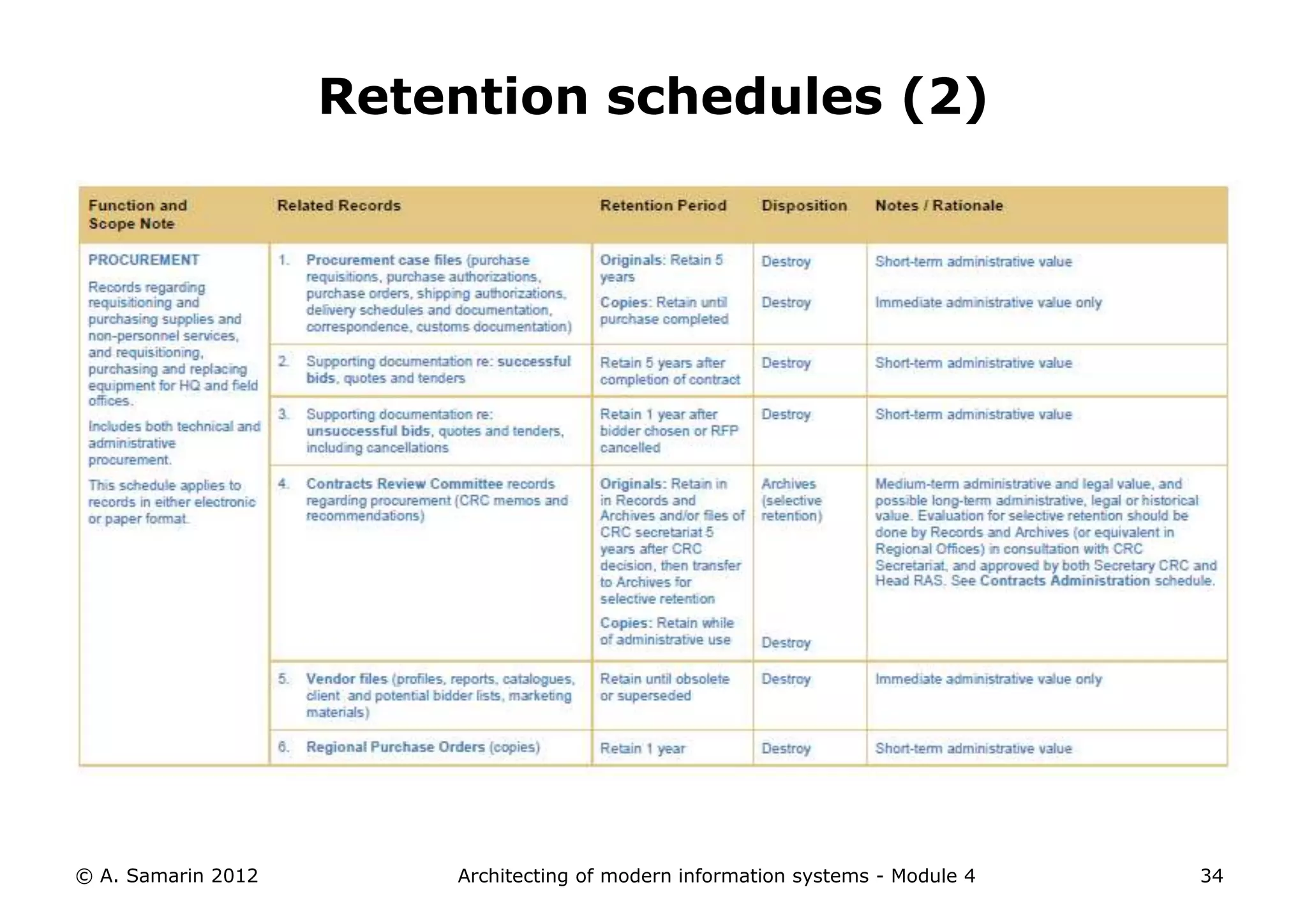
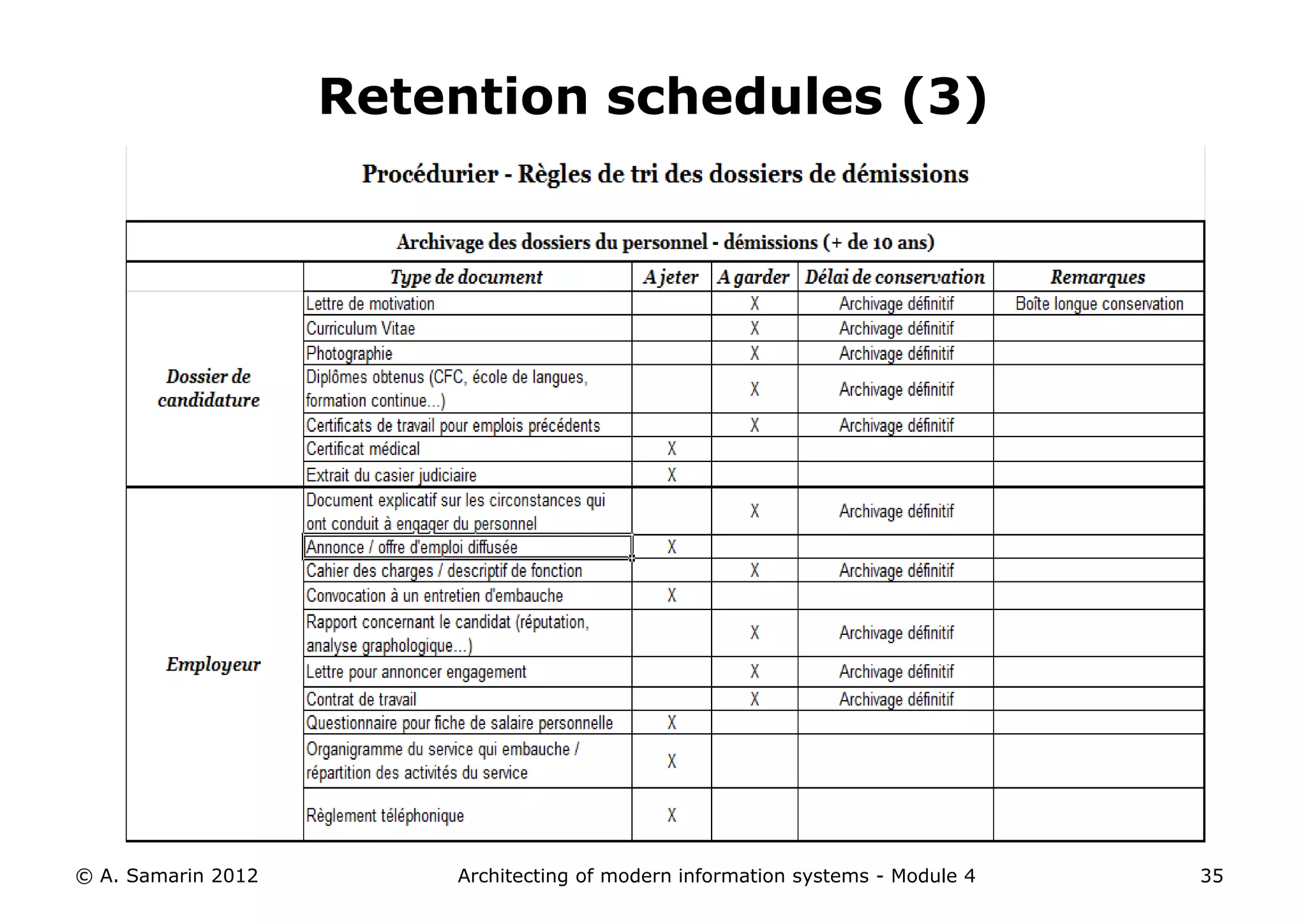
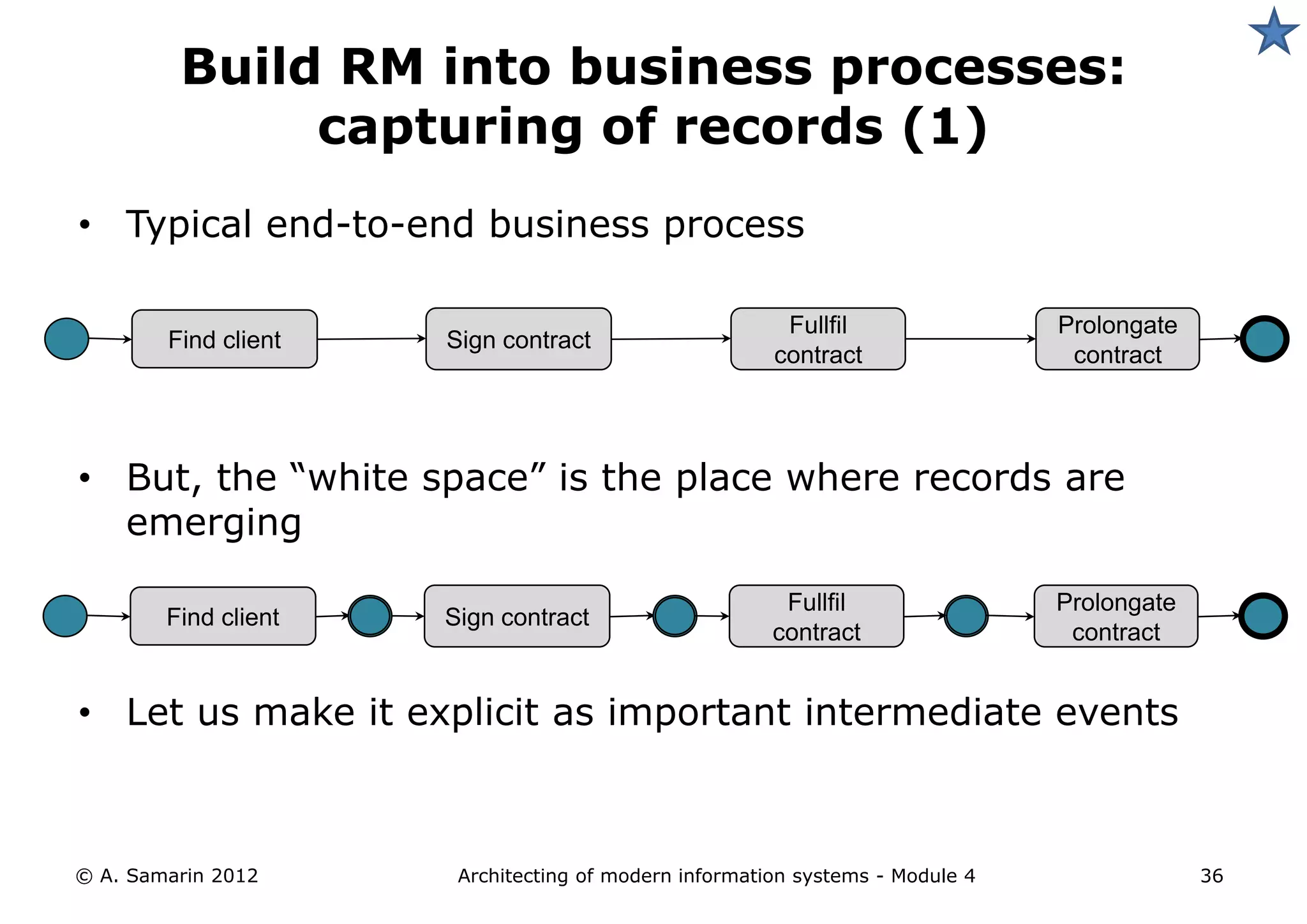
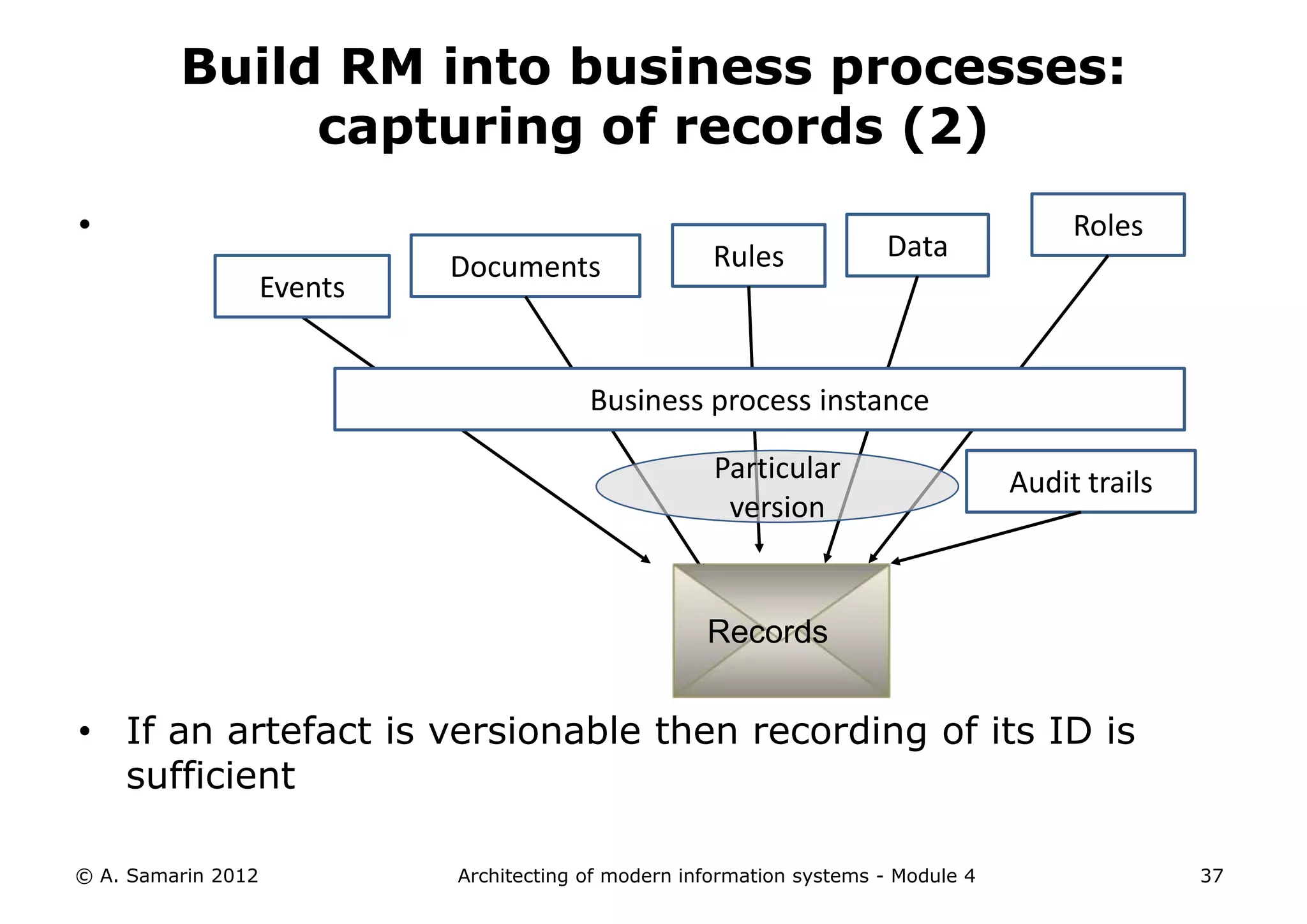
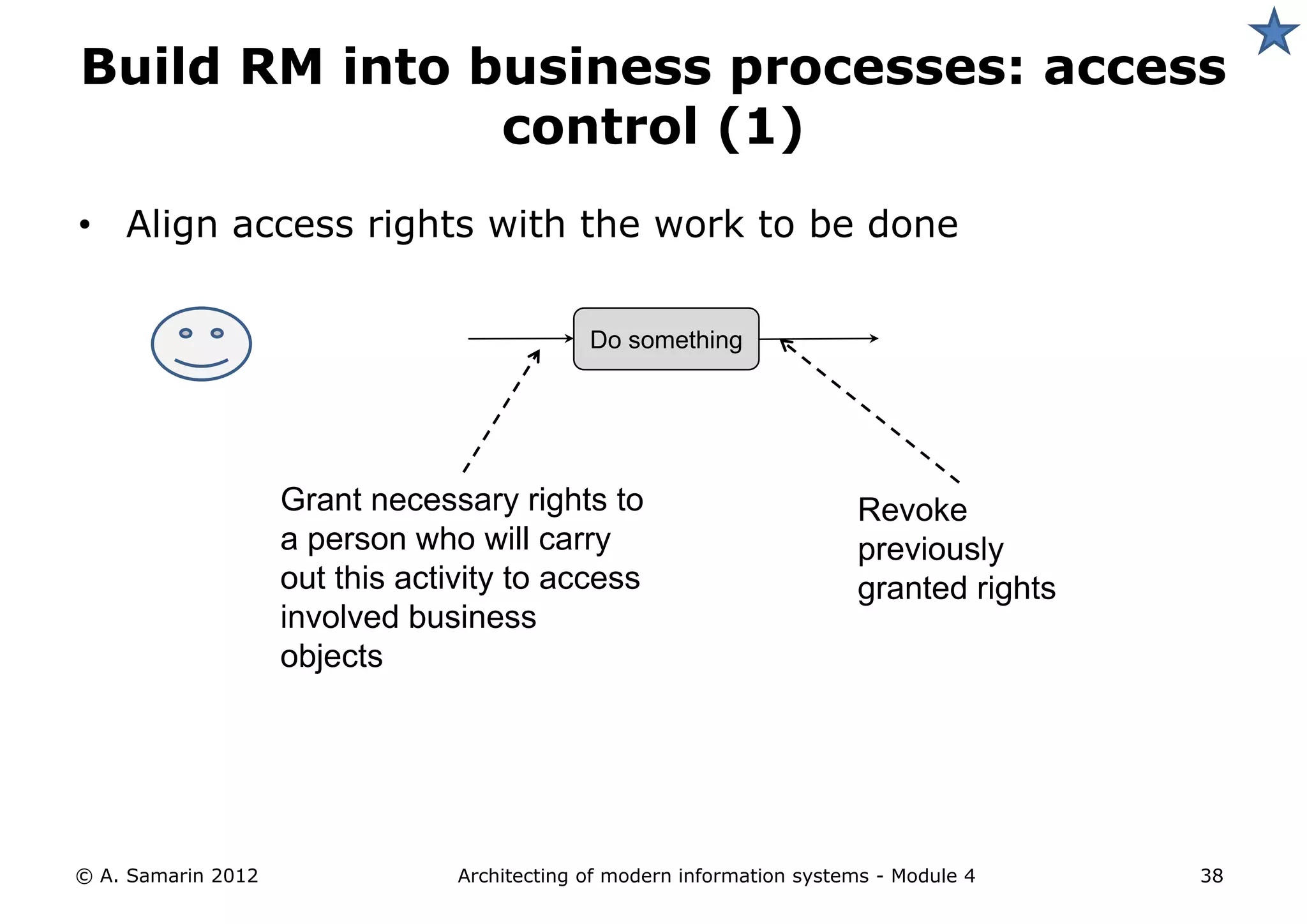
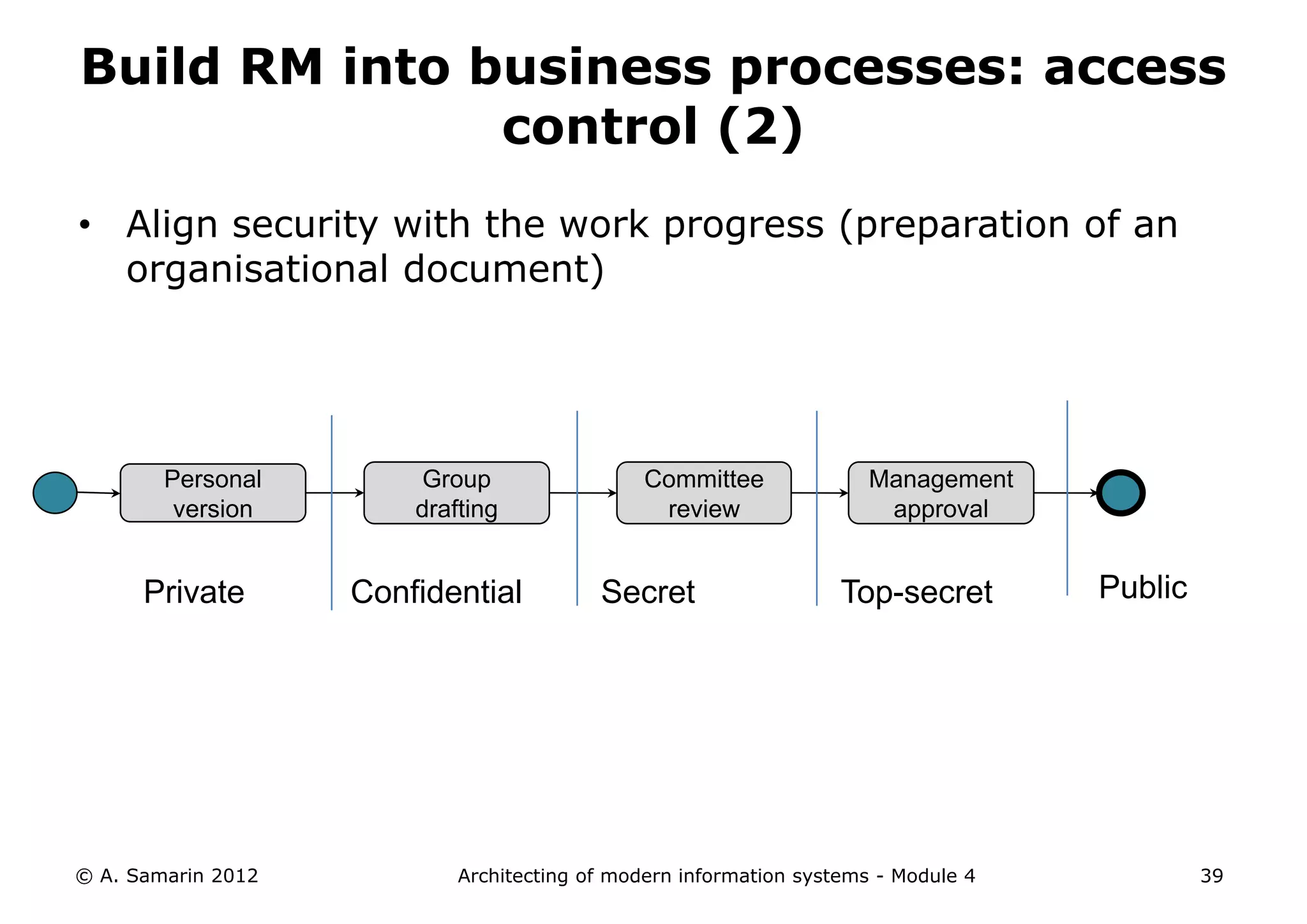
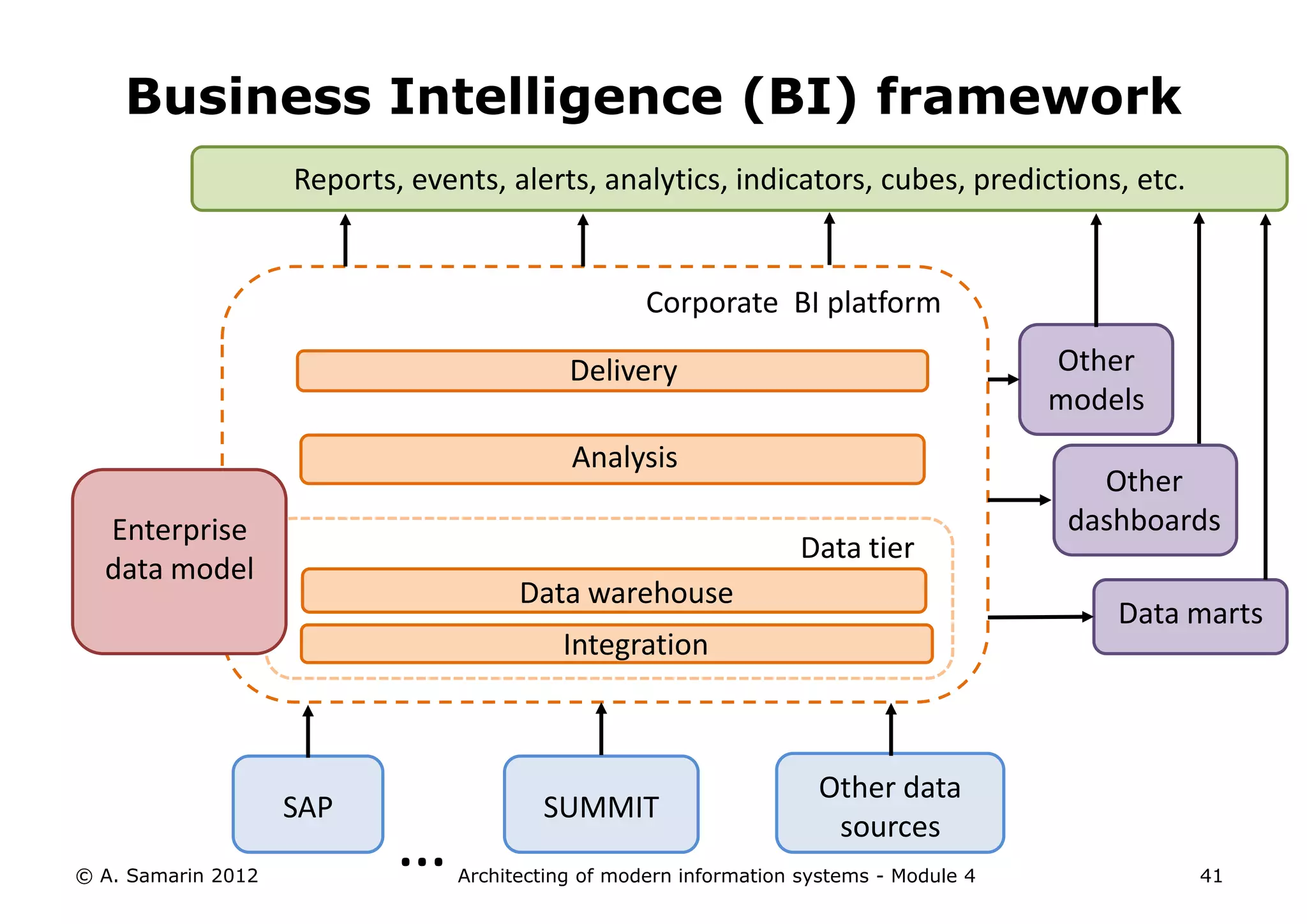
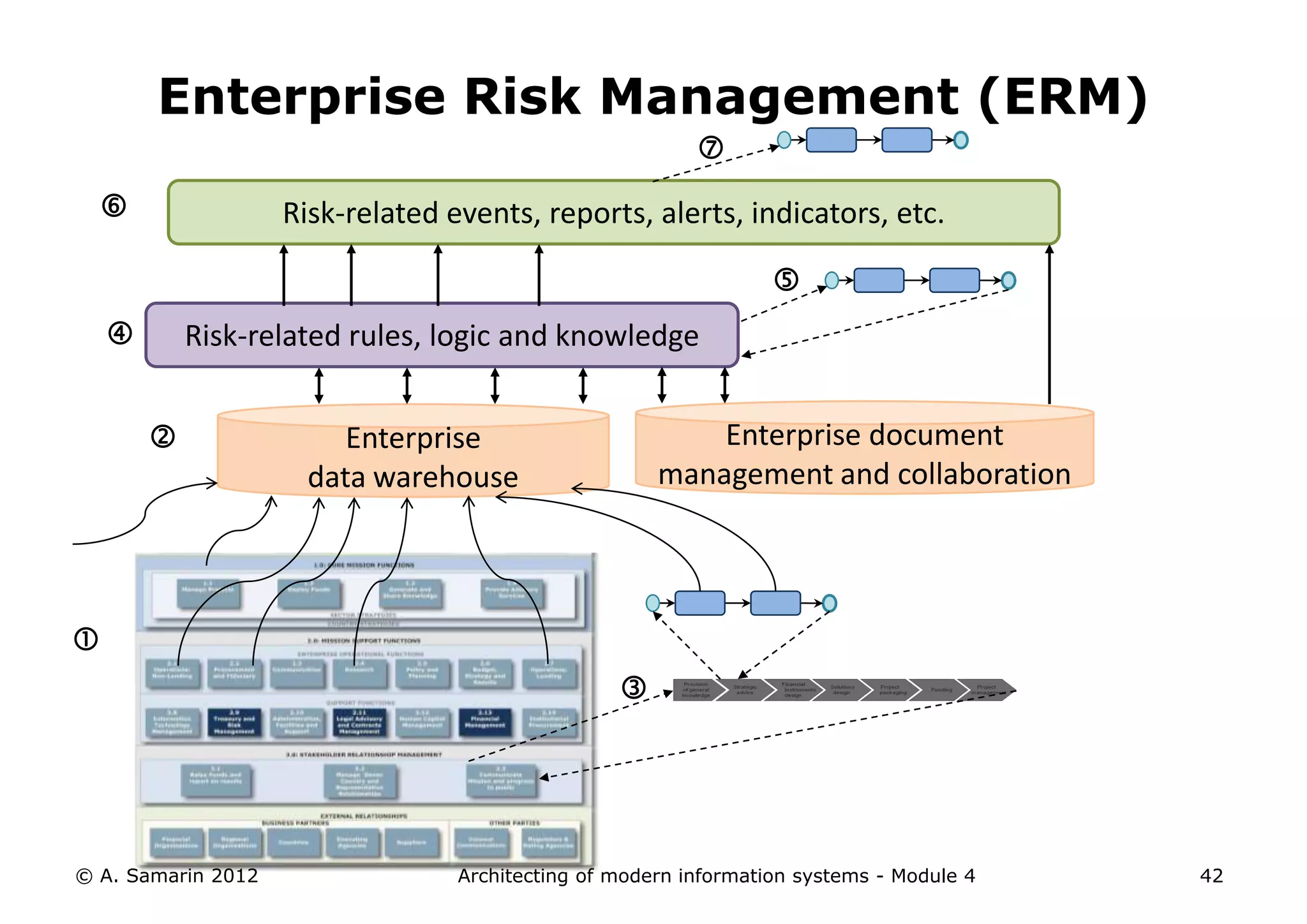
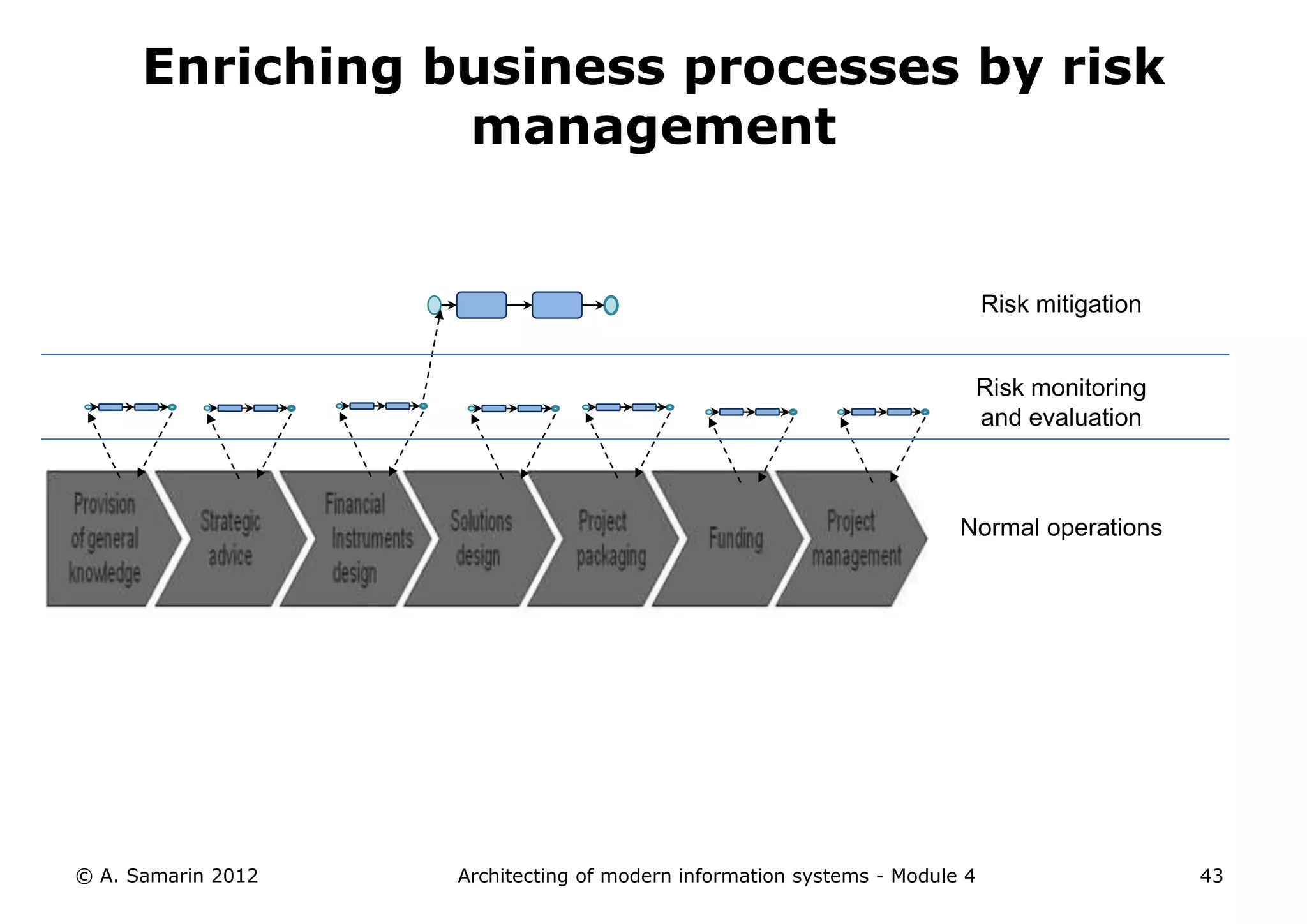
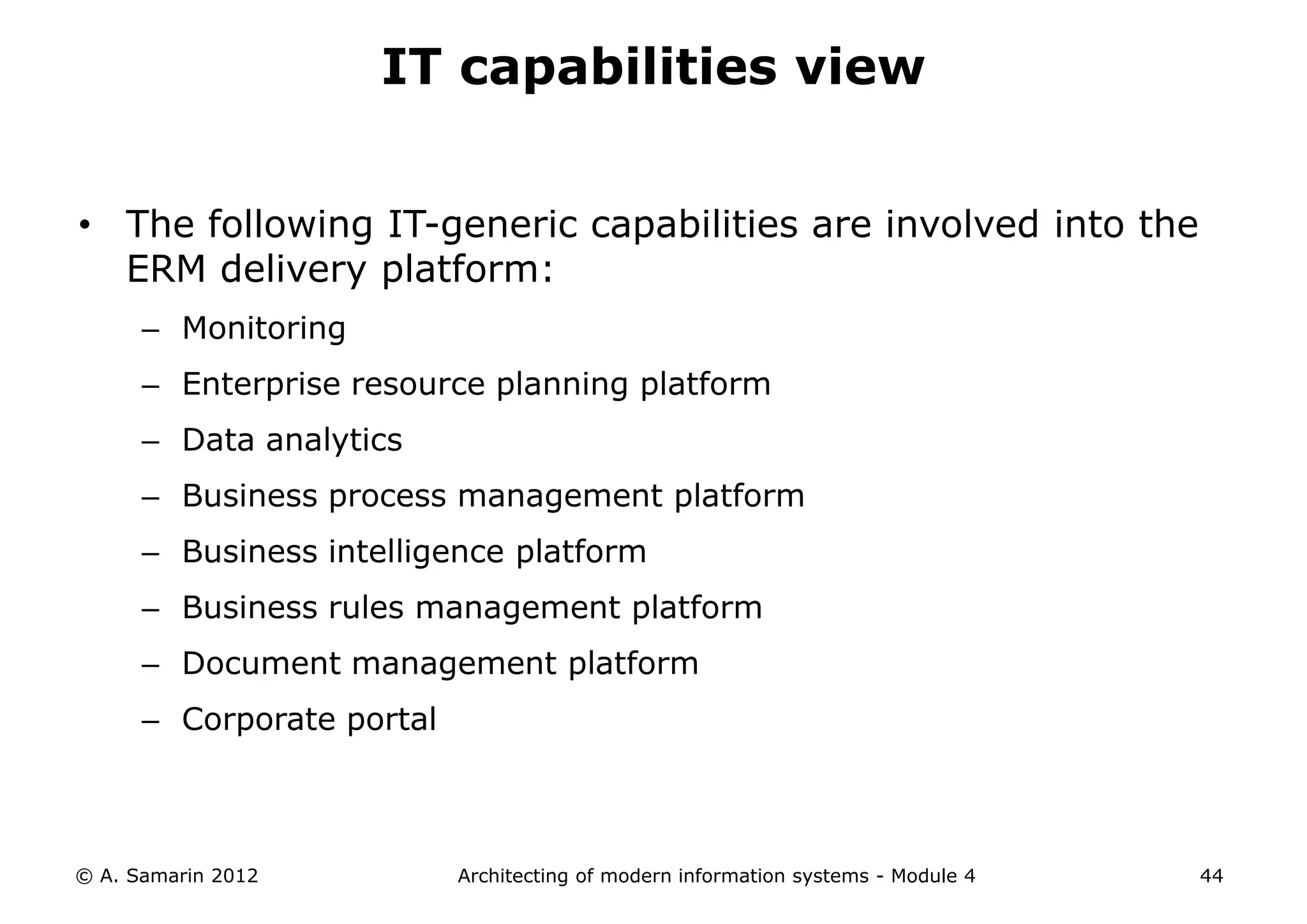
The document outlines the architecture of modern information systems, focusing on enterprise content management (ECM) and its key features such as document management, collaboration, search, and preservation strategies. It discusses the development costs and time estimates for implementing collaborative applications within corporate platforms, as well as detailing the lifecycle of documents, from creation to disposition. Additionally, it covers the integration of records management into business processes and the importance of compliance with regulations.