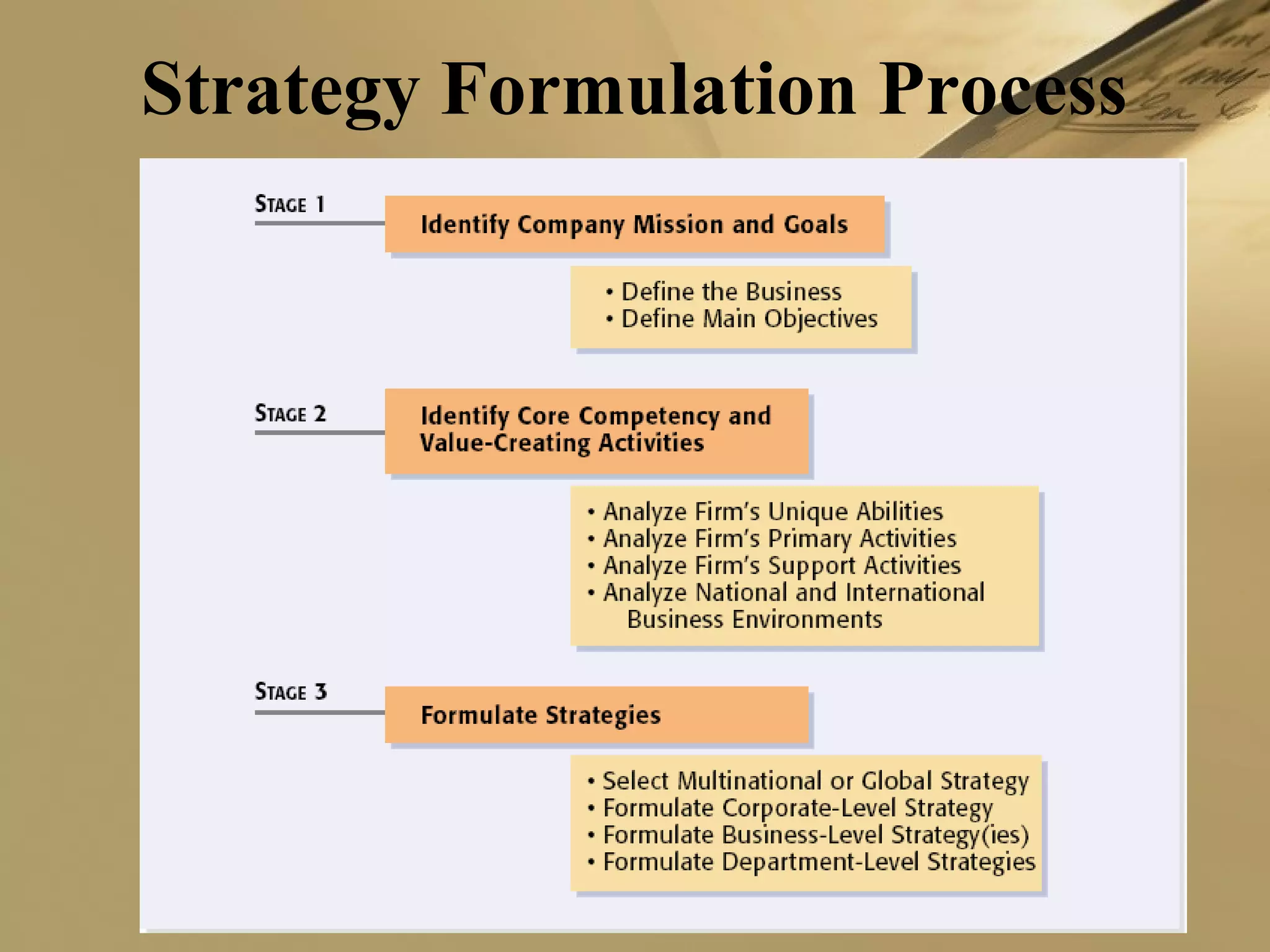
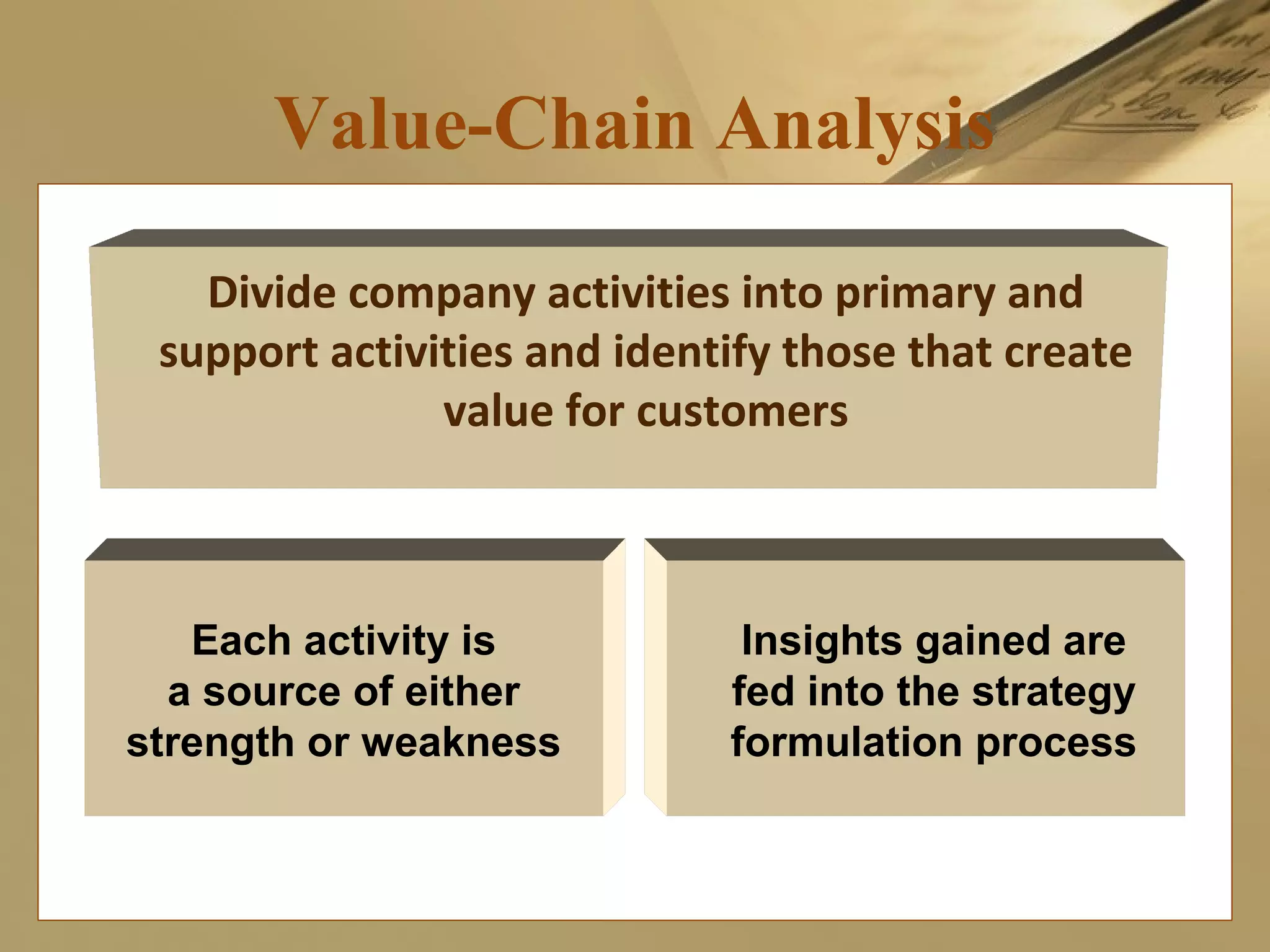
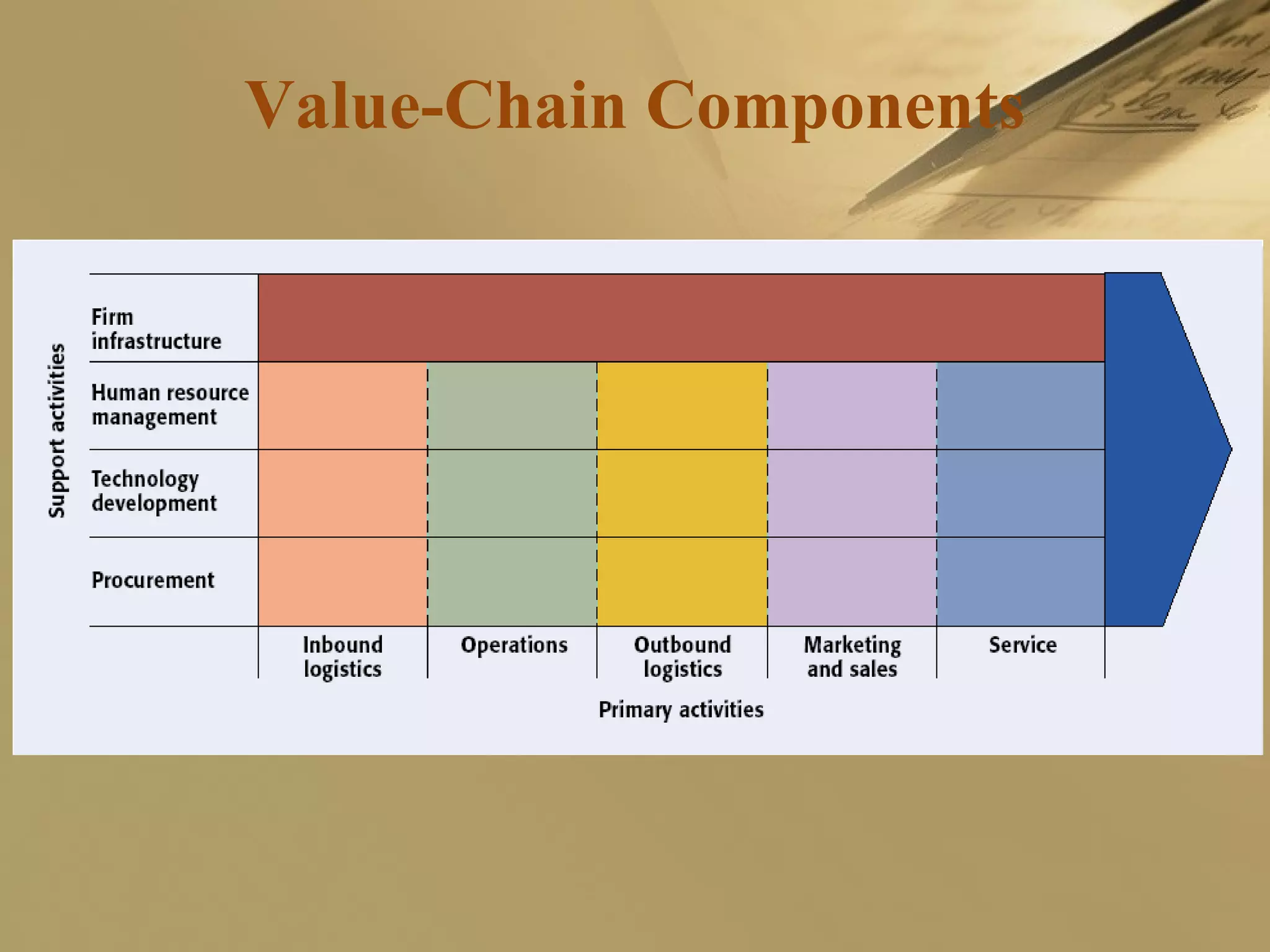
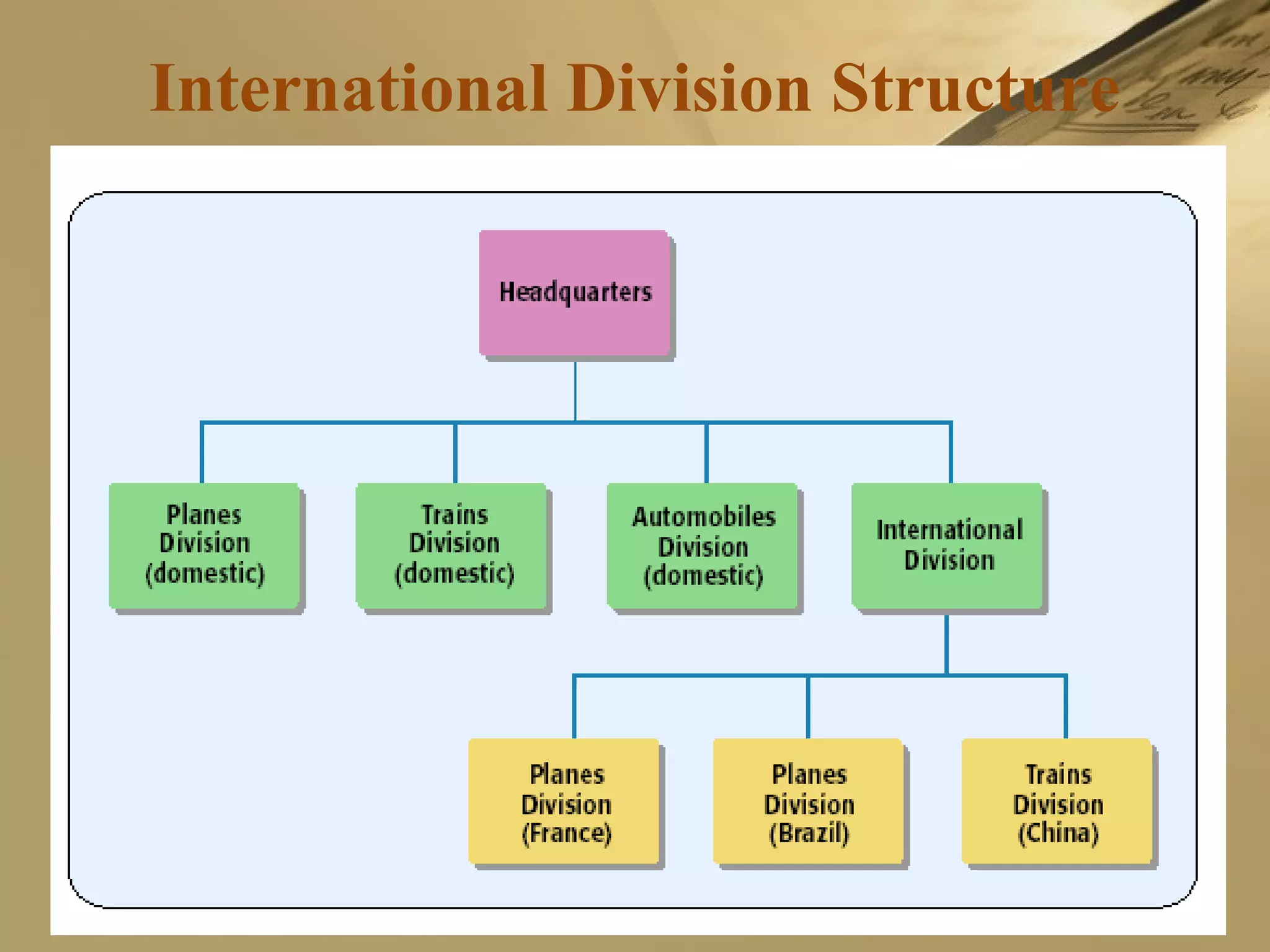
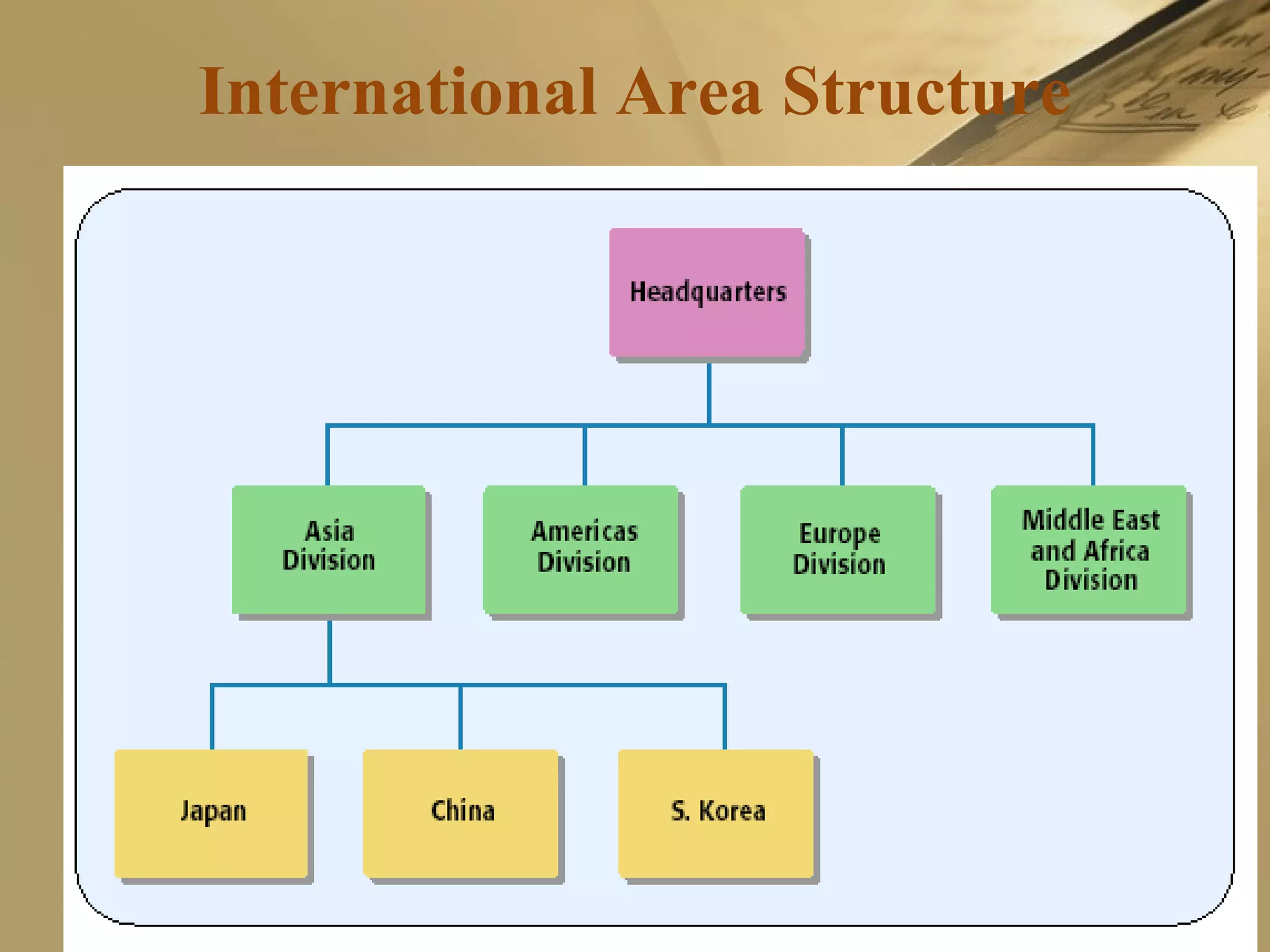
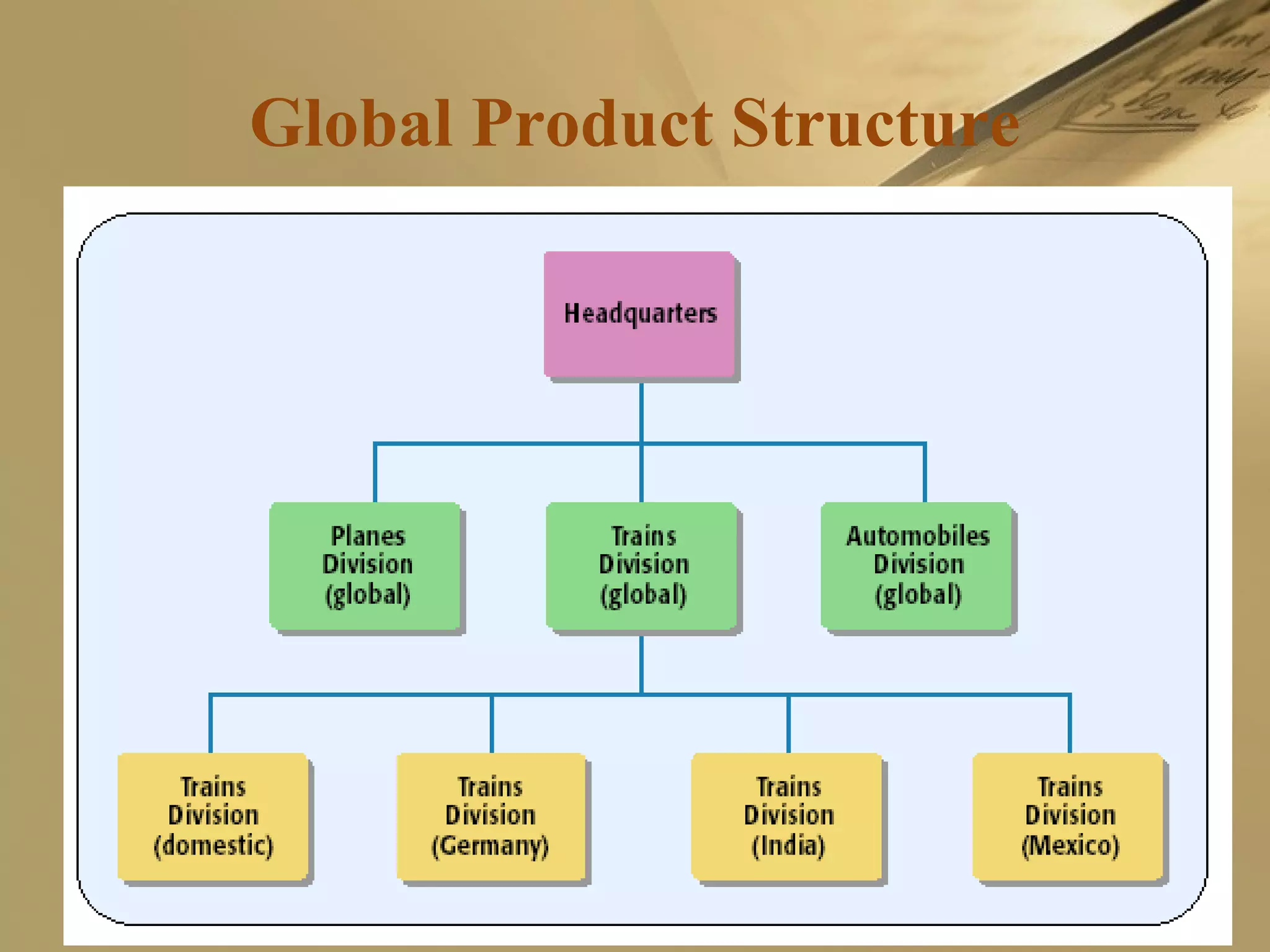
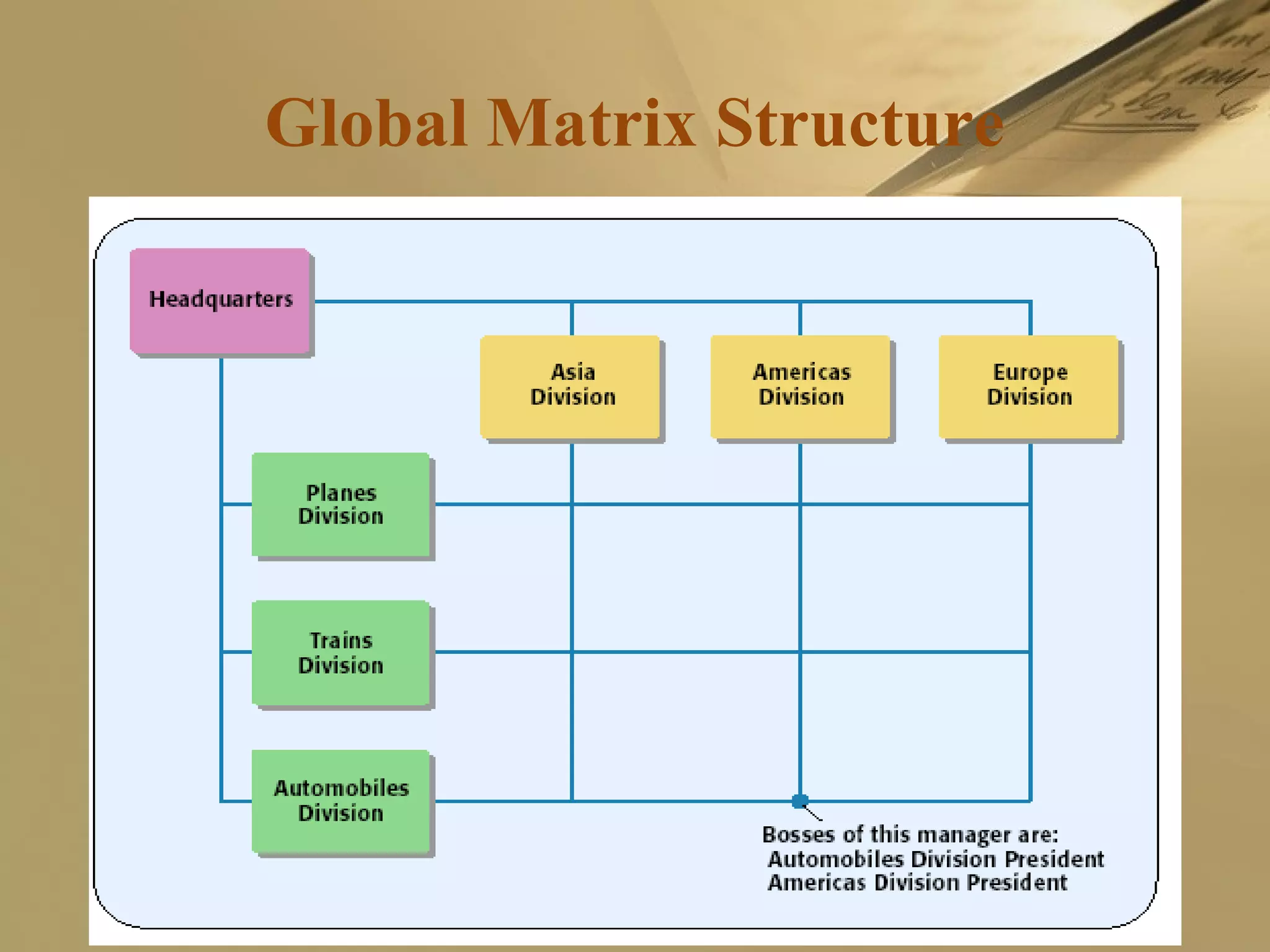
The document discusses international strategies and organizational structures in global business, outlining strategy formulation processes, including identifying missions, core competencies, and value-creating activities. It explores various international strategies, such as multinational and global strategies, alongside corporate-level strategies to manage organizational growth. Additionally, it addresses organizational structures, emphasizing centralization versus decentralization and the importance of teamwork in achieving company objectives.