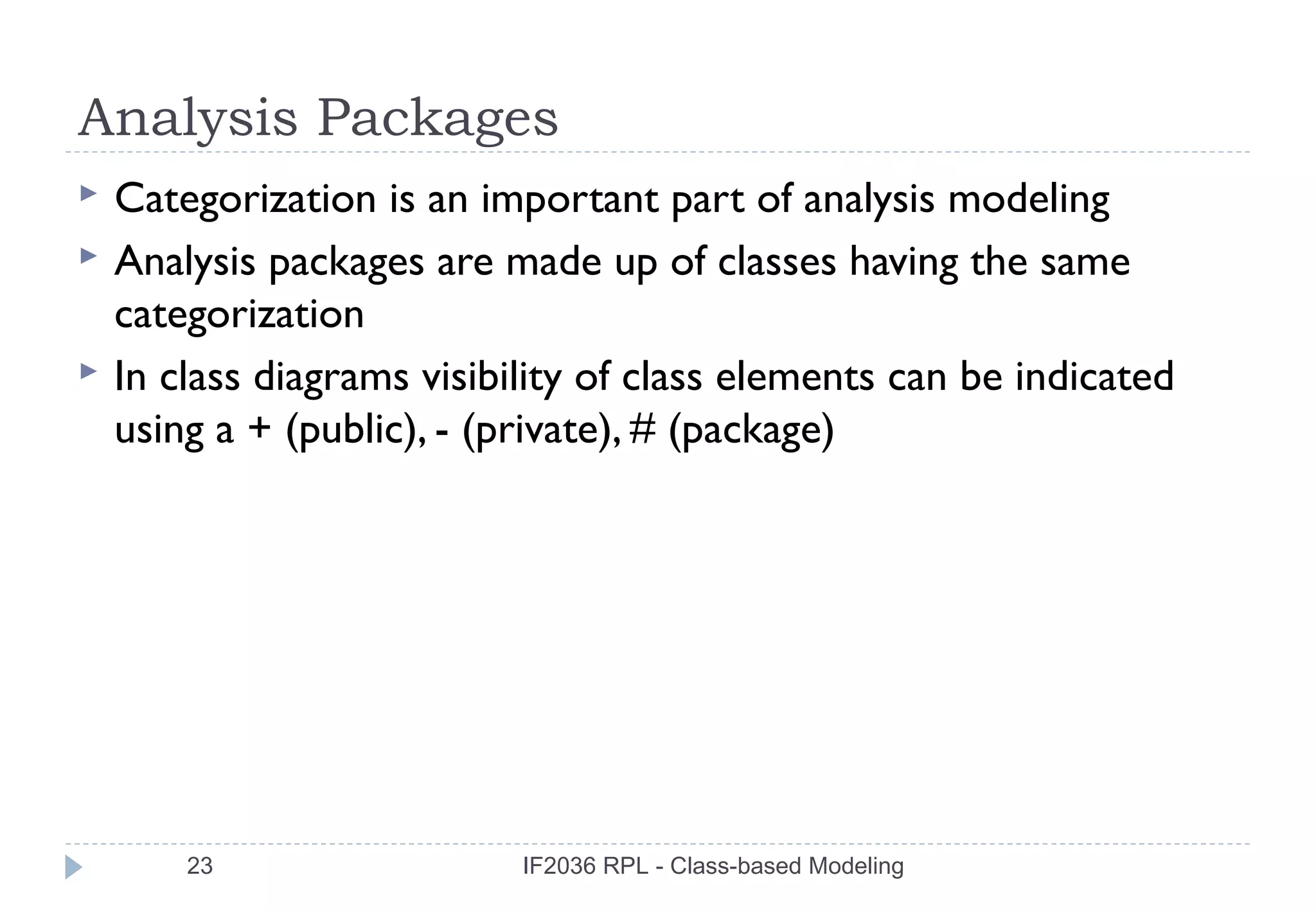
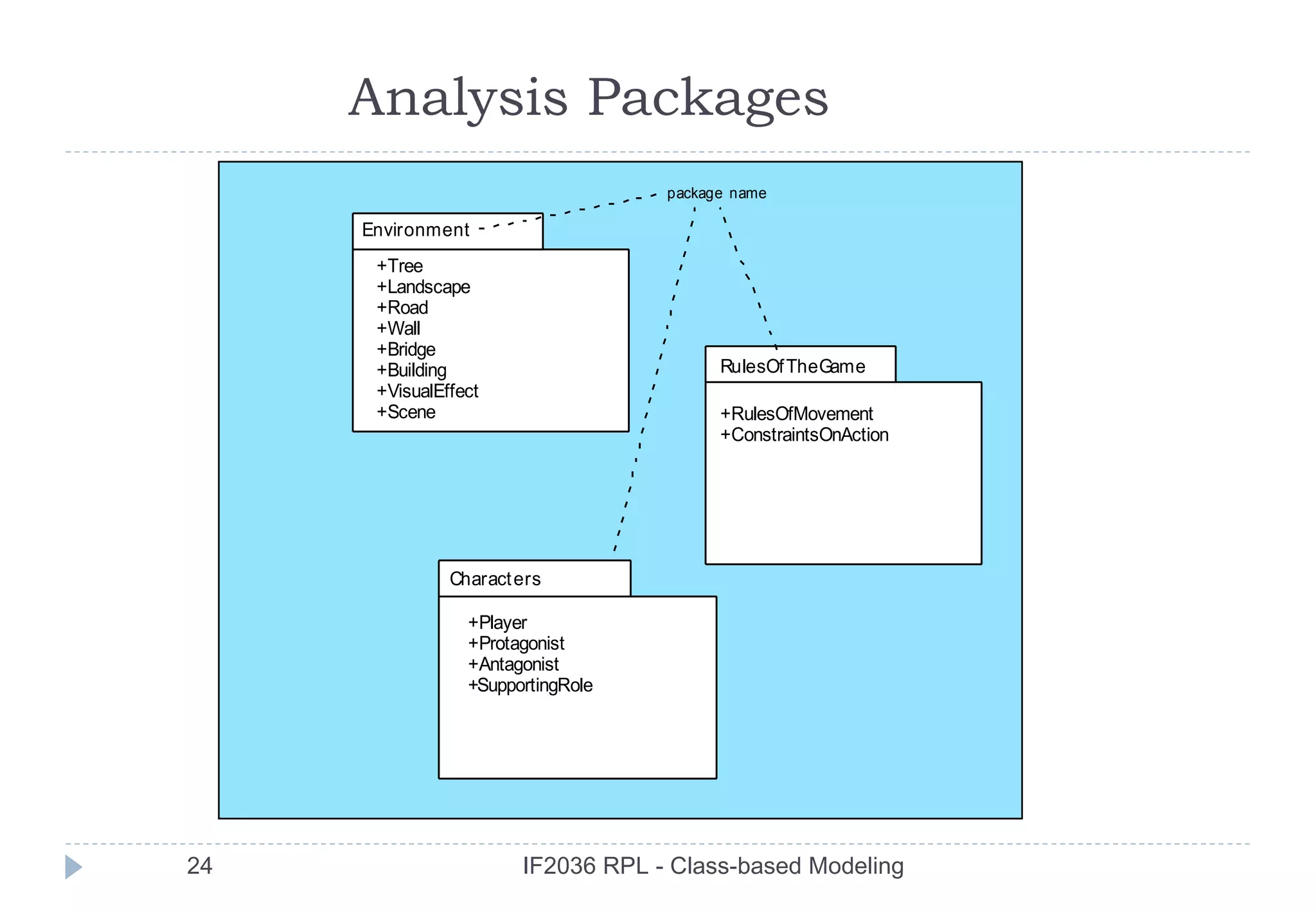
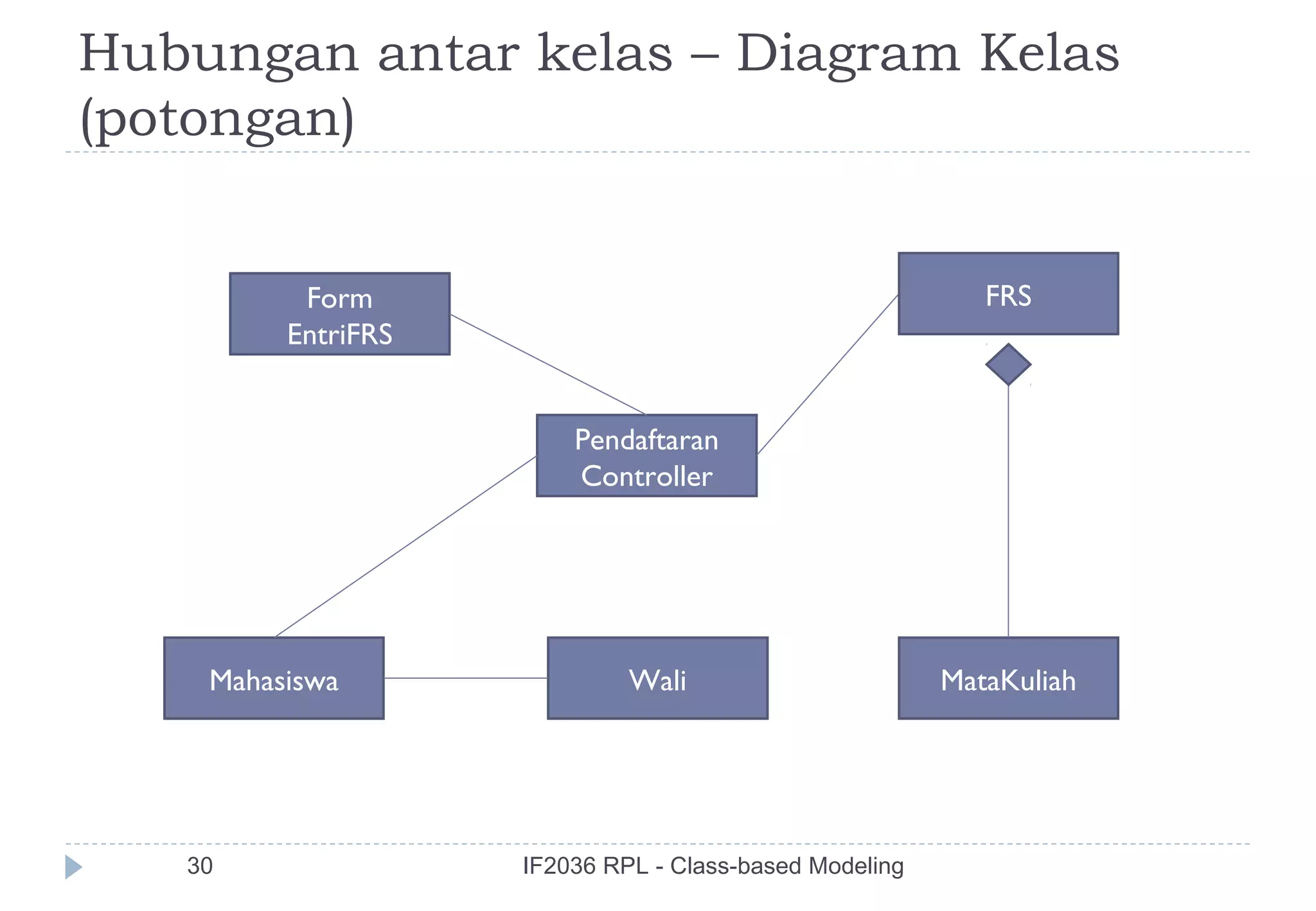
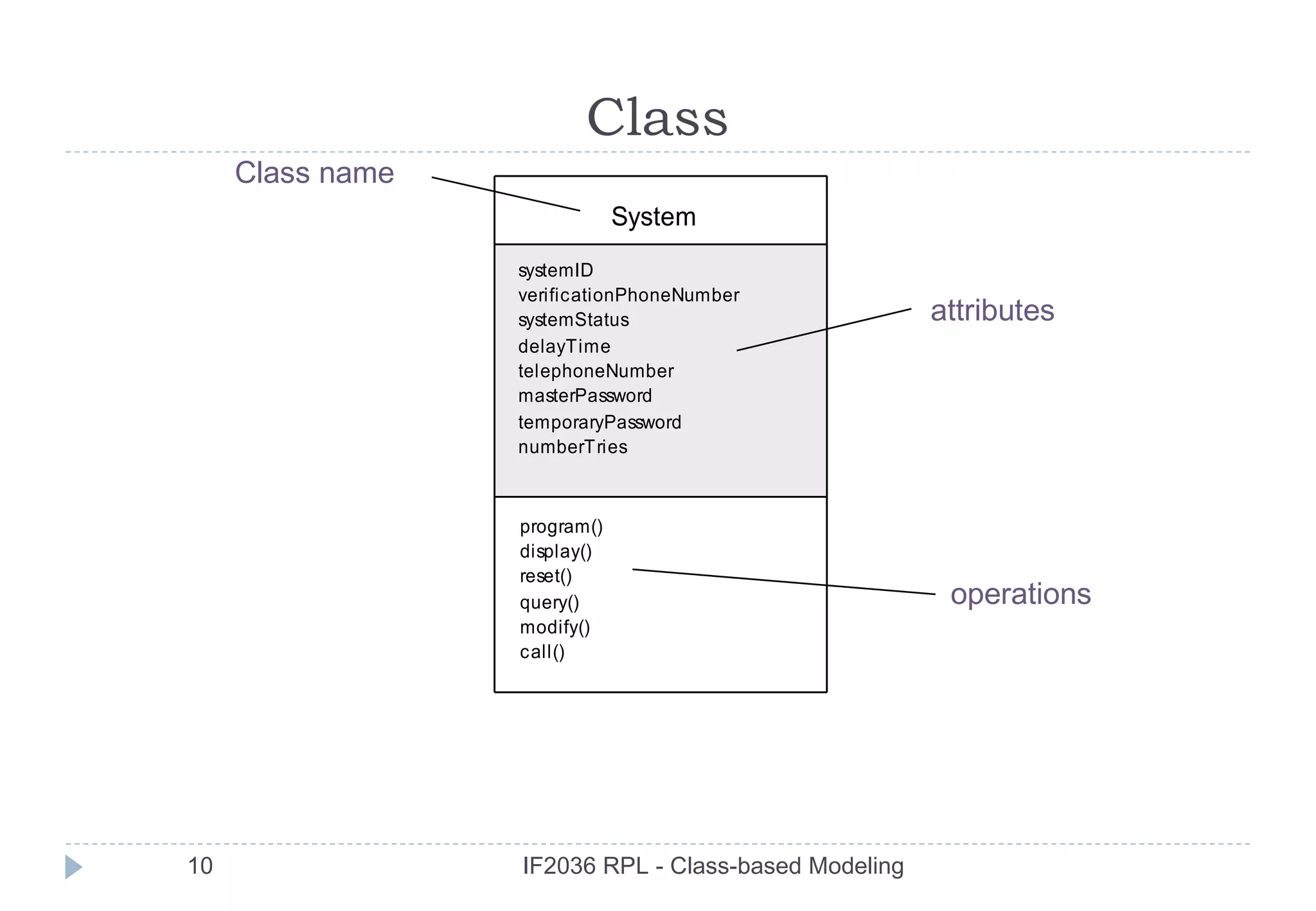
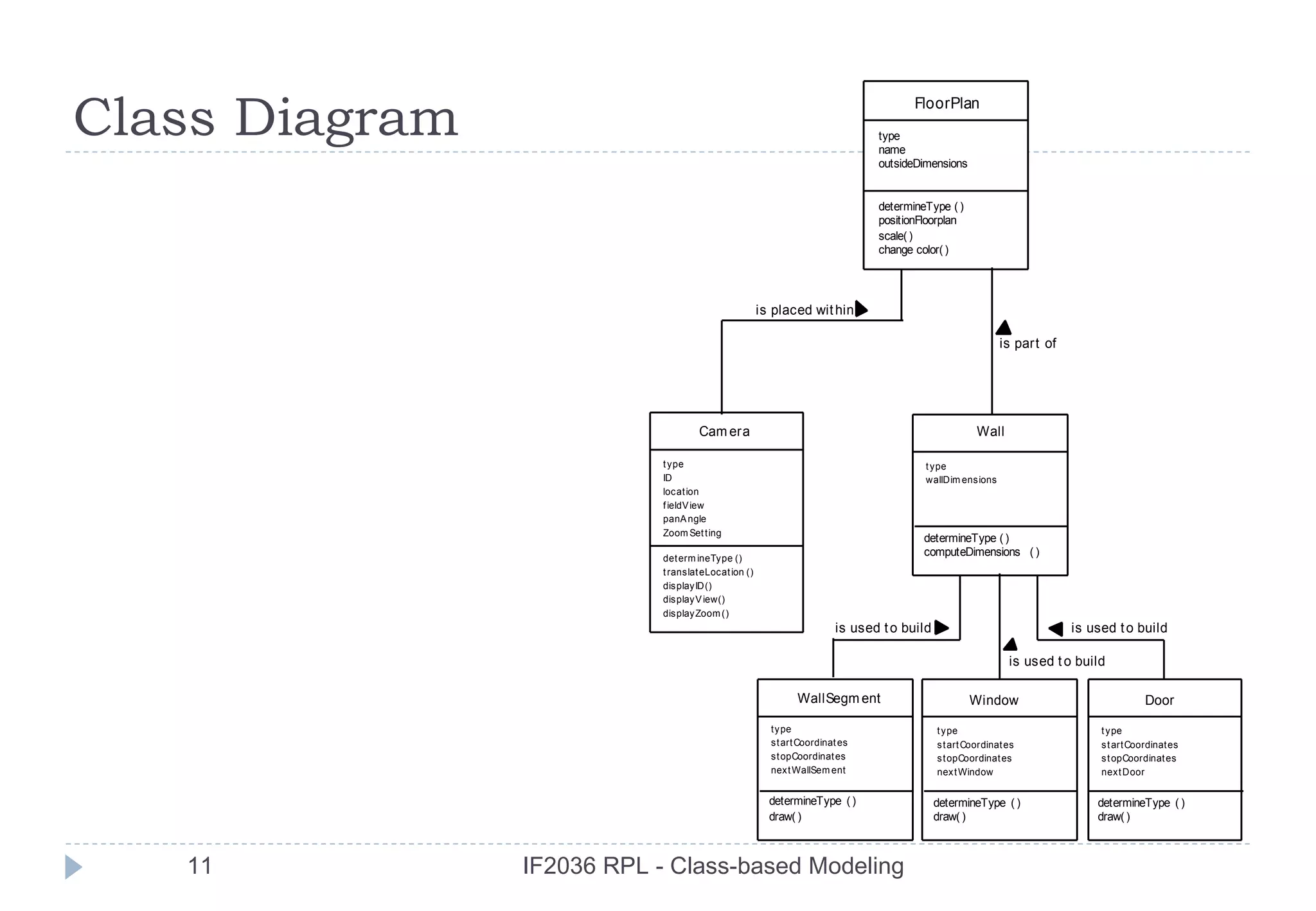
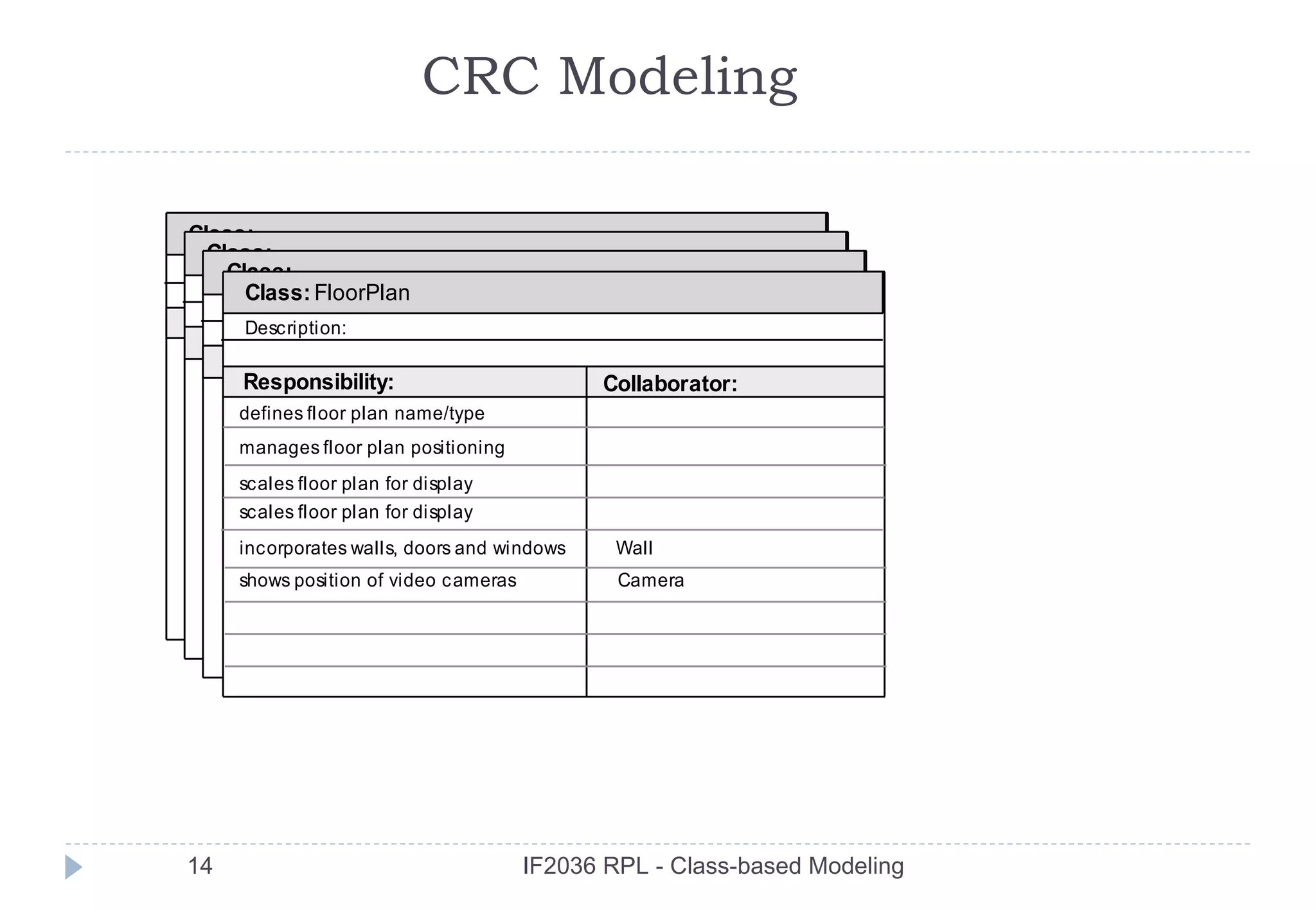
The document discusses class-based modeling in software engineering. It describes class-based modeling as representing the objects in a system, their operations, and collaborations. The key steps in class-based modeling are: identifying classes, determining attributes, operations, relationships between classes, creating class diagrams, and package diagrams if needed. Classes have attributes that define them and operations that manipulate the attributes. Relationships between classes like aggregation and association are also important to model collaborations between classes. The document provides guidance on identifying classes and their responsibilities and collaborations to create effective class models.








![Collaborations (2)
Classes fulfill their responsibilities in one of two ways:
A class can use its own operations to manipulate its own attributes, thereby fulfilling a particular
responsibility, or
a class can collaborate with other classes.
Collaborations identify relationships between classes
Collaborations are identified by determining whether a class can fulfill each responsibility
itself
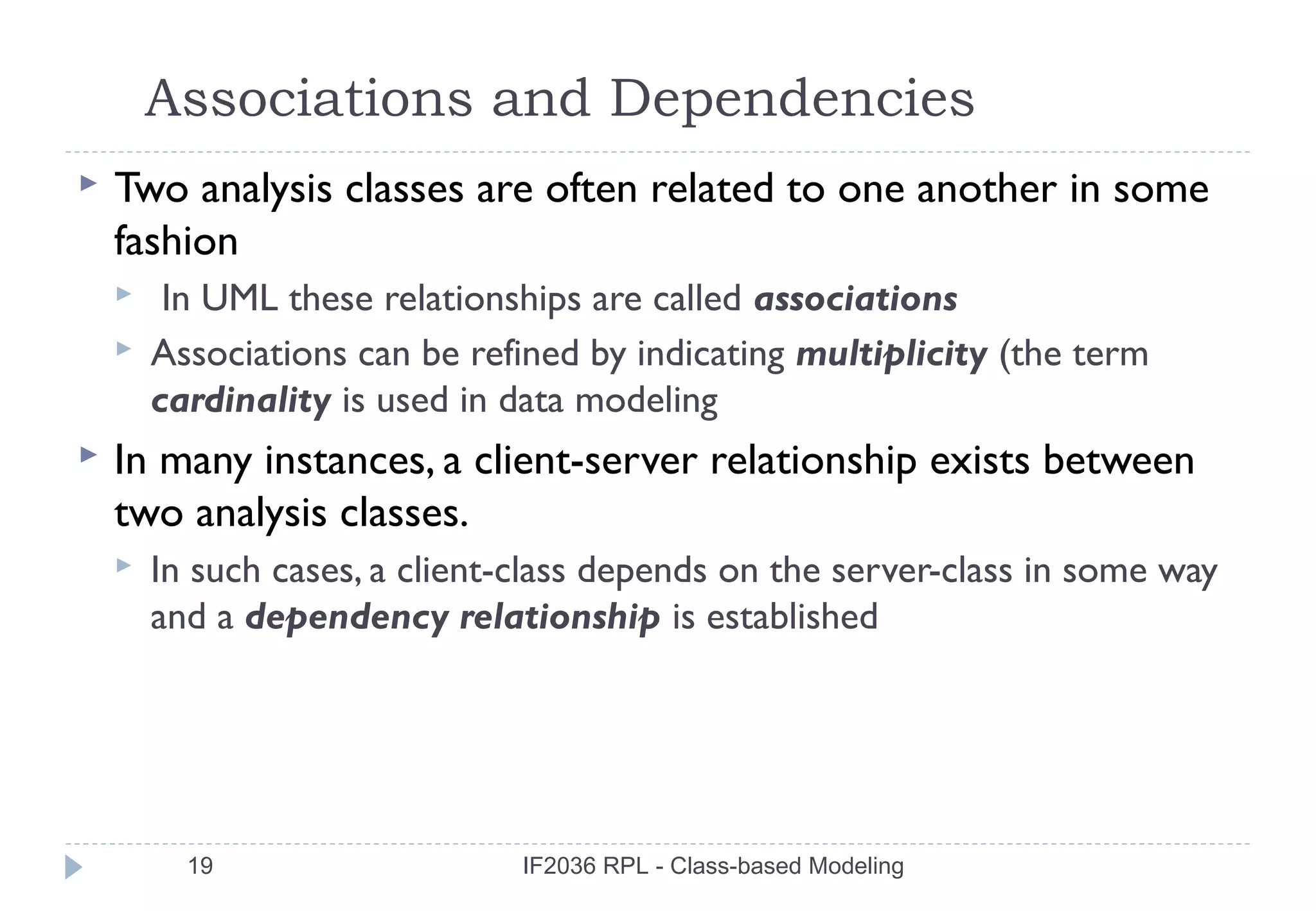
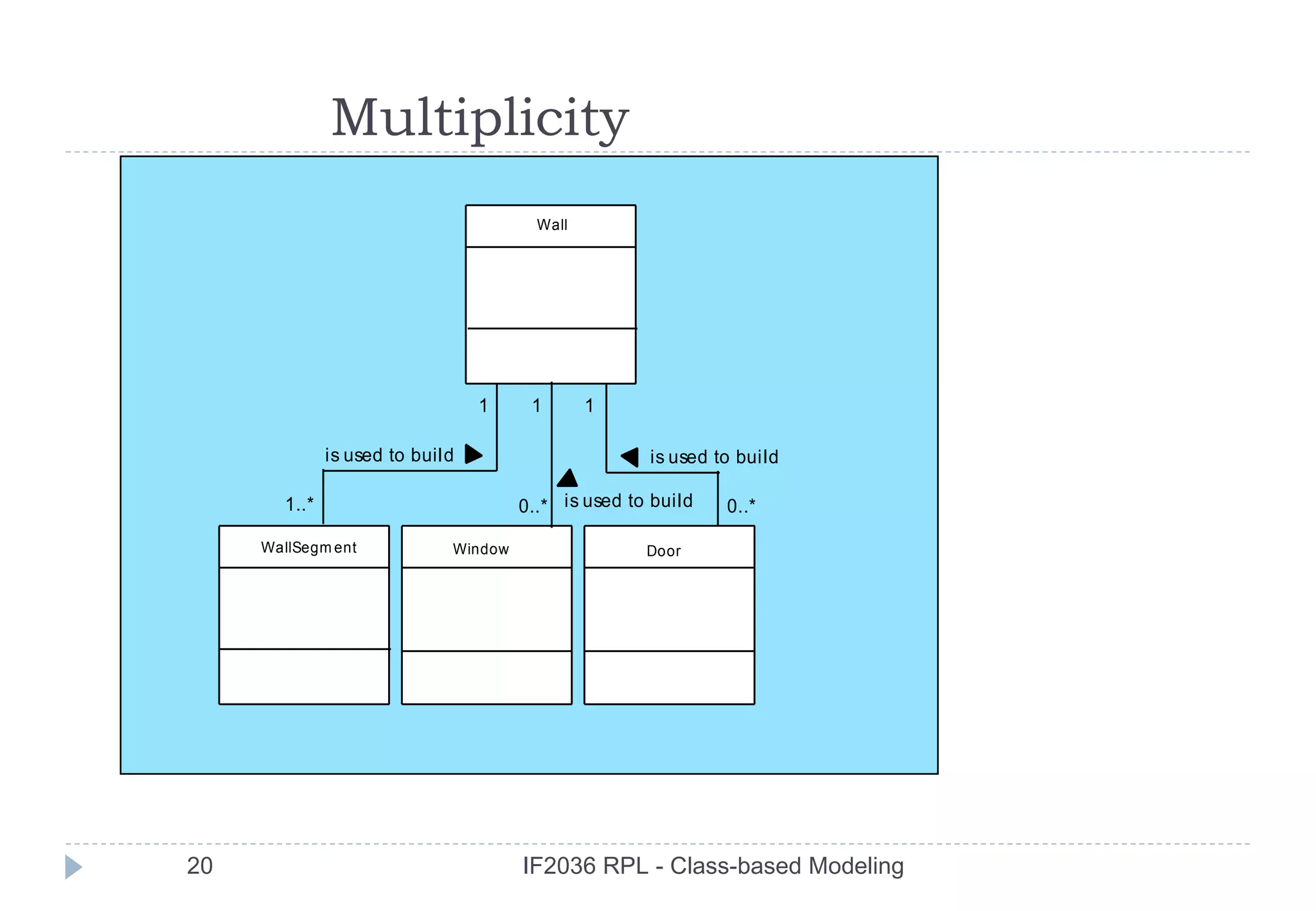
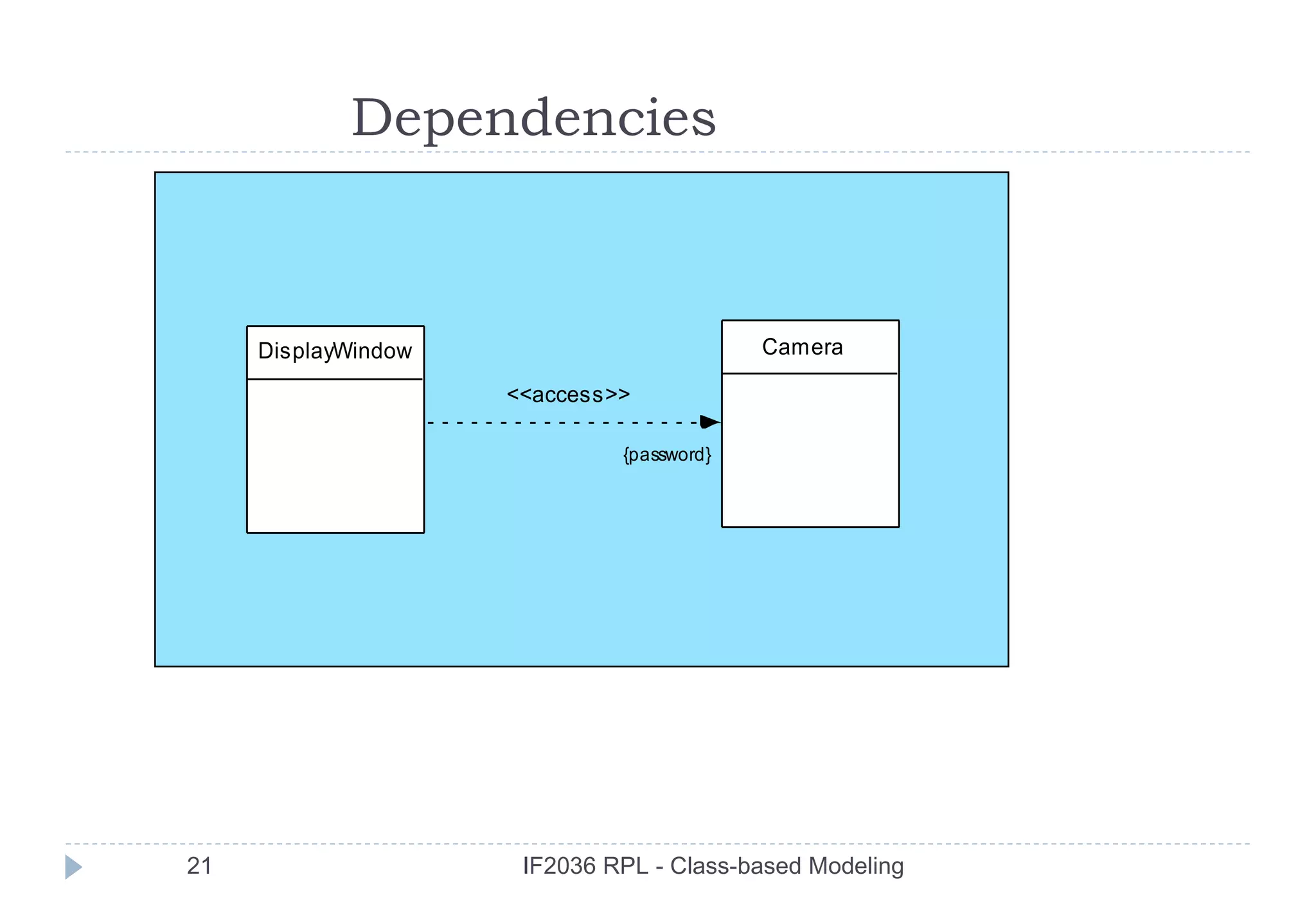
three different generic relationships between classes [WIR90]:
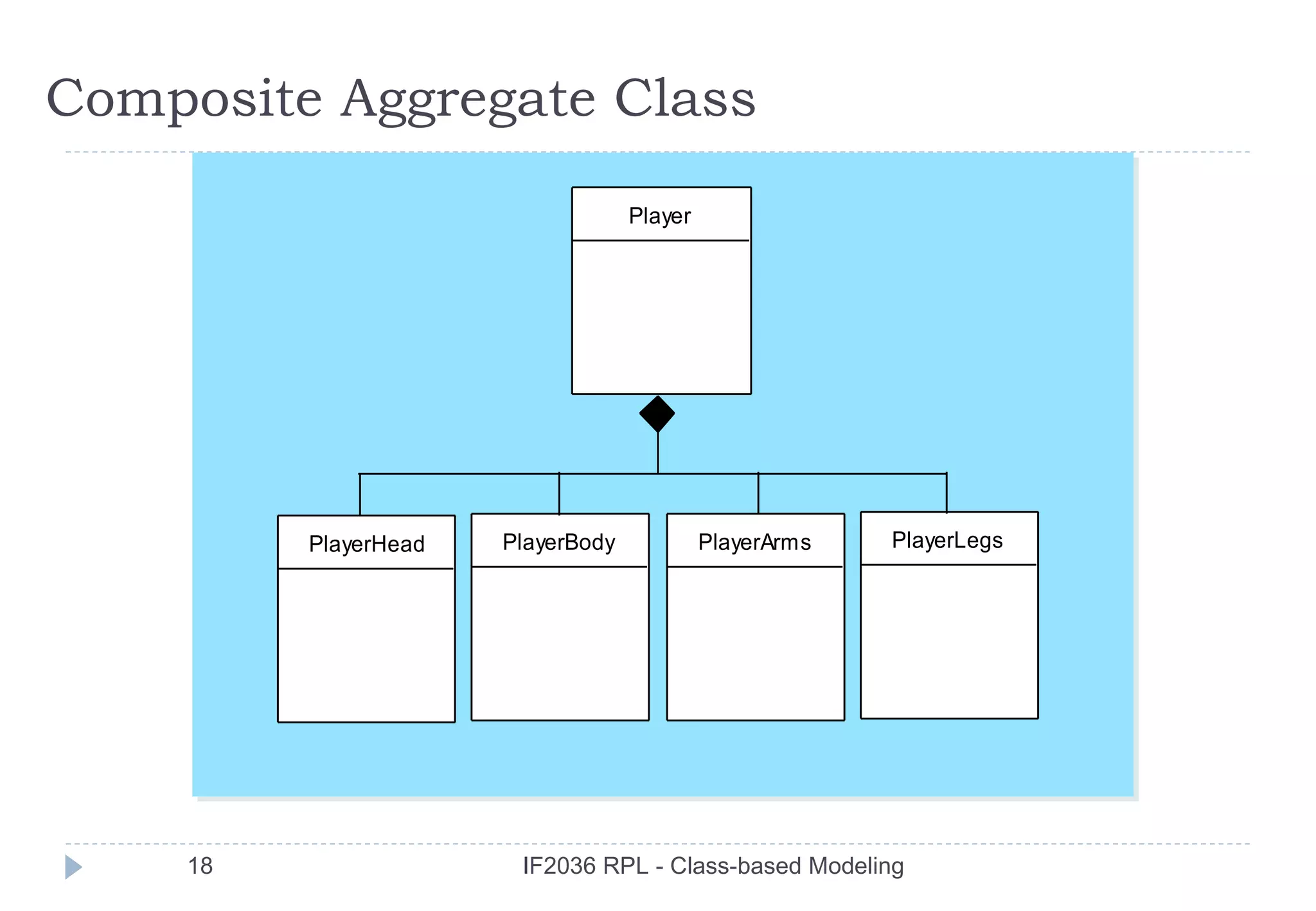
the is-part-of relationship
the has-knowledge-of relationship
the depends-upon relationship
17 IF2036 RPL - Class-based Modeling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/if2036class-basedmodeling-130318214421-phpapp02/75/If2036-class-based-modeling-17-2048.jpg)