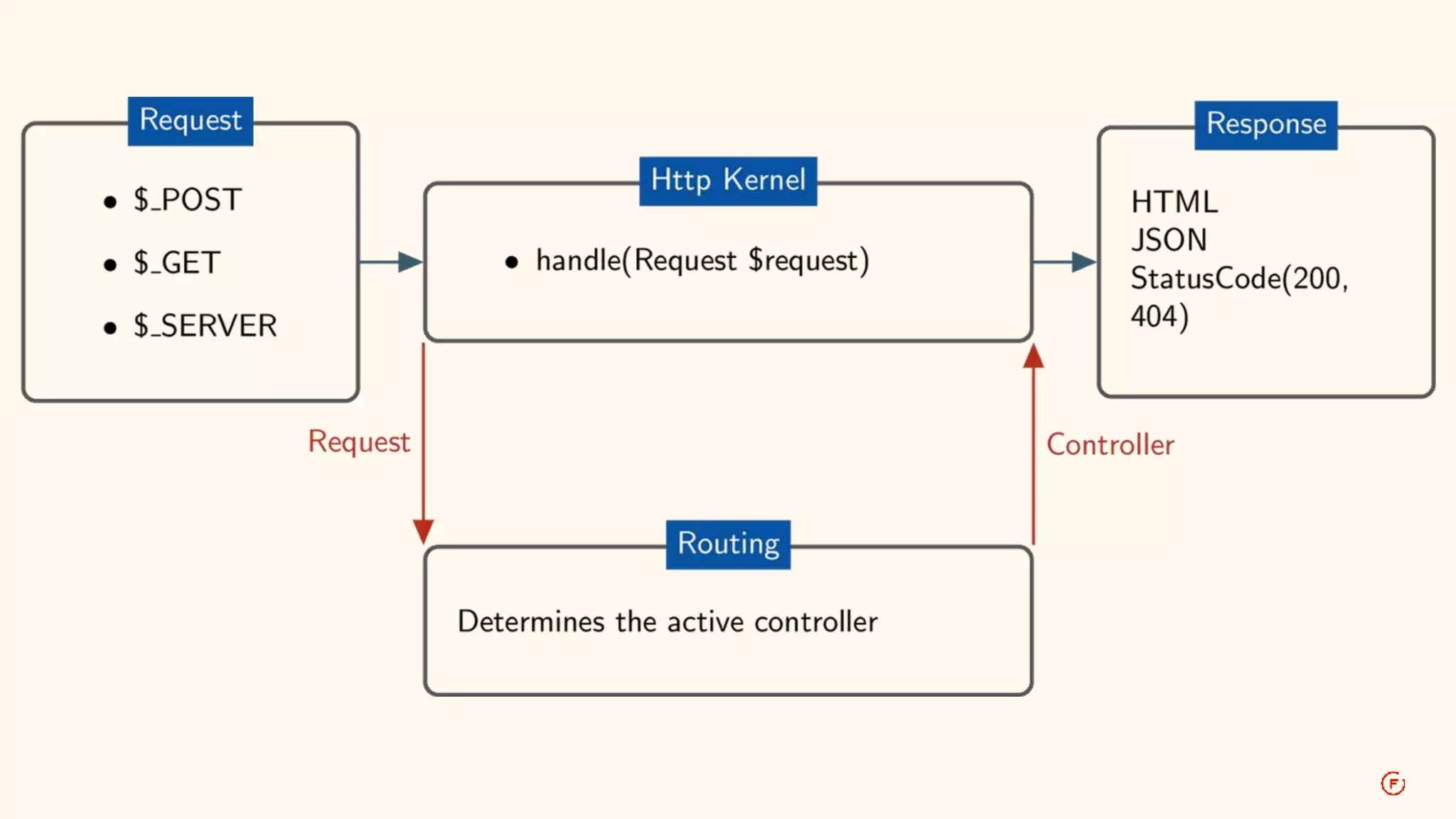
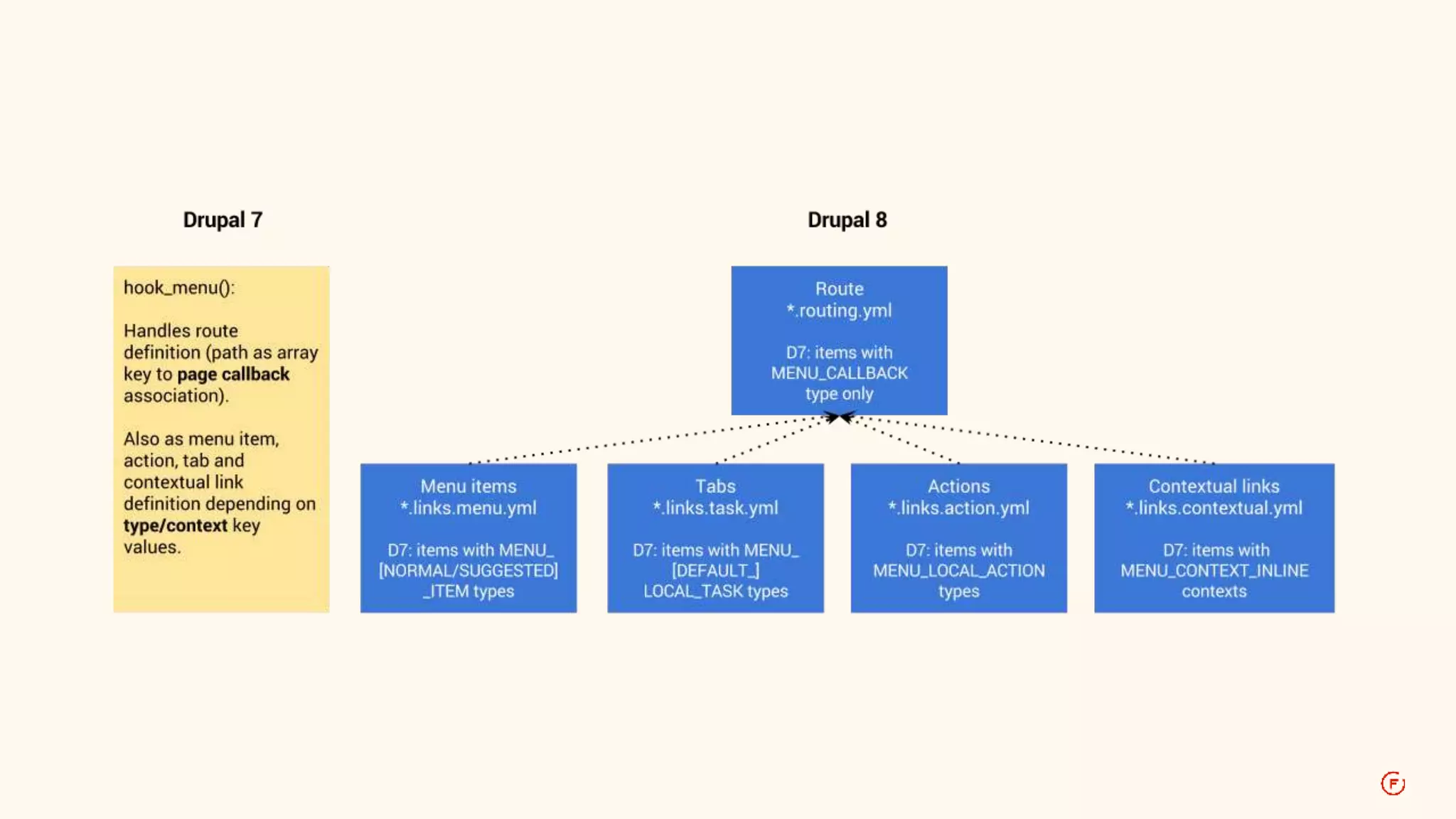
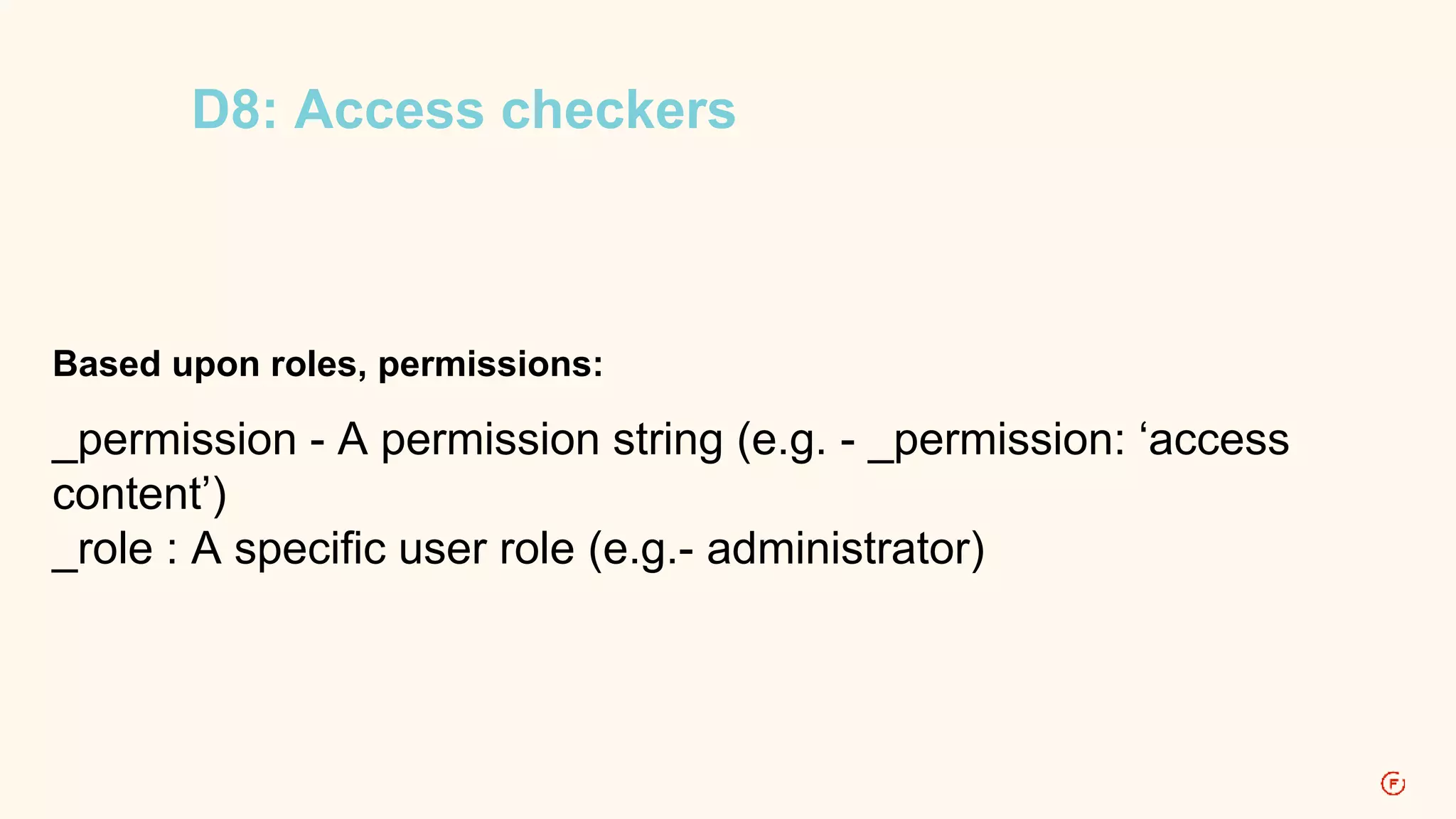
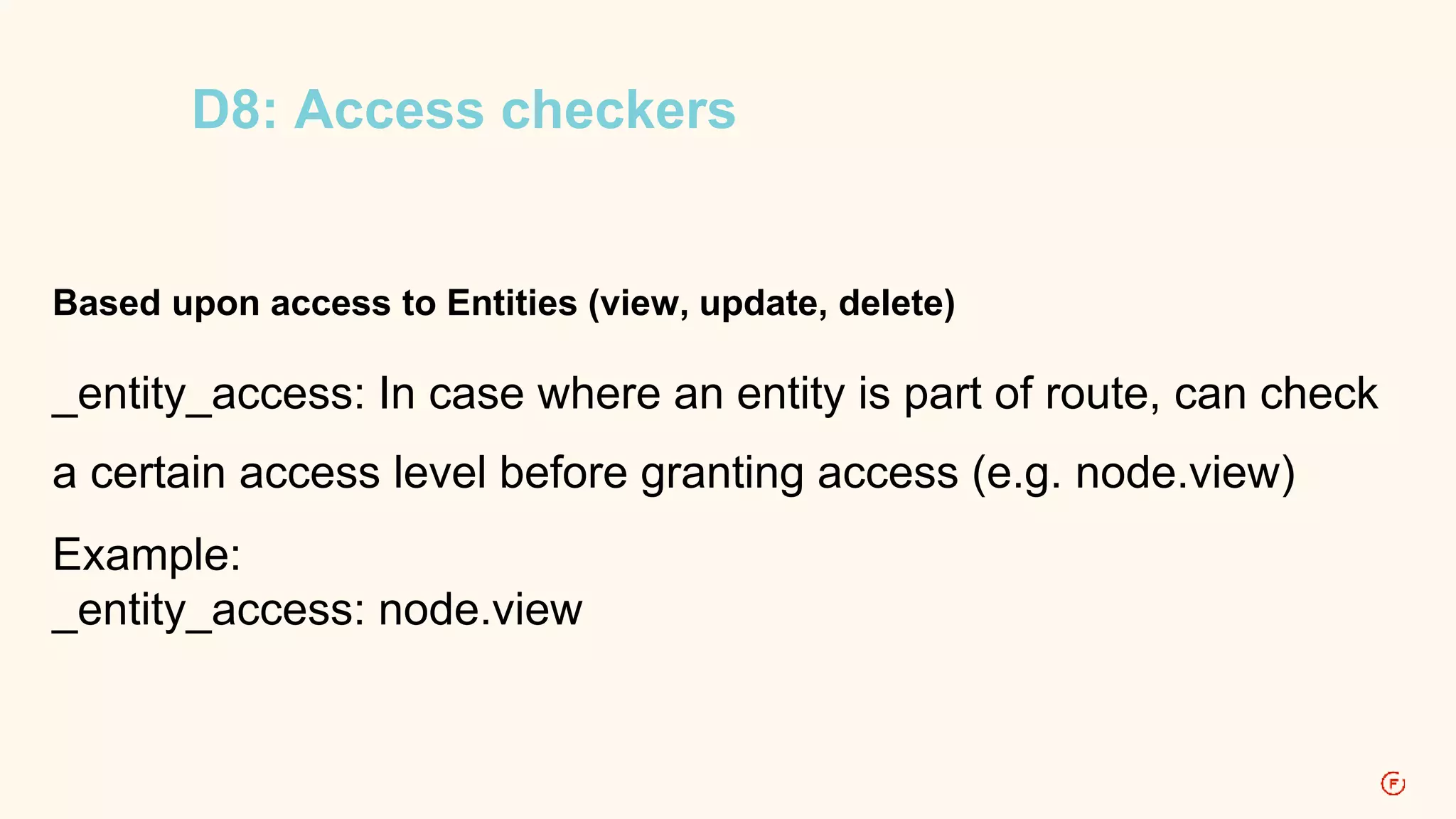
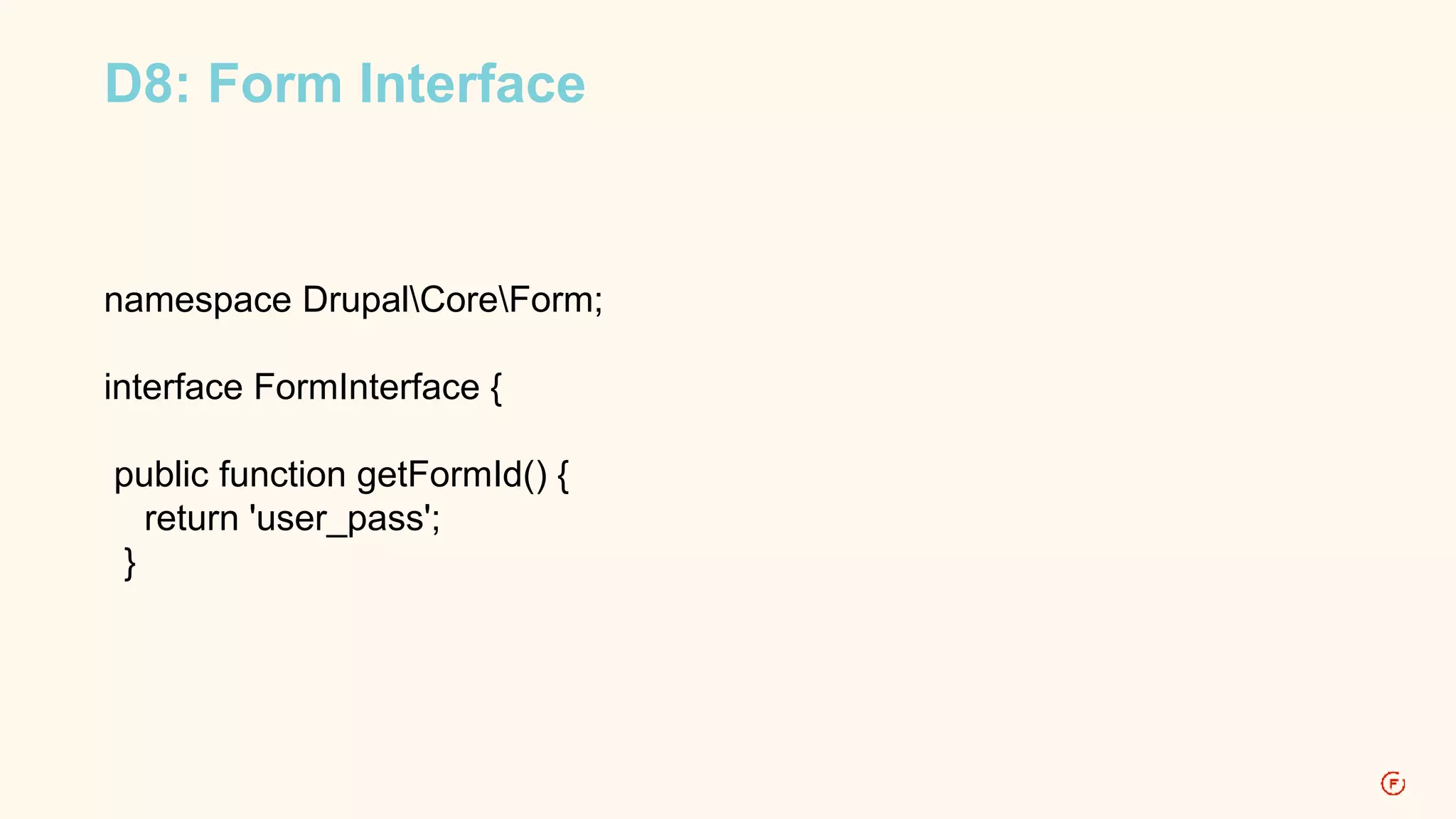
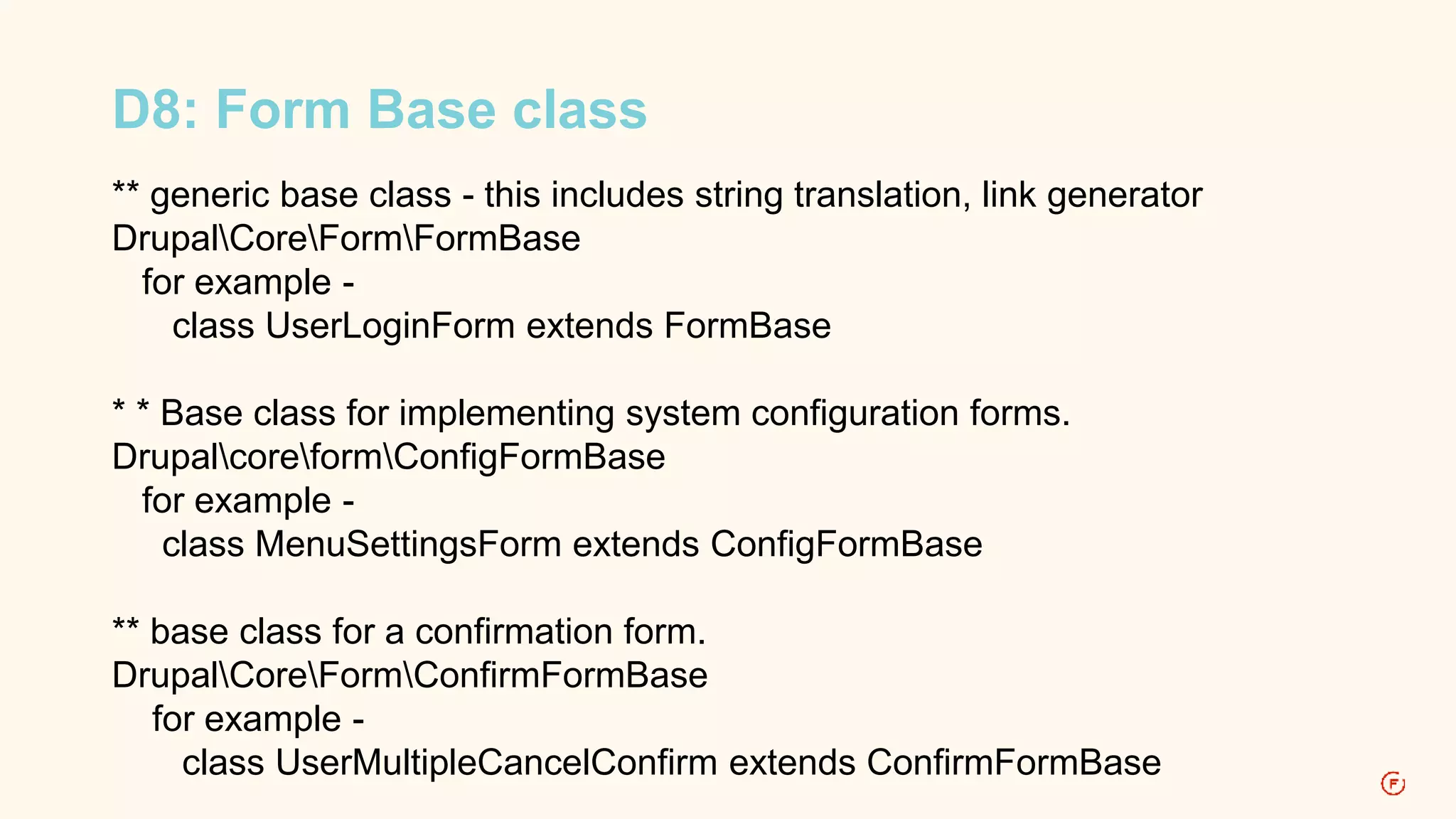
This document provides an overview of routing in Drupal 8. It explains that routing replaces hook_menu() from Drupal 7 and uses route files to define paths and callbacks. Paths can map to multiple routes and dynamic placeholders are supported. Forms are classes that implement interfaces rather than functions. Access, local tasks, actions and contextual links are also defined through route files rather than hook_menu.







![D7: hook_menu()
function user_menu() {
$items['user/logout'] = array(
'title' => 'Log out',
'access callback' => 'user_is_logged_in',
'page callback' => 'user_logout',
'weight' => 10,
'menu_name' => 'user-menu',
'file' => 'user.pages.inc',
);
return $items;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingindrupal8-2-141113111805-conversion-gate01/75/Routing-in-Drupal-8-12-2048.jpg)












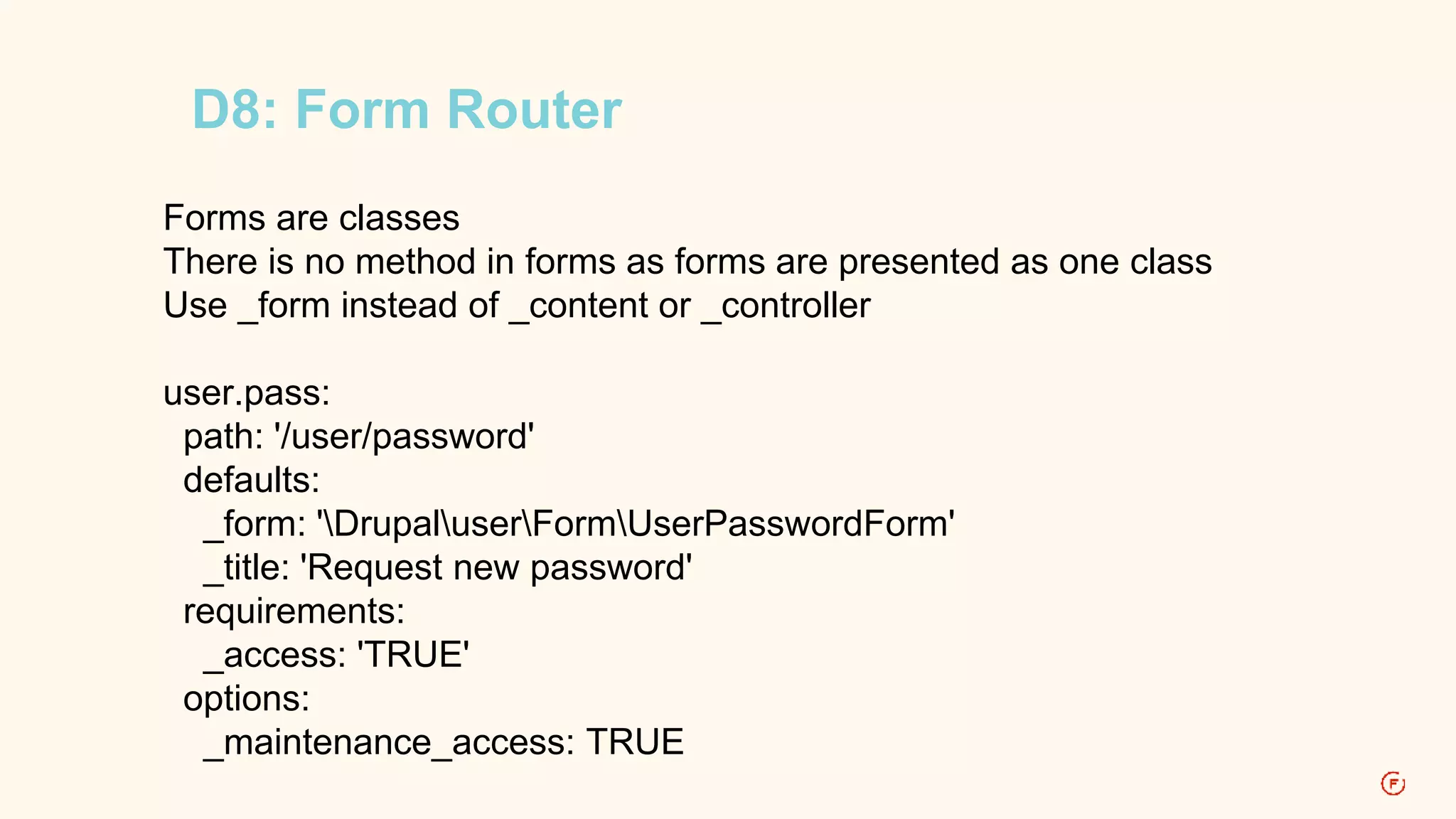
![D7: Form Router
$items['user/password'] = array(
'title' => 'Request new password',
'page callback' => 'drupal_get_form',
'page arguments' => array('user_pass'),
'access callback' => TRUE,
'type' => MENU_LOCAL_TASK,
'file' => 'user.pages.inc',
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingindrupal8-2-141113111805-conversion-gate01/75/Routing-in-Drupal-8-30-2048.jpg)
![D7: User Password Form
function user_pass() {
$form['name'] = array(
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => t('Username or e-mail address'),
'#size' => 60,
'#maxlength' => max(USERNAME_MAX_LENGTH,
EMAIL_MAX_LENGTH),
'#required' => TRUE,
'#default_value' => isset($_GET['name']) ? $_GET['name'] : '',
);
[...]
}
function user_pass_validate($form, &$form_state)
function user_pass_submit($form, &$form_state)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingindrupal8-2-141113111805-conversion-gate01/75/Routing-in-Drupal-8-31-2048.jpg)
![D8: Form Interface
public function buildForm(array $form, FormStateInterface $form_state) {
$form['name'] = array(
'#type' => 'textfield',
'#title' => $this->t('Username or email address'),
'#size' => 60,
'#maxlength' => max(USERNAME_MAX_LENGTH,
Email::EMAIL_MAX_LENGTH),
'#required' => TRUE,
'#attributes' => array(
'autocorrect' => 'off',
'autocapitalize' => 'off',
'spellcheck' => 'false',
'autofocus' => 'autofocus',
),
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingindrupal8-2-141113111805-conversion-gate01/75/Routing-in-Drupal-8-34-2048.jpg)



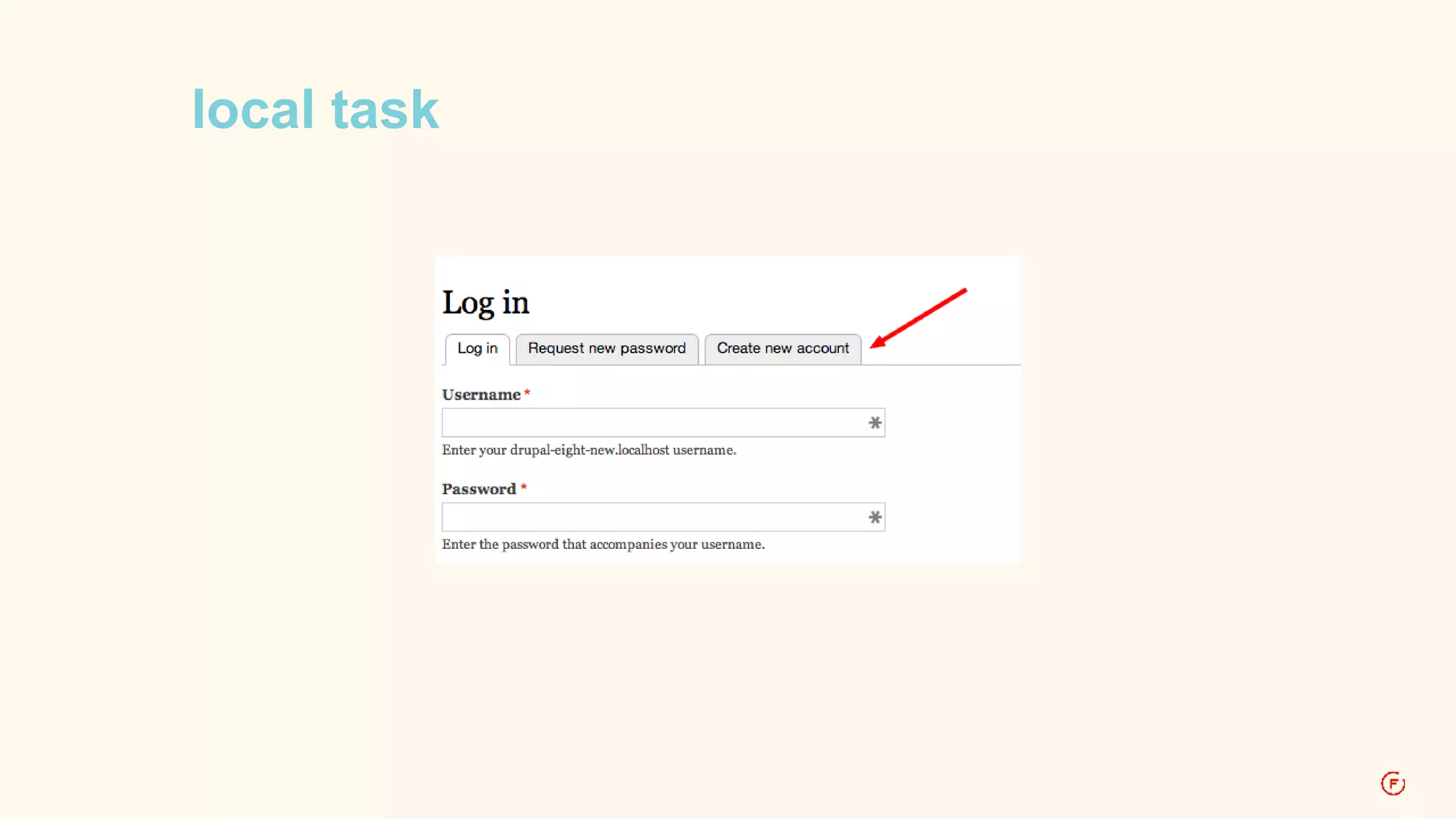
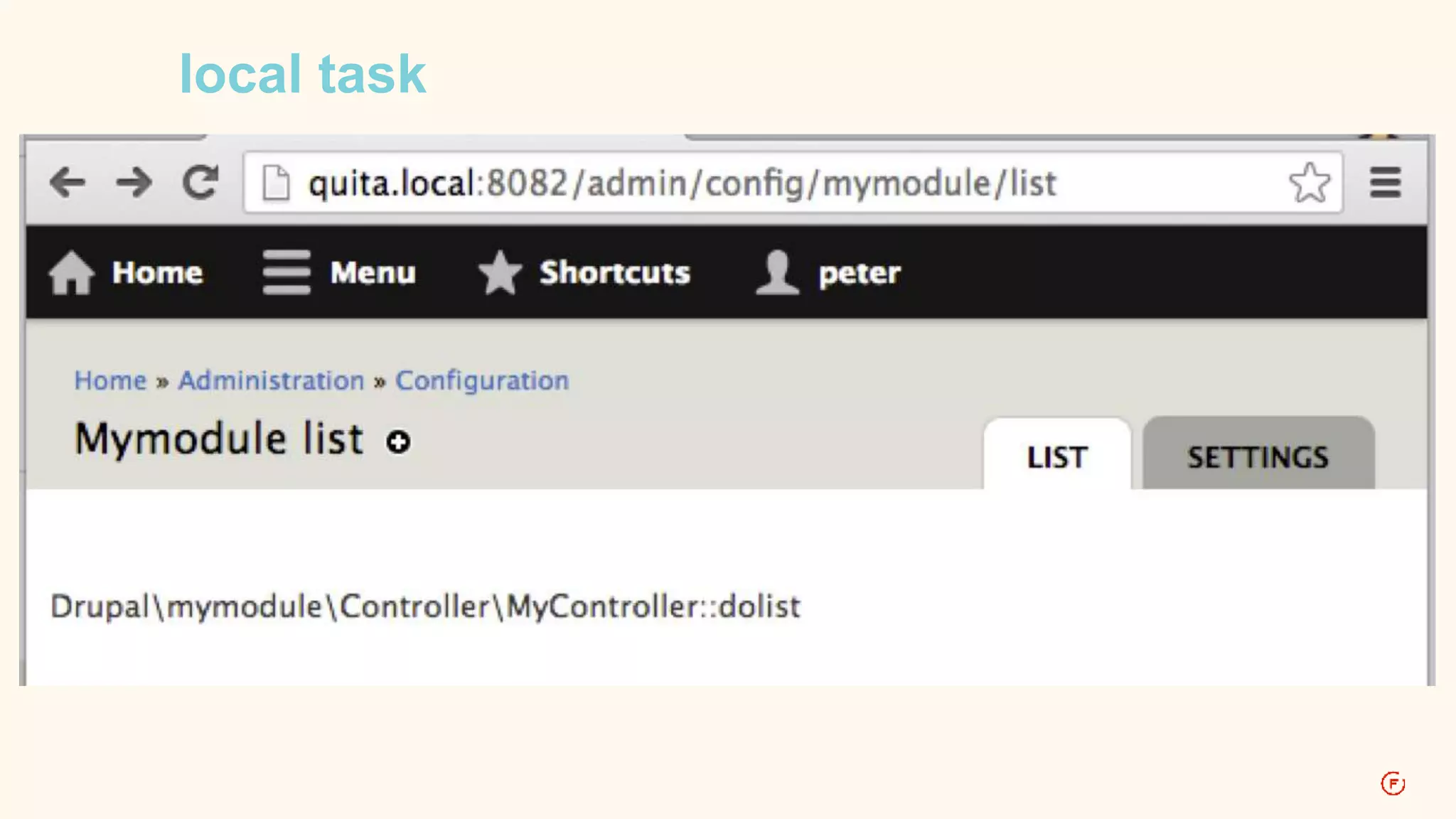
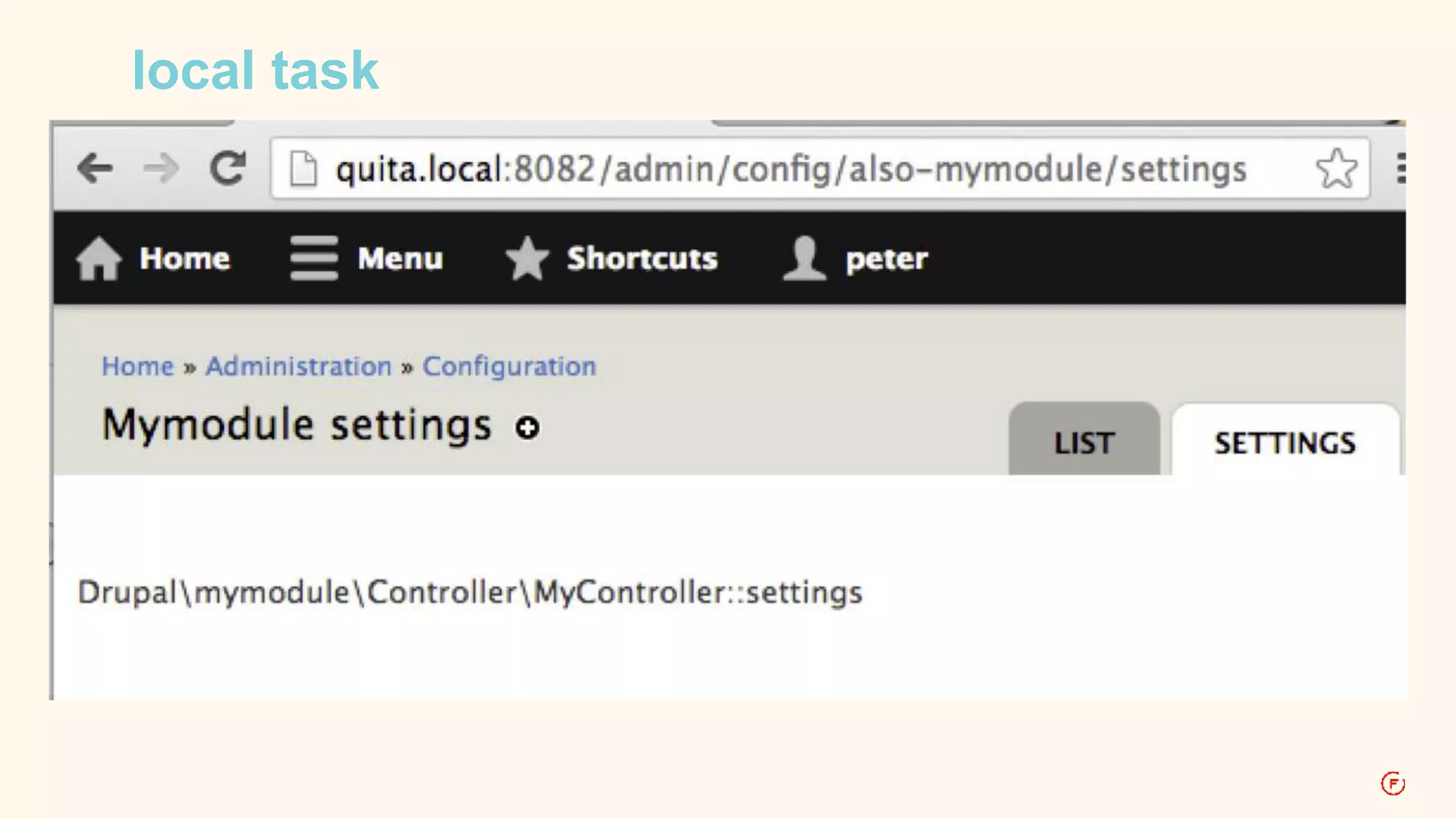
![D7: menu local tasks
$items['user/password'] = array(
'title' => 'Request new password',
'page callback' => 'drupal_get_form',
'page arguments' => array('user_pass'),
'access callback' => TRUE,
'type' => MENU_LOCAL_TASK,
'file' => 'user.pages.inc',
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingindrupal8-2-141113111805-conversion-gate01/75/Routing-in-Drupal-8-42-2048.jpg)

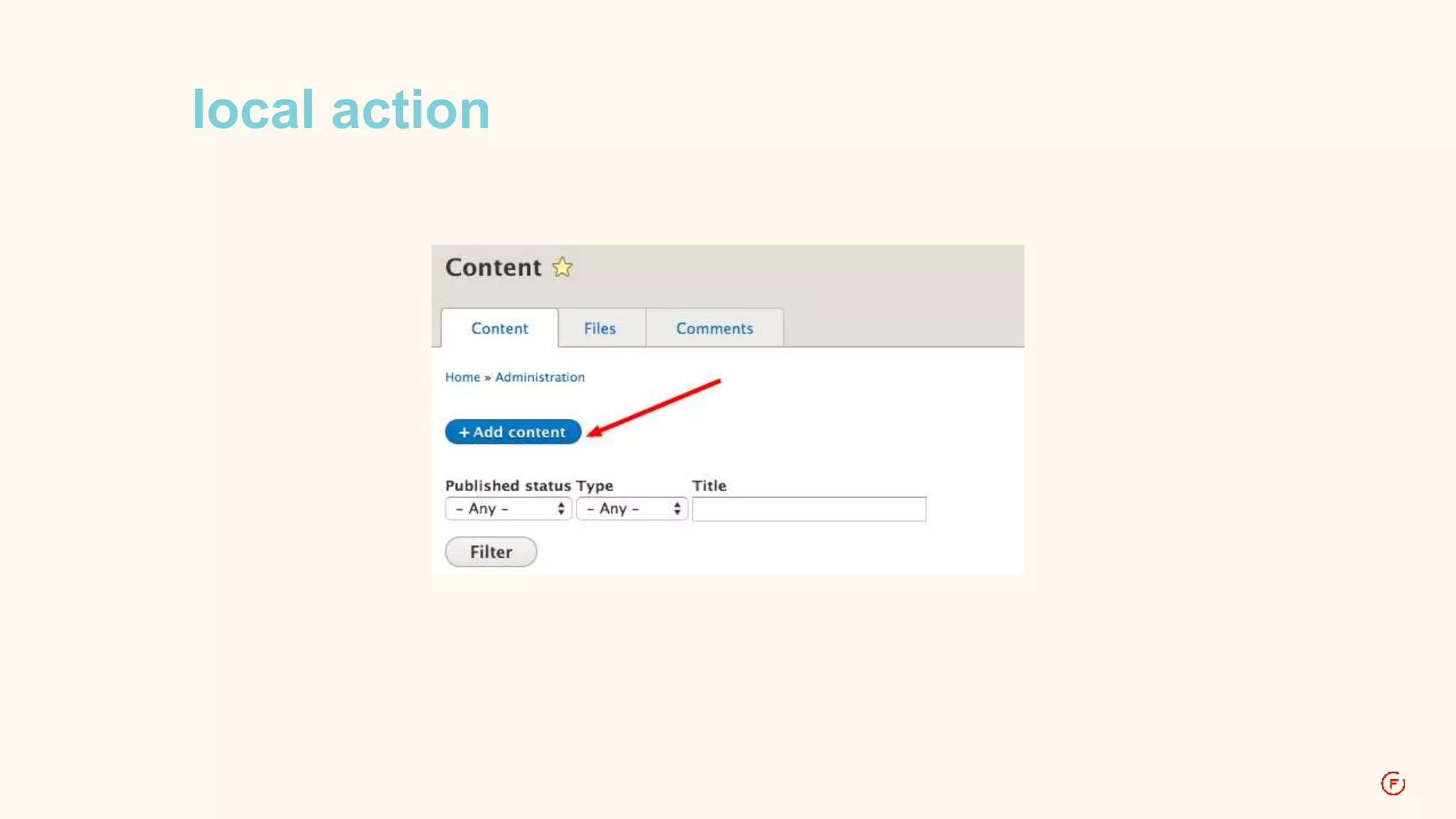
![D7: Local action
$items['admin/structure/types/add'] = array(
'title' => 'Add content type',
'page callback' => 'drupal_get_form',
'page arguments' => array('node_type_form'),
'access arguments' => array('administer content types'),
'type' => MENU_LOCAL_ACTION,
'file' => 'content_types.inc',
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingindrupal8-2-141113111805-conversion-gate01/75/Routing-in-Drupal-8-45-2048.jpg)


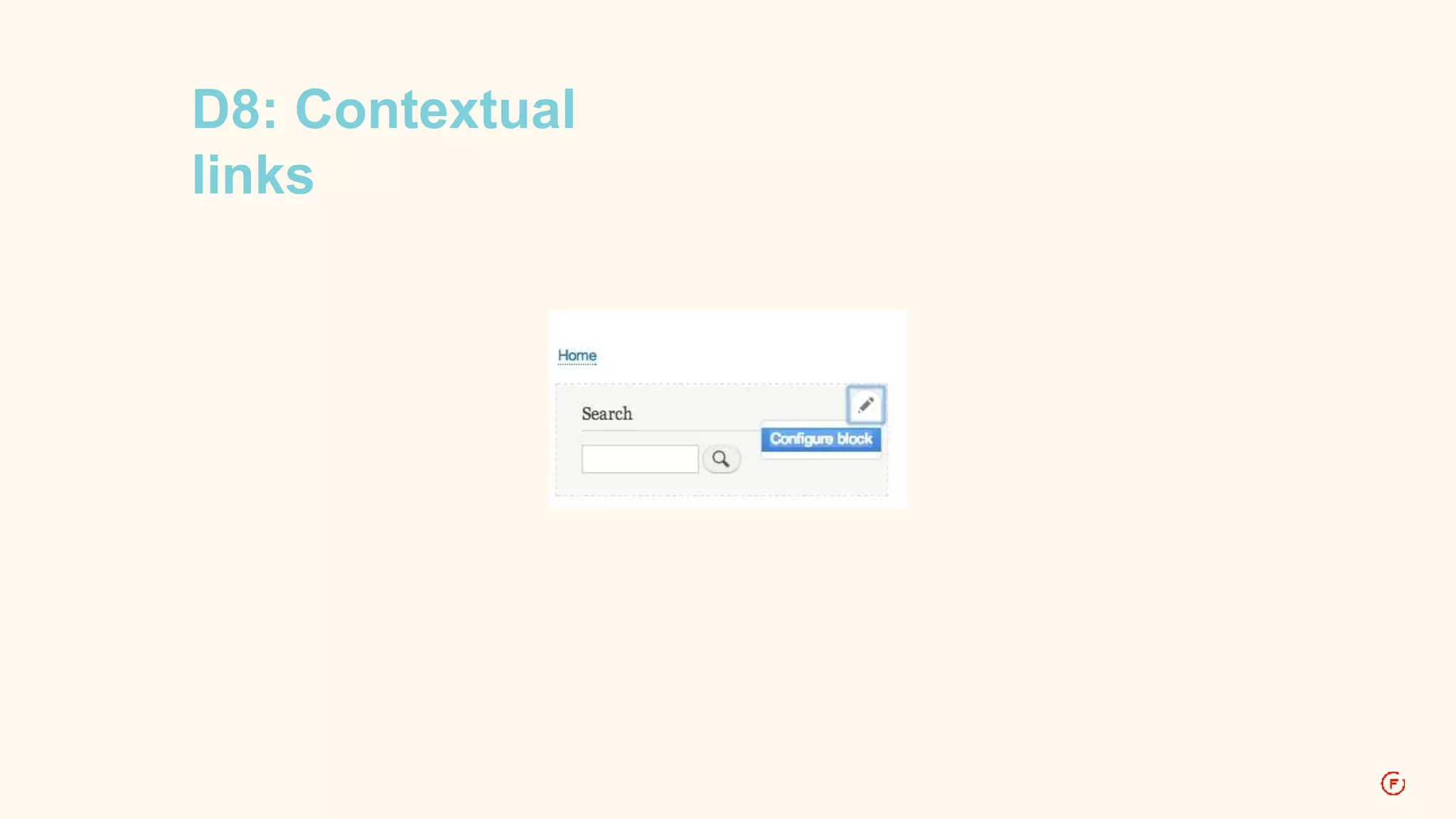
![D7: Contextual
links $items['admin/structure/block/manage/%/%/configure'] = array(
'title' => 'Configure block',
'type' => MENU_DEFAULT_LOCAL_TASK,
'context' => MENU_CONTEXT_INLINE,
);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/routingindrupal8-2-141113111805-conversion-gate01/75/Routing-in-Drupal-8-49-2048.jpg)