P4 p5 p6 resource
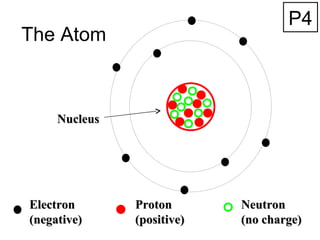
- 1. The Atom Nucleus Electron (negative) Proton (positive) Neutron (no charge) P4
- 2. Charging by Friction Duster ends up with negative charge Rod ends up with positive charge Duster rubbed over surface of Glass - Friction causes outer electrons of atoms near the edge to be removed. Glass Rod - showing atoms (enlarged) with only outer electron showing. Electron Negative Charge Nucleus Positive Charge Some outer electrons rubbed onto the duster - leaving atoms behind with a net positive charge
- 3. Charging by Friction Rubbing the Glass rod strips some of the __________ from some of the atoms at the edge of the rod. This leaves these atoms with a net ________ charge. This means that overall the Glass rod has a __________ charge as the other atoms have equal numbers of positive and __________ charges (called neutral). Perspex and Acetate also behave like this. In other materials such as Polythene the electrons are rubbed off the cloth onto the insulator, giving the material a net __________ charge. Electrostatic Law :- “ Like charges _______ ; ______ charges ________”.
- 4. Charging by Friction Rubbing the Glass rod strips some of the __________ from some of the atoms at the edge of the rod. This leaves these atoms with a net ________ charge. This means that overall the Glass rod has a __________ charge as the other atoms have equal numbers of positive and __________ charges (called neutral). Perspex and Acetate also behave like this. In other materials such as Polythene the electrons are rubbed off the cloth onto the insulator, giving the material a net __________ charge. Electrostatic Law :- “ Like charges _______ ; ______ charges ________”. electrons positive positive negative negative repel Unlike attract
- 5. Static Electricity : Charging Problem Planes become charged as dusty air rubs against them in flight They are earthed by connection to the ground when refuelling. This stops sparks jumping near the fuel nozzle.
- 7. Static Electricity : Useful Charging The paint is charged as it comes out of the nozzle. The paint is attracted to the car. The car must be earthed or connected to a positive voltage.
- 8. Another use of static: Electrostatic Precipitators.
- 11. live earth neutral fuse cord grip
- 16. How does it work? The waves are reflected off the different layers
- 17. Is this a stable (balanced) atom? Why? What is the MASS NUMBER? 5 (three Protons & two Neutrons)
- 18. He 2 4 MASS NUMBER = number of protons + number of neutrons SYMBOL ATOMIC NUMBER = number of protons
- 19. What do you notice? So, what is an alpha particle?
- 20. What do you notice? The Atomic number decreases by a value of 1.
- 21. What do you notice? The atomic structure doesn’t fundamentally change.
- 22. Half Life
- 23. The gamma radiation from the radioactive source is picked up above the ground, so the leak in the pipe can be detected. Gamma - tracers Radiotherapy Gamma source
- 25. Nuclear Fission
- 27. The Earth and the Moon The Earth’s gravity attracts the Moon, in the same way the Moon’s gravity attracts the Earth. It is the gravitational attraction of the Moon which causes the tides in the oceans on Earth. gravitational force Provides centripetal force Faster Heavier Smaller circle/ ellipse BIGGER Centripetal force P5
- 28. Resultant Force When two forces act at different angles on a body, the resultant force is calculated using the parallelogram of forces... Force from tug 1 Force from tug 2 Resultant force
- 29. Constant Acceleration Formulas - Summary We have 4 formulas. These formulas will help you calculate any motion problem in which a body undergoes zero or constant acceleration. Whenever you have any 3 of the five ‘v-u-s-t-a’ unknowns, you can find out the remaining 2 unknown values by using one or more of the above formulas… acceleration time taken distance travelled initial velocity final velocity Meaning m/s v m/s u m/s 2 a s t m s Unit Symbol s = (u + v ) x t 2 s = ut + ½at 2 v 2 = u 2 + 2as v = u + at Formulas
- 30. A tourist drops a croissant from the top of the Eiffel Tower. The croissant falls for 8 seconds. Ignoring air resistance, how high is the Eiffel Tower? Example Use... s = ut + ½ at 2 s = 0 x 8 + ½ x 10 x 8 2 The Eiffel Tower is 320m tall s = 320m v = u = s = t = a = 0 8 10
- 31. Horizontal Vertical Ignoring air resistance , the only force acting on a projectile during the flight is gravity . Projectiles have a downward acceleration (due to gravity) and this only affects the vertical velocity . For a projectile there is no acceleration in the horizontal direction . Projectile Motion - Forces Acting
- 32. Calculating Time Taken Example: Calculate the time taken, from firing, for the cannon ball to hit the target. t = d/s t = 48/24 Time taken is 2s t = 2 t = d/s is a formula that can be applied to solve problems, whenever velocity is constant... Velocity is constant in the horizontal vector...
- 33. Calculate the final vertical velocity of the cannon ball as it hits the target. In this case a = g = 9.8ms -2 (9.8m/s 2 ) Calculating Final Velocity Example: v = u + at v = 0 + 9.8 x 2 v = 19.6m/s v = u + at is a formula that can be applied to solve problems, whenever acceleration is constant... Final vertical velocity is 19.6m/s v = 0 + 19.6
- 35. Impulse & Momentum - Summary An impulse is a sudden force applied for a short period of time. An impulse causes (and is equal to) the change in momentum. = Force x Time = Change in Momentum Impulse The units of impulse are Ns
- 36. Geostationary - Equatorial Orbiting Satellites Geostationary satellites are used for telecommunication purposes, and they are also known as geosynchronous satellites. Geostationary satellites are used for telephone signals and satellite TV broadcasts. Three satellites can cover the whole surface of the Earth. Pacific Ocean Atlantic Ocean Indian Ocean
- 37. Microwaves - Satellite Communications Microwaves pass through the Earth’s atmosphere with less interference than longer wavelengths (radio waves), so they are used to carry signals to satellites orbiting the Earth.
- 38. Polarisation Polarising filters polarise light because they are composed of long-chain molecules, which are aligned within the filter in the same direction, (e.g. vertically). As unpolarised light strikes the polarising filter, the portion of the waves vibrating in any plane other than vertical, (e.g. horizontal waves) are absorbed by the filter. light beam beam of polarised light polarising filter
- 39. Electromagnetic waves obey the wave formula: Wave Equation Write the 3 formulas... Wavelength ( ) (v) (f) ( ) Frequency (f) x = Wave Speed (v) (metre/second, m/s) (Hertz, Hz) (metre, m)
- 40. Interference can be demonstrated using two speakers (1 metre apart), producing the same frequency sounds. Constructive and Destructive Interference The sound waves produced from these speakers cause interference. 1 metre Constructive interference Destructive interference Peak Trough
- 41. Snell's law also states that the refractive index of a medium can be calculated from the angles of incidence and refraction: Refraction at a Boundary The refractive index of the glass block is 1.54 Glass Air n = sin i sin r n = sin 57 º sin 33 º n = 0.838 0.544
- 42. Total Internal Reflection 42 º is known as the critical angle. Above this angle the light ray is reflected internally. This is known as total internal reflection and it is the phenomenon exploited by fibre optic cable technology. Use the angle slider to see what happens when the angle at which the light enters a glass block is increased...
- 43. Convex Lenses - Light Ray Diagrams The principal focus of a biconvex lens...
- 44. Convex Lenses - Light Ray Diagrams
- 45. Resistance The resistance of a component can be calculated using Ohm’s Law: P6 Georg Simon Ohm 1789-1854 Resistance is anything that will RESIST a current. It is measured in Ohms, a unit named after me. Resistance = Voltage (in V) (in ) Current (in A) V R I
- 46. Current-voltage graphs 1. Resistor 2. Bulb Explain the shape of each graph I V I V
- 48. Motor Effect – left hand rule
- 50. 1) Alternating current into the primary coil 2) Current, passing through a coil, generates a magnetic field 3) Because the current is alternating, it generates a changing magnetic field 4) A changing magnetic field induces a current in the secondary coil
- 52. Full-wave rectified How does it work? +6V -6V
- 55. AND GATE OR GATE 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 OUTPUT B A 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 OUTPUT B A
- 56. A NOT gate swaps 0’s to 1’s and 1’s to 0’s. If it is placed after AND or OR gates, its turns them into NAND (NOT AND) and NOR (NOT OR) gates. It is sometimes called an inverter.
- 57. NAND GATE NOR GATE
- 58. The basis of a latch is this pattern of linked NOR gates. They can also be made with NAND gates in a similar pattern. NOR gates work with negative pulses, NAND gates work with positive pulses. A brief high (1) signal at one input results in a permanent high (1) signal at the latch output. A brief high (1) signal at the other input causes a low (0) signal at the latch output. A low (0) signal at both inputs leaves the latch output signal unchanged.