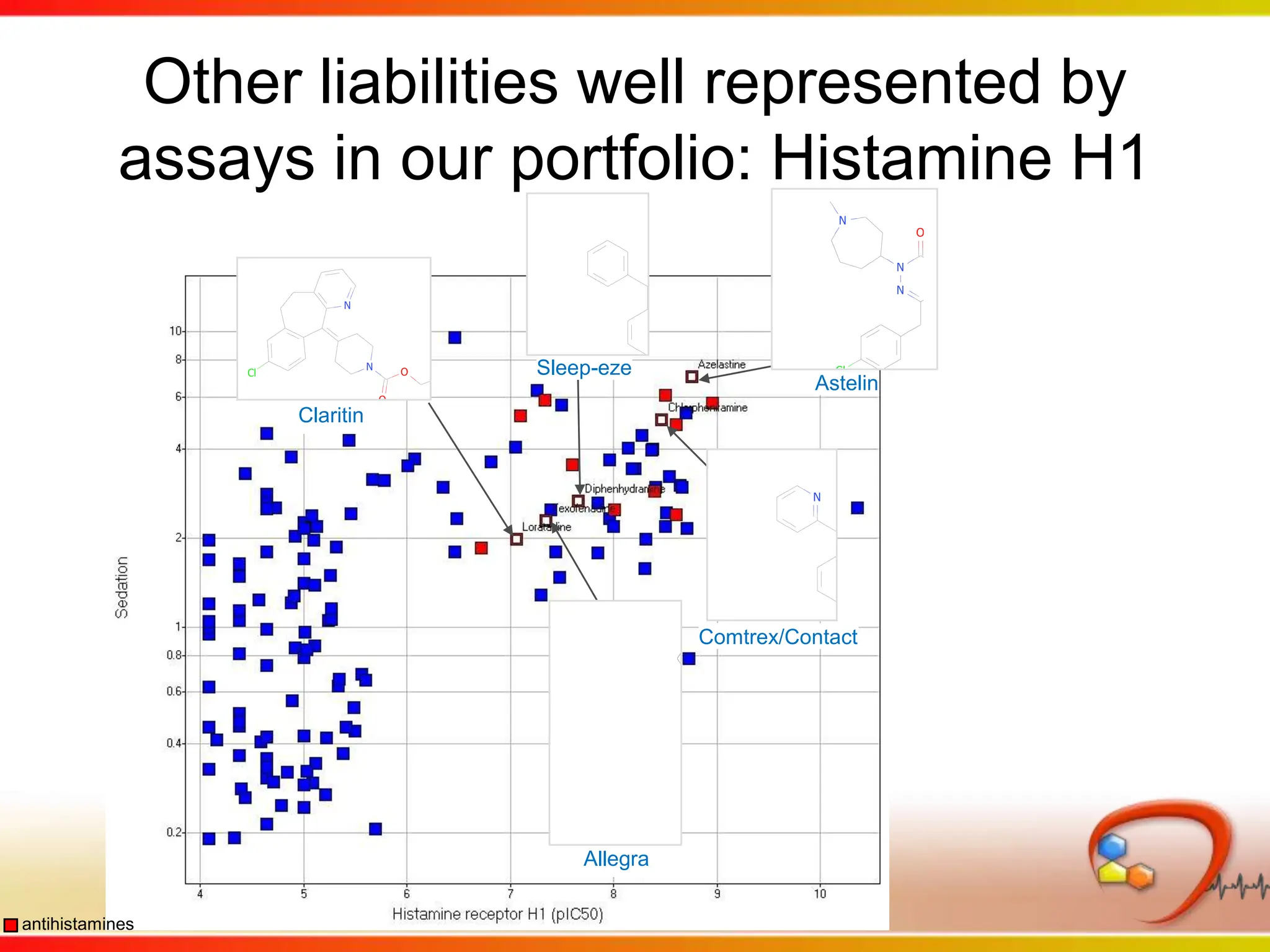
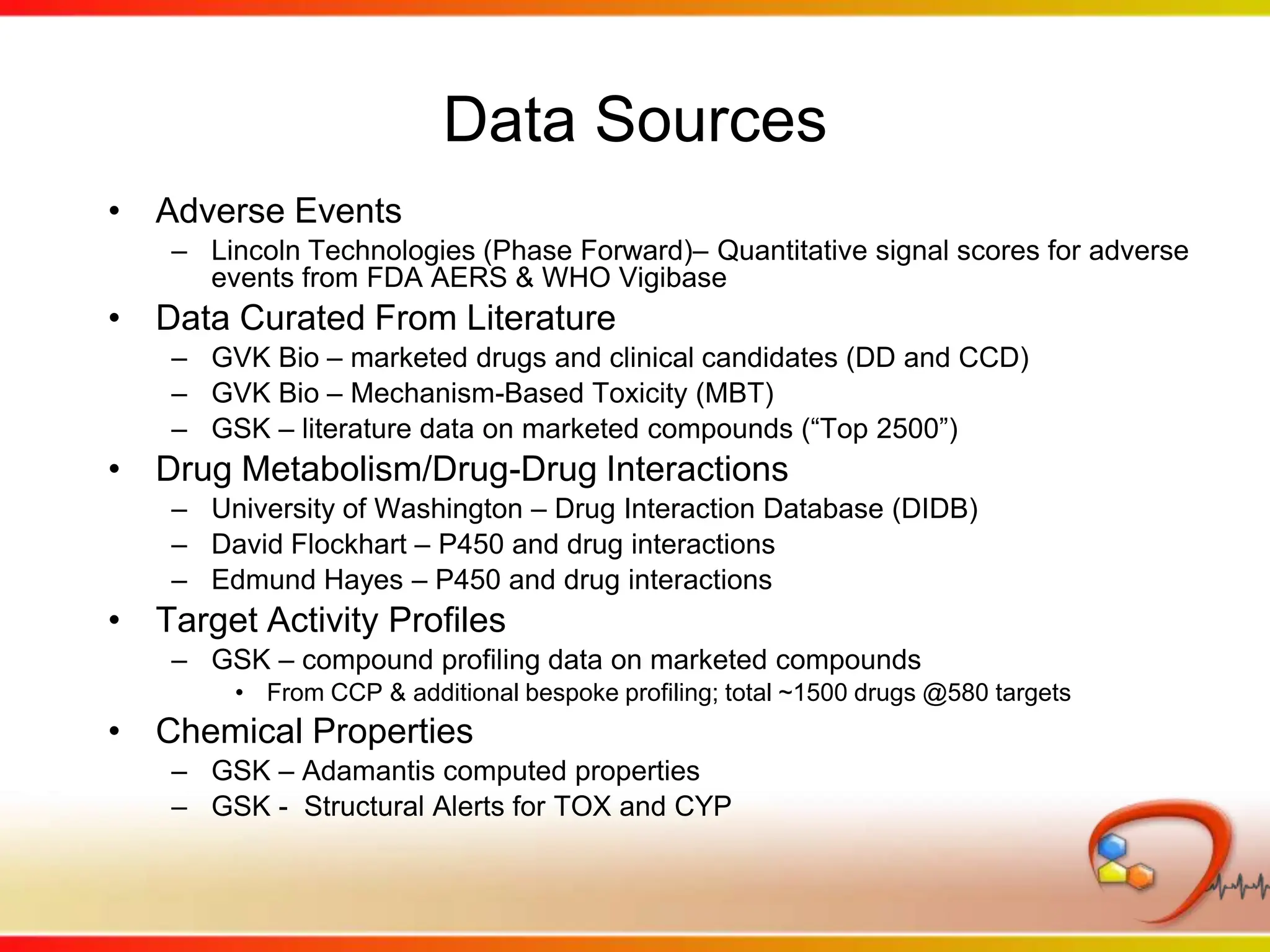
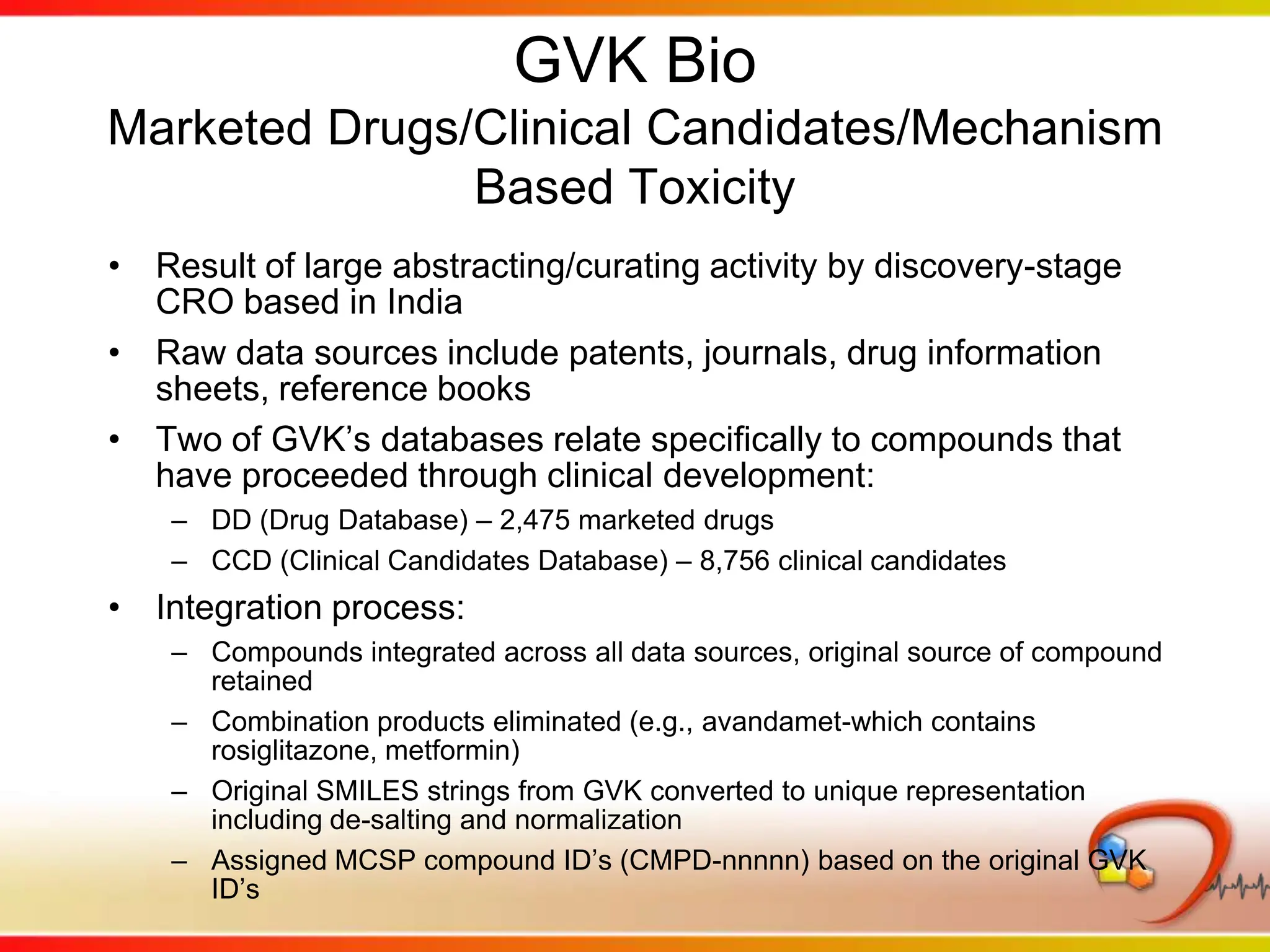
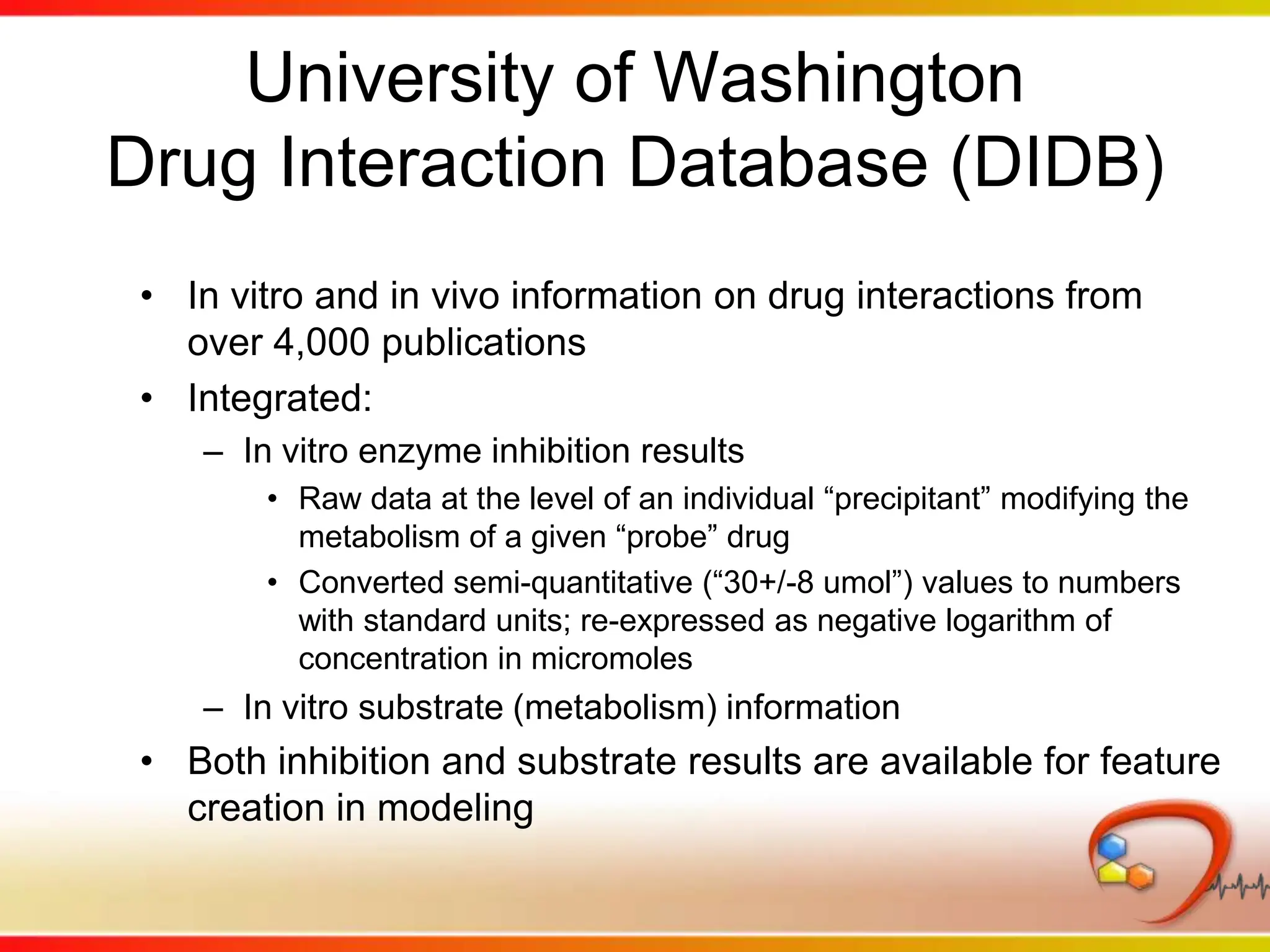
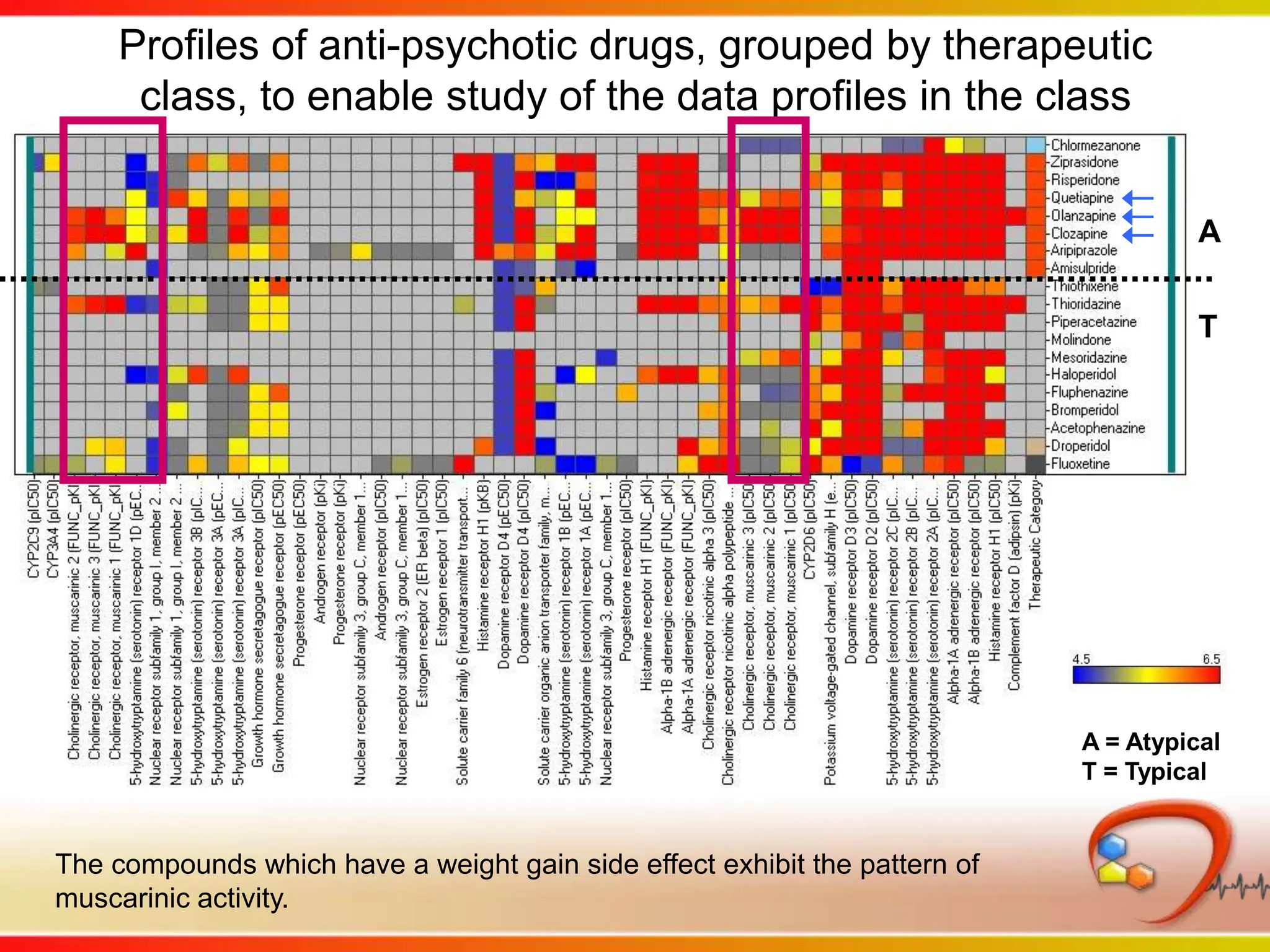
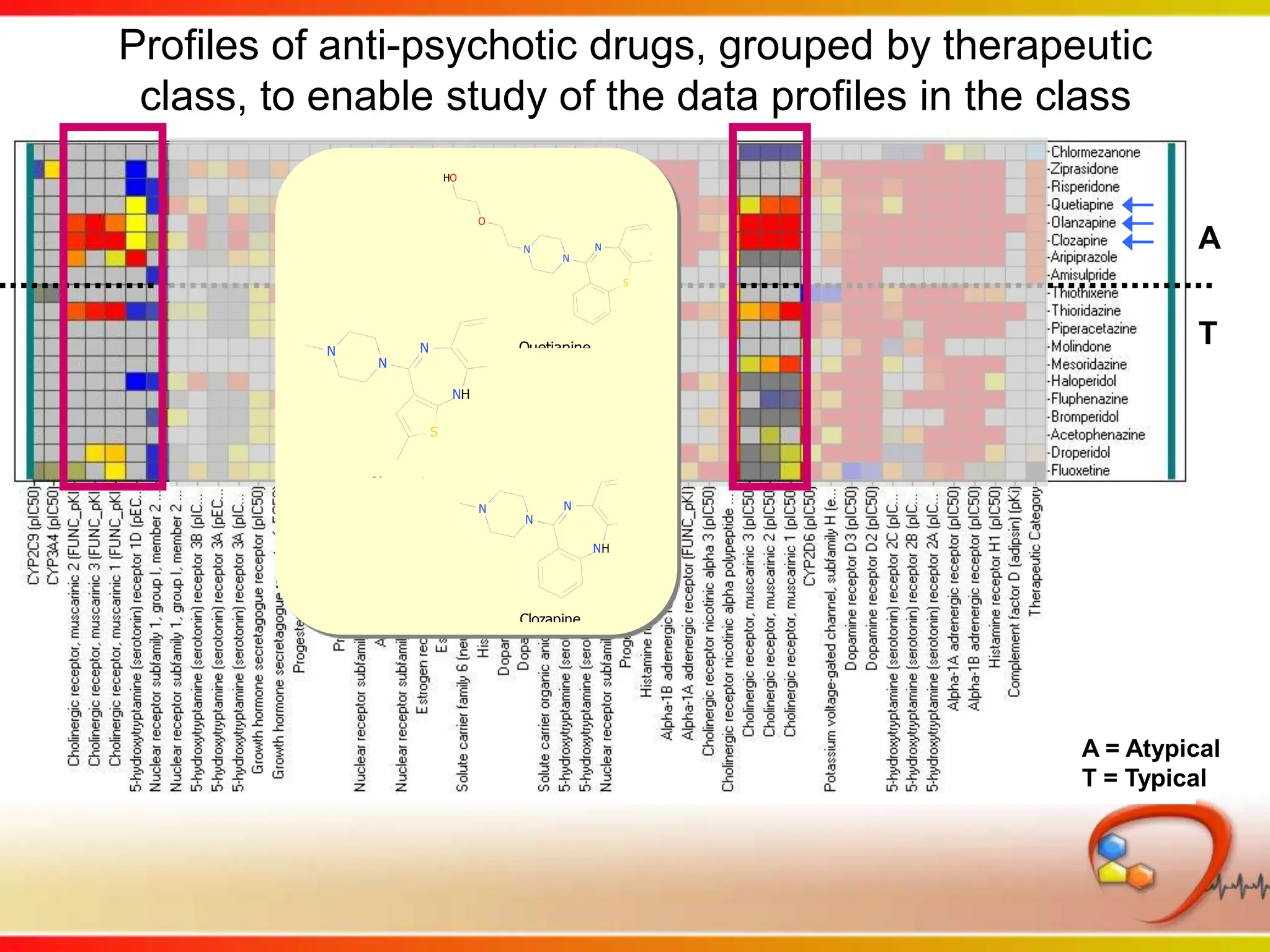
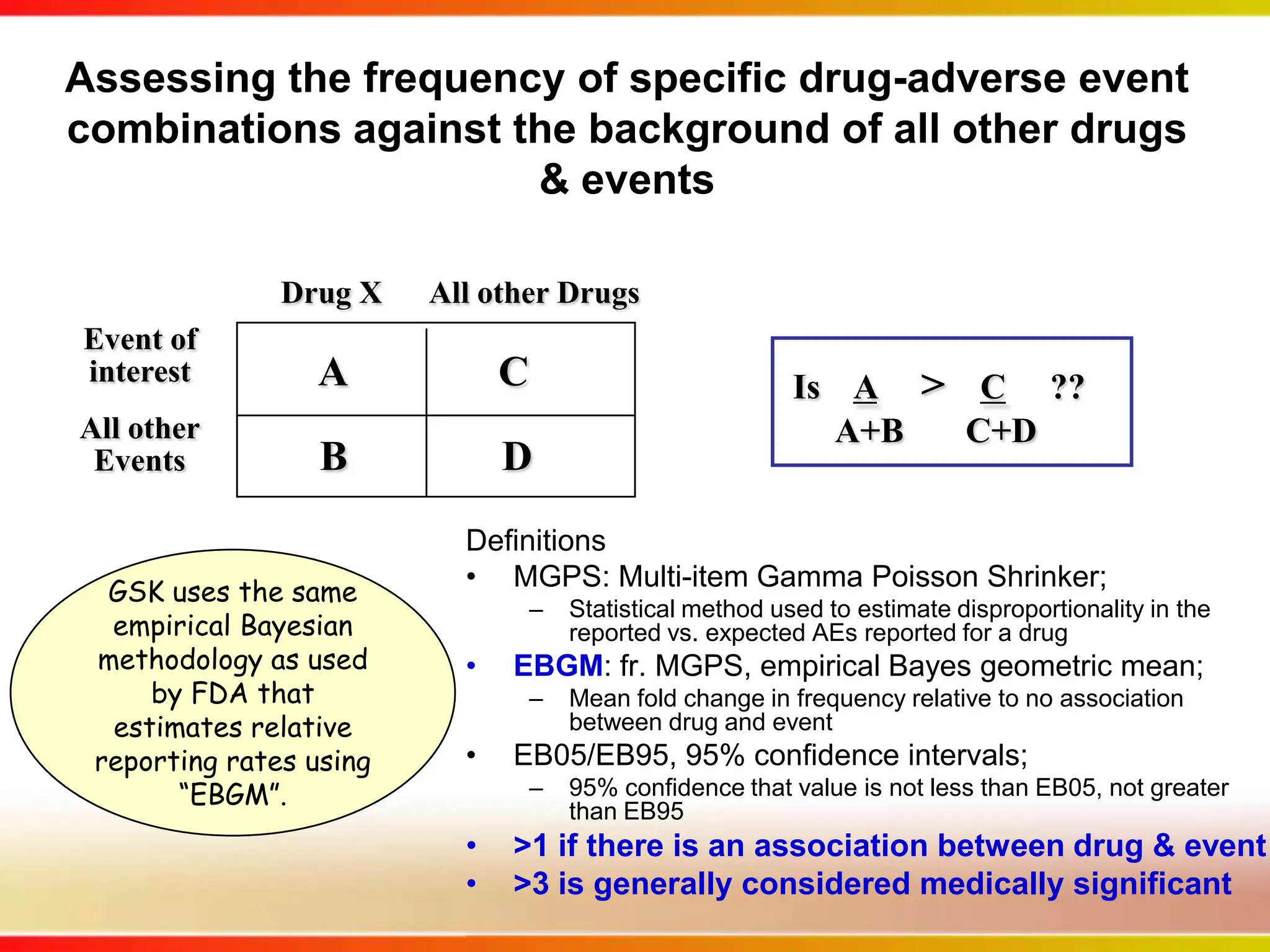
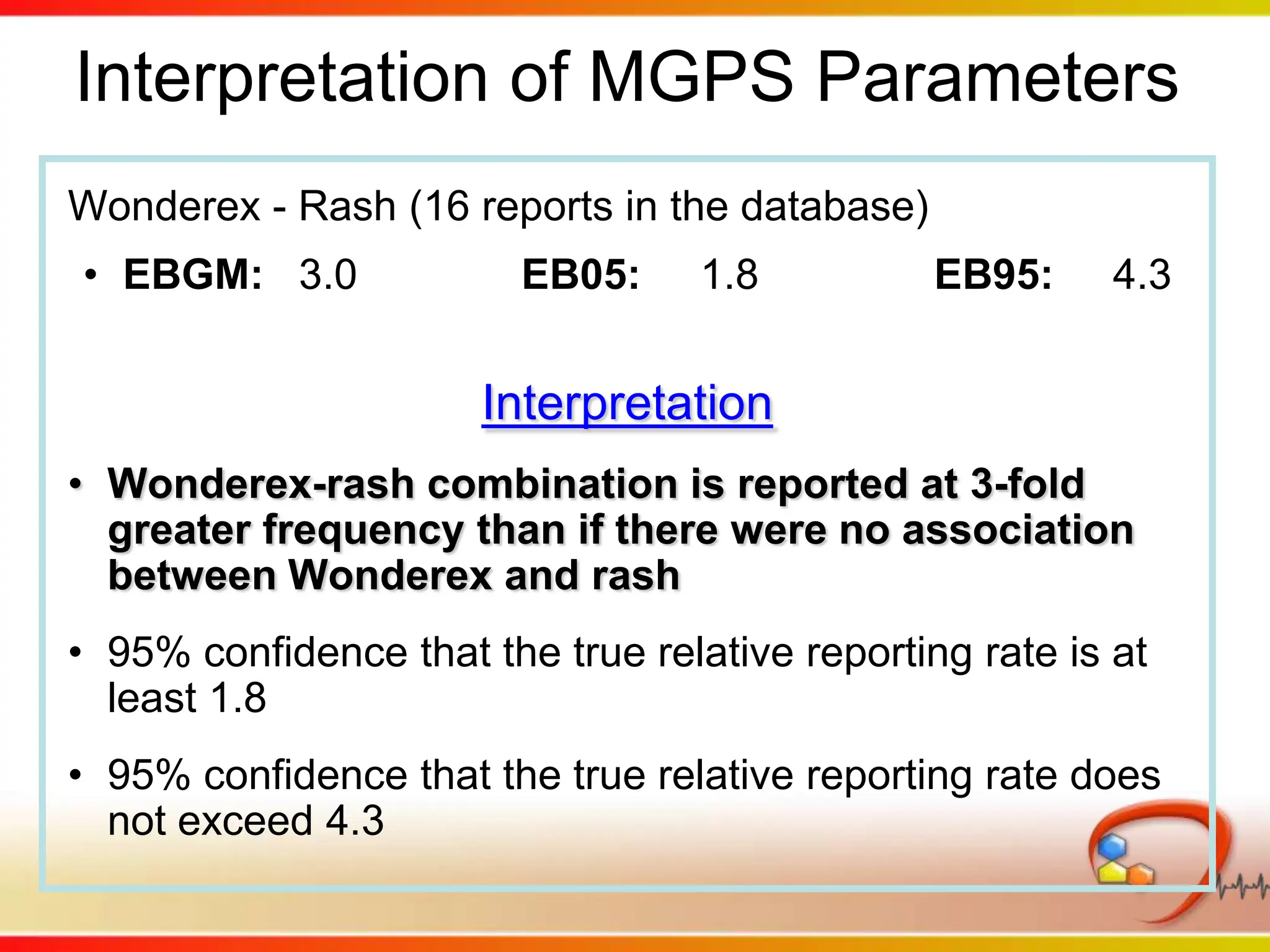
Dana Vanderwall, Associate Director of Cheminformatics at Bristol-Myers Squibb, presented at Drexel University for Jean-Claude Bradley's Chemical Information Retrieval class on December 2, 2010.
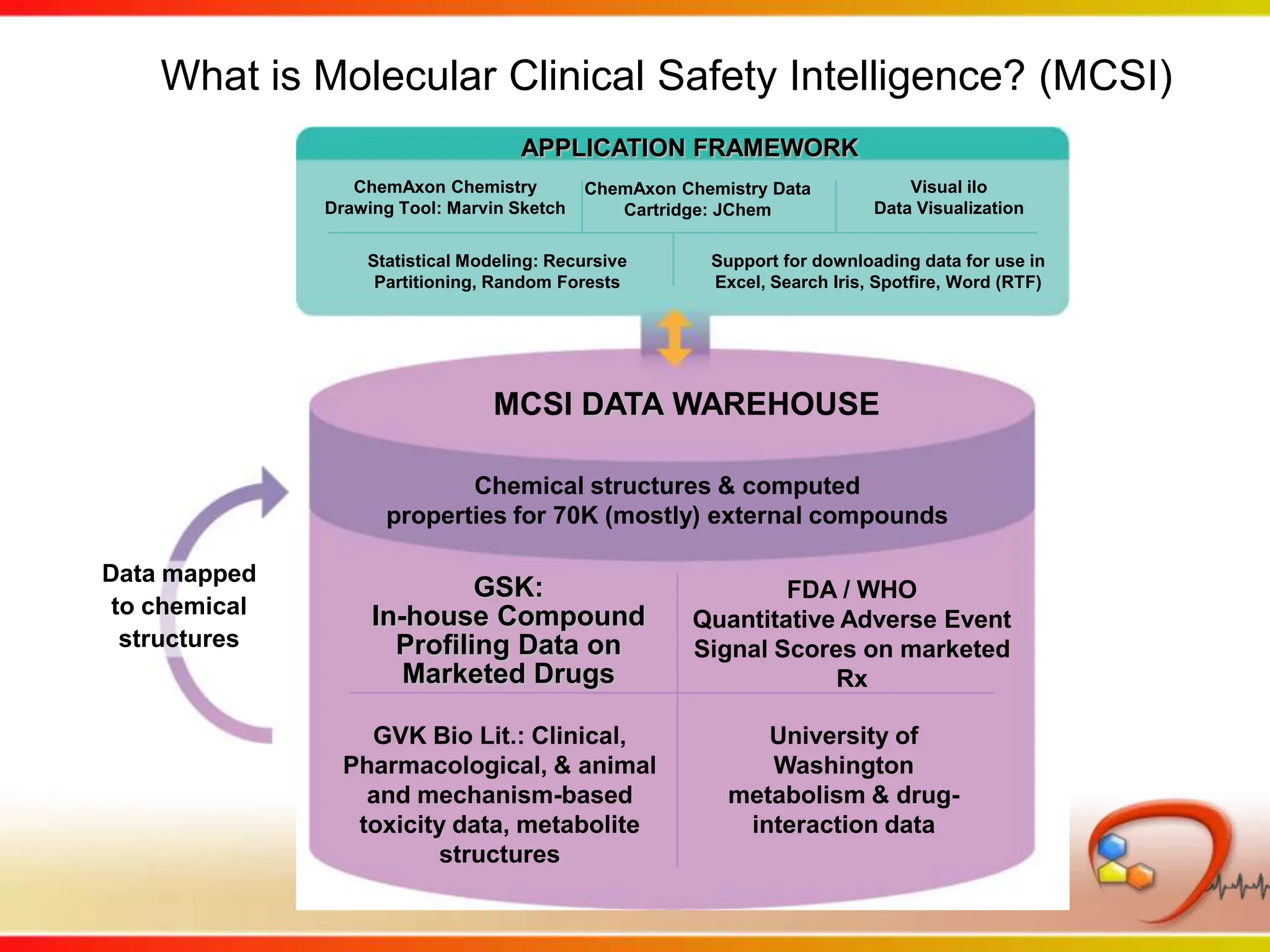
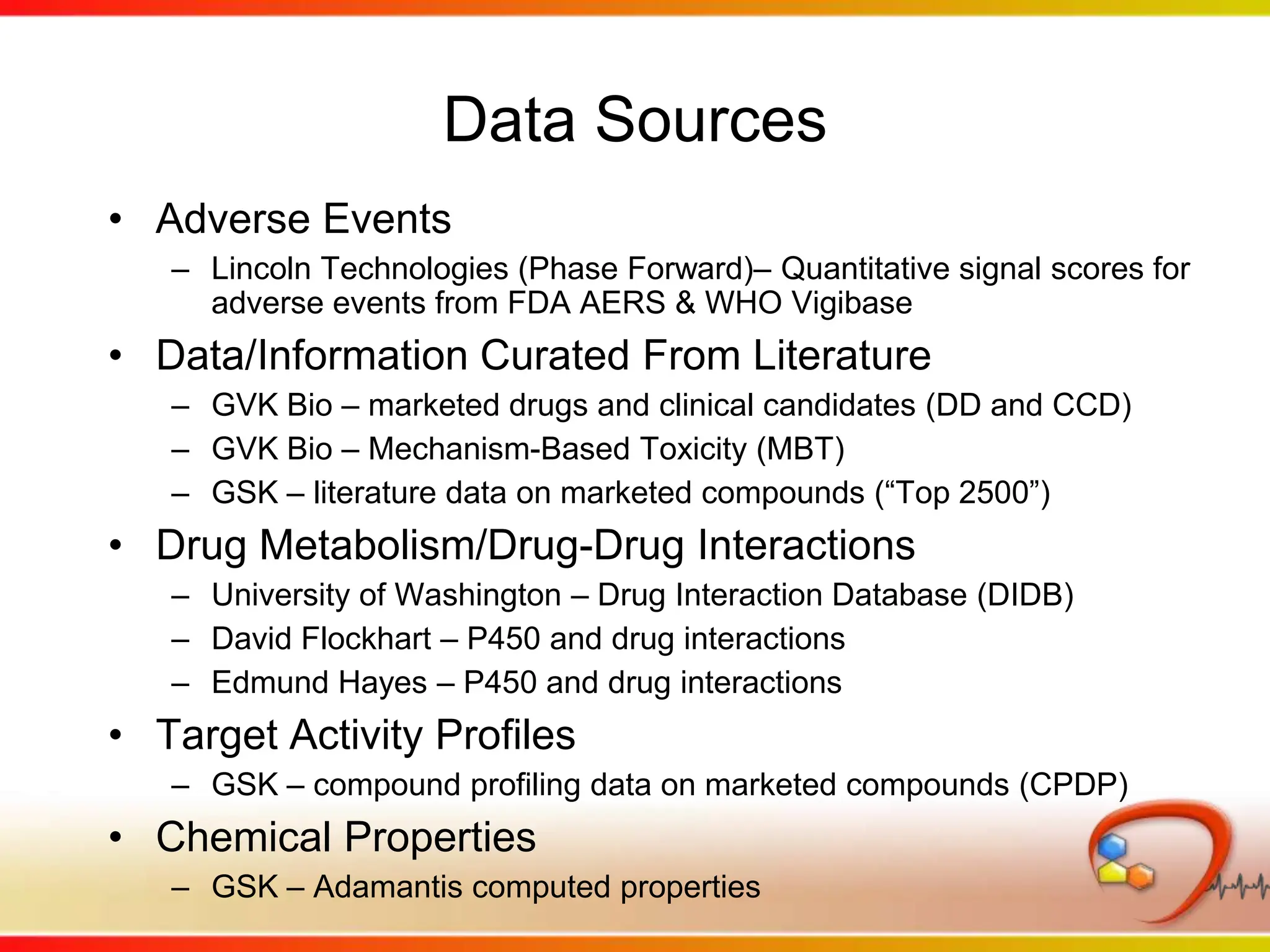
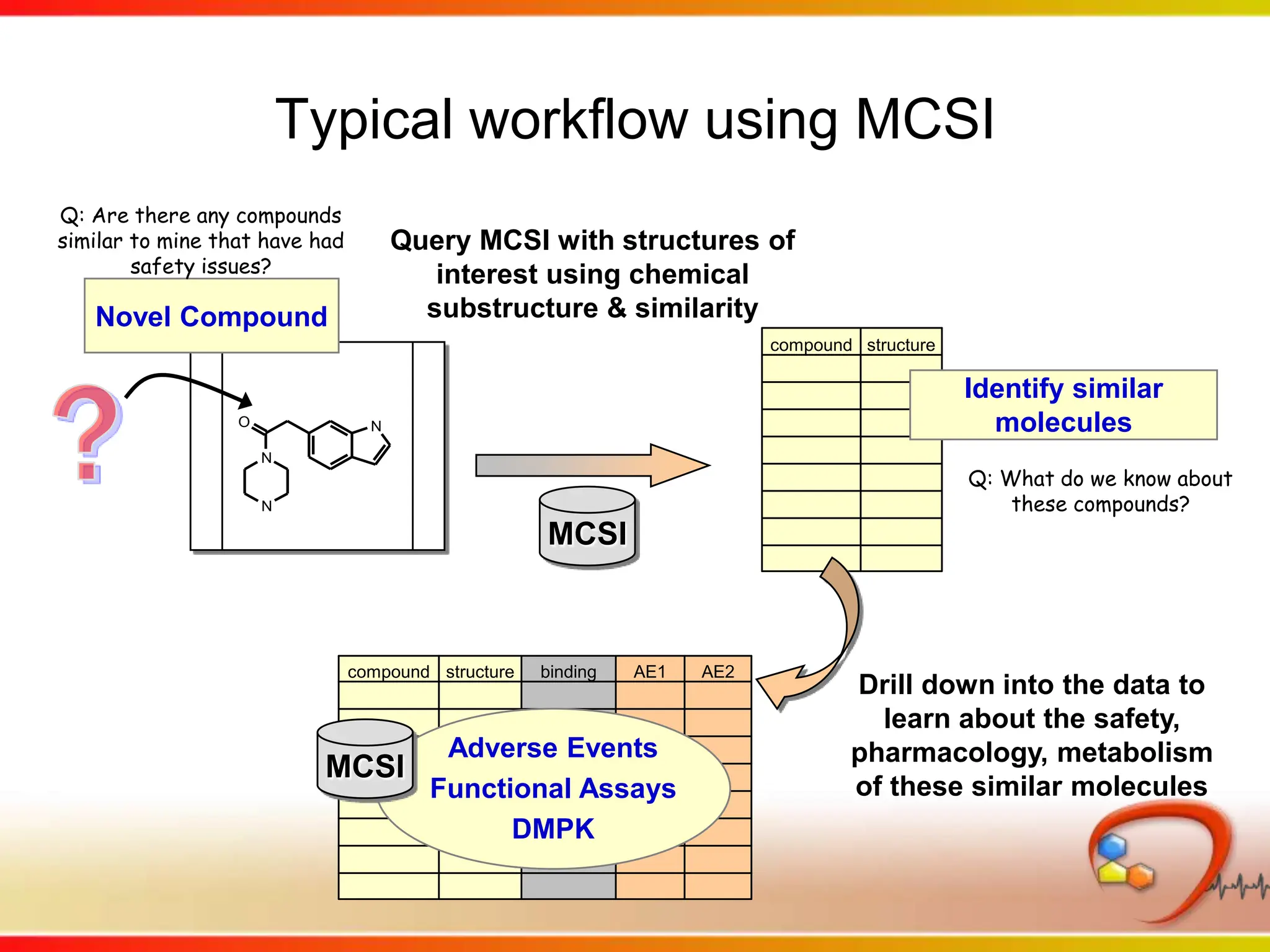
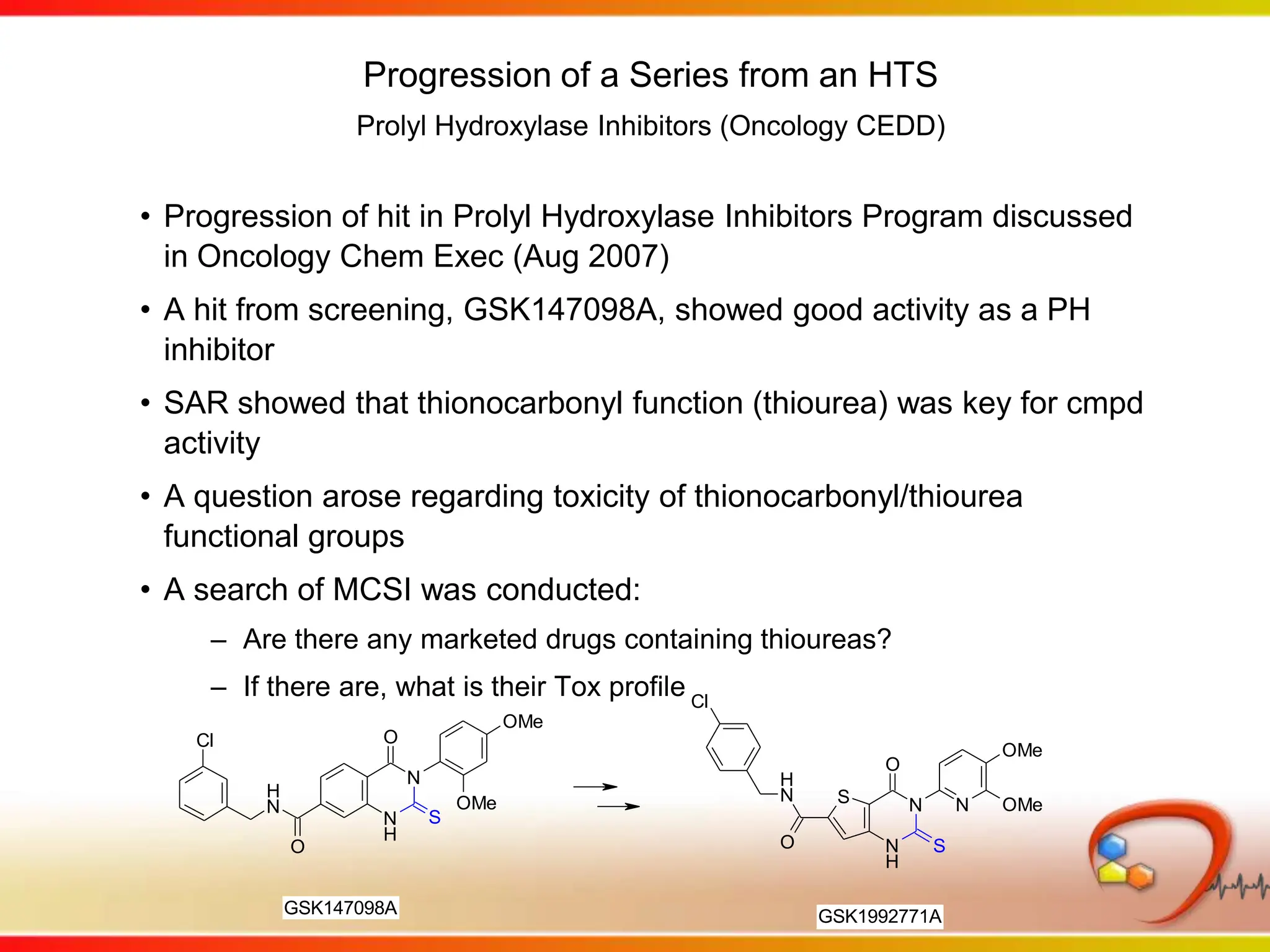
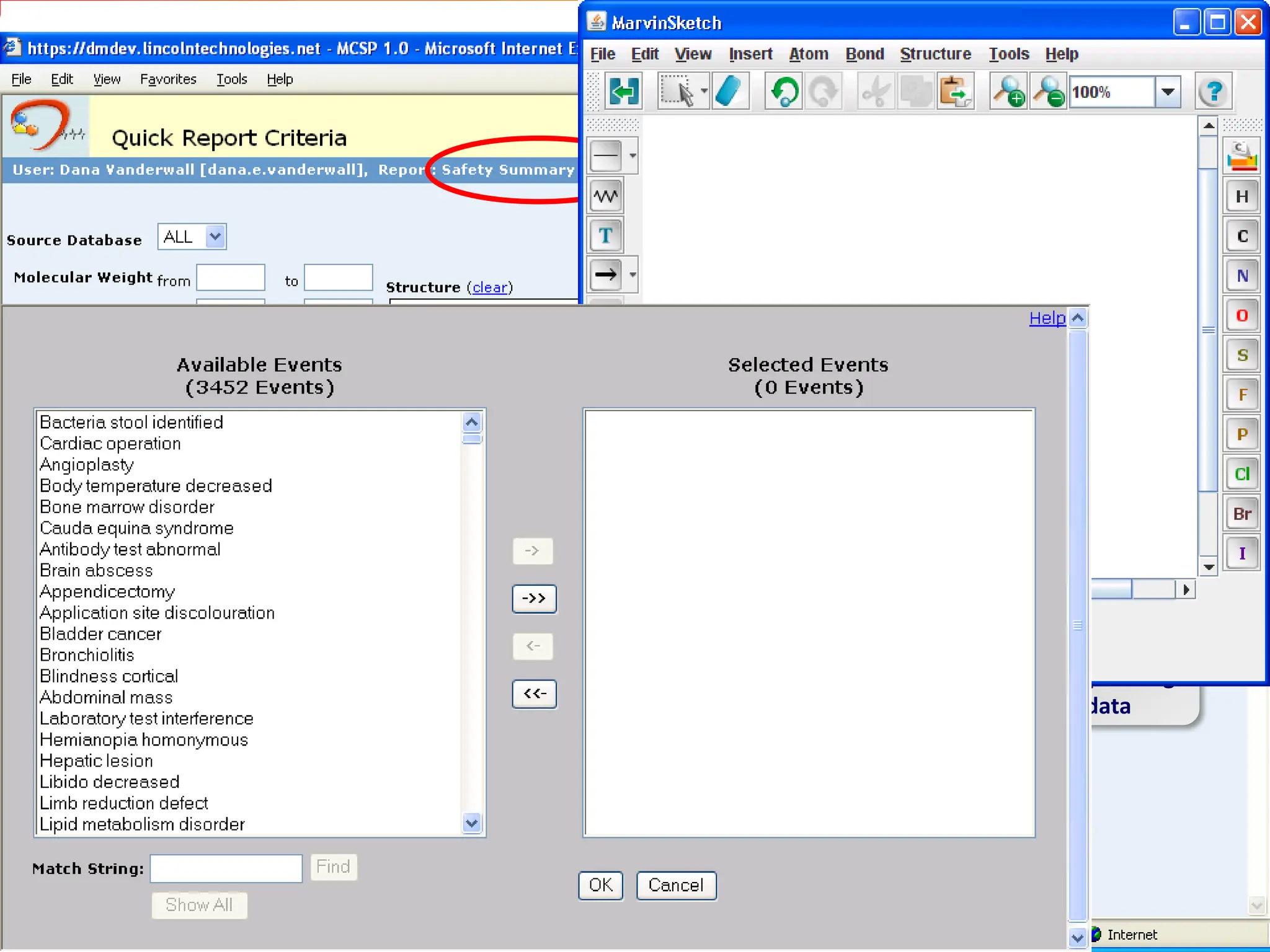
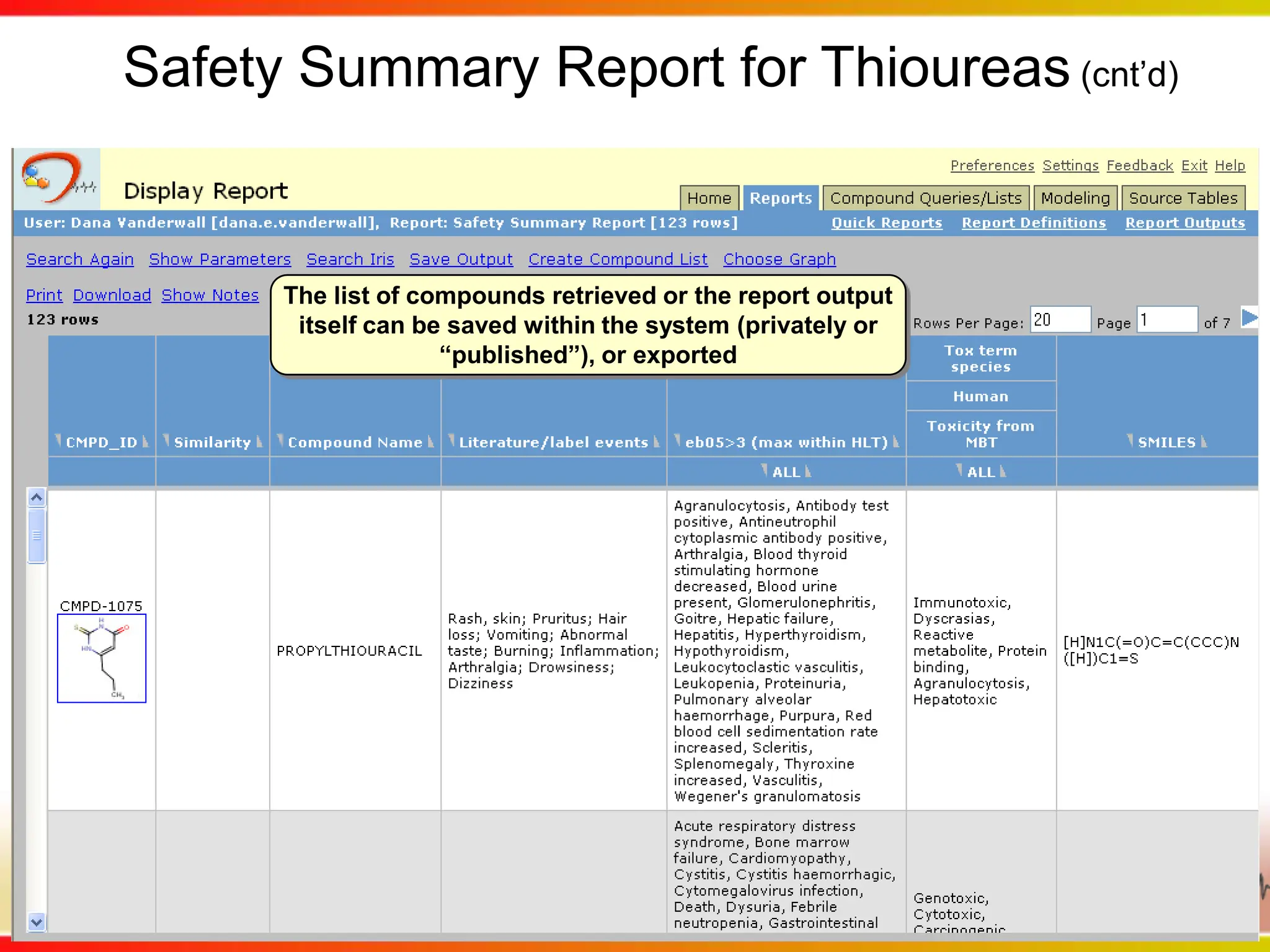
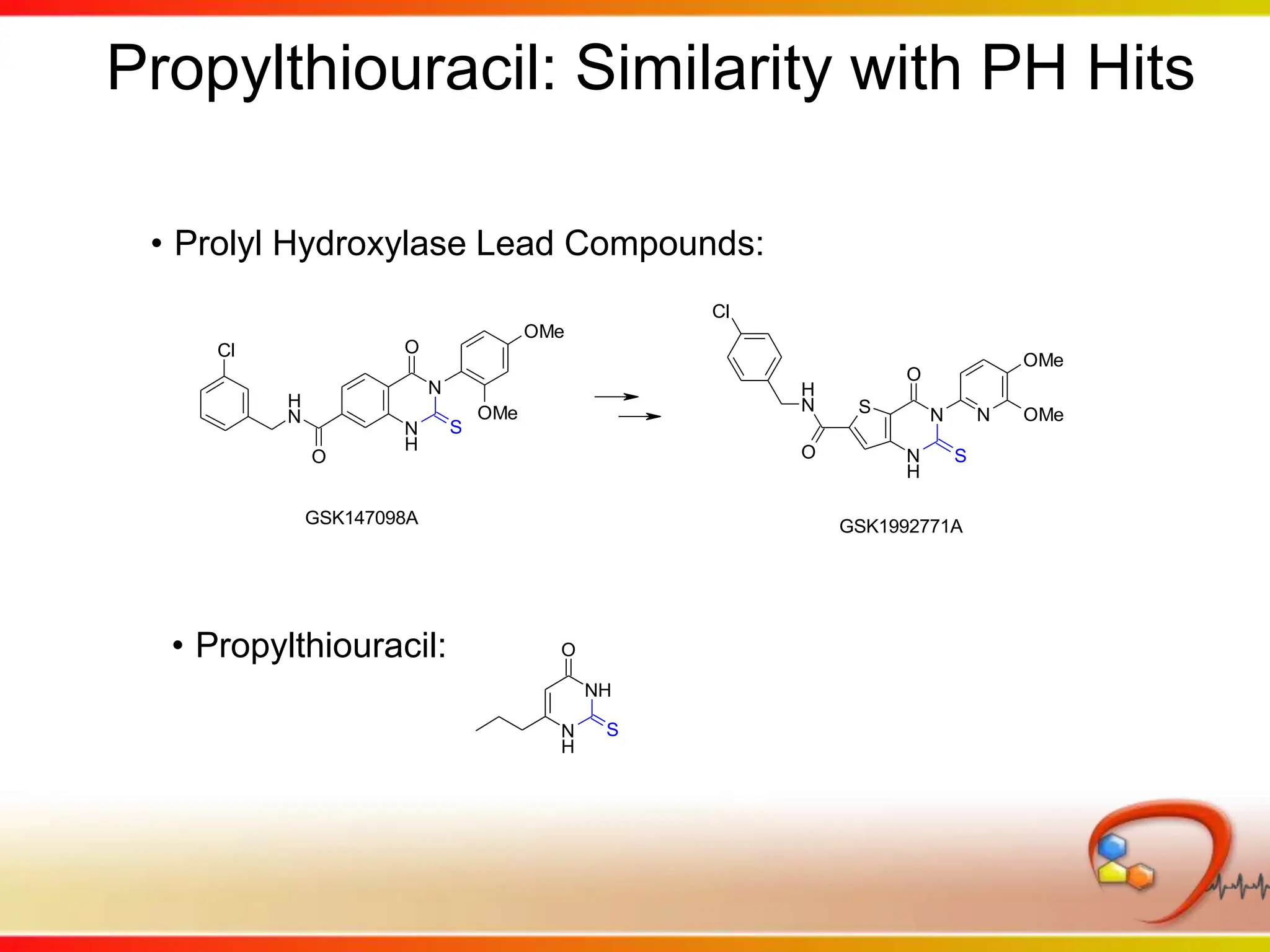
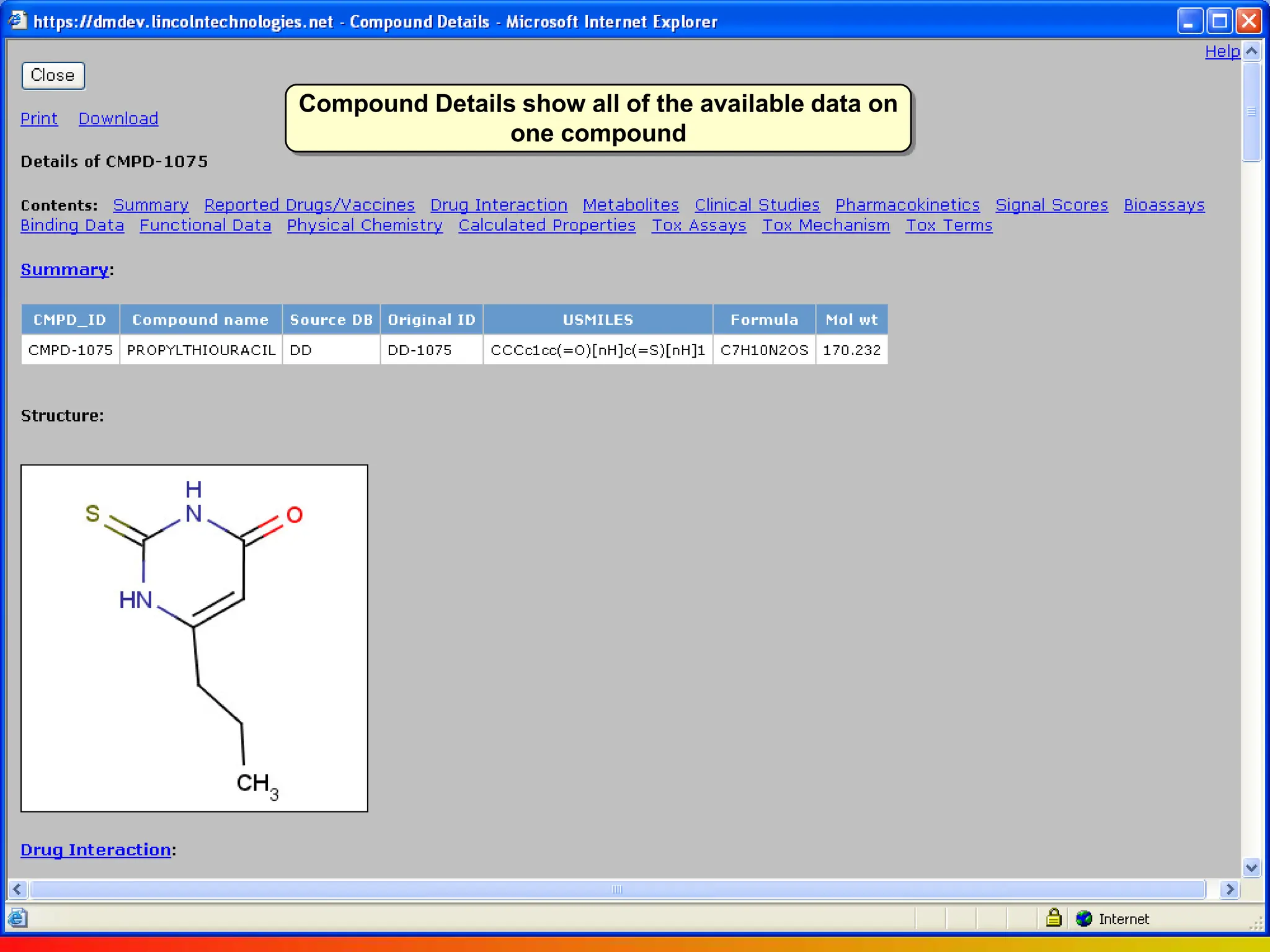
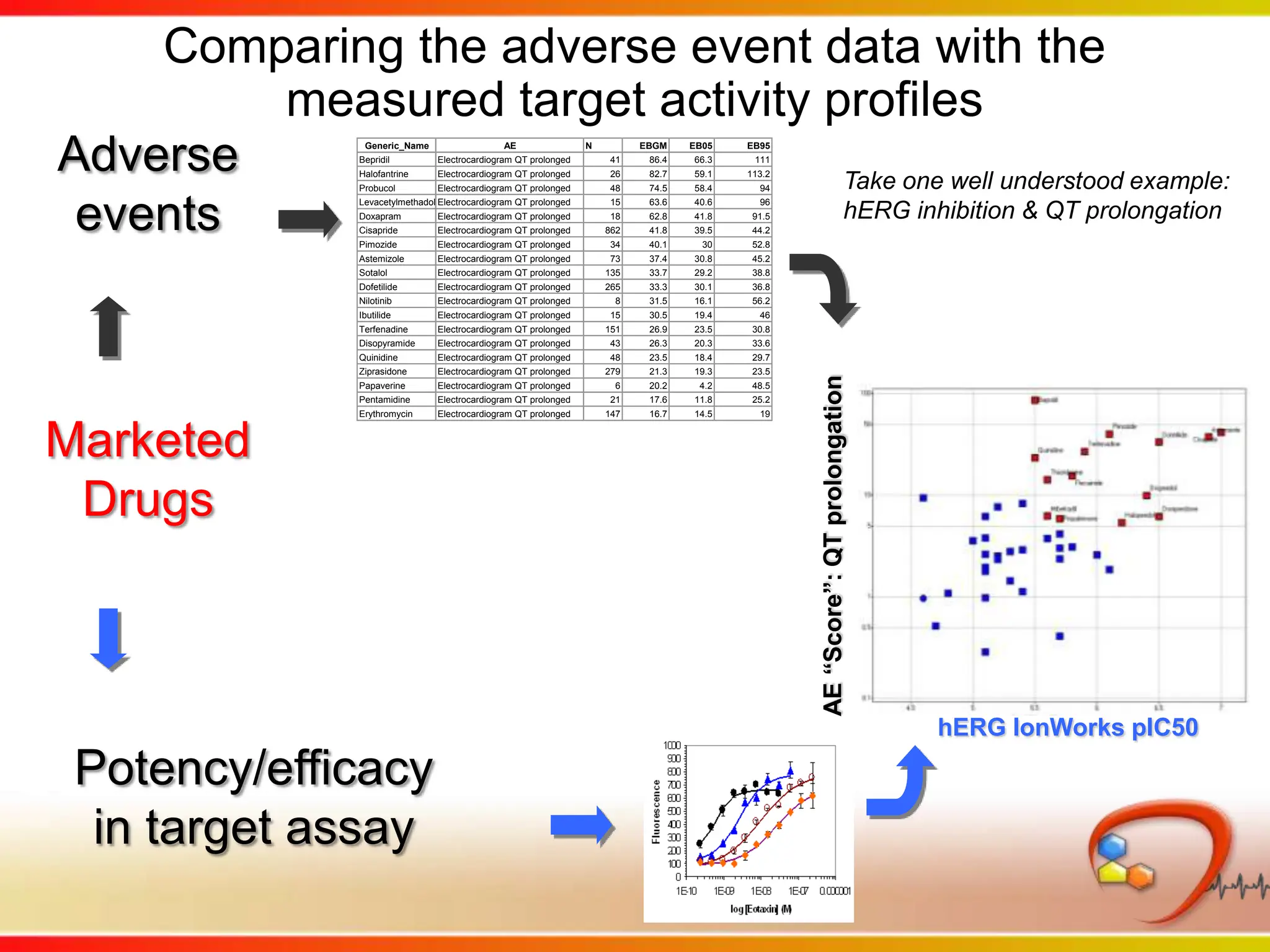
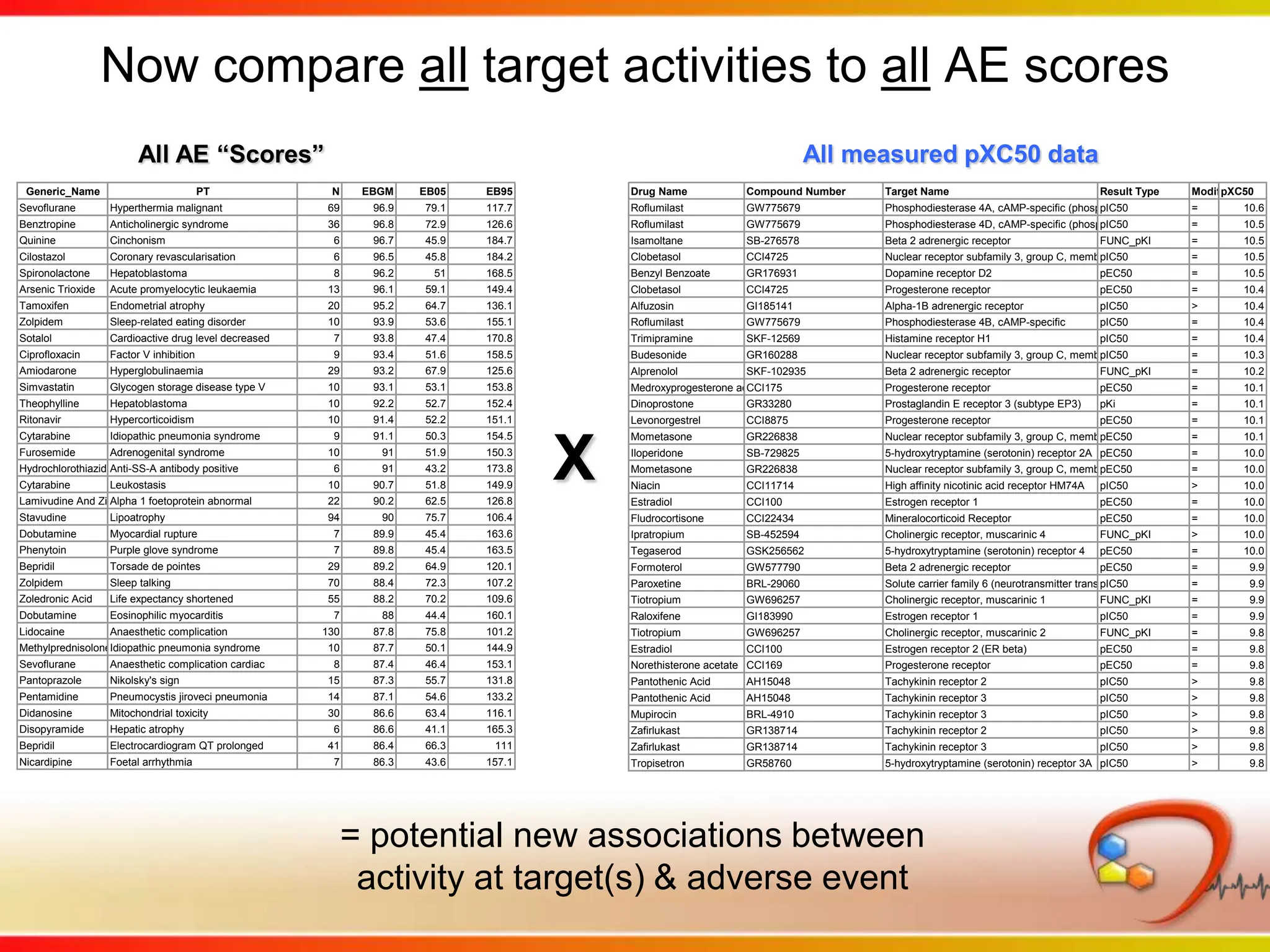
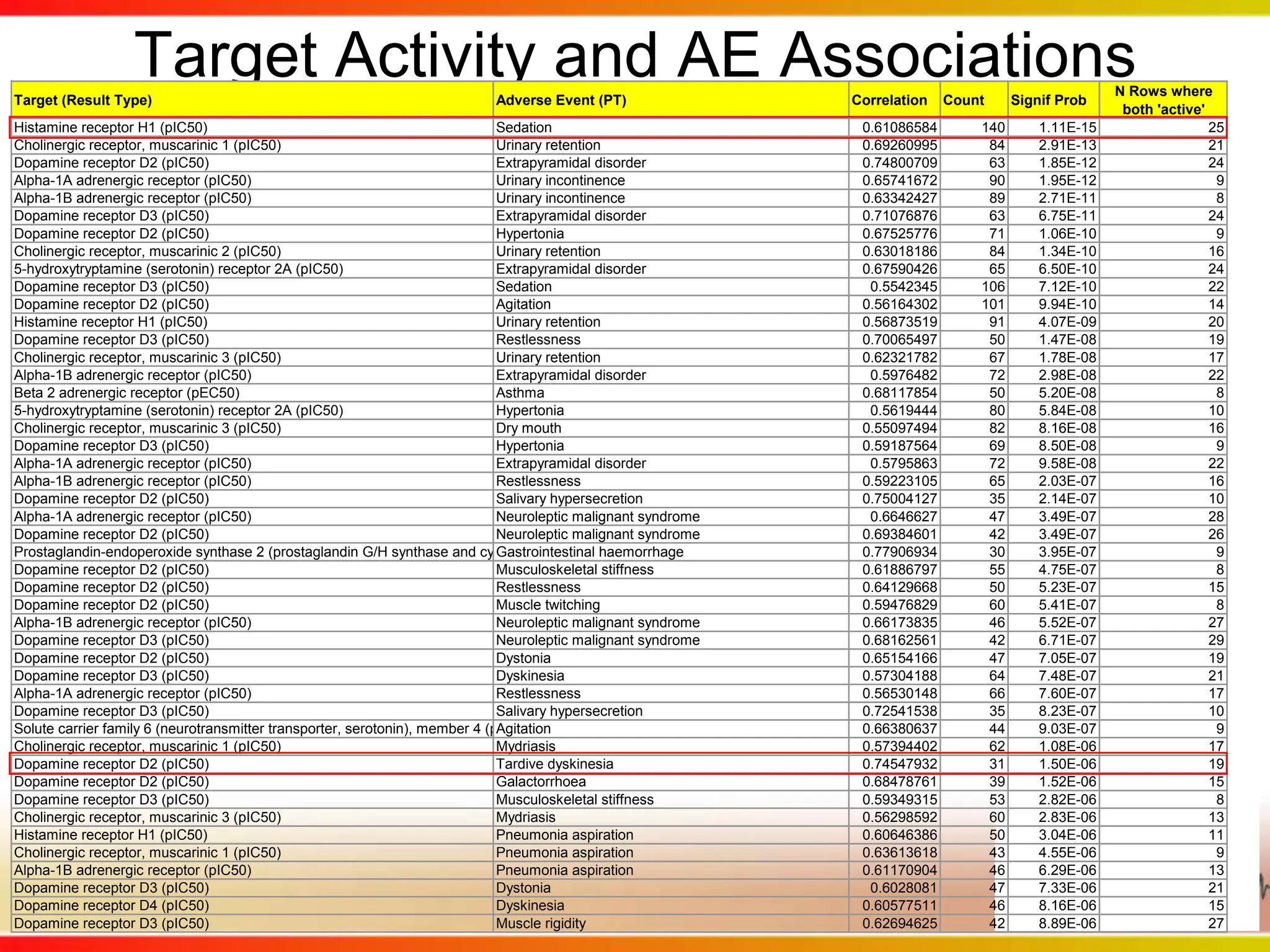
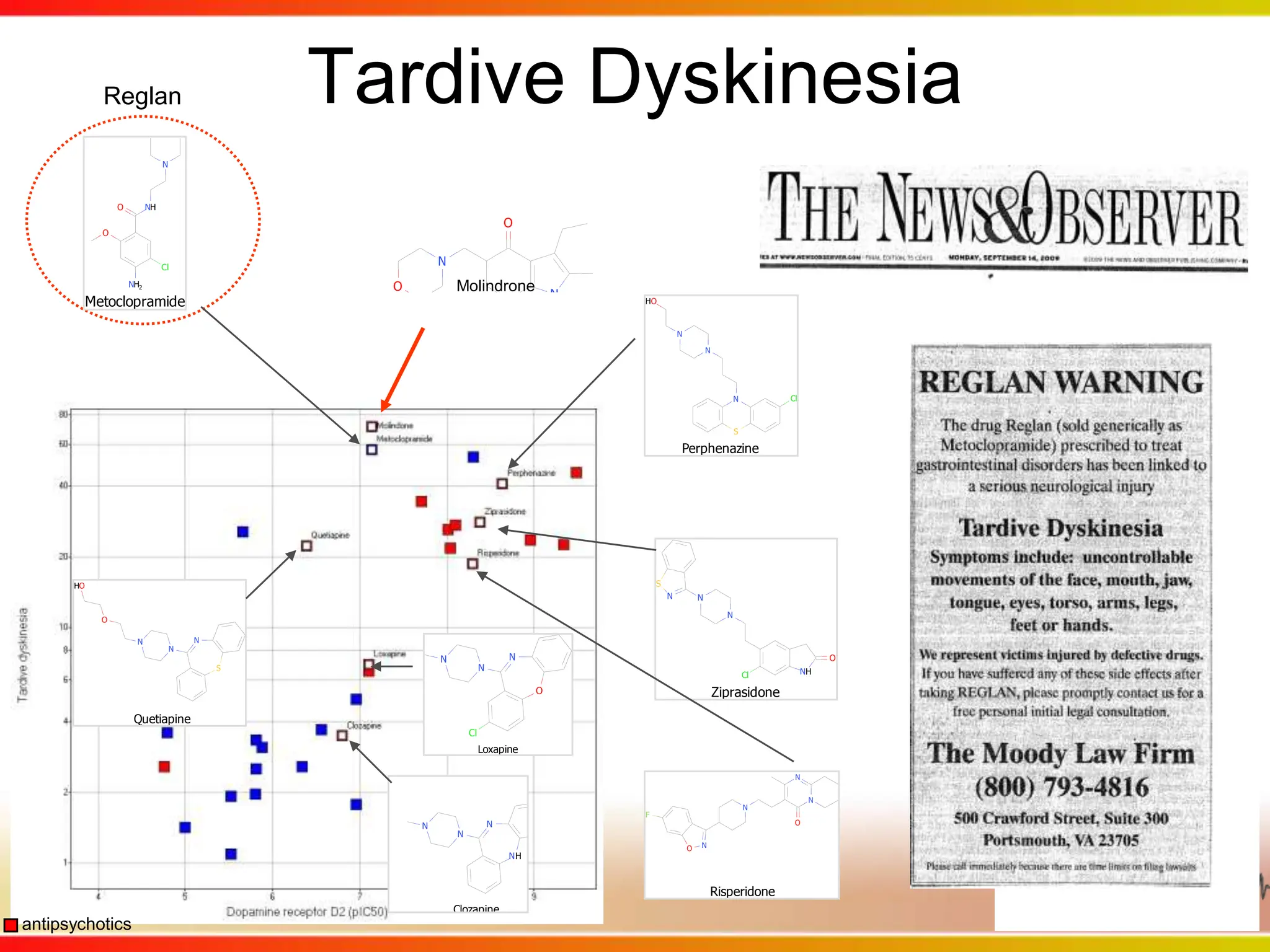
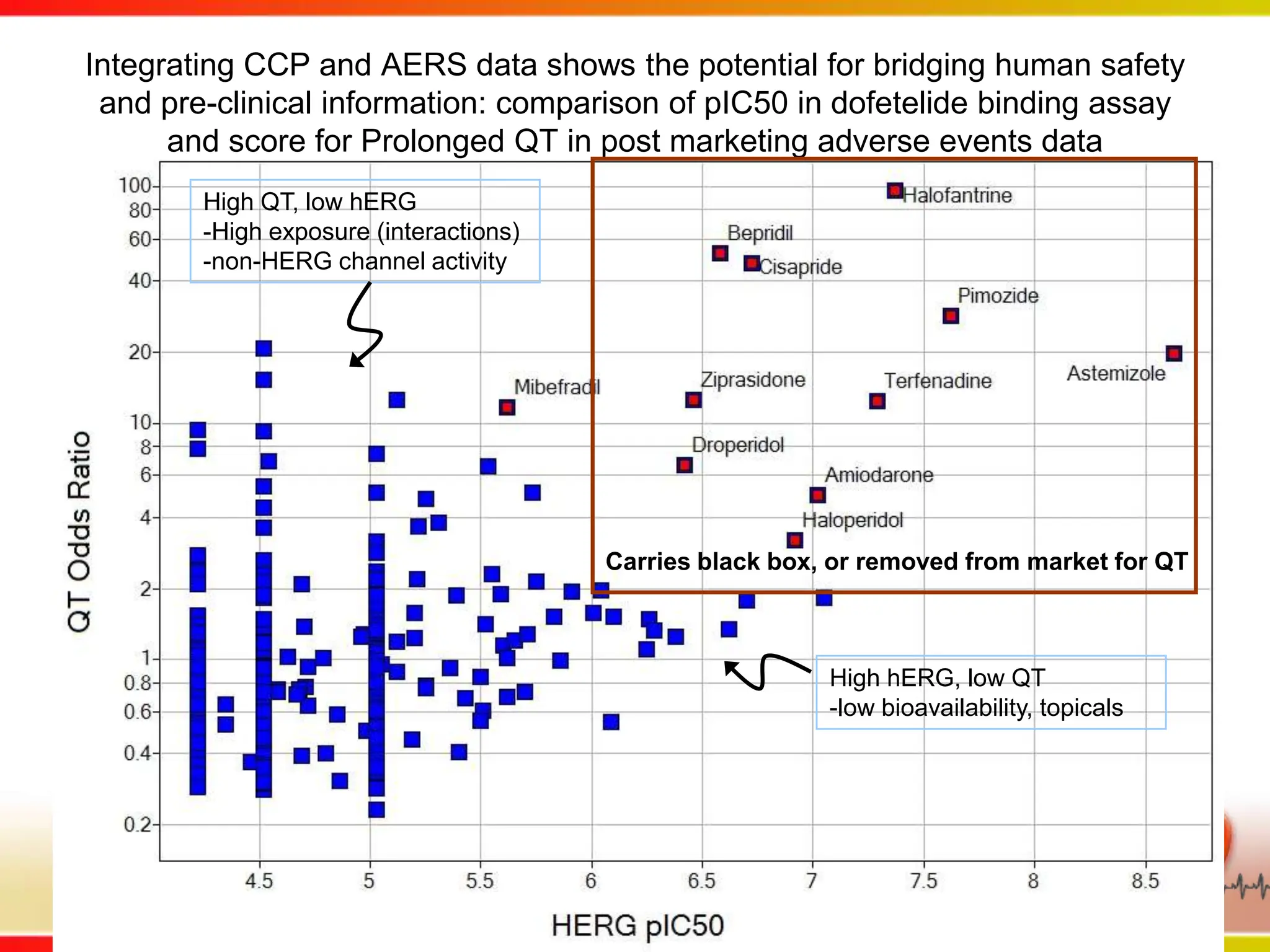
This second part describes a project based on "Molecular Clinical Safety Intelligence", where tracking side effects from approved drugs can help in the design of new drugs