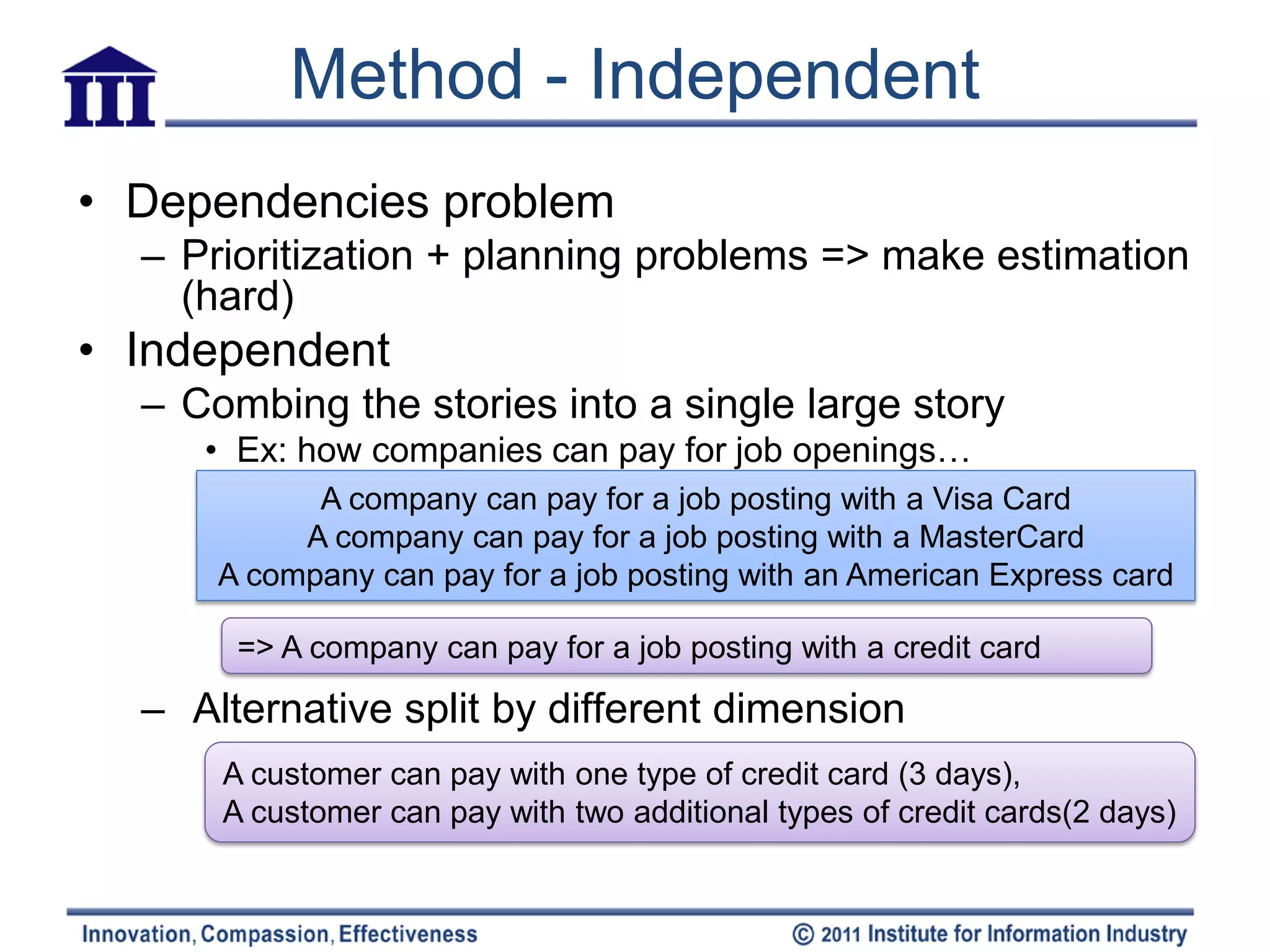
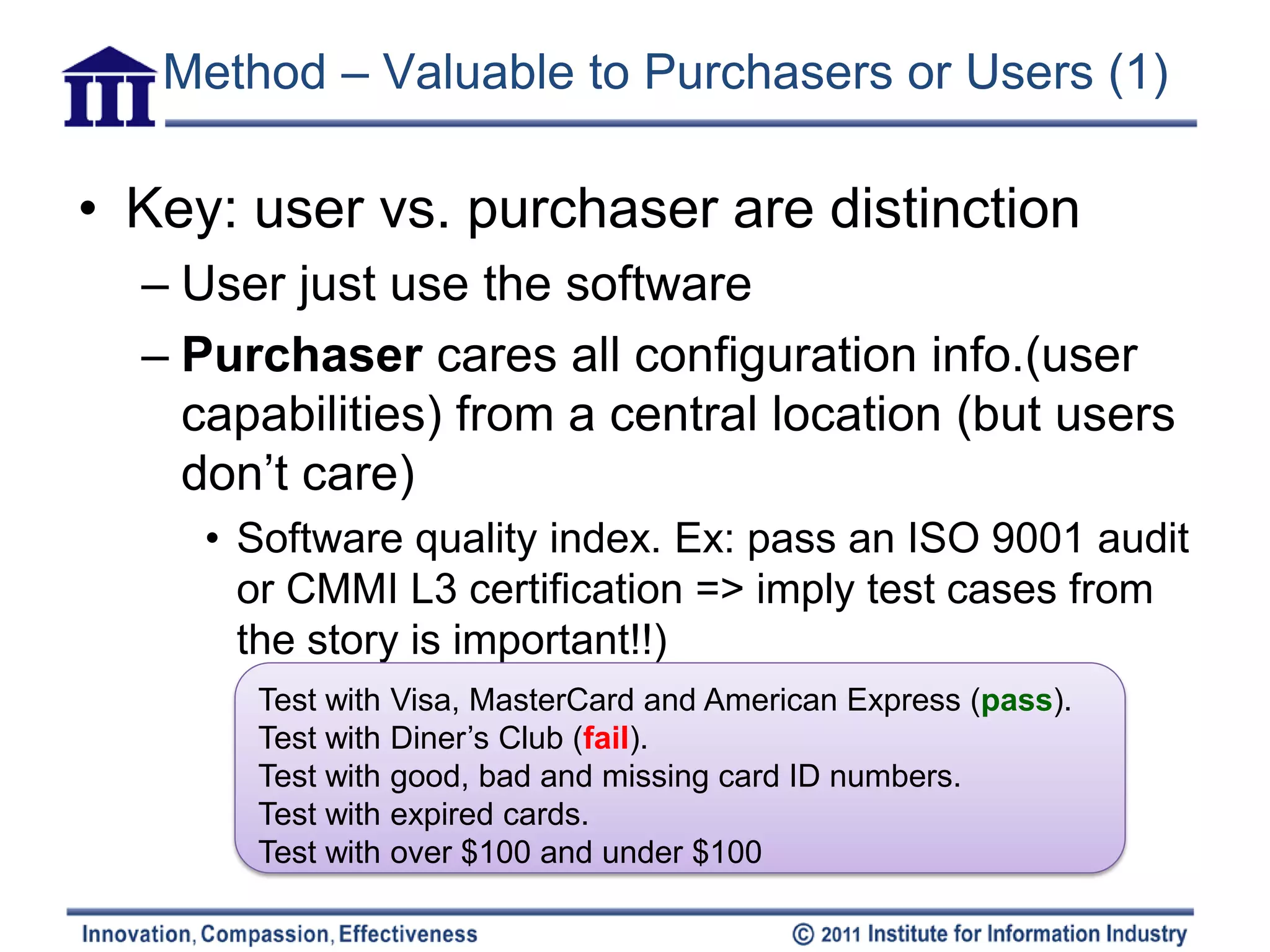
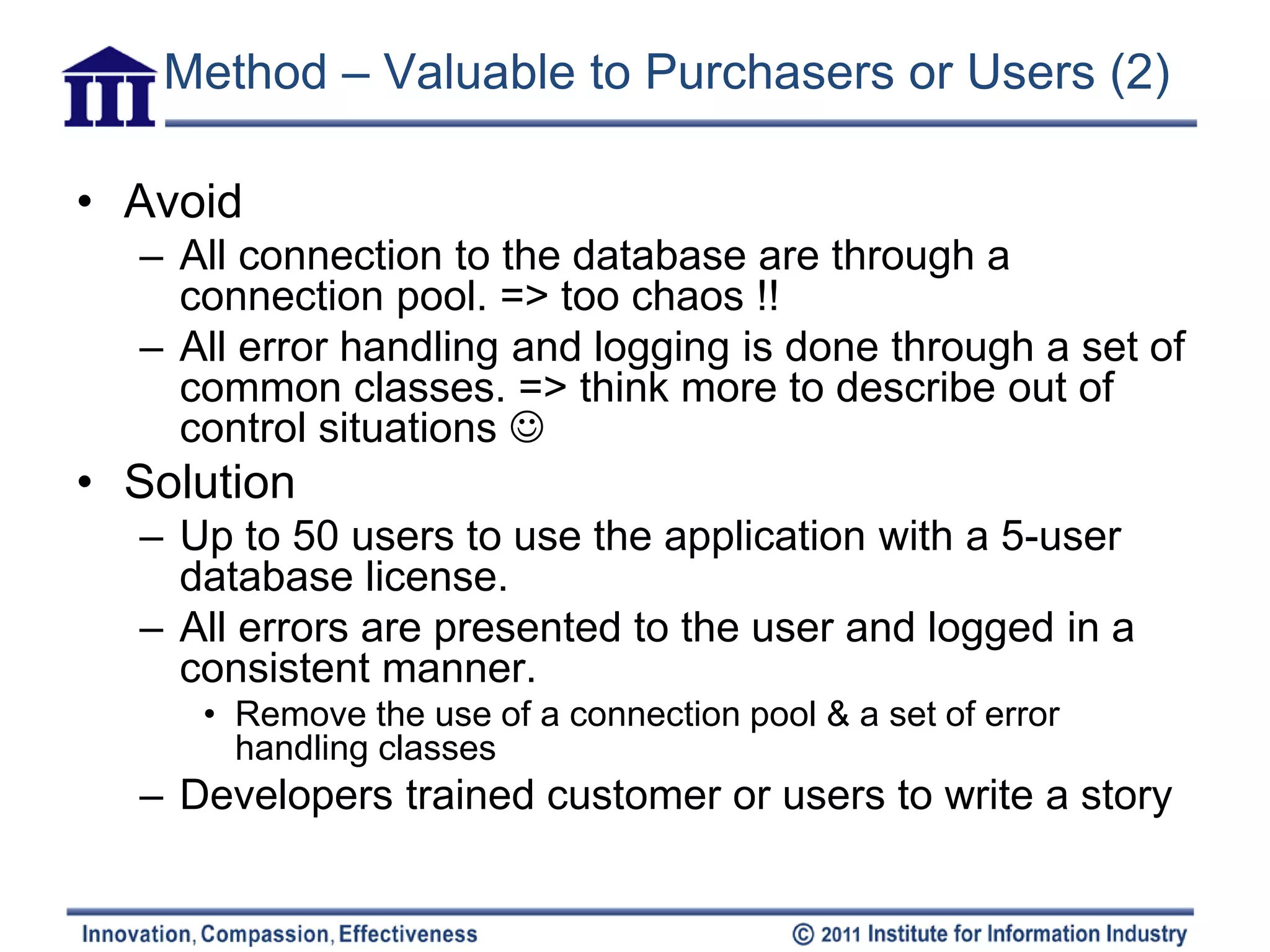
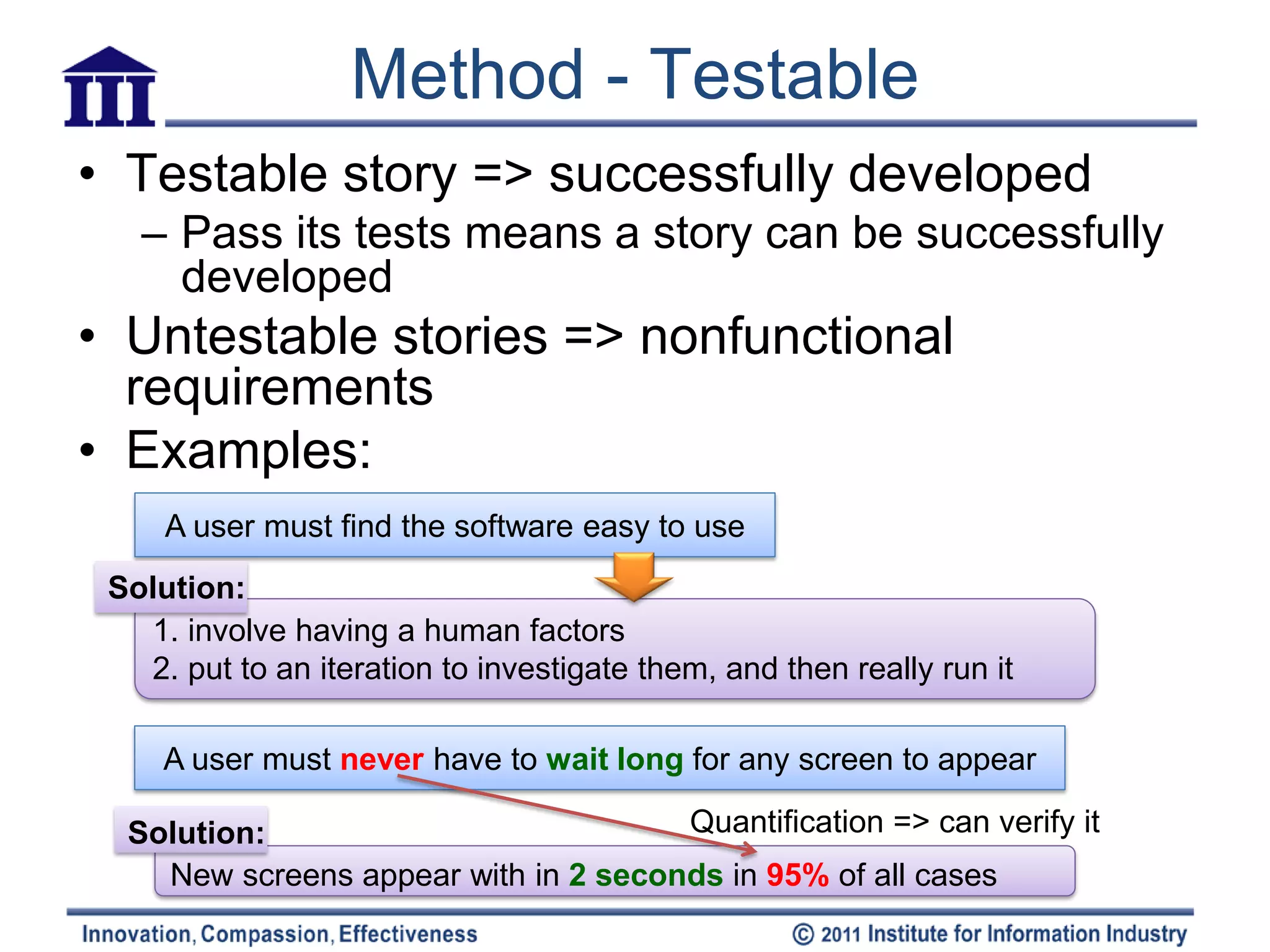
The document discusses six attributes for writing good user stories for agile software development: independent, negotiable, valuable, estimatable, small, and testable. It provides examples and methods for ensuring stories have these attributes, such as splitting large compound stories into smaller individual stories, adding notes for negotiation, and making stories focused on functionality that can be tested.