Plant Fertilization
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
6 likes•10,371 views
Plant fertilization
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Pollen pistil interaction, Self Compatibility, Pollen grain rejection, Double fertilization, Endospermic and non endospermic seedsPollen pistil interaction, Self Compatibility, Pollen grain rejection, Double...

Pollen pistil interaction, Self Compatibility, Pollen grain rejection, Double...HARINATHA REDDY ASWARTHA
Recommended
Pollen pistil interaction, Self Compatibility, Pollen grain rejection, Double fertilization, Endospermic and non endospermic seedsPollen pistil interaction, Self Compatibility, Pollen grain rejection, Double...

Pollen pistil interaction, Self Compatibility, Pollen grain rejection, Double...HARINATHA REDDY ASWARTHA
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Fertilzation and Gametogenesis in Flowering plants

Fertilzation and Gametogenesis in Flowering plants
Similar to Plant Fertilization
Similar to Plant Fertilization (20)
Recently uploaded
Mehran University Newsletter is a Quarterly Publication from Public Relations OfficeMehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024

Mehran University Newsletter Vol-X, Issue-I, 2024Mehran University of Engineering & Technology, Jamshoro
Recently uploaded (20)
Z Score,T Score, Percential Rank and Box Plot Graph

Z Score,T Score, Percential Rank and Box Plot Graph
Unit-IV; Professional Sales Representative (PSR).pptx

Unit-IV; Professional Sales Representative (PSR).pptx
Web & Social Media Analytics Previous Year Question Paper.pdf

Web & Social Media Analytics Previous Year Question Paper.pdf
Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi

Russian Escort Service in Delhi 11k Hotel Foreigner Russian Call Girls in Delhi
Beyond the EU: DORA and NIS 2 Directive's Global Impact

Beyond the EU: DORA and NIS 2 Directive's Global Impact
Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes

Mixin Classes in Odoo 17 How to Extend Models Using Mixin Classes
This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.

This PowerPoint helps students to consider the concept of infinity.
Ecological Succession. ( ECOSYSTEM, B. Pharmacy, 1st Year, Sem-II, Environmen...

Ecological Succession. ( ECOSYSTEM, B. Pharmacy, 1st Year, Sem-II, Environmen...
Plant Fertilization
- 2. Pollination Pollination is the process by which pollen (containing male sex cells) is placed on the female stigma. Birds, water and animals other than insects are all vectors of pollination. Two types: Self-pollination Cross-pollination
- 4. Starter – Put the following statements in the correct order to describe fertilization. A. Within the pollen tube is the nucleus that will produce the sperm. B. Pollen germinates to produce pollen tube C. The sperm moves from the tube to combine with the egg of the ovule to form a zygote. D. Pollen tube grows down the style of the carpel. E. The pollen tube completes its growth by entering an opening at the bottom of the ovary.
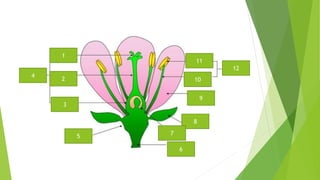
- 5. Fertilization Once pollination has occurred, next step is fertilization. Male and female sex cells unite to form a diploid zygote. Female sex cells are present within the ovules of the flower. Ovules are present within the ovary of the carpel. 1. Pollen germinates to produce pollen tube 2. Pollen tube grows down the style of the carpel. 3. Within the pollen tube is the nucleus that will produce the sperm. 4. The pollen tube completes its growth by entering an opening at the bottom of the ovary. 5. The sperm moves from the tube to combine with the egg of the ovule to form a zygote. Once the zygote is formed, it develops the surrounding tissue into the seed. As the seed is developing, the ovary around the ovule matures into a fruit. The fruit encloses and helps to protect the seed.
- 6. The seed – For example pea seed (pisum sativum)
- 7. Conditions needed for Germination Germination is the process by which a seed emerges from a period of dormancy and starts to sprout For germination to occur, a seed requires a combination of: Oxygen: For aerobic respiration (need ATP in order to grow) Water: To metabolically activate the cells Temperature: For the optimal function of enzymes In addition, particular seed species may require other specialised conditions, such as: • Fire • Light or darkness • Freezing • Prior animal digestion •Erosion of the seed coat • Washing (to remove inhibitors)
- 8. Unusual germination – Jack Pines
- 9. Artic Poppy – (Papiver radicatum)
- 10. Seed Germination
- 11. Storing seeds in case of extinction Hope to store 25% of seeds from plants around the world by 2020.
- 12. Metabolic Processes during germination of a seed Begins with absorption of water. 1. Gibberellin released after water uptake. 2. Gibberellin is a growth substance (plant growth hormone) and triggers the production of amylase. 3. Amylase hydrolyses starch into maltose. Starch is present in the seeds endosperm. 4. Maltose is then further hydrolysed into glucose that can be used for cellular respiration or cellulose (condensation). 5. Cellulose is necessary to produce the cell walls of new cells being produced.
- 13. Control of flowering in angiosperms Light is an important factor Plants detect the presence of light, its direction, wavelength, and even intensity. Photoperiodism is the plant’s response to light involving the relative lengths of day and night In order to survive plants must flower when pollinators are available and when necessary resources are plentiful. Plant type Flowering and light Examples Long-day plants Bloom when days are longest and nights are shortest Radishes, spinach, and lettuce Short-day plants Bloom in spring, late summer, and autumn when days are shorter Poinsettias, chrysanthemums, and asters Day-neutral plants Flower without regard to day length Roses, dandelions, and tomatoes
- 14. How is the flowering process controlled? Plants actually depend on the amount of uninterrupted darkness to flower Control by light is brought about by a special blue/green pigment called phytochrome Inactive Pr Active Pfr Red light (660nm) cause inactive form to become active In Far Red light (730nm) the active form reverts back quickly to the inactive form. In darkness the active form slowly converts back to the inactive form
- 17. Mechanism behind flowering The search for the substance that causes the development of meristematic tissue into flowers was focused on the identification of 'florigen', the flowering hormone. Phytochrome Fr is the biologically active form of phytochrome but it is florigen. Most research indicates that phytochrome cannot move from the leaf cells to the meristem tissue.