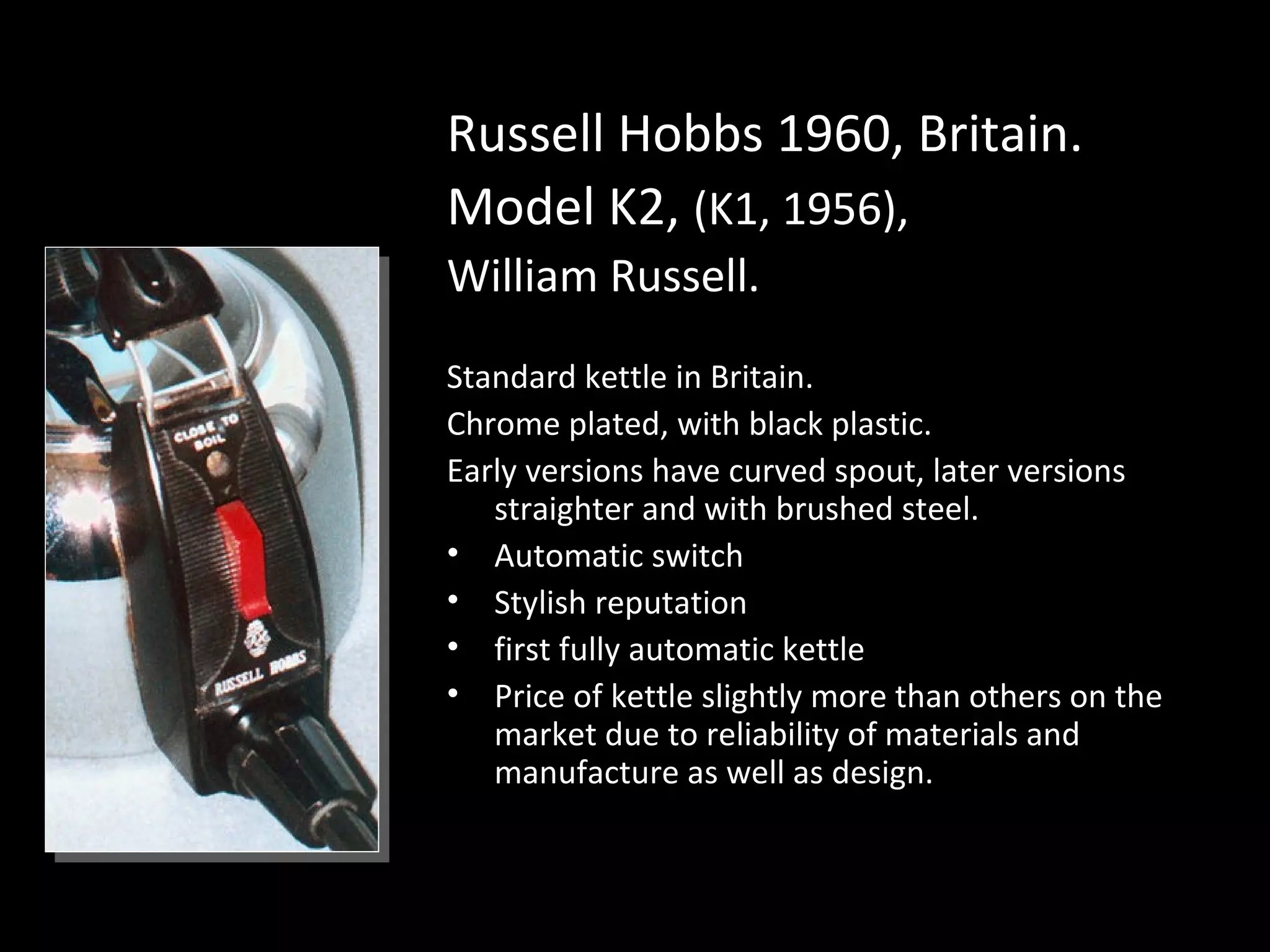
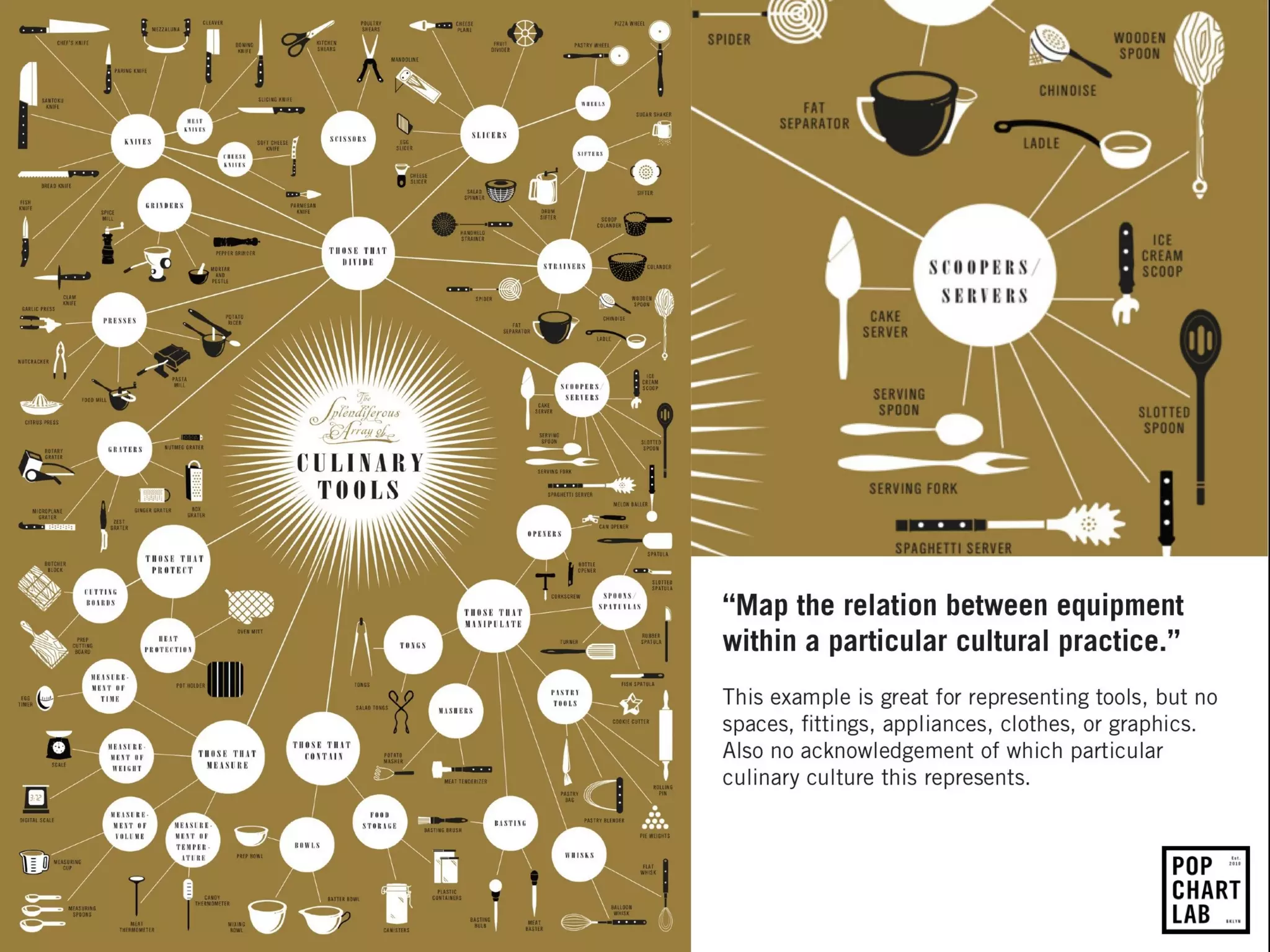
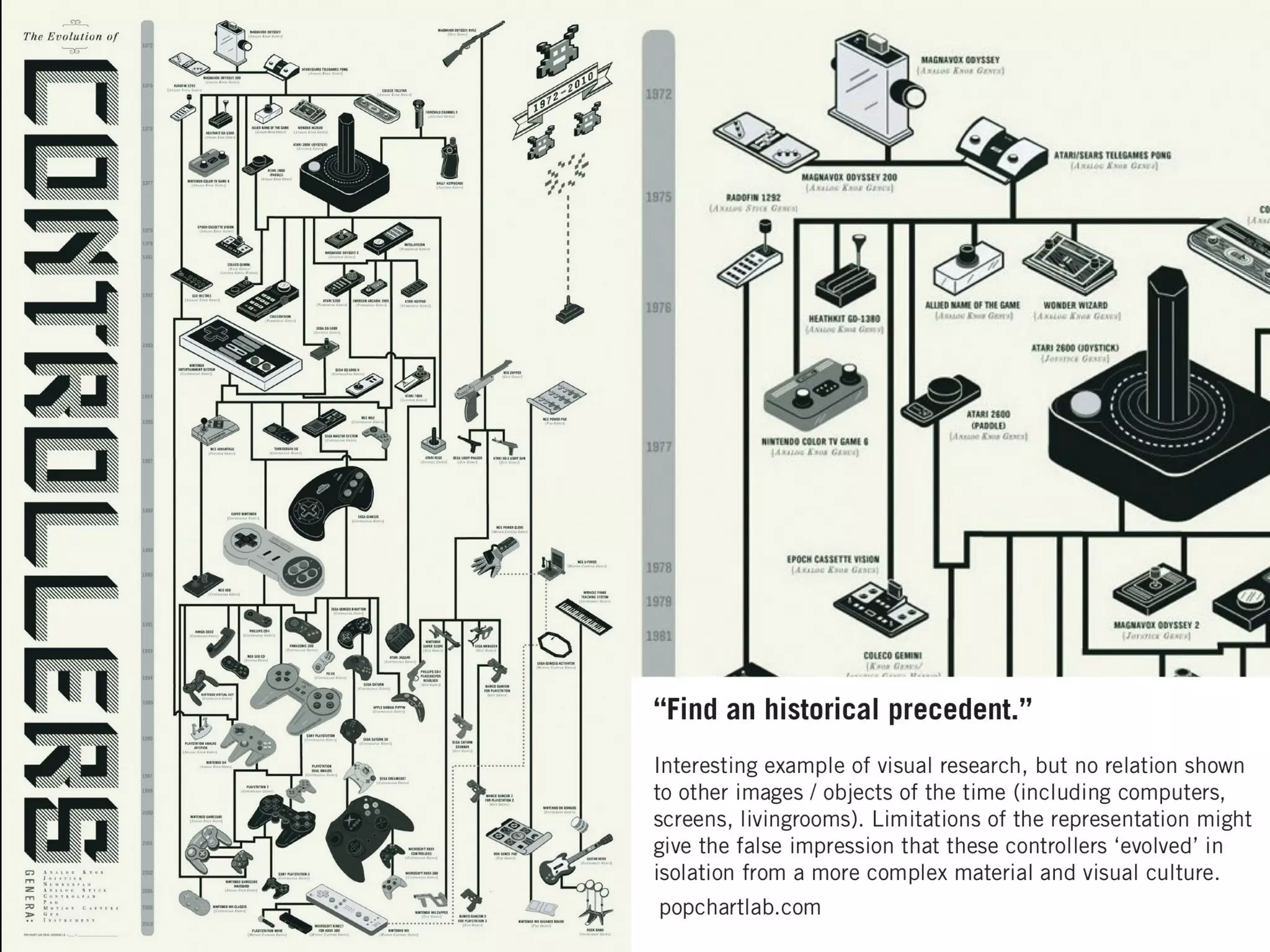
Design history is concerned with various design fields including architecture, product design, fashion, and graphic design. It examines how design has influenced individuals, society, and culture over time as well as how societal and cultural factors have shaped design. Studying design history provides important knowledge about vocabulary, tools, materials, and stylistic elements used in design. It also helps understand how technological, social, and political changes have impacted design. Design history is an important way to critically analyze design and contextualize one's own style, as well as study social and cultural history through everyday objects.