The document discusses odd behaviors in Python related to identity, mutability, and scope. It provides examples testing the identity and mutability of various Python objects. It also discusses issues that can arise from using mutable default arguments and provides tips on how to avoid these issues, such as using None as a default instead of a mutable object.










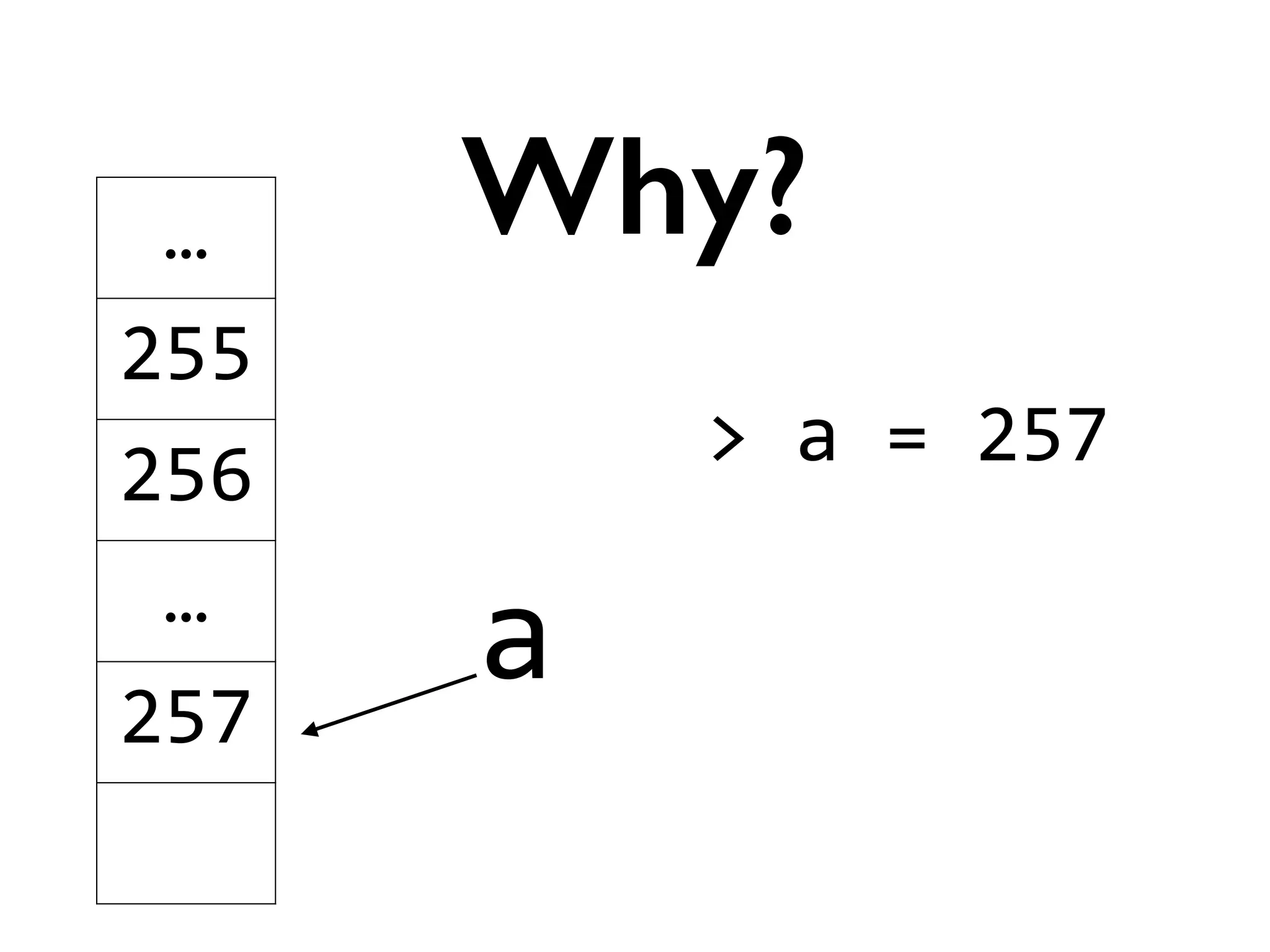
![>
[]
is
[]
???
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-11-2048.jpg)
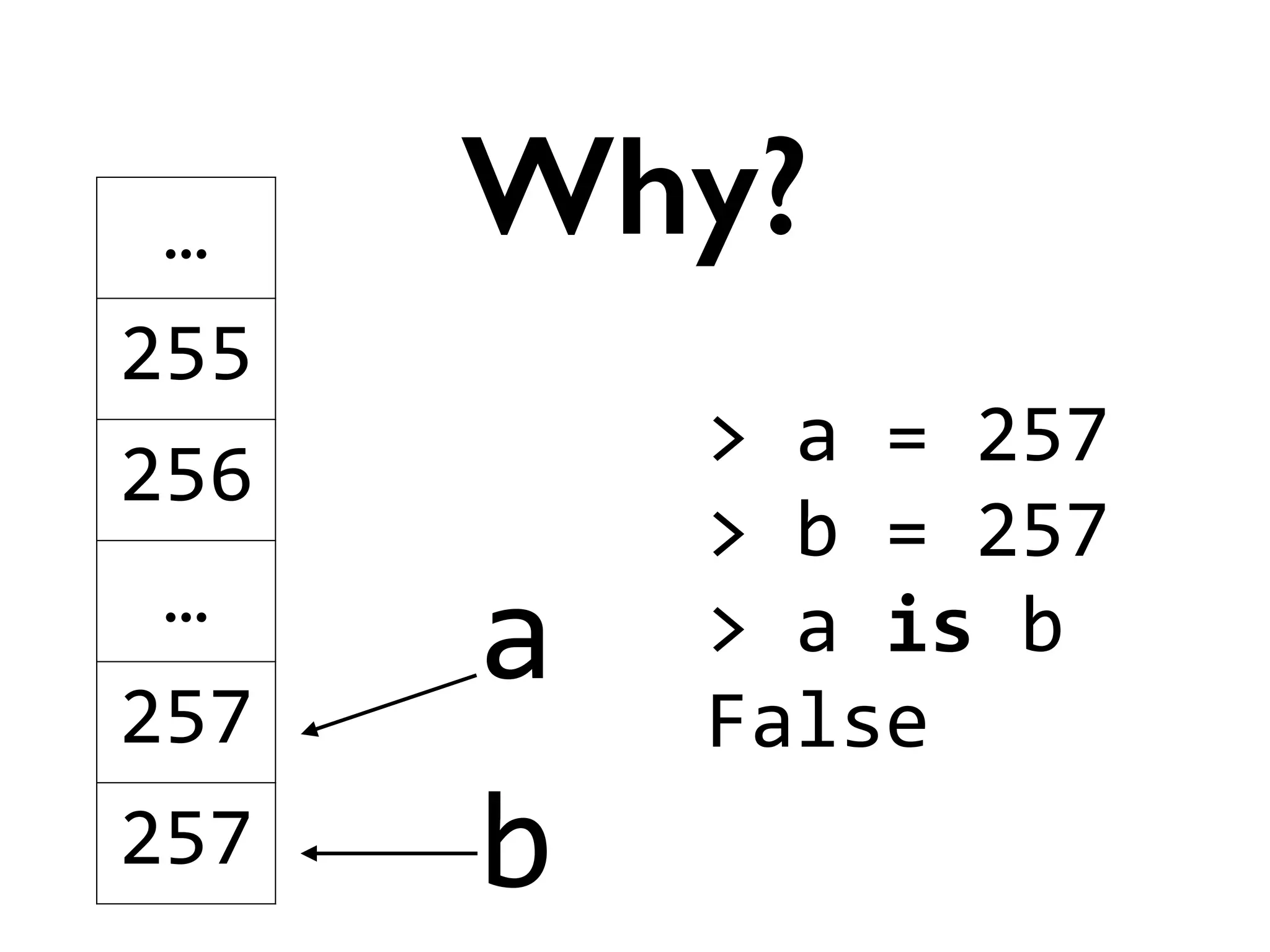
![>
[]
is
[]
False
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-12-2048.jpg)








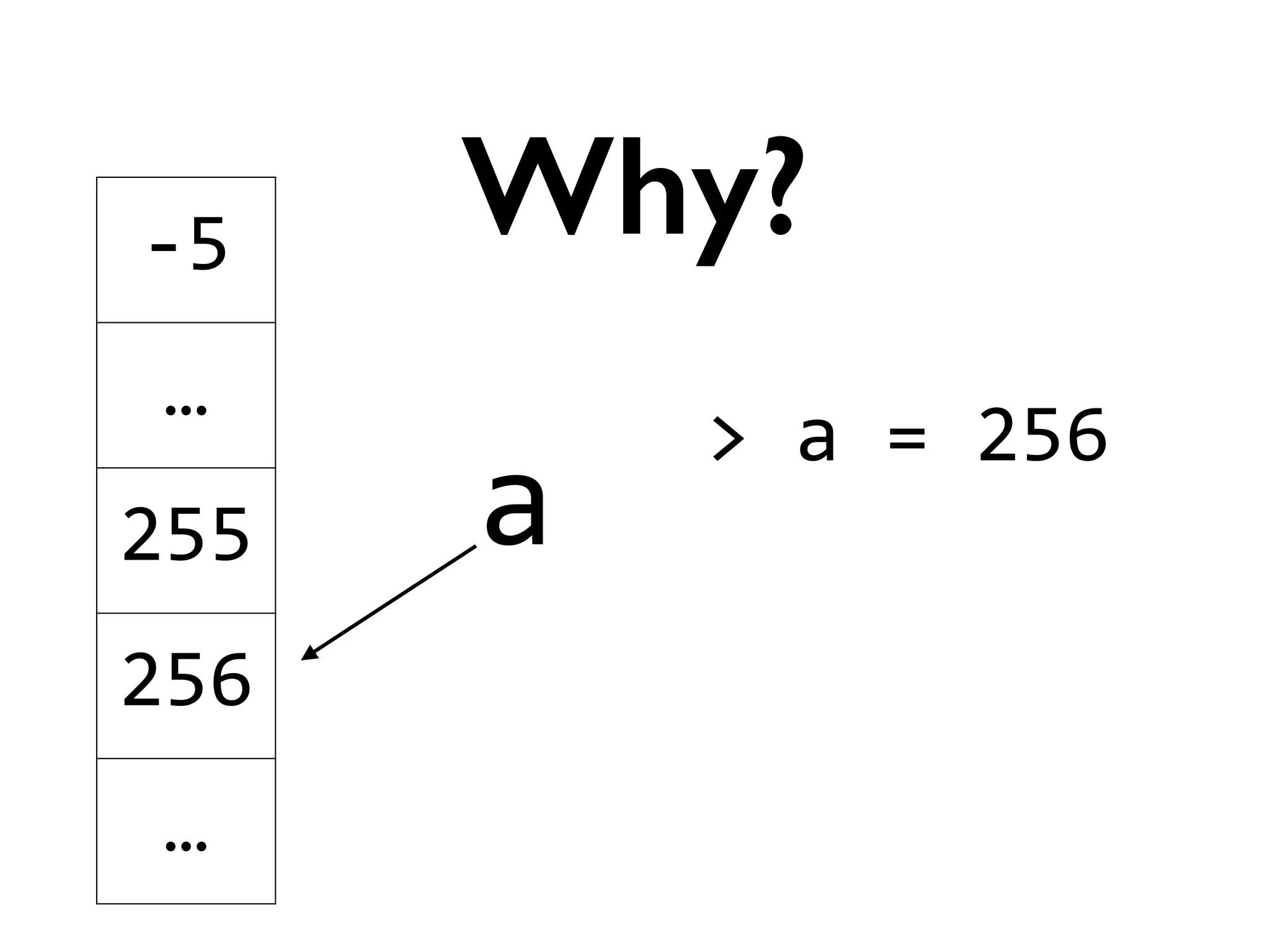
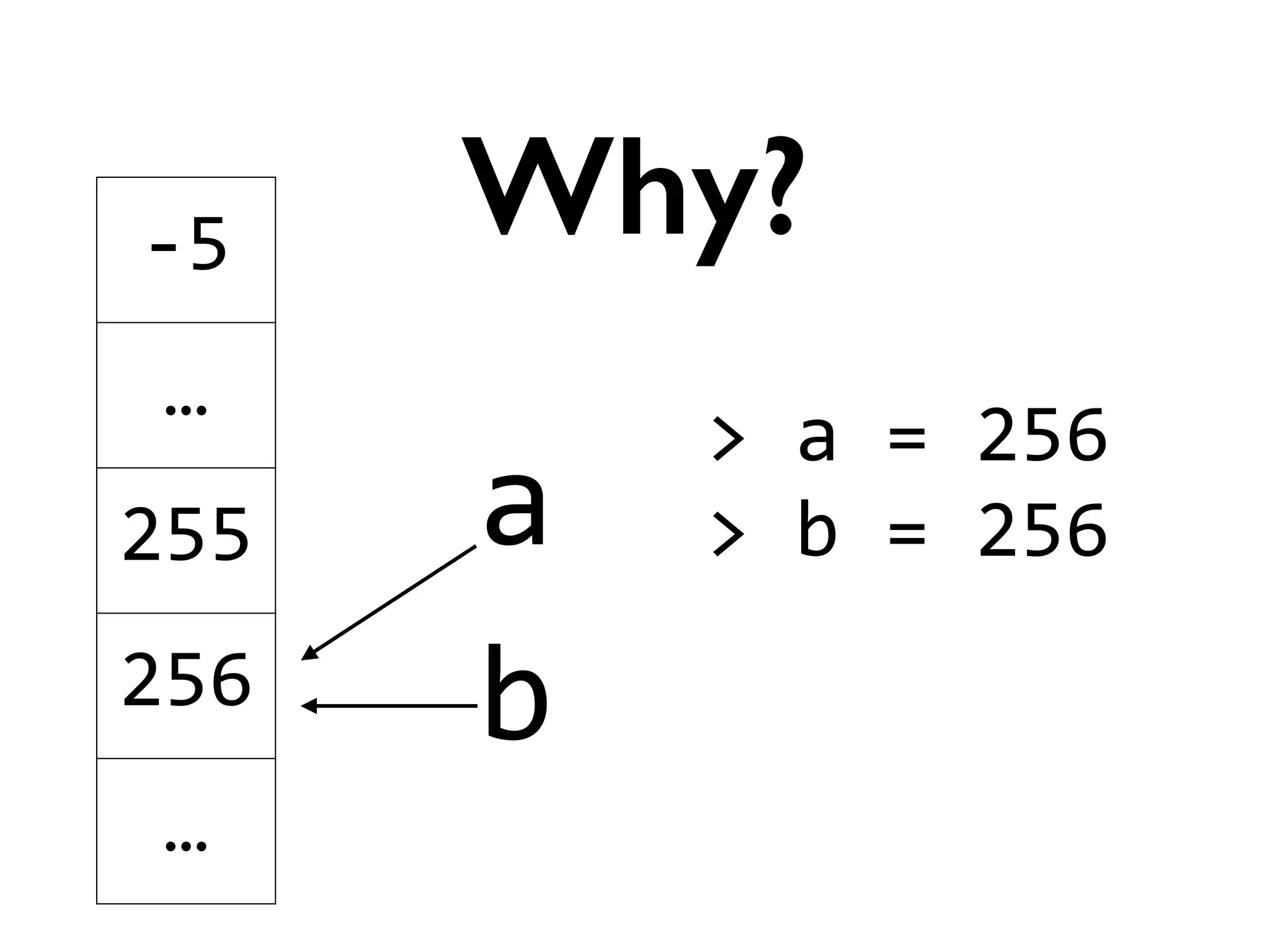
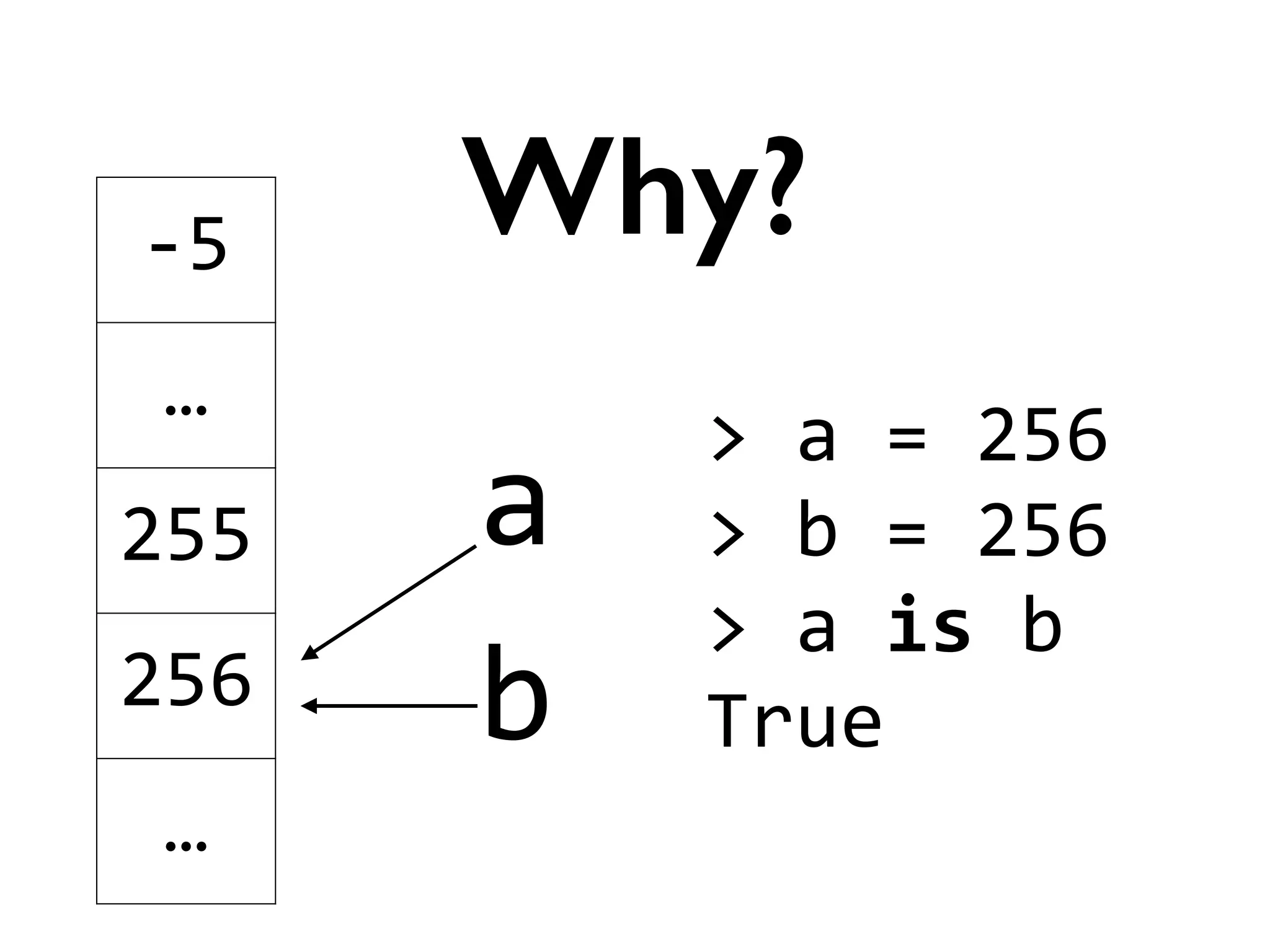
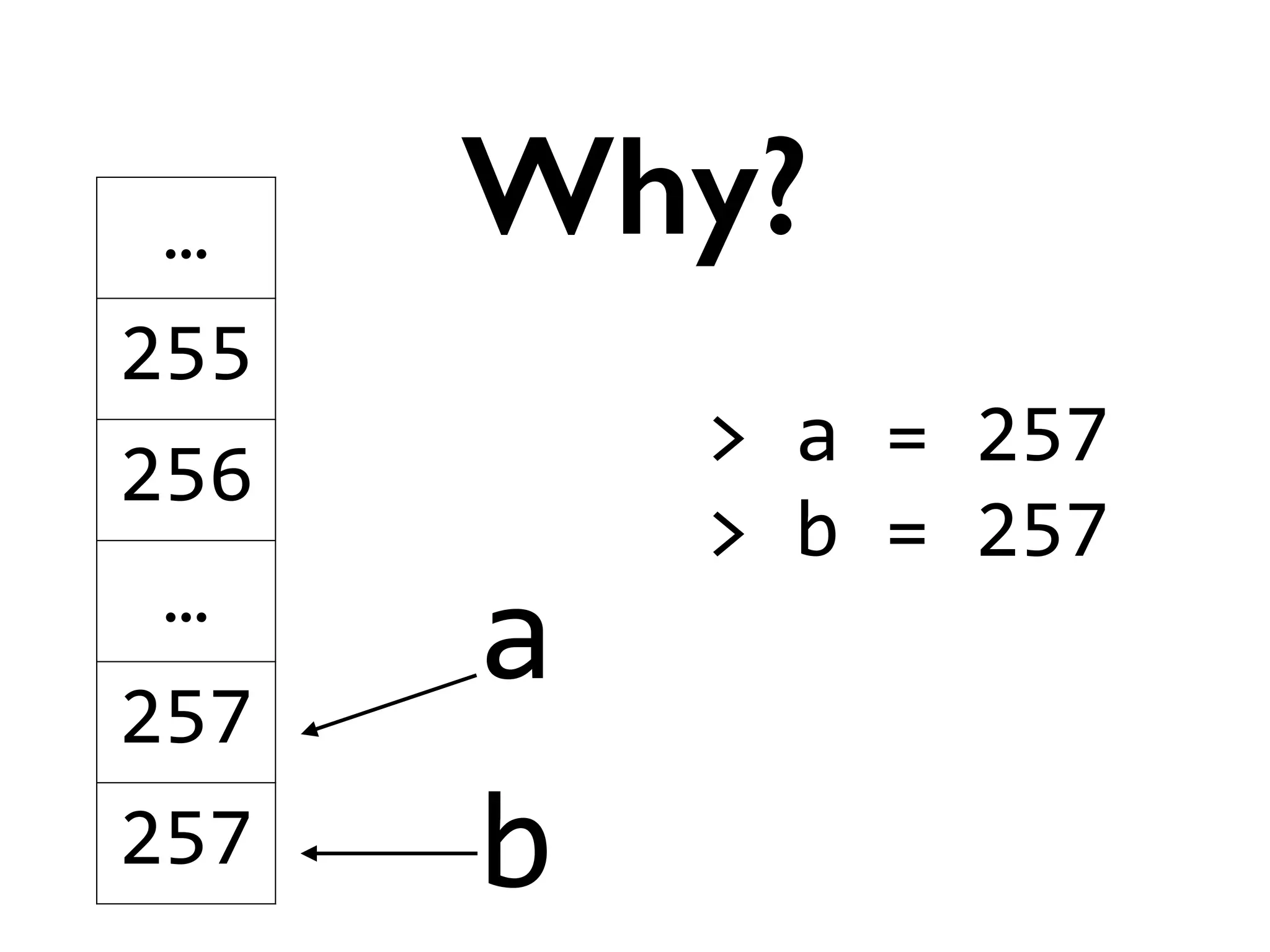




![>
faves
=
["cats",
"dragons"]
!
!
!
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-31-2048.jpg)
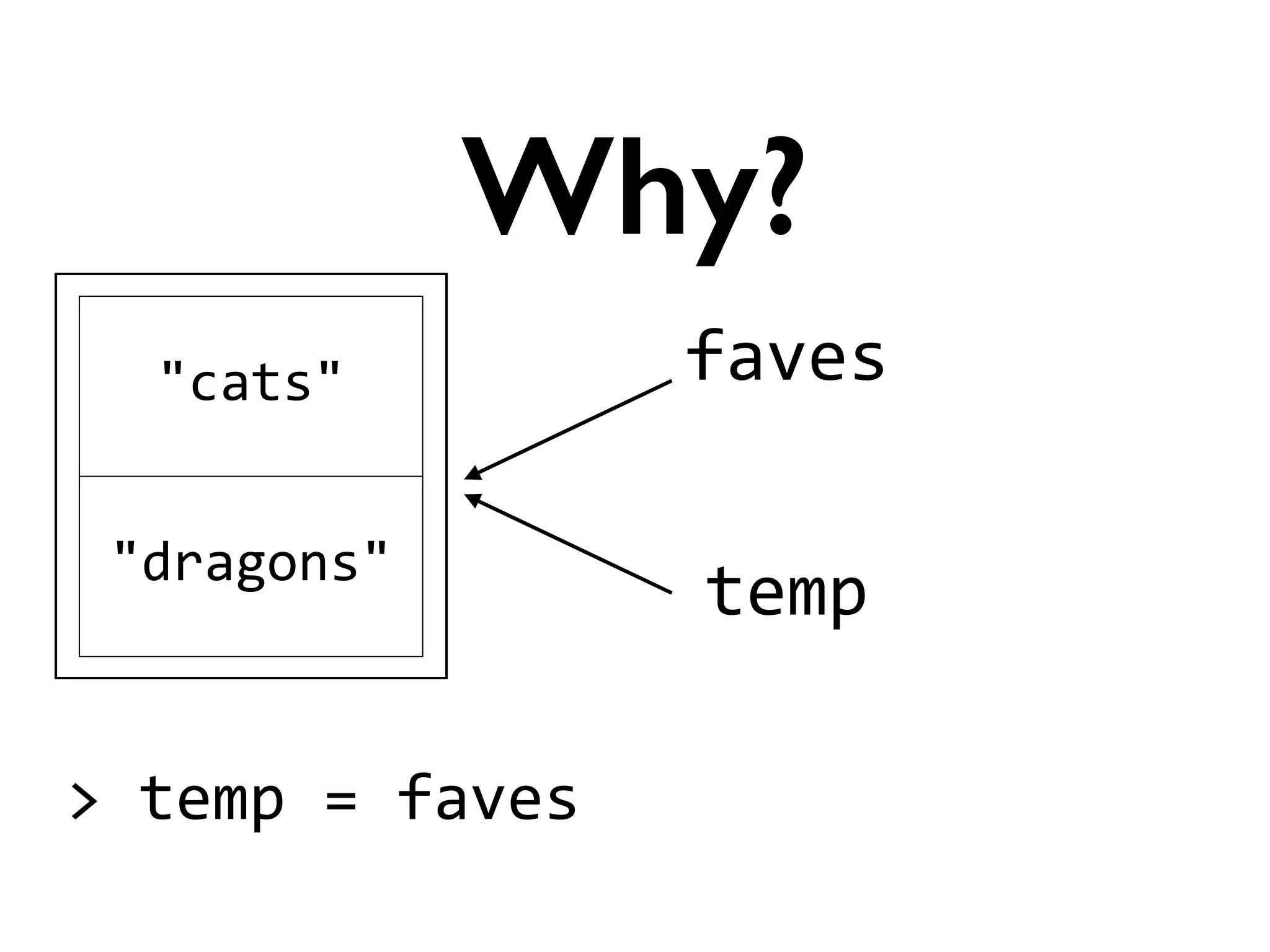
![>
faves
=
["cats",
"dragons"]
>
temp
=
faves
!
!
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-32-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
["cats",
"dragons"]
>
temp
=
faves
>
temp.append("rainbows")
!
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-33-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
["cats",
"dragons"]
>
temp
=
faves
>
temp.append("rainbows")
>
temp
???
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-34-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
["cats",
"dragons"]
>
temp
=
faves
>
temp.append("rainbows")
>
temp
["cats",
"dragons",
"rainbows"]
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-35-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
["cats",
"dragons"]
>
temp
=
faves
>
temp.append("rainbows")
>
faves
???
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-36-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
["cats",
"dragons"]
>
temp
=
faves
>
temp.append("rainbows")
>
faves
["cats",
"dragons",
"rainbows"]
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-37-2048.jpg)
![faves
Why?
"cats"
"dragons"
>
faves
=
["cats",
"dragons"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-38-2048.jpg)

![• lists []
• dictionaries {}
• sets ()
Tip: Mutable Objects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-41-2048.jpg)
![>
temp
=
faves[:]
>
temp
=
list(faves)
Tip: Make Real Copies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-42-2048.jpg)
![>
temp
=
[]
>
for
element
in
faves:
temp.append(element)
Tip: Shallow Copy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-43-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
[["cats",
"dragons"]]
!
!
!
Tip: Deep Copy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-44-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
[["cats",
"dragons"]]
>
temp
=
faves[:]
!
!
Tip: Deep Copy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-45-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
[["cats",
"dragons"]]
>
temp
=
faves[:]
>
temp[0].append("rainbows")
!
Tip: Deep Copy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-46-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
[["cats",
"dragons"]]
>
temp
=
faves[:]
>
temp[0].append("rainbows")
>
faves
???
Tip: Deep Copy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-47-2048.jpg)
![>
faves
=
[["cats",
"dragons"]]
>
temp
=
faves[:]
>
temp[0].append("rainbows")
>
faves
[["cats",
"dragons",
"rainbows"]]
Tip: Deep Copy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-48-2048.jpg)


![def
append_cat(l=[]):
!
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-51-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append(‘cat’)
return
l
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-52-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append(‘cat’)
return
l
!
>
append_cat()
???
!
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-53-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append(‘cat’)
return
l
!
>
append_cat()
[‘cat’]
!
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-54-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append(‘cat’)
return
l
!
>
append_cat()
[‘cat’]
>
append_cat()
???
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-55-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append(‘cat’)
return
l
!
>
append_cat()
[‘cat’]
>
append_cat()
[‘cat’,
‘cat’]
Trivia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-56-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append(‘cat’)
return
l
!
>
append_cat.func_defaults
???
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-57-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append(‘cat’)
return
l
!
>
append_cat.func_defaults
([],)
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-58-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append('cat')
return
l
!
>
append_cat()
>
append_cat.func_defaults
???
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-59-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=[]):
l.append('cat')
return
l
!
>
append_cat()
>
append_cat.func_defaults
(['cat'],)
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-60-2048.jpg)
![>
append_cat.func_defaults
(['cat'],)
!
!
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-61-2048.jpg)
![>
append_cat.func_defaults
(['cat'],)
>
_[0].append('dragon')
!
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-62-2048.jpg)
![>
append_cat.func_defaults
(['cat'],)
>
_[0].append('dragon')
>
append_cat()
???
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-63-2048.jpg)
![>
append_cat.func_defaults
(['cat'],)
>
_[0].append('dragon')
>
append_cat()
['cat',
'dragon',
'cat']
Why?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-64-2048.jpg)

![def
append_cat(l=None):
if
l
is
None:
l
=
[]
!
Tip: Use None](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-66-2048.jpg)
![def
append_cat(l=None):
if
l
is
None:
l
=
[]
l.append(‘cat')
return
l
Tip: Use None](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-67-2048.jpg)

![def
sorting_hat(student,
cache={}):
if
student
in
cache:
print
"Used
cache!"
return
cache[student]
else:
!
!
Tip: Take Advantage!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-69-2048.jpg)
![def
sorting_hat(student,
cache={}):
if
student
in
cache:
print
"Used
cache!"
return
cache[student]
else:
house
=
slow_alg(student)
cache[student]
=
house
return
house
Tip: Take Advantage!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyhanlonwats-140816121034-phpapp01/75/Python-WATs-Uncovering-Odd-Behavior-70-2048.jpg)



















