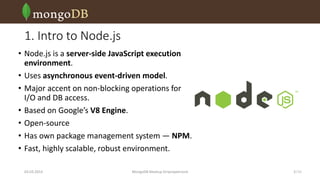
The document discusses Mongoose, an object modeling library for MongoDB and Node.js. It introduces Mongoose and its features, including validation, casting, encapsulation, middlewares, population, and query building. The presentation covers the disadvantages of using MongoDB's native driver, demonstrates Mongoose's schema-driven design, and provides useful links.



![3. Mongoose setup
var mongoose = require('mongoose');
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/mycollection');
var Schema = mongoose.Schema;
var PostSchema = new Schema({
title: { type: String, required: true },
body: { type: String, required: true },
author: { type: ObjectId, required: true, ref: 'User' },
tags: [String],
date: { type: Date, default: Date.now }
});
Reference
Simplified declaration
Default value
mongoose.model('Post', PostSchema);
03.03.2014
Validation of presence
MongoDB Meetup Dnipropetrovsk
6 /16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ybo-mongodb-meetup-140304132121-phpapp01/85/Mongoose-MongoDB-object-modelling-for-Node-js-6-320.jpg)

![3. Mongoose features: casting
• Each property is cast to its
mapped SchemaType in the
document, obtained by the query.
• Valid SchemaTypes are:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
String
Number
Date
Buffer
Boolean
Mixed
ObjectId
Array
03.03.2014
var PostSchema = new Schema({
_id: ObjectId, // implicitly exists
title: { type: String, required: true },
body: { type: String, required: true },
author: { type: ObjectId, required: true, ref: 'User' },
tags: [String],
date: { type: Date, default: Date.now },
is_featured: { type: Boolean, default: false }
});
MongoDB Meetup Dnipropetrovsk
8 /16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ybo-mongodb-meetup-140304132121-phpapp01/85/Mongoose-MongoDB-object-modelling-for-Node-js-8-320.jpg)







