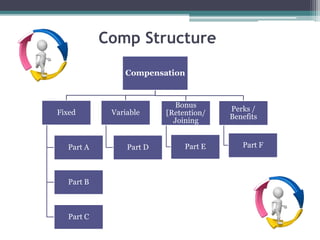
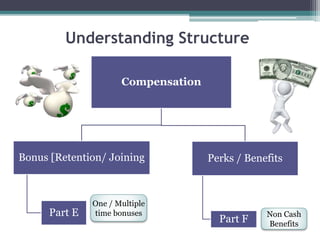
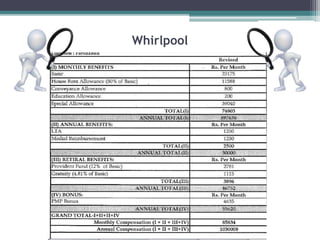
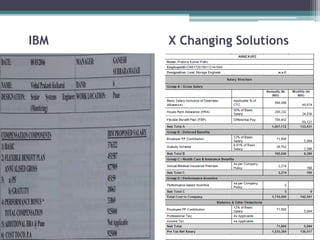
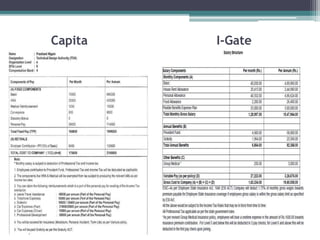
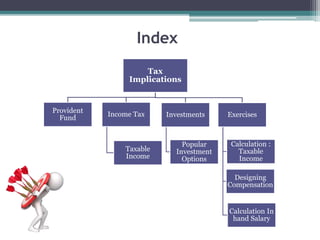
The document discusses various components of compensation including fixed pay, variable pay, perks and benefits, and bonuses. It also covers tax implications related to compensation, explaining concepts like provident fund, income tax, and taxable income. Finally, it provides examples of how to structure compensation and calculate taxable income and taxes.


![Compensation
Fixed
Part A
Part B
Part C
Understanding Structure
[Basic Wages]
Basic & DA
[Retirals]
PF & Gratuity
[Choice Pay]
Reimbursements](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-4-320.jpg)
![Compensation
Variable
Part D
Understanding Structure
[Performance
Linked Payments]
Incentives](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-5-320.jpg)


![All you want to know about PF
• Employees’ Provident Fund Scheme, (EPF)1952
• Employees’ Deposit Linked Insurance
Scheme,(EDLIS) 1976
• Employees’ Pension Scheme, 1995 [EPS]
(replacing the Employees’ Family Pension
Scheme, 1971)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-13-320.jpg)

![Smart Facts about PF
• Not compulsory for all
• Your EPF account does not earn compounded interest each year
on the total monthly contribution.
• Withdrawing EPF during job change illegal
• Can be withdrawn on special occasions
• Allows voluntary contribution
• Every employee had a PF account number which was
associated with the employer. [Till Oct 2014 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-15-320.jpg)


![PF Calculation [Basic Salary >RS.15,000/-]
Option - 1
Contribution Towards Calculation Amount
EPF Employees share 20000 x 12% 2400
EPS Employer share 15000 x 8.33% 1250
EPF employer share 20000 x 12% (-) 1250 1150
EDLI charges 20000 x 0.5% 220
EPF Admin charges 20000 x 1.1% 220
EDLI Admin charges 20000 x 0.01% 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-18-320.jpg)
![PF Calculation [Basic Salary >RS.15,000/-]
Option - 2
Contribution Towards Calculation Amount
EPF Employees share 20000 x 12% 2400
EPS Employer share 15000 x 8.33% 1250
EPF employer share 15000 x 3.67% 550.5
EDLI charges 15000 x 0.5% 75
EPF Admin charges 15000 x 1.1% 165
EDLI Admin charges 15000 x 0.01% 1.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-19-320.jpg)
![PF Calculation [Basic Salary >RS.15,000/-]
Option – 3
Contribution Towards Calculation Amount
EPF Employees share 15000 x 12% 1800
EPS Employer share 15000 x 8.33%
1249.5(round
ed to 1250)
EPF employer share 15000 x 3.67%
555.5
(rounded to
555)
EDLI charges 15000 x 0.5% 75
EPF Admin charges 15000 x 1.1% 165
EDLI Admin charges 15000 x 0.01% 1.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-20-320.jpg)


![Basic Tax Jargons
1. Financial Year (FY) [2014-15] – Income Earned
2. Assessment Year (AY) [2015-16] – Income Assessed
3. Previous Year (PY) [2014-15]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-23-320.jpg)

![Income Tax Slab For Financial Year 2014-15
General (M/F) Senior Citizen [60 to 80] Income Tax
0-250000 0-300000 No Tax
250000-500000 300000-500000 10%
500000-1000000 500000-1000000 20%
Above-1000000 Above-1000000 30%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-25-320.jpg)

![Popular Investment Options
For Tax exemption
▫ Section – 80 C
Section – 80 CCC [LIC Annuity Plan / Pension Fund]
Section – 80 CCD(1) [National Pension Scheme- Employee]
Section – 80 CCD(1B) [National Pension Scheme- Employee]
Section – 80 CCD(2) [National Pension Scheme - Employer]
Section – 80 D [Medical Insurance]
Section – 80 E [Loan for Higher Education]
Section – 80 GG [HRA]
▫ Section – 24 [Home Loan]
▫ Section – 10 (13A) [HRA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-27-320.jpg)

![Deduction for the interest that you pay on your home
loan
[Limit: Rs.2,00,000/- for Self occupied property]
[No Cap on property that is not self-occupied]
Deductions – Home Loan Benefit u/s 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-29-320.jpg)
![1. Actual HRA
OR
2. Actual rent paid by you minus 10% of your basic salary
and other allowances (excluding HRA)
OR
3. 50% of your basic salary [Metro] / 40% [Non Metro]
Deductions – HRA [Section 10(13A)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-30-320.jpg)


![Do You Know..??
▫ Gratuity – 4.81% [Why]
▫ Difference b/w last year & this Year
investment plans
▫ LTA [Twice in 4 Years]
▫ Slab for Super Senior Citizens
▫ Can HRA & Home loan benefit could be
availed simultaneously
▫ Whether PAN of the Landlord is mandatory
for HRA claim – What’s the limit
▫ Is producing Rent Receipts necessary for
claiming HRA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/14d32765-b19b-479b-b3b0-55e2cfe49374-160401053723/85/Calculation-Taxable-Income-33-320.jpg)
