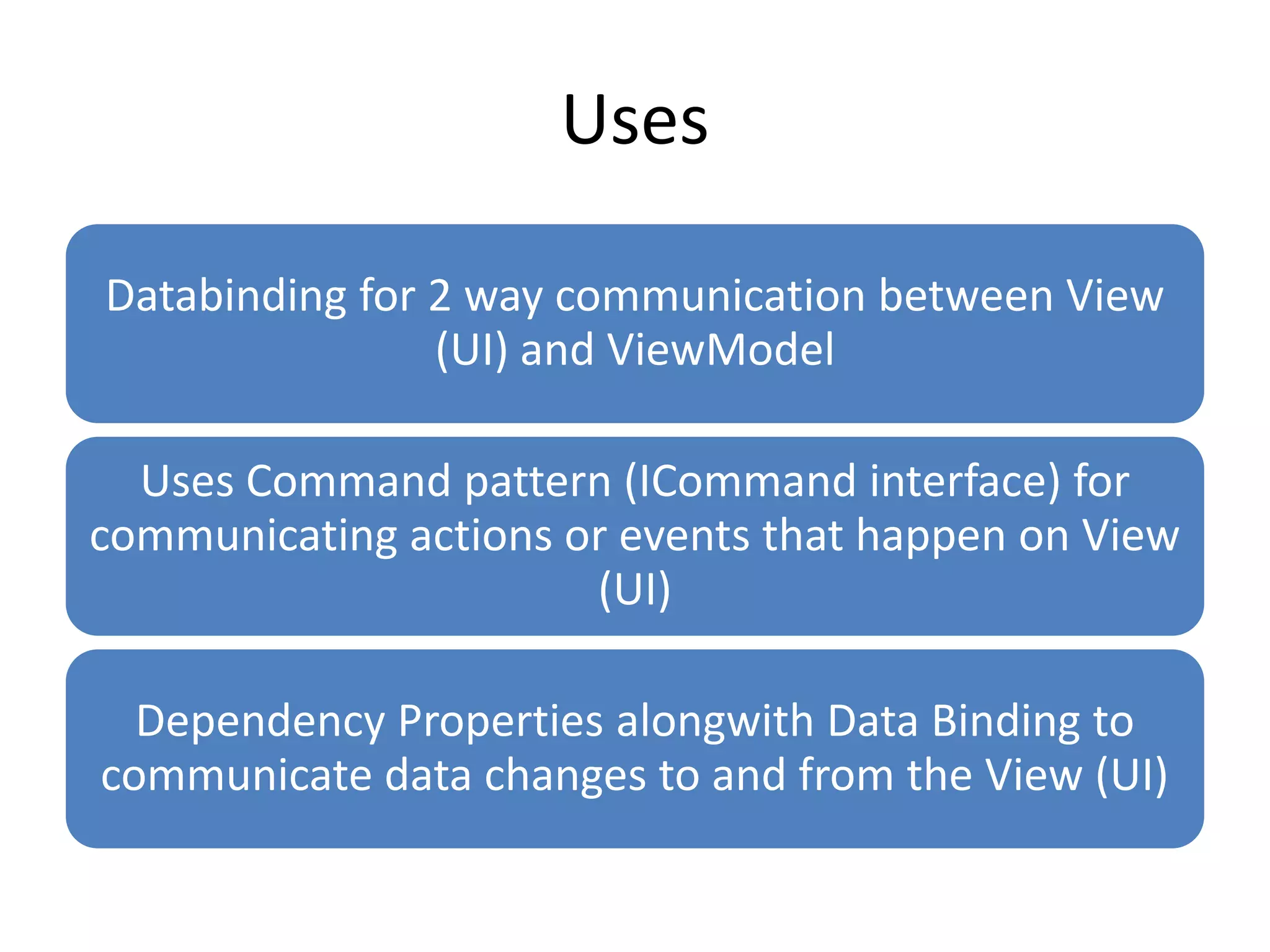
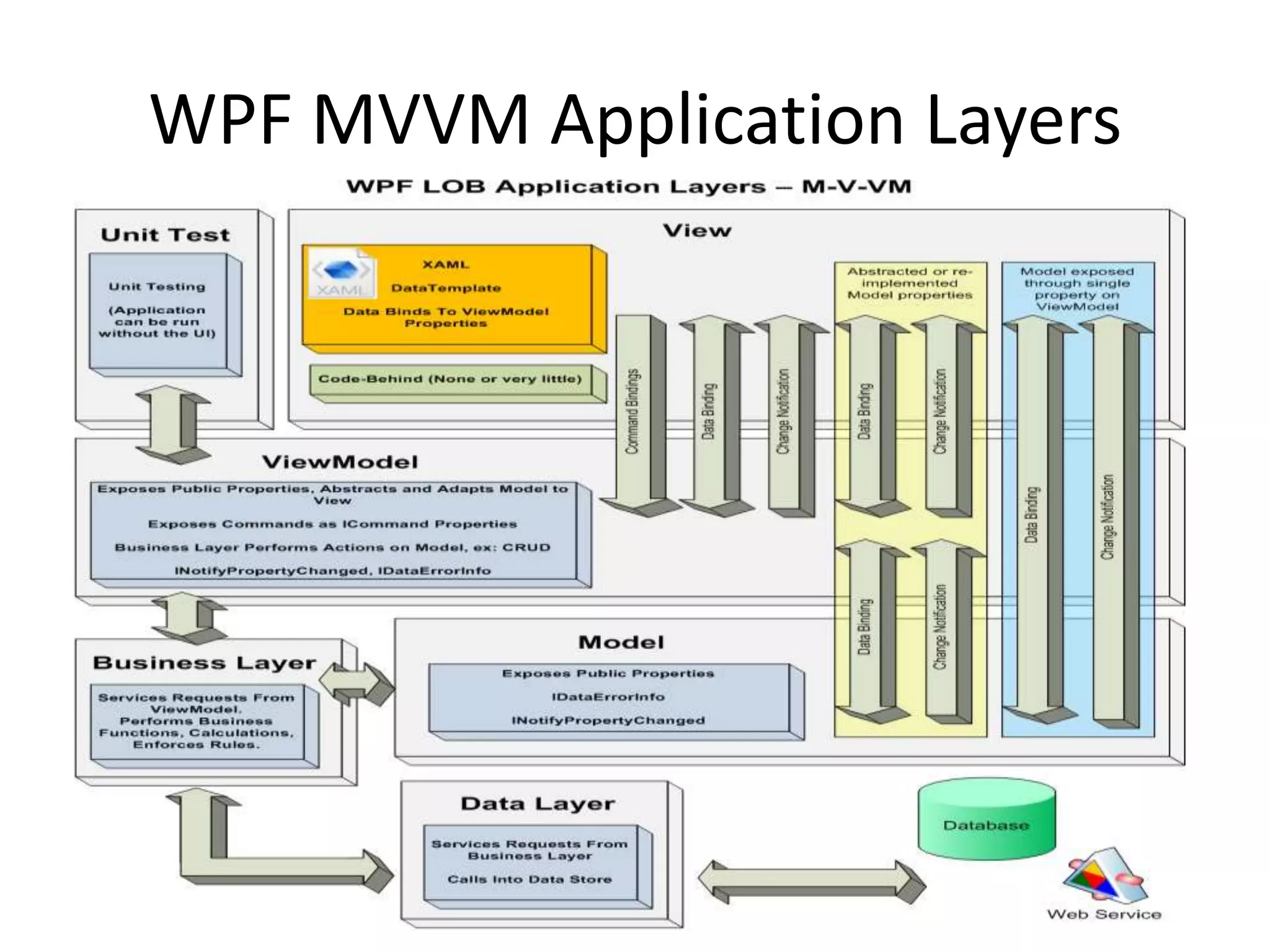
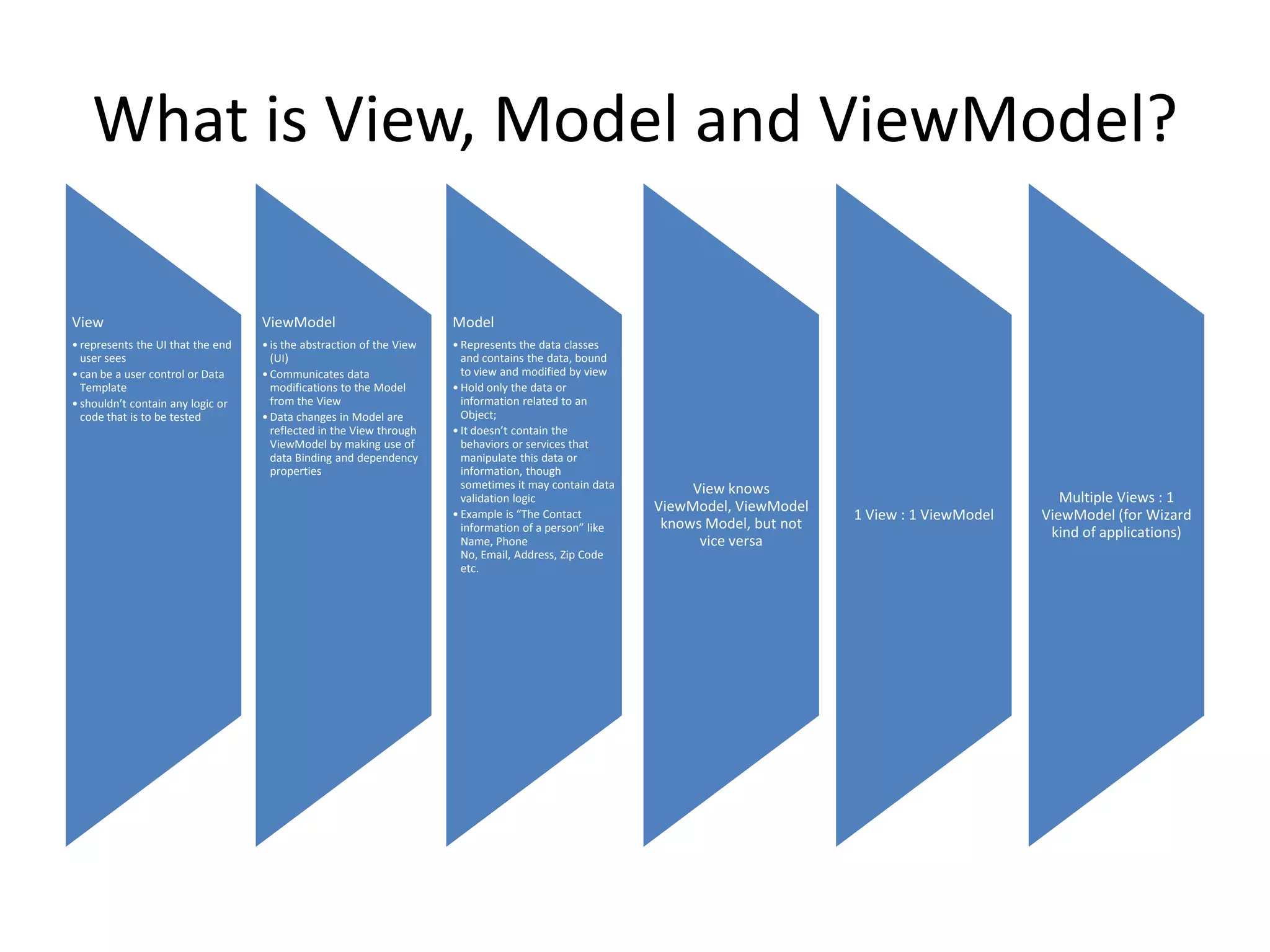
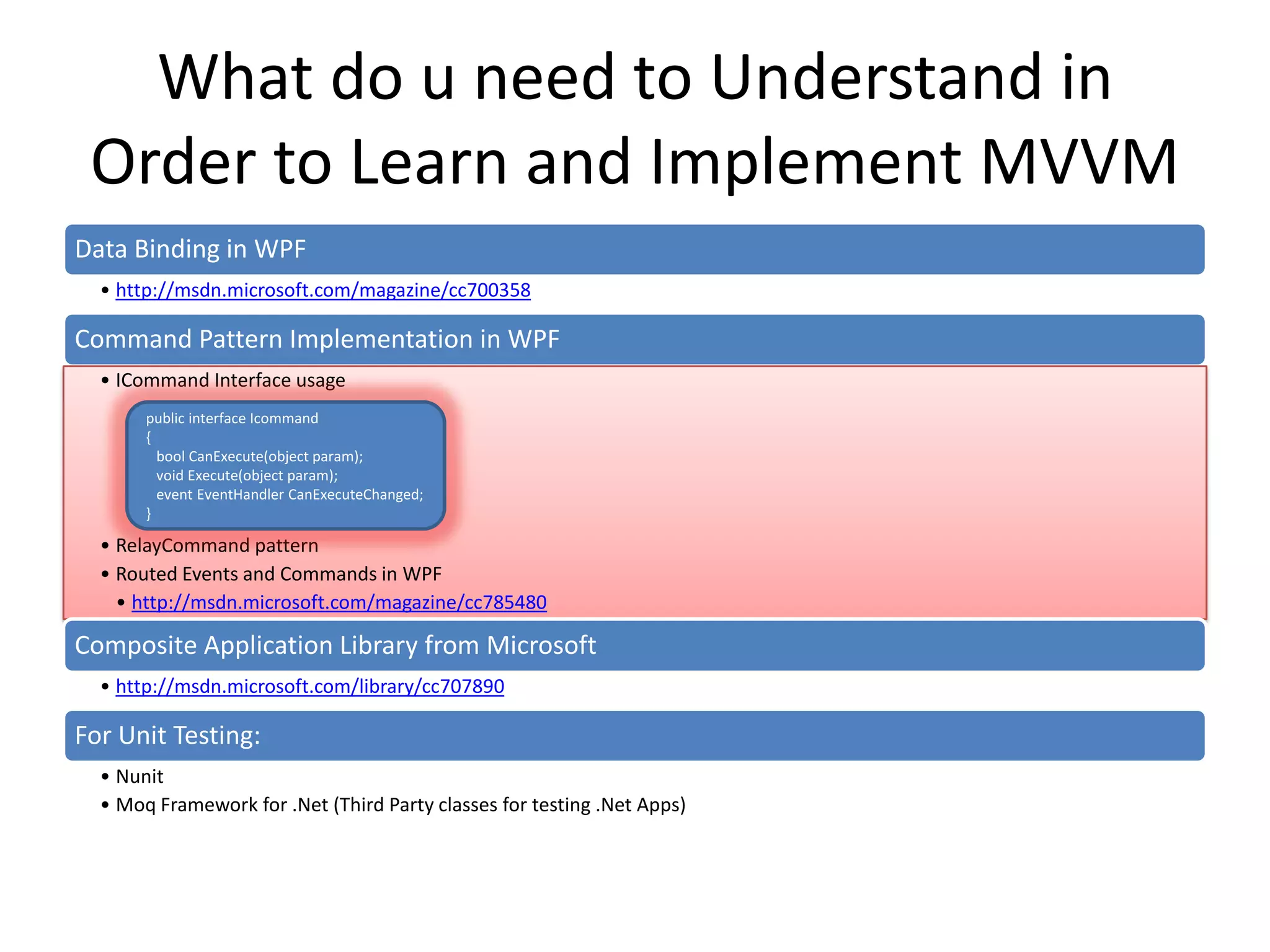
The document discusses the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) pattern for WPF applications. MVVM allows for a separation of concerns between the data/business logic (Model), user interface (View), and logic that coordinates between them (ViewModel). Key aspects of MVVM include using data binding and commands to communicate between the View and ViewModel, keeping the View focused on presentation and the ViewModel on coordinating changes to the Model. Adopting MVVM allows for cleaner separation of concerns, easier testing, and more flexibility when updating the user interface.