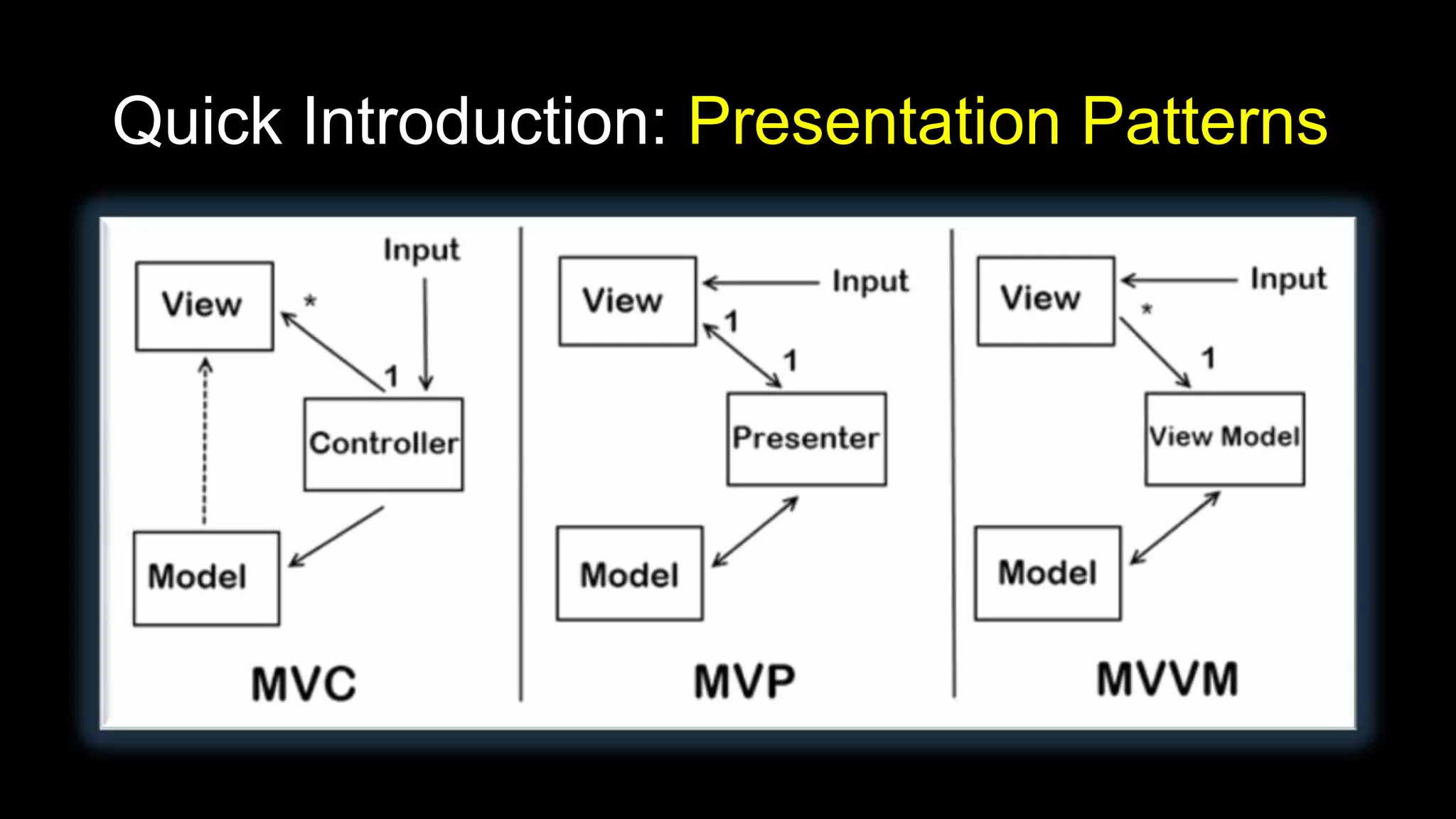
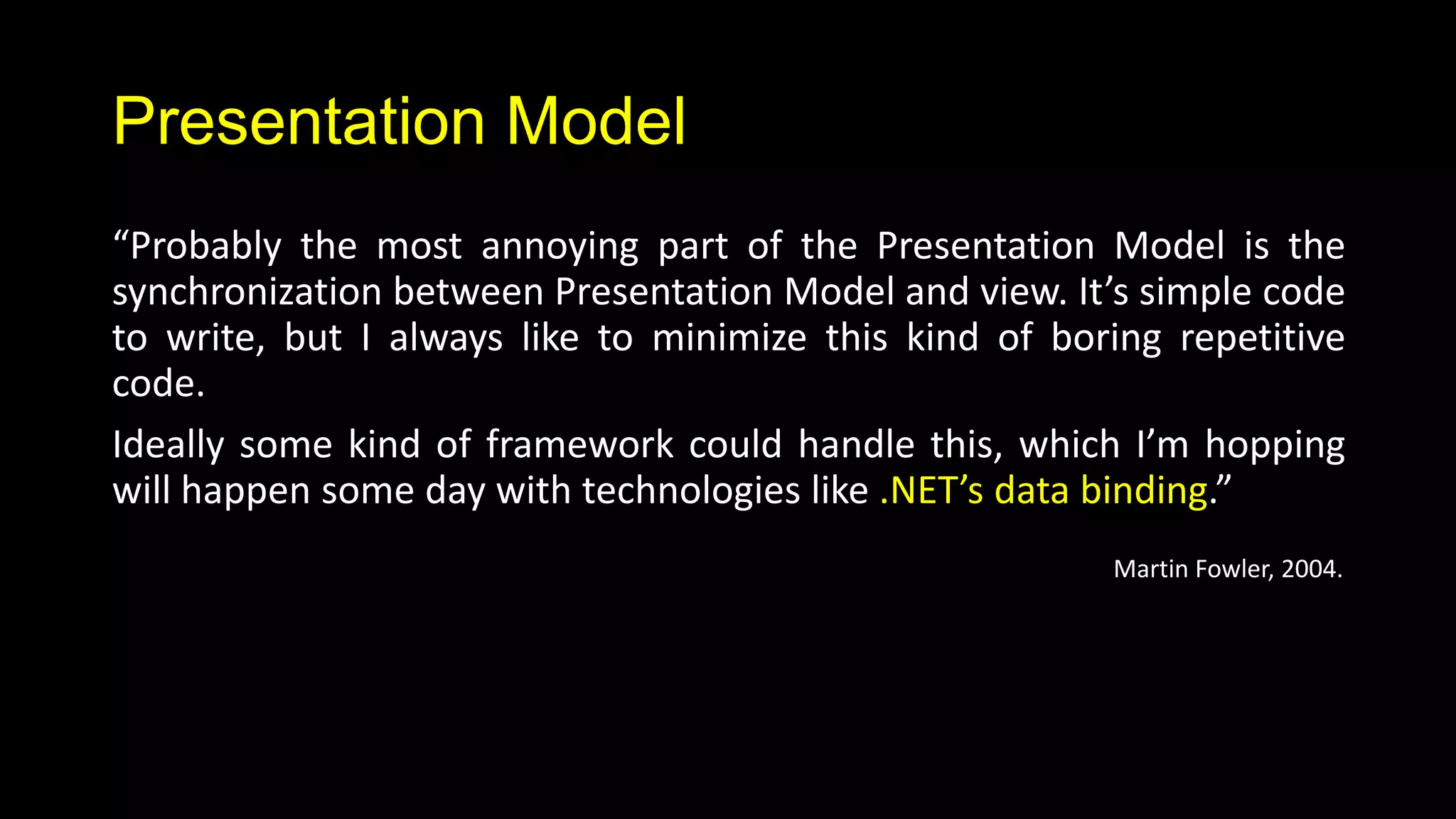
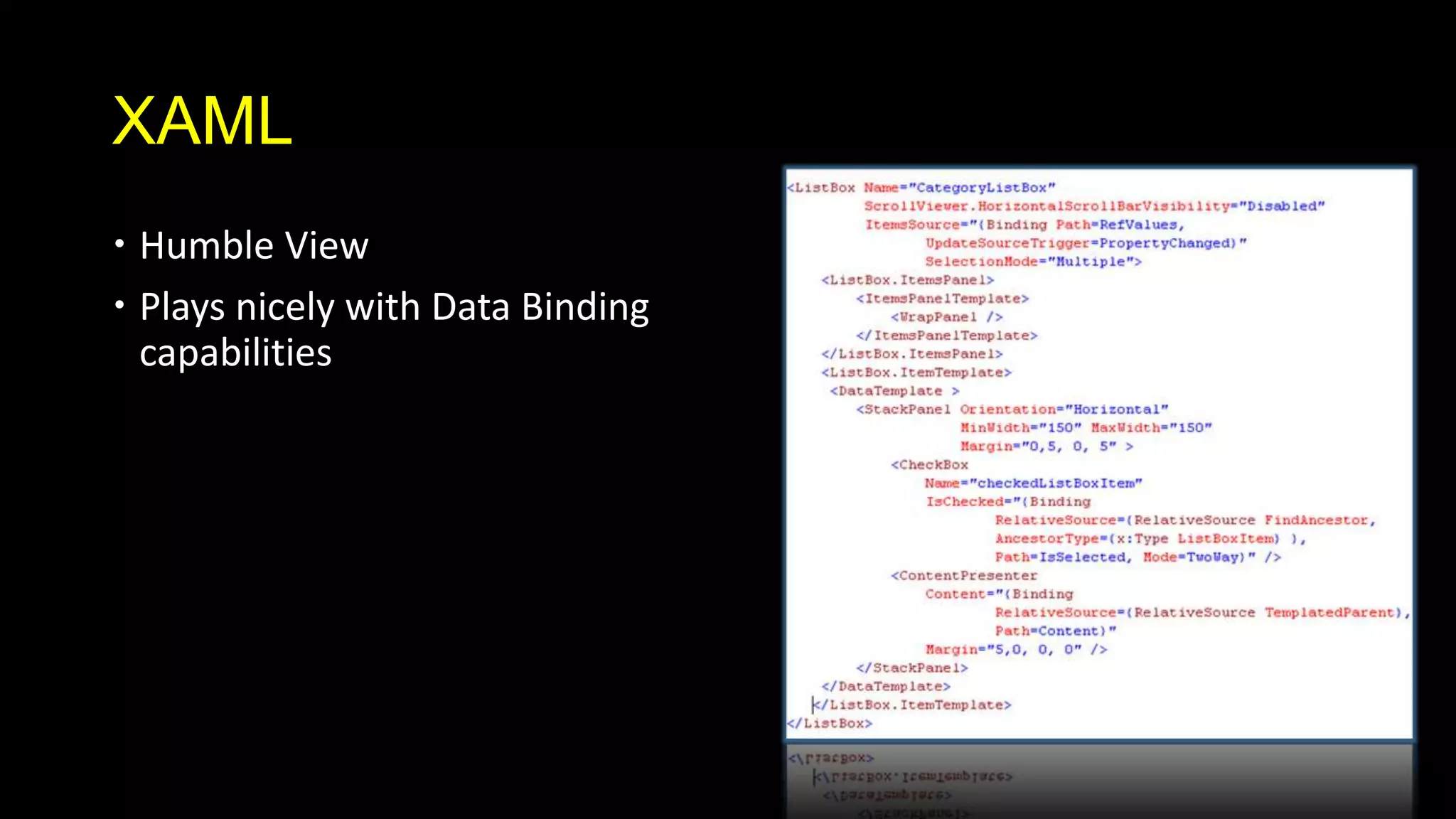
The document summarizes the presentation model pattern and Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) design pattern. It discusses how MVVM is an implementation of the presentation model pattern for WPF and Silverlight applications. It outlines key aspects of MVVM like separating the view and view model, using XAML for views, data binding between views and view models, commands, validation, messaging between components, and view model locators. The document provides examples of how to implement features like data binding, commands, and validation using MVVM.