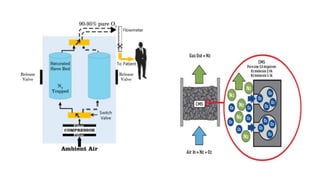
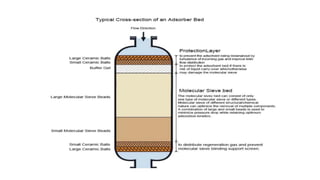
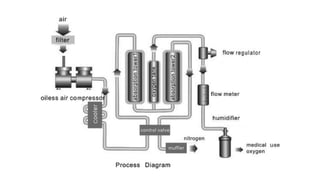
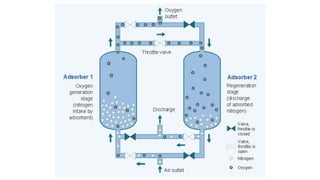
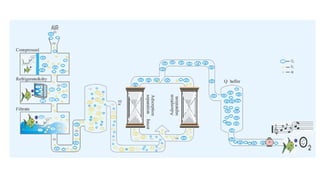
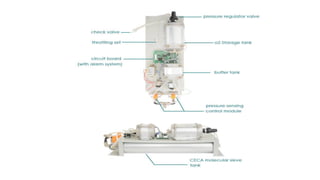
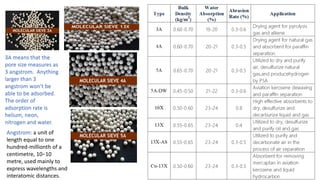
Molecular sieves are synthetic zeolite materials engineered with pores of precise and uniform size that allow them to preferentially adsorb gases and liquids based on molecular size and polarity. They work by absorbing nitrogen from pressurized air, leaving purified oxygen that can be collected. The molecular sieves then discharge the adsorbed nitrogen back into the air when decompressed, in a cyclical process used in oxygen generators.