NOTES ON PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING
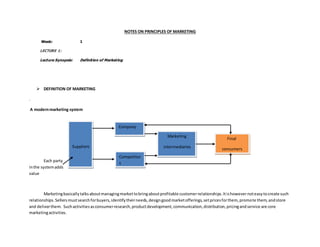
- 1. NOTES ON PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING Week: 1 LECTURE 1: Lecture Synopsis: Definition of Marketing DEFINITION OF MARKETING . A modernmarketing system Each party inthe systemadds value Marketingbasicallytalksaboutmanagingmarkettobringaboutprofitable customerrelationships.Itishowevernoteasytocreate such relationships.Sellersmustsearchforbuyers,identifytheirneeds,designgoodmarketofferings,setpricesforthem,promote them,andstore and deliverthem. Suchactivitiesasconsumerresearch,productdevelopment,communication,distribution,pricingandservice are core marketingactivities. Suppliers Company Competitor s Marketing intermediaries Final consumers
- 2. Marketinginnot justdone by sellersare mostpeopleare ledtobelieve,itcanalsobe done by buyers,this isdone throughtheirsearch for products,interactwithcompaniestoobtaininformationandmake theirpurchases. The figure above showsthe mainelementsinamarketingsystem.Marketingisnotalwaysasmoothride,butit alsoinvolvesservinga marketof final customerseveninthe face of ‘aggressive’competitors.The companiesandcompetitors researchthe marketandinteractwith consumerssotheycan be betterpositionedtounderstandtheirneeds.Thentheycanpackage andsendtheirmarketofferingsandmessagesto consumers,eitherdirectlyorthroughmarketintermediaries.Itisgoodto note that each partyin the marketingstructure is affectedbymajor environmental forces(demography,economic,natural,technological,political andsocial/cultural). Each party alsoadds value forthe nextlevel.The arrowsrepresentrelationshipsthatmustbe developed,maintainedandmanaged.Asa result,acompany’ssuccessat buildingprofitablerelationshipsdependsnotonlyonitsownactionsbutalso onhowwell the entire system servesthe needsof final consumers.SierraLeone BottlingCompanyforexamplecanneverbe able toprovide cheapproductsif itssuppliersare not able andwillingtosupplymerchandiseatlowcost. Designinga customer-drivenmarketingstrategy: Afterfullyunderstandingthe marketplaceandthe targetcustomers,the marketingmanager’s nextjobwill be todesign aneffective customer- drivenmarketingstrategy,alsoknownasmarketingmanagement;anart andscience of choosingtargetmarketsandbuildingprofitable relationshipwiththem.The desire of everymarketeristofind,attract,keepandgrow targetcustomersby creating,delivering and communicatingsuperiorcustomervalue. To designanattractive and winningmarketingstrategy,the marketingmanagermustanswertwomajorquestions; whatcustomerswillwe serve (targetmarket)?and howcanweserve thesecustomersbest? (i) SelectingCustomerstoserve:Everycompanymustfirstdecide the setof people itwill serve,thisisachievedbydividingthe market intosegments –marketsegmentationandthenselectingwhichsegmentof the markettogo after – target marketing. (ii) ChoosingaValue Proposition:The companymustalsodecide howitwill serve targetcustomers –whichdifferentwillitcreate and howwell isitreadyto positionitself inthe marketplace. (iii) MarketingManagementOrientations:Marketingmanagementalwayswantstodesignstrategiesthatare benton buildingprofitable relationshipswithtargetconsumers. Butwhatare the guidingprinciplesorphilosophiesof suchmarketingstrategies?Howfar shouldtheygoin consideringthe interestof the customers,the organization,andthatof the society?Oftenatime,these interests have conflicted.
- 3. There are basicallyfive alternative conceptsthroughwhichorganizationsdesignandcarryout theirmarketingstrategies,theyare asfollow; The ProductionConcept The Product Concept The SellingConcept The MarketingConceptand The Societal MarketingConcept The ProductionConcept: thisconceptwhichisone of the oldestholdsthatconsumerswill alwaysfavourproductsthatare available andhighly affordable,asaresult,managementshouldfocusonimprovingproductionanddistributionefficiencyinordertoattract and retainmore customers. The Product Concept:This conceptalsoholdsthatconsumerwill favourproductsthatofferthe mostin termsof quality,performance and innovative features.Goingbythisconcept,producersshouldfocusandstayfocusedonimprovingthe qualityof theirproducts. The SellingConcept:The sellingconceptisfollowedbymost companies;itstatesthatconsumerswill notbuymuchof a company’sproducts unlessit’sfullyengagedin sellingandpromotioneffort. The MarketingConcept: Thisconceptholdsthat organizational goalscanonlybe achievedif the companyhasvastknowledge onthe needsand wantsof the targetmarketsand doingall itcould todeliverthose marketneedsandwantsbetterthantheircompetitors. The Societal Marketing Concept:Thisconceptsholdsthat all marketingstrategiesshouldbe gearedtowardsthe deliveringof value tothe target customersina way that improvesboththe consumer‘s andsociety’swelfare.Inthisdirection,mostbigbusinessesandmarketersare now preachingthe conceptof sharedvalue,somethingthatrecognizessocietal needsandnotjusteconomicneedsdefine markets. Construct an integratedmarketingprogramme that deliverssuperiorvalue The marketingstrategyof everycompanyshouldoutline whichcustomersitwill serveandhowitwill create value forthem.Nexttocreating value forcustomers,the marketerwill thencome upwithanintegratedmarketingprogramme thatwill actuallydeliverthe intendedvalue to the target customers.Suchmarketingprogramme shouldbe able toestablishorbuildagoodcustomerrelationshipbytransformingthe marketingstrategyintoaction.The marketingprogramme consistsof the firm’smarketingmix;thisisaset of marketingtoolsthatfirmsuse to implementtheirmarketingstrategies.
- 4. The MarketingMix Simplyputthe MarketingMix is a tool usedby businessesandMarketerstohelpdetermine aproduct or brandsoffering.The 4P’shave been associatedwiththe MarketingMix since theircreationby EdmundJerome McCarthy (February20, 1928 – December3,2015) in1960. Product - The Productshouldfitthe taskconsumerswantit for,it shouldworkandit shouldbe whatthe consumersare expectingto get. Place – The productshouldbe available fromwhereyourtargetconsumerfindsiteasiesttoshop.Thismaybe HighStreet,Mail Orderor the more current optionviae-commerce oranonline shop. Price – The Productshouldalwaysbe seenasrepresentinggoodvalue formoney.Thisdoesnotnecessarilymeanitshouldbe the cheapestavailable;one of the maintenetsof the marketingconceptisthatcustomersare usuallyhappytopay a little more for somethingthatworksreallywellforthem. Promotion – Advertising,PR,SalesPromotion,Personal Sellingand,inmore recenttimes,Social Mediaare all keycommunicationtools for an organisation.These toolsshouldbe usedtoputacrossthe organisation’smessage tothe correctaudiences inthe mannerthey wouldmostlike tohear,whetheritbe informativeorappealingtotheiremotions. In the late 70’s it was widelyacknowledgedbyMarketersthatthe MarketingMix shouldbe updated.Thisledtothe creationof the Extended MarketingMix in 1981 by Booms& Bitnerwhichadded3 newelementstothe 4 P’sPrinciple.ThisnowallowedtheextendedMarketingMix to include productsthatare servicesandnot justphysical things. Extended7 P’s: People – All companiesare reliantonthe people whorunthemfromfrontline Salesstaff tothe ManagingDirector.Havingthe right people isessential because theyare asmucha part of your businessofferingasthe products/servicesyouare offering. Processes–The deliveryof yourservice isusuallydonewiththe customerpresentsohowthe service isdeliveredisonce againpartof whatthe consumerispayingfor. Physical Evidence – Almostall servicesincludesome physical elementsevenif the bulkof whatthe consumerispayingforisintangible. For example ahairsalonwouldprovide theirclientwithacompletedhairdoandaninsurance companywouldgive theircustomerssome
- 5. formof printedmaterial.Evenif the material isnotphysicallyprinted(inthe case of PDF’s) theyare still receivinga“physical product”by thisdefinition. Thoughin place since the 1980’s the 7 P’sare still widelytaughtdue totheirfundamentallogicbeingsoundinthe marketingenvironmentand marketersabilitiestoadaptthe Marketing Mix to include changesincommunicationssuchassocial media,updatesinthe placeswhichyoucan sell aproduct/service orcustomersexpectationsinaconstantlychangingcommercial environment. Is there an 8th P? In some spheresof thinking,there are 8 P’sinthe MarketingMix. The final Pis ProductivityandQuality.Thiscame fromthe oldServices MarketingMix and is foldedintothe ExtendedMarketingMix bysome marketerssowhatdoesitmean? The 8th P of the Marketing Mix: Productivity& Quality - ThisP asks“is whatyou’re offeringyourcustomeragooddeal?”Thisis lessaboutyouas a businessimproving your ownproductivityforcostmanagement,andmore abouthowyourcompanypassesthisontoits customers. Evenafter31 years (or54 in the case of the original P’s) the MarketingMix isstill verymuchapplicable toamarketer’sdayto daywork.A good marketerwill learntoadaptthe theoryto fitwithnotonlymoderntimesbuttheirindividual businessmodel. Buildprofitable relationships and create customerdelight: The firstthree stepsinthe marketingprocesscombined,leadstothe fourthandmost importantstepof all:buildingandmanagingprofitable customerrelationships. CustomerRelationshipManagement:Customerrelationshipmanagement(CRM) isprobablythe mostimportantconceptof modernmarketing. It has to dowiththe effective managementof detailedinformationabout individual customersandcarefullymanagingcustomertouch-pointsin orderto maximize customerloyalty. Most marketershave howevercavedabroadermeaningforthe CRMconcept,to them;CustomerRelationshipManagementisthe overall processof buildingandmaintainingprofitable customerrelationshipbydeliveringsuperiorcustomervalue andsatisfaction. Itdealswithall aspectsof acquiring,keepingandgrowingcustomers.
- 6. The two mainrelationshipbuildingblocksare; CustomerValue CustomerSatisfaction CustomerValue:The majorkeyto buildinglastingcustomerrelationshipistocreate superiorcustomervalue.Attractingandretaining customersisneveraneasytask. Customersare oftenfacedwithwide range of productsandservicesfromwhich theyare tochoose. Customers oftenbuy fromfirmsthat offerthe highestcustomer-perceivedvalue. CustomerSatisfaction: Thistalksabout the product’sperceivedperformanceinrelationsto the buyer’sexpectationsof the product. If the product’sperformance fallsshortof the expectations,the customerisdissatisfied.Butif itmatchesexpectations,the customerissatisfied.If performance exceedsexpectations,the customerishighlysatisfiedordelighted. Capture value from customers to create profitsand customerequity:The firstfourstepsinthe marketingprocessemphasize building customerrelationshipsbycreating anddeliveringsuperiorcustomervalue.The fifthandfinal stepinvolvescapturingvalue inreturnin the form of sales,marketshare andprofits.Bybasicallycreatingsuperiorcustomervalue,the firmhassucceededincreatinghighly satisfiedcustomerswhowithall thingsremainingthe same canstayloyal andbuy more and more of the firm’sproducts.Thiswill meangreaterlong-runreturnsforthe firm. Outcomesof Creating CustomerValue. CustomerLoyalty and Retention Share of Customers CustomerEquity CustomerLoyalty and Retention:A goodcustomerrelationshipmanagementcreatescustomersatisfaction.Asaresult,asatisfiedcustomer remainsloyal and talkswell toothersaboutthe companyand itsproducts. GrowingShare of Customer:Way beyondsimplyretaininggoodcustomerstocapture customerlifetimevalue, agoodcustomer relationshipmanagementcanhelpmarketersincrease theirshare of customers – the share theygetof the customer’spurchasing in theirproductcategories. CustomerEquity: The ultimate goal of customerrelationshipmanagementistoproduce highcustomerequity.Thisisthe total combinedcustomerlifetime value of all of the company’scurrentandpotential customers.
- 7. Week: 3 LECTURE 3: The changing MarketingLandscape -the changingeconomicEnvironment,the digital Age THE CHANGING MARKETING LANDSCAPE. There isa popularlyheldviewthatthe onlypermanentthinginlife is‘change’,toa verylarge extent,thissayingistrue. As inmanyotherspheres of life,dramaticchangeskeep occurringona dailybasisinthe marketplace.AsRichardLove of HP putit ‘The pace of change is sorapid that the abilitytochange has nowbecome acompetitive advantage.’Yogi Berra,the legendaryNew York Yankeescatcherand manageralsosaid,‘The future ain’twhatit usedtobe.’As the marketplace keepschanging,somustthose who operate init. Under thistopic,we will examine five majordevelopmentsthathave changedandkeepchangingthe marketplace: the changing economicenvironment the digital age the growth of not-for-profitmarketing rapid globalizationand the call for more ethics and social responsibility
- 8. The changing economicenvironment:Asrecentas in2008, the UnitedStatesexperiencedaGreatRecession,a terribleeconomicmeltdown, the firstof itskindsince the Great Depressioninthe 1930s. The stock marketcrushedand trillionsof dollarsof marketvalue simply evaporated.The financial crisisleftconsumersshortof bothmoneyandconfidence inthe financial system. The Recessioncausedmostconsumerstosettheirspendingprioritiesrightandcutdownon theirbuying.Afteryearsof overspending, consumerswere tightenedtheirpursescutbackon theirspending. The Digital Age:The explosivegrowthindigital technologyhasfundamentallychangedthe marketplace.Ithaschangedthe waywe live, think,communicate, shop,share information,accessinformationetc.Thishashada major impacton the waycompaniesbringvaluesto theircustomers.Be thatas itmay,technologyhasbecome anintegerandnecessarypartof us. The growth of not-for-profitmarketing:inrecenttimes,the act of marketinghasbecome a majorpart of the strategiesof manynot-for- profitorganizations,suchas colleges,Universities, hospitals,museums,zoosetc.These not-for-profitsface stiff competitionforsupportand membership.A soundmarketingstrategycanhelpthemattract not only membershipbutfundsandsupport. Rapid globalization:Asmarketersare redefiningtheircustomerrelationships,theyare alsotakingafreshlookat the waysinwhichthey relate withthe broaderworldaroundthem.In the worldtoday,everycompany,large orsmall,istouchedinone wayor the otherby global competition. The call for more ethicsand social responsibility:Marketersare alsorapidlyrethinkingtheirrelationshipswithsocial valuesand responsibilitiesandwiththe veryenvironmentinwhichtheyare operating. Today,marketersare calledupontodevelopsustainableand environmentallyfriendlymarketingstrategies. Inmostcompanies,corporate ethicsandsocial responsibilityhave becomeahottopic for discussion.Everycompany’sactioncanaffectcustomerrelationships.Mostcustomersaroundthe worldtodayexpectcompaniestodeliver value ina sociallyandenvironmentallyresponsible way.
- 9. Week: 4 LECTURE 4: The Global Market place Lecture Synopsis: Looking at the global marketing environment, Deciding whether to go global, Deciding of which market place to enter, Deciding how to enter the market LOOKING AT THE GLOBAL MARKET ENVIRONMENT Previously,mostcompaniespaidlittle ornoattentionatall tointernational trade.Managersdidnotneedtolearnotherlanguages, deal withstrange changingcurrencies,face political aswell aslegaluncertainties,orevenadapttheirproductstodifferentcustomer needs expectations. Today however with globalization taking its toll on human activities, the situation has changed dramatically. Most organizations have now taken a global dimension and have gone global. But before deciding to go global, a company must understand the international marketing environment. That environment have over the years gone through a great deal of changes creating both new opportunities and problems. The International Trade System: Firmsthatwantto global muststartbyunderstandingthe internationaltrade system.Whensellingtoanothercountry,afirmmay be faced with series of restrictions. Governments may charge tariffs, taxes on certain imported products in their bid to raise revenue orprotectdomesticfirms.Mostgovernmentsaroundthe worlduse tariff toforce favourable trade behaviousfromother nations.
- 10. Countriesmayalsosetquotasor limitsonthe amountof foreignimportsthattheywill acceptincertainproductscategories.This is often done to conserve the foreign exchange and protect local industries and employment. Firms may also be faced with challengesfromexchange controls – thislimitsthe amount of foreignexchange andthe exchange rate againstother currencies. There could also be some nontariff trade barriers,suchas biasesagainstits bids,restrictive productstandardsorexcessivehost- country regulations or enforcements. However, there are still established institutions around the world that can help facilitate easier trade between nations of the world. Example, World Trade Organization (WTO) and various regional free trade agreements. -The WorldTrade Organization: The General AgreementonTariffsand Trade (GATT),establishedin1947 and modifiedin 1994, was designed to promote world trade by reducing tariffs and other international trade barriers. Thisbody was later replaced by the WorldTrade Organization in1995 andnowcarries outthe functionsonce dedicatedtoGATT.Previously,GATTandnowWTO members,currentlyconstitutingof 153 nations,have at leastroundsof negotiationstoreassesstrade barriersandestablishnew rulesfor international trade.The WTOalso has powerto impose international trade sanctionandmediate global trade disputes. The WTO has so far been very successful, in its first seven round negotiations, it succeeded in reducing the average worldwide tariff on manufactured goods from 45% to just 5%. -Regional Free Trade Zone: Certain countries have formed Free Trade Zones or Economic Communities.These are groups of nations organized to work toward common goals in the regulation of international trade. Such as the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) - 1975, European Union (EU) – 1957. Both set out to create a single economic zone for their individual regions byreducingbarriersto the free flowof products,services,finances,andlabouramong membercountriesand developing policies on trade with member countries. The Economic Environment: The international marketershave the dutyof studyingthe economyof eachcountry.Two basiceconomicfactorsmake a country attractive as a market: its industrial structure and its income distribution. INDUSTRIAL STRUCTURE The country’s industrial structure shapes its product and service needs, income levels, and employment levels. There are four main types of industrial structures: Subsistence economies: In a subsistence economy, the vast majority of the people engage in simple agriculture. They consume most of their output and barter the rest for simple goods and services. This sort of economy offers very few market opportunities. Many African countries fall into this category.
- 11. Raw material exporting economy: These are rich economies in one or more natural resources but poor in other ways. Much of their revenue comes from exporting these resources. These countries are also good markets for large equipment, tools and supplies and trucks. Emergingeconomies(industrializingeconomies): Inthissortof economy,fastgrowthinthe manufacturingresultsinrapid overall economicgrowth.Asmanufacturingincreasesinsuchcountries,thereisalsoanincreasingneedforimportedraw materials. Industrialeconomies: Theyare majorexportersof manufacturedgoods,servicesandinvestmentfunds.Theytrade goods among themselves and also export them to other types of economies for raw materials and semi-finished goods. INCOME DISTRIBUTION This is the second economic factor that attracts a state as a market to international firms.Industrialized nations may have low,medium,andhigh-income households.Incontrast,countrieswithsubsistence economiesconsistmostlyof households withverylow familyincomes.Butothercountriesmaystill have householdswitheitherverylowor very highincome.Even poor or emerging economies may be attractive markets for all kinds of goods. These days, companies in a wide range of industries are increasingly becoming interested in even low and middle income consumers in emerging economies. Political-Legal Environment: Every country in the world has its own political-legal system,and largely differs from state to state. In considering therefore whether to do business in a particular country, a company should consider factors such as the country’s attitudes toward international buying, government bureaucracy, political stability and monetary regulations. Cultural Environment: Each country has its own culture, tradition, norms and taboos. In strategizing for a global marketing venture, companies must understand how culture affects consumer reactions in each of its world markets. In turn, they must also understand how their strategies affect local cultures. DECIDING WHETHER TO GO GLOBAL Notall companiesneedtoventureintointernationalmarketstosurvive.Forexample,mostlocal businessesneedtotrade wellonly in theirlocal marketplaces.Most often,operating domesticallyiseasierandsafer.Operatingwithintheircountries,companiesdo not need to learn another country’s language and laws. They also do not have to deal with unstable currencies, face political and legal uncertainties, andredesign theirproductstosuitdifferentcustomerexpectations.However,companiesoperatinginthe global
- 12. industries,where their strategic positions inspecific markets are affectedstronglyby their overall global positions,must compete on a regional or worldwide basis to succeed. Before goingglobal,acompanymustweighseveral risksandanswermanyquestionsaboutitsabilitytooperate inthe global arena; - Can the company learn to understand the preferences and buyer behavior of consumers in other countries? - Can it offer competitively attractive products? - Will it be able to adapt to other countries’ business cultures and deal effectively with foreign nationals? - Do the company’s managers have the necessary international experience? - Has management considered the impact of regulations and the political environments of other countries? DECIDING WHICH MARKET(S) TO ENTER Before going abroad, the company should try to define its international marketing objectives and policies. It should decide what volume of foreign sales it wants. Most companies start small when they go abroad. Some even decide to stay small, viewing international salesasa small part of theirbusiness.Othercompanieshave biggerplans,however,seeinginternational businessas equal to or even more important than their domestic business. In deciding which marketsto enter, the company must decide on the following; - The company needstodecide onhow manycountriesit wantsto market.Companiesmustbe verycareful not to spread themselves too thin or expand beyond their capabilities by operating in too many countries too soon. - The companyneedstodecide onthe typesof countriesto enter.Howattracta countryislargelydependsonthe product, geographical factors, income and population, political climate, and other considerations. - After listing possible international markets, the company must carefully evaluate each one. Possible global marketsshouldbe rankedon several factors,includingmarketsize,marketgrowth,the costof doingbusiness,competitive advantage, and risk level. This is to be able to determine the potential of each market. DECIDING HOW TO ENTER THE MARKET As long as a company has to sell in a foreign country, it must determine the best mode of entry. Its choices are exporting, joint venturing, and direct investment. Exporting: The simplest way to enter a foreign market is through exporting. The company may passivelyexport its surpluses from time to time,orit maymake an active commitmenttoexpandexportstoa particularmarket.Ineithercase,the companyproducesall its goods in its home country. It may or may not modify them for its export market. Joint Venturing:
- 13. This is the second methodexposedtocompaniesforenteringthe foreignmarket;Joiningwithforeigncompaniestoproduce or marketproductsor services. Jointventure is differentfromexportinginthat,ina jointventure,the companyjoinswithahostof country partnersto sell ormarket abroad.It also differsfromdirectinvestmentinthatan associationisformedwithsomeonein the foreigncountry.There are basicallyfourtypesof jointventures;Licensing,ContractManufacturing,ManagementContracting, and Joint Ownership. - Licensing: This is a simple way for a manufacturer to enter the international market. The company enters into an agreement with a licensee in the foreign market. For a fee or royalty payments, the licensee buys the right to use the company’s manufacturing process, trademark, patent, trade secret, or other items of value. - Contract Manufacturing: Another option is contract manufacturing, this is a situation in which the company makes agreementswithmanufacturers inthe foreignmarketto produce its productsor provide itsservices.The disadvantages of this type of joint venture are decreased control over the manufacturing process and loss of potential profits on manufacturing.The benefitshoweverare the chance tostartfaster,withlessrisk,andthe lateropportunityeithertoform a partnership with or buy out the local manufacturer. - ManagementContracting:Underthistype of venture,thedomesticfirmprovidesthemanagementknow-howtoaforeign companythat suppliesthe capital. Orbetterstill,the domesticfirmexportsmanagement services rather than products. - Joint Ownership: Here, one company joins forces with foreign investors to create a local business in which they share possessionandcontrol.A companymaybuyaninterestinalocal firm,orthetwopartiesmayformanewbusinessventure. Sometimes this sort of venture is needed economic and political reasons. Direct Investment: Thisis the biggestformof investmentina foreignmarket.Thishasto do withthe companydevelopingaforeign-basedassembly or manufacturingfacilities. Fordforexample hasmade several directinvestmentsinmostAsiancountriesoverthe pastdecades.
- 14. Week: 5 LECTURE 5: Product, Services and Brands Lecture Synopsis: Definition of Product Product and services decision Services Marketing PRODUCTS, SERVICES AND BRANDS: In orderfor marketerstosuccessfullyestablishandmaintainaverygoodcustomerrelationship,amongotherthings,theymustalso developandmanage productsandbrandsthat connectwithcustomers.Butfirstly,we will take alookatsome keydefinitions;Products, Servicesand Experiences Product: Product couldbe definedasanythingtangible orintangible thatcanbe offeredtoa marketfor attention,acquisition,use or consumptionthathasthe abilitytosatisfyawantor need. Services:Broadlydefined,are aset of productsthat constitute activities,benefits,andevensatisfactionsofferedforsale thatare essentiallyintangibleanddonot resultinthe ownershipof anything. Experiences:experienceshave alwaysbeenaveryimportantpartof marketingforthe most companiesaroundthe world.Today,itis importantto note thatall mannerof firmsare recastingtheirtraditional goodsandservicestocreate experiences.Companiesthat marketexperiences have realizedthatcustomersare reallybuyingwhatthose offerswill doforthem.A recentBMW ad puts itthis way:‘We realizedalongtime agothat whatyou make people feel isjustasimportantaswhat youmake.’ Levelsof Product and Services
- 15. Productplannersneedtothinkaboutproductsand servicesonthree levels.Eachlevel of productaddsmore customervalues.The mostbasic level isthe core customervalue,anditaddressesthe question:What isthe buyerreallybuying?Anytimeamarketerwantstodesignaproduct, theyshouldfirstdefinethe core,orproblem-solvingbenefitsorservicesthatthe productissetto renderinrelationtowhatthe target consumersare seeking. At the secondlevel,productplannersmustturnthe core benefitintoanactual product.Theyneedat thisstage to developproductandservice features,adesign,aqualitylevel,abrandname and packaging. Lastly,productplannersmustbuildanaugmentedproductaroundthe core benefitandactual productby offeringadditional customerservices and benefits. Forexample,the iPadismore thanjusta digital device,itprovidescustomerswithacomplete connectivitysolutions. In a nut shell,whendevelopingaproduct,marketersmustfirstidentifythe core customervalue thatconsumersseekfromthe product.Then designthe actual product,and finallyfindwaystoaugmentittocreate thiscustomervalue andthe most satisfyingbrandexperience. Product and Service Classification Productsare broadlyclassifiedintotwomaincategories; ConsumerandIndustrial Products. ConsumerProducts: Theyare those goodsand servicesthatare boughtby final consumersforpersonal use orconsumption. Industrial Products: these are goodsand servicesboughtbyindividuals and/ororganizations forfurtherprocessingoruse inconductinga business. PRODUCT AND SERVICE DECISIONS Marketershave the responsibilityof makingdecisionswhenitcomestoproductand service inthe industryandsuchdecisions are made atthree basiclevels; Individual product and service decision Product line decision Product mix decision Individual Product and Service Decision:Thisis basicallywithimportantdecisionstakeninthe developmentandmarketingof individual productsand services.Itrangesfromdecisionabout productattribute,branding, packaging, labelingrightthroughto product support services.
- 16. . Product and Service Attributes:Developingaproductlargelyinvolvestakingcrucial decisiononthe benefitsthatproductwill offerorthe problemsitissetto solve.Suchbenefitsare communicatedbythe attributesof the product,suchas quality,features and style and design. i. Product quality:Thisisone major tool inthe handsof the marketer.Qualityaffectsproductorservice performance,itistherefore closelylinkedtocustomervalue andsatisfaction.Siemensdefinesqualityas ‘qualityiswhenourcustomerscome backandour productsdon’t.’ ii. Product Features: A product can be offeredwithvaryingfeatures. Featuresare acompetitive tool of differentiatingthe company’s productsfrom those of itscompetitors.A companycan be able to decide onwhatand whatfeaturestoadd on itsproductsby conductinga regularsurveyamongitscustomersandsuch questionsas;howdoyou like the product?Whichspecificfeaturesdo youlike moston the product?Whichfeaturescouldwe addto improve the product? Couldbe putto them,answerstosuch questionscouldprovidethe companywithrichlistof productfeatures ideas. iii. Product Style andDesign: Thisisanotherway bywhichmarketerscan addcustomervaluestotheirproductto distinguishthem fromthose of theircompetitorsandattractcustomers.Style anddesignare howeverslightlydifferent,whereasstyle describesthe appearance of a product.It can be eye catching;a sensational stylemaygrabattentionandproduce pleasingaesthetics,butdoes not necessarilymake the productperformbetter.Designismore thanskin deep;itgoestothe veryheartof the product.A good designaddsto the product’susefulnessaswell astoitslooks. . Product Branding: One of the most outstandingskillsof professional marketingistheirabilitytodesignandmanage abrand.Brand isa name, term,sign,symbol,ordesign,ora combinationof all these,thatidentifiesthe productsservicesof one company,sellerorgroupof sellersand differentiatesthemfromthose of competitors. . Product Packaging: Packagingsimplymeansdesigningthe containerorwrapperforthe product. The major ideabehindpackagingwastohold and protectthe product.This has howeverchangedoverthe yearsaspackaginghas become animportantmarketingtool aswell.Asone packagingexpertputit;‘Noteveryconsumerseesabrand’sadvertisingorisexposedtothe excitingsocial mediathatyour brandis doing.Butall of the consumerswhobuyyourproductsdo interactwith yourhumble package.’ Companieshave largelybecome aware of the powerof goodpackagingtocreate immediate consumerrecognitionof abrand. .Product Labeling:This range fromsimple tagsattachedto productsto complex graphicsthatare part of the packaging.Labelingperforms several functionsonaproduct.At least,the label identifiesthe productorbrand.Labelsmightalsodescribe several thingsaboutthe product – whomade it, itscontents,howitisto be usedandhow touse itsafe.
- 17. . Product Support Services:Thisalsoknownas customerservice isanotherelementof productstrategy.A company’sofferusuallyconstitutes some supportservices,whichcanbe incorporatedasminoror major part of the total offering. Supportservicesmaysuchhelptocustomersas, droppingordersat theirhomes,cleaninguptheircarsas theyshopin yourstore,helpthemcarry theirluggage aftershop, etc. Product line decisions:Besidesdecidingwhattoproduce as a company,productstrategyalsocallsfor buildingaproductline.A ProductLine isa range of similarorcloselyrelatedproductsproducedbythe same company,functioninasimilarmanner,soldtothe same customergroups, theyare marketedthroughthe same typesoutletsorfall withinagivenprice ranges. Forexample,the SierraLeone BottlingCompanyproduces wide range of softdrinks. Product mix decisions:Anorganizationwithseveral productlinesissaidtohave a Product Mix.A ProductMix (ProductPortfolio) istherefore made up of all the productline anditemsthata particularselleroffersforsale. Exercise One:Please think of a company within Sierra Leone that has a Product Mix. SERVICES MARKETING In recentyears,serviceshave undergone adramaticincrease andare nowresponsibleforawhopping65% of the US GDP forexample.Service industriesvaryalot.Governmentsaroundthe worldforexample renderservicesthroughcourts,employment services,hospitals,military services,policeandfire departments,etc.Private not-for-profitorganizationsofferservicesthroughcharities,Churches,Universities,Colleges, Foundations,etc.BusinessOrganizationsdoitthroughairlines,hotels,insurance companies,etc. The Nature and Characteristics ofa Service: In designingamarketingprogramme companiesmustconsiderfourbasiccharacteristicsof service:intangibility,inseparability,variability,and perishability. Service Intangibility:thissimplymeansthatservice cannotbe perceivedbyanyof the five senses,ie itcannotbe seen,tasted,heard, felt,orsmelledbefore theyare bought.However,toreduce the levelof uncertainty,buyusuallylookforsignals of servicequality.They oftendrawconclusionsaboutqualityfromthe place,people,price,equipmentandcommunicationthattheycansee.Asa result,the service providerhasthe taskof makingthe service tangible inone ormore waysand sendsthe rightsignal aboutthe quality of the service. Service Inseparability:Thismeansthatyou cannotseparate servicesfrom theirproviders,whetherthe service providersare people or machines.
- 18. Service Variability:Thismeansthat the qualityof a particularservice dependsonwhoprovidesit,when,where andhowitisprovided. Service Perishability:Thismeansthatservicescannotbe storedforlatersale or use. Marketing Strategiesfor service Firms: Like manufacturingcompanies,service firmsalsouse marketingstrategiestopositionthemselveswellinthe marketplace.Mostoften,theydoit throughtraditional marketingmix activities.However,becauseservicesdifferfromtangible products,theyoftenrequire additional marketing approaches. The Service ProfitChain: In the service business,the front-line service employees andthe customerofteninteracttoco-create the service.However,sucheffective interactionlargelydependsonthe skillsof the front-line service employeesandthe supportprocessesbackingthe employees.Therefore, mostservice companiesfocustheir attentionsonboththeiremployee andtheircustomer.Theybasicallyunderstandthe service profitchain whichservesasa linkbetweenthe service firmprofitsandwithemployeeandcustomersatisfaction.The service profitchainconsistsof five linkswitheachpreviouslinkleadingtoa newone: Internal Service Quality: Superioremployee selectionandtraining,aconducive workenvironment,andstrongsupportforthose dealingdirectlywithcustomers. Thisleadsto… Satisfiedand Productive Service Employees:more satisfied,loyal andhardworkingemployees.Thisresultsin…. GreaterService Value:More effective andefficientcustomervalue creationandservicedelivery,whichresultsin… Satisfiedand Loyal customers: a satisfiedcustomermayremain loyal,make repeatedpurchasesandevenreferothercustomersto the service,thiscanresultin… Healthy Service profitsand growth: superiorservice firmperformance. Service marketingrequiresmuchmore thanjustthe traditional external marketingusingthe 4Ps,italsorequireswhatisknownas Internal Marketing.Internal marketingrequiresthatservice firmsmustorientate andmotivate itscustomer-contactemployeesandsupportingservice people toworkas a teamto provide customersatisfaction.Marketersmustgeteveryoneinthe firmtobe customercentered. Interactive Marketing whichalsomeansthatservice qualitylargelydependsonthe quality of buyer-sellerinteractionduringthe service encounterisalsoa veryimportantservice marketingtool tobe engaged.
- 19. In today’smarketplace,ascompetitionandcostsincrease,andasproductivityandqualitydecrease, thereisanincreasingneedforservice marketingsophisticationisneeded.Service companies are facedwiththree majormarketingtasks:Theywantto increase their service differentiation,service quality,andservice productivity. (i) Managing Service Differentiation:Inthe currentprevailingmarketplacewith intense price competition,service marketersoften complainaboutthe difficulttaskof differentiatingtheirservicesfromthose of competitors.Toan extentthatevencustomersfindit difficulttodifferentiatebetweenservicesprovidedbydifferentservice provider,infactmostof themcare lessaboutthe provider than theydothe price.The solutiontosuchprice competitionis todevelopadifferentiatedoffer,delivery,andimage. (ii) Managing Service Quality: Ina tensedcompetitivemarketplace like ourstoday,aservice firmcandifferentiateitself bydelivering consistentlyhigherqualitythanitscompetitors canoffer. (iii) Managing Service Productivity:withtheirhighrisingcost,service firmsare underhighpressure toincrease serviceproductivity.And thiscan be done inseveral ways.Constanttraininganddevelopment(T&D) of employeesorhire newones whowill workharderand more skillfully.Orbetterstill improve the quantityof theirservice bygivingupsome quality.
- 20. WEEK: 6 LECTURE 6: PRICING:UNDERSTANDING AND CAPTURING CUSTOMER VALUE -Definition of price, Major Price strategies, Factors affecting pricing decision WHAT IS A PRICE? Price isbasicallythe amountof moneychargedfora productor service.Ina broadersense however,we candefine price asthe sumtotal of all the valuesa customerisable,willingandreadytogive upto gain the benefitsof havingorusingaproduct or service.Price hasalwaysbeenthe majorfactor affectingthe buyerchoice.Butinthe recentpast,non-price factorshave gainedincreasing importance. Of all the marketingmix,price isthe onlyone thatproducesrevenue andit’sthe mostflexible,all othersrepresentcosts. Atthe same time, pricingisone of the majorproblemsfacedbymarketingexecutivesandsadto saythat many companiesdonothandle pricingwell. Major Pricing Strategies:Pricesof commoditiesandservicesare oftensetbetween twoextremes;eithertoolowto produce a profitor too highto produce anydemand.Insettinga price ceilinghowever,customer’sperceptionof the product’svalue formsthe basis. Onthe one hand,whencustomersperceivethatthe product’sprice isgreaterthan itsvalue,theymaywithdrawentirelyfrombuyingit.Onthe otherhand,if the company’ssetprice isbelowitscost,the company’sprofitwill suffer.Therefore,insettingitsprice betweenthese two extremes,the companymustconsiderthe followinginternal aswell asexternal factors;competitors’strategiesandprices,the overall marketingstrategyandmix,andthe nature of the marketand demand. As a resulttherefore,there are three majorpricingstrategies:customervalue-basedpricing,cost-basedpricingandcompetition-based pricing.
- 21. (ii) CustomerValue-BasedPricing:The consumerisalwaysthe lastpersontodecide whetheraproduct’sprice isright.Thusin makingdecisionaboutpricing,customervalue mustbe stronglyconsidered.Anytime,acustomerbuys a product,they exchange somethingof value (price) togetsomethingof value (thebenefitsof havingorusingthe product).Effective customer-orientationpricingtherefore involvesunderstandinghowmuchvalue consumersplace onthe benefitsthey receive fromthe productandsettinga price that capturesthat value. (iii) Cost-BasedPricing: Thisinvolvessettingpricesbasedonthe costof production,distributionanda fairrate of returnfor its effortandrisks.For some companies,their costof productionisoftenanimportantelementinitspricingstrategy. Companieswithlowercostof production,oftensetlowerpricesthatresultinsmallermarginsbutgreatersalesandprofits. There are twomajor typesof cost; fixedandvariable cost. - FixedCost: A company’sfixedcosts,alsoknownasoverheadcostsare the costs that donot change withchange in productionorsaleslevel.Forinstant,regardlessof acompany’soutput,itmustpay bills,interestrate,salariesetc. - Variable Cost: These sortsof costsvary directlywiththe levelof production.Theyare calledvariablesbecause the total varieswiththe numberof unitsproduced.These twocombinedisknownasthe total cost at everylevel of production. (iv) Competition-BasedPricing: Thisbasicallyinvolvessettingupaprice basedon competitor’sstrategies,costs,prices,and marketofferings.Here,consumersbase theirjudgmentsof aproduct’svalue onthe pricesthat competitorscharge for similarproducts. In assessingacompetitor’spricingstrategies,the companyshouldaskseveral questions.Firstly,howdoesthe company’s marketofferingcompare withcompetitors’offeringsintermsof customervalue?If consumersperceive thatthe company’s productor service providesgreatervalue,the companycancharge a higherprice.If consumersperceive lessvaluerelative to competitors’products,the companymusteithercharge alowerprice orchange customerperceptionstojustifyahigher price.Secondly,howstrongare currentcompetitorsandwhatare theircurrentpricingstrategies?If the companyisfaced witha host of smallercompetitorscharginghigherpricesrelative tothe value theydeliver,itmightcharge lowerpricesto drive weakercompetitorsfromthe market.Inthe similarvein,if the marketisdominatedbylarger,lower-price competitors, the companymay decide totargetunservedmarketnicheswithvalue addedproductsathigherprices. FACTORS AFFECTING PRICE DECISIONS.
- 22. Factor affectingprice decisionscanbe broadly dividedintoInternal andExternal factors. Internal Factors affectingprice decisioninclude the company’soverall marketingstrategy,objectives,andmarketingmix,aswellasotherorganizational considerations. External Factorsinclude the nature of the marketand demandandotherenvironmental factors. - Overall marketing strategy, objectives,andmarketing mix Price isonlyone elementof the company’sbroadermarketingstrategy. Therefore,before settingupanyprice,the companymustdecide onits overall marketingstrategyforthe productorservice. There are timeswhenthe company’soverall marketingstrategyisestablishedaroundprice andvalue history.Forinstance,if acompanyselects a particulartarget marketand positioningverycarefully, thenitsmarketingmix includingprice,willbe fairlystraightforward.Pricingcanplaykey role inhelpingafirmaccomplishitsobjectivesatmanylevels.A firm forexample cansetpricestoretainexistingcustomersandattractnew ones.Itcan evensetpriceslowtopreventcompetitorsfromenteringthe marketorsetit at competitors’ level tostabilize the market.Itcan set price to keepthe loyaltyandsupportof resellersandtopreventoravoidgovernmentintervention.Firmscanalsoset price forcreate excitement for newproductsand/orbrands.Or a particularproduct can be pricedto helpthe salesof otherproductsinthe company’sline. Price decisiontherefore shouldbe properlycoordinatedwithproductdesign,distribution,andpromotiondecisiontoforma consistentand effectiveintegratedmarketingmix programme. -Organizational Considerations At organizational level,managementshoulddecide whosetsprices.Companieshandle pricinginvariousways.Insmallerfirms,pricesare often setat topmanagementlevelsinsteadof bythe marketingorsalesdepartments.Inlarge companies,pricinginhandledbydivisional orproduct managers. Inthe industrial market,salespeoplemaybe allowedtonegotiate withcustomerwithincertainprice ranges,butevenso,top managementsetsthe pricingobjectivesandpolicies,andoftenapprovesthe pricesproposedbylower-level managementorsalespeople. -The Market and Demand As statedearlier,goodpricingbeginswithaverygoodunderstandingof howcustomers’perceptionsof value affectthe pricestheyare willingto pay.Both consumerandindustrial buyersbalance the price of aproductsor service againstthe benefitsof owningit.Therefore,beforesettinga price,the marketermusthave a properunderstandingof the relationshipbetweenprice anddemandforcompany’sproduct. Belowisan analysisof the price-demandrelationshipandhowitvariesfordifferenttypesof markets.
- 23. Pricingin Different Types ofMarkets The level of freedom thatsellershave overpricingvariesaspermarket.Economistsrecognize fourtypesof marketswitheachpresentinga differentapricingchallenge.(i) Underpure competition, (ii) Undermonopolisticcompetition(iii) Underoligopolisticcompetition(iv)Underpure monopoly. (i) Underpure competition:Thismarketconsistsof manybuyersand sellerswhotrade inauniformcommodity,suchassugar, wheat,copper,orfinancial security.Inthissortof market,no single buyerorsellerhasmucheffectonthe goingmarket price.Also,inthissortof market,marketingresearch,productdevelopment,pricing,advertising,andsalespromotionplay little ornorole.Therefore,sellersdonotspend muchresource onmarketingstrategy. (ii) UnderMonopolisticCompetition:The marketismade up of many buyersaswell assellerswhotrade overa range of prices rather thana single marketprice.Differentpricesare oftensetupinthe marketbecause sellerscandifferentiate theiroffers to buyers.Because there are series of competitors, eachfirminthe marketplace is lessaffectedbycompetitors’pricing strategiesthantheywouldinanoligopolisticmarket. Sellerstryhardto developdifferentiatedoffersfordifferentcustomer segmentsand,inadditiontoprice,freelyuse branding,advertisingandpersonal sellingtosettheiroffersapart. (iii) UnderOligopolisticCompetition:Here the marketismade upof justa fewlarge sellers.Forinstant,onlytwocompanies (Airtel andAfricel) control over80%of the SierraLeone mobile networkservice providermarket.Becausethere are veryfew sellersinthismarket,eachsellerisalertandveryresponsivetocompetitors’pricingstrategiesandmarketingmoves. (iv) Undera Pure Monopoly: Thismarketisbasicallydominatedbyasingle seller.Thissingle sellermaybe agovernment monopoly(EDSA,SLPOST),aprivate regulatedmonopoly(supersport),ora private unregulatedmonopoly.Ineachof these cases,pricingishandleddifferently. An analysisofthe Price-DemandRelationship Each time a companymakesany change in itsprices,itwill leadtoa differentlevel of demand.The relationshipbetweenthe price changedand the resultingdemandlevel isshowninthe demandcurve below.
- 24. Price 𝑃2 𝑃12 𝑃1 𝑃11 𝑄2 𝑄1 𝑄12 𝑄11 Quantitydemandedperperiod Quantitydemandedper period A. Inelasticdemand B. Elastic demand The above demandcurve showsthe numberof unitsthe marketwill buyina givenperiodatdifferentpricesthatmightbe changed.Invery normal situations,demandandprice are inverselyrelated,ie,the higherthe price,the lowerthe quantitydemanded.Therefore,the company wouldsell lessif itraiseditsprice from 𝑃1to𝑃2. In short,consumerswithlimitedresource willprobablybuylessof somethingif itsprice istoo high. A goodunderstandingof abrand’sprice-demandcurve isverycrucial togoodpricingdecisions. Price Elasticity of Demand Lookingat the two demandcurvesabove,infigure A,aprice shift(increase) from𝑃1to𝑃2 leadstoa relativelysmalldropindemandfrom 𝑄1to 𝑄2. In figure B,however,the same price increase leadstoa large dropin demandfrom𝑄1to 𝑄2. If demand hardlychangeswithasmall change in price, we say thatthe demandisinelastic.If onthe otherhand,the demandchangesgreatly,inthatcase the demandinelastic.The price elasticityof demandisgiveninthe followingformula: Price elasticityof demand= %𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑑𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑑 %𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒𝑖𝑛 𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒 -The Economy The economicconditionscanhave a verystrongimpact onthe firm’spricingstrategies.Economicfactorlike growthorrecession,inflation,and interestratesaffectpricingdecisionsbecause theyaffectconsumerspending,consumerperceptionsof the product’sprice andvalue,andthe company’scostsof producingandselling the product. -OtherExternal Factors
- 25. Beyondthe marketandthe economy,the companymustconsiderseveralotherfactorsinitsenvironmentwhensettingprices. The firmmustbe able to knowwhicheffectitspriceswillhave onotherpartiesinitsenvironment.Howwillresellersreacttovariousprices?Companiesshould therefore setpricesthatgive resellersafairprofit,encourage theirsupport,andhelpthemtosell the producteffectively.