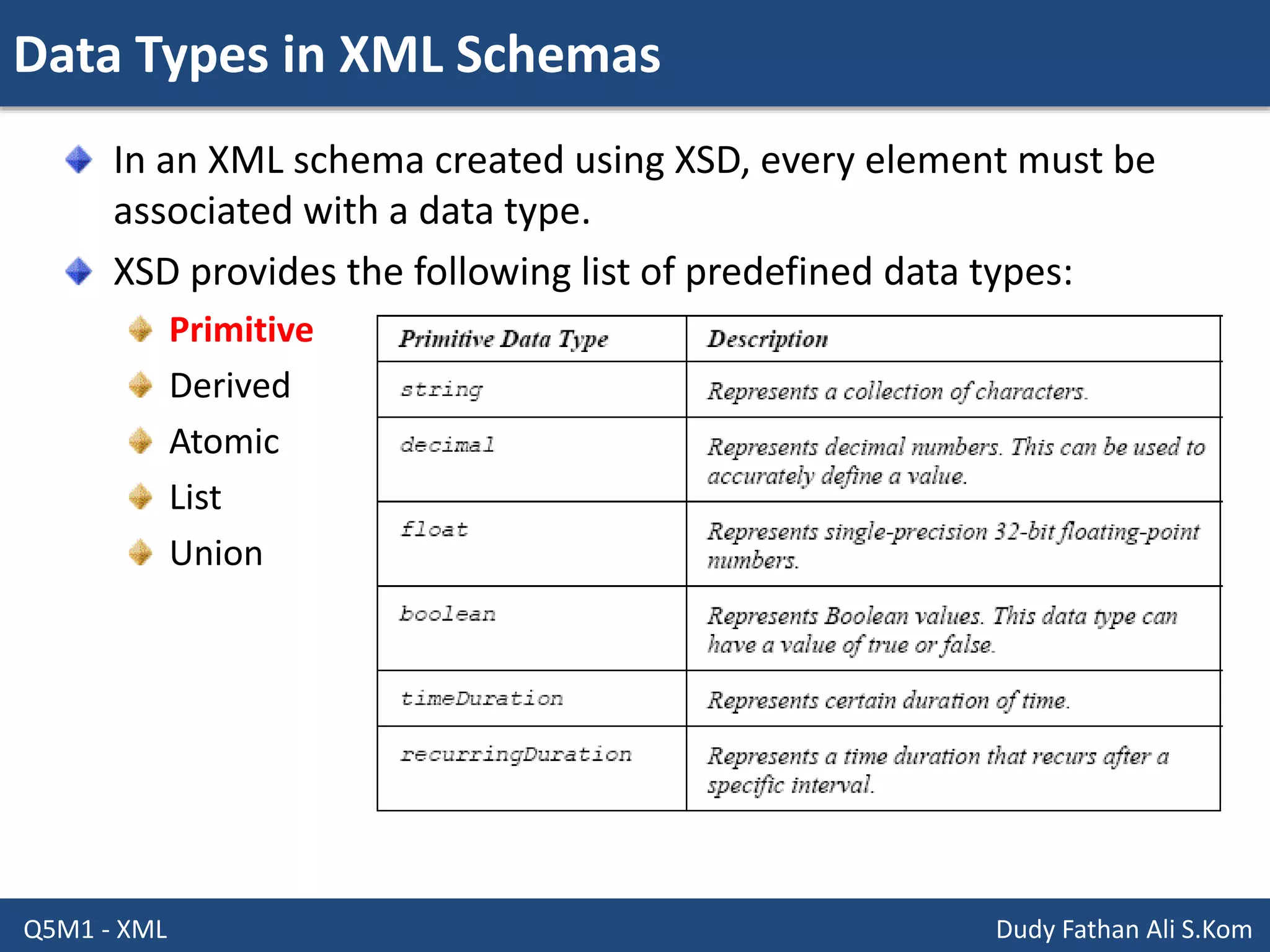
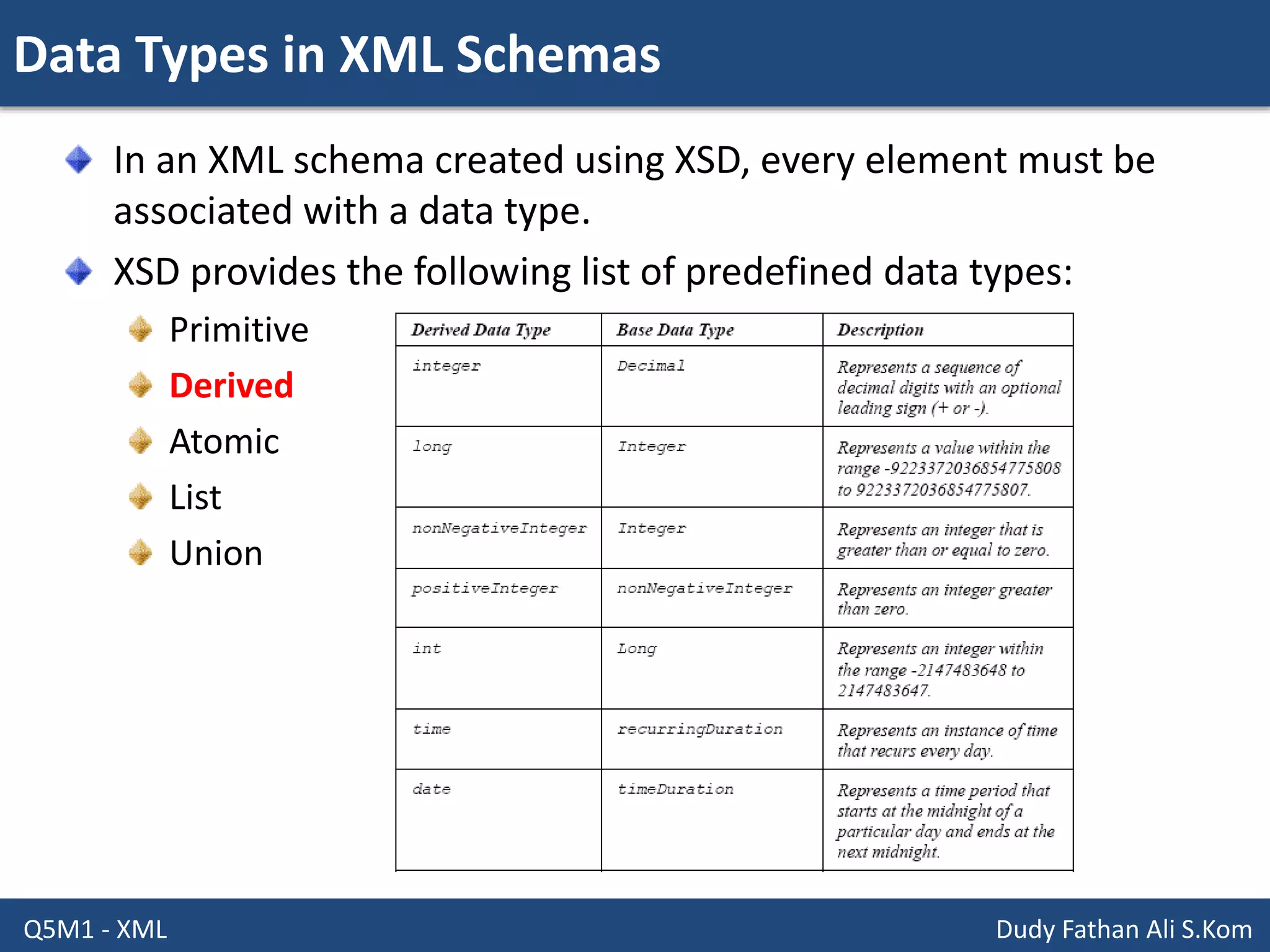
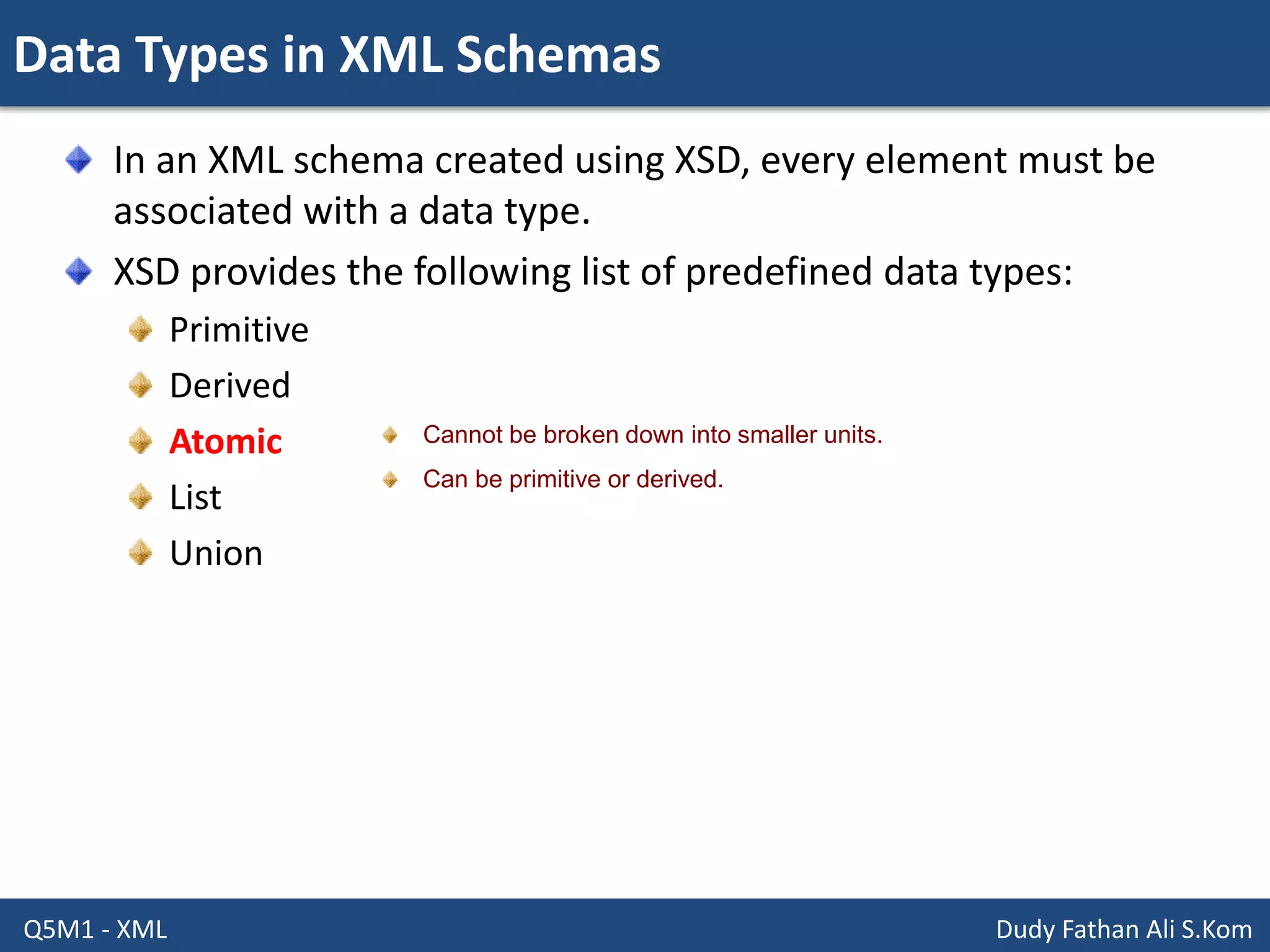
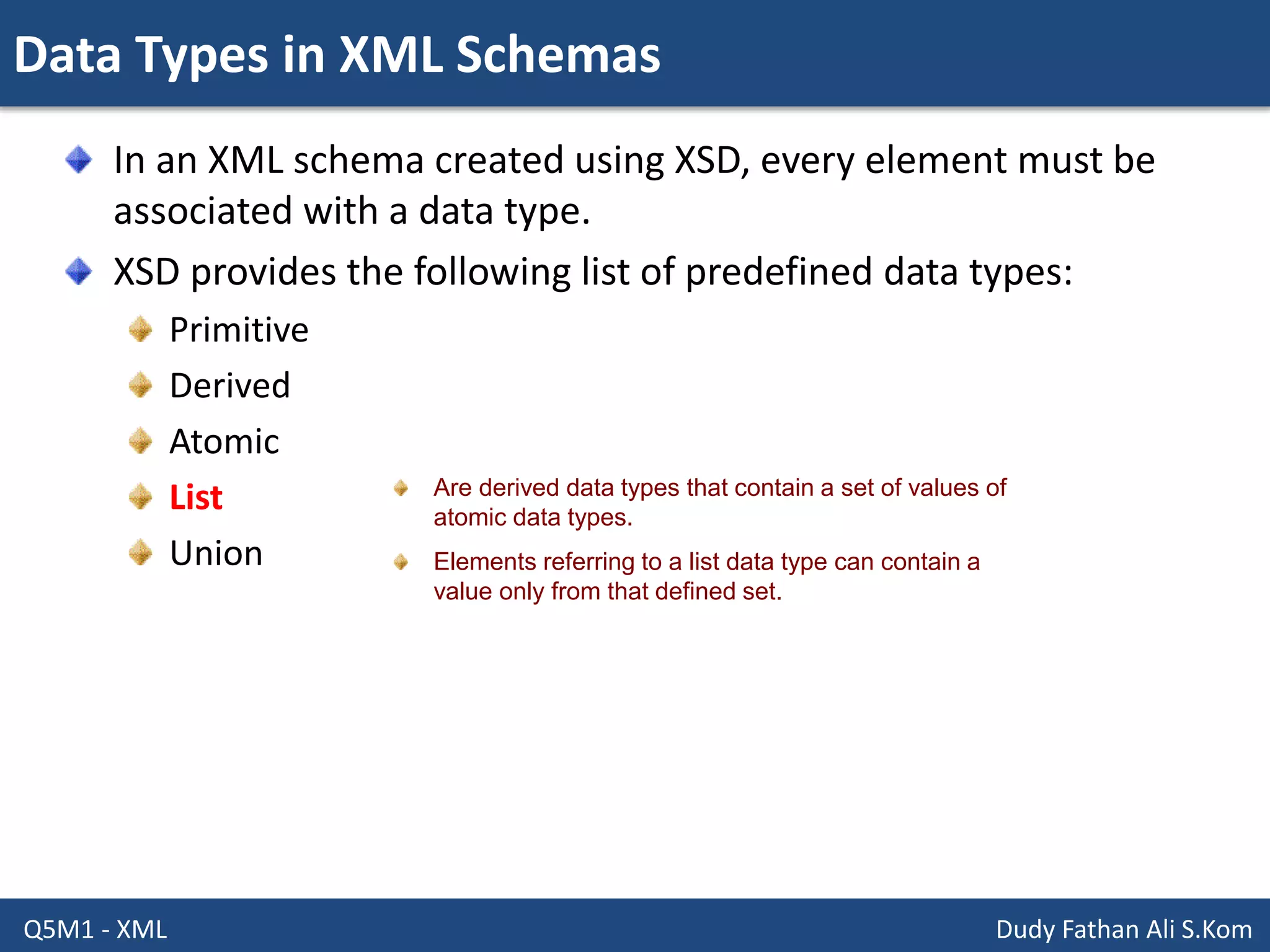
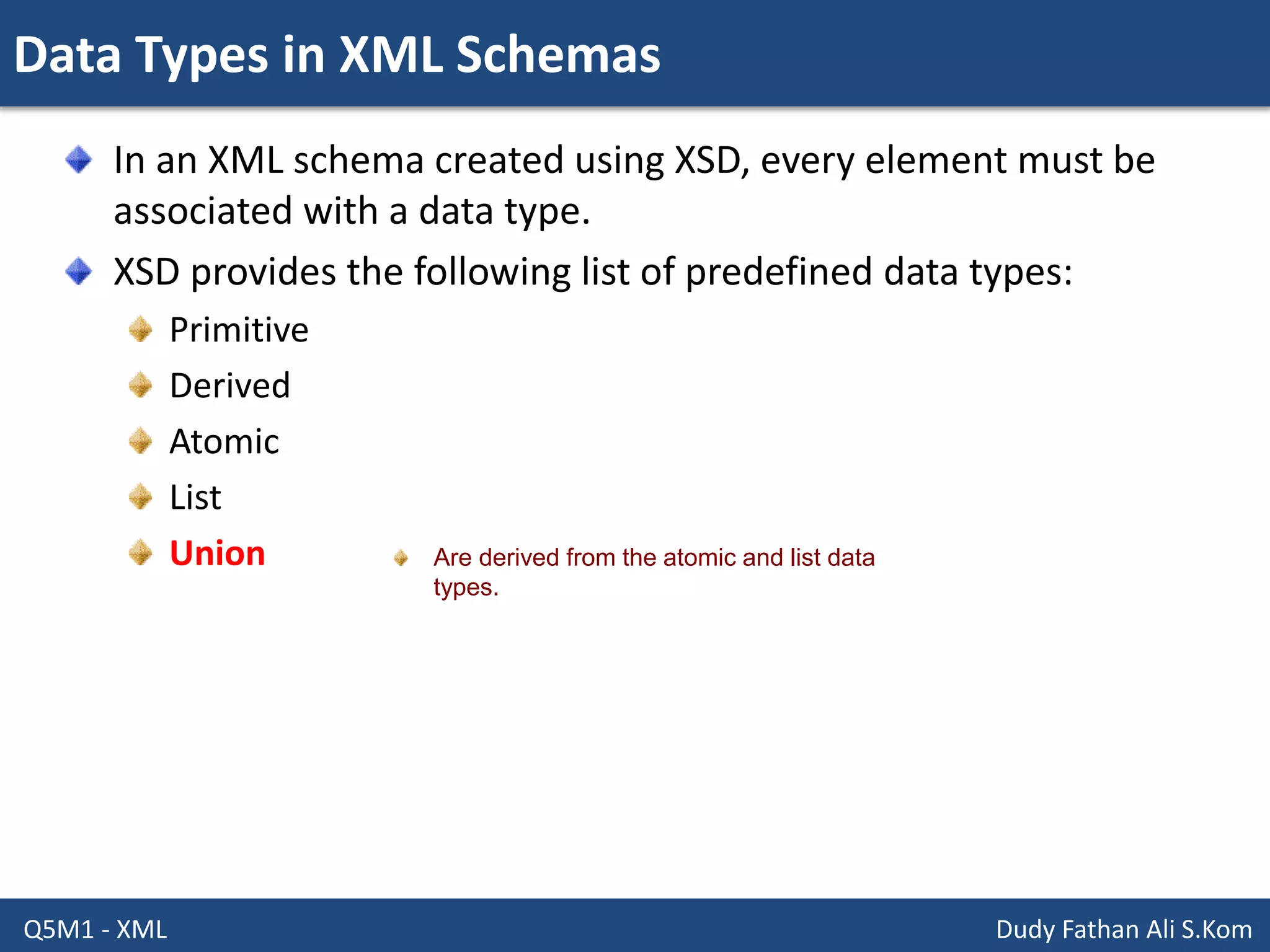
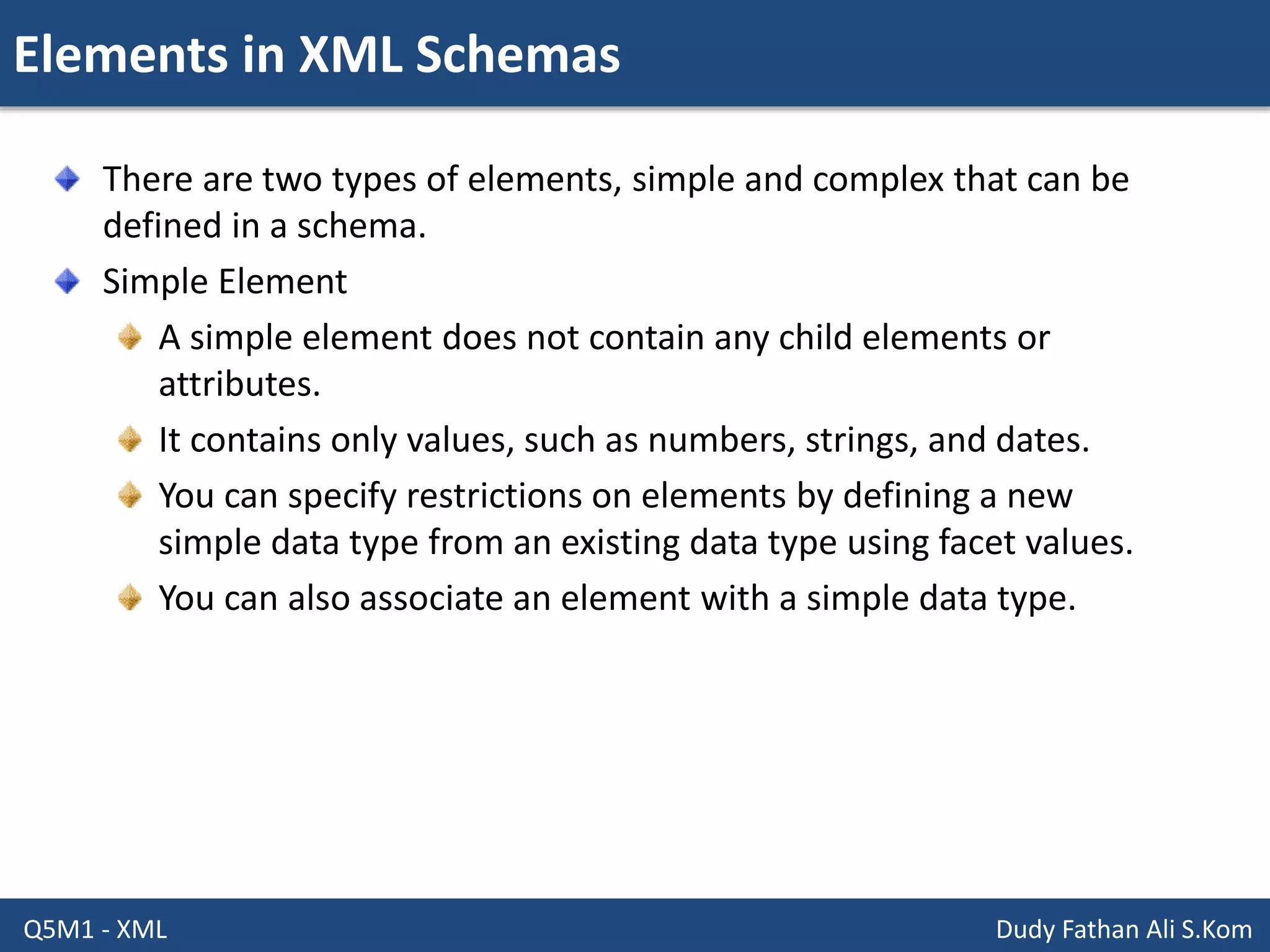
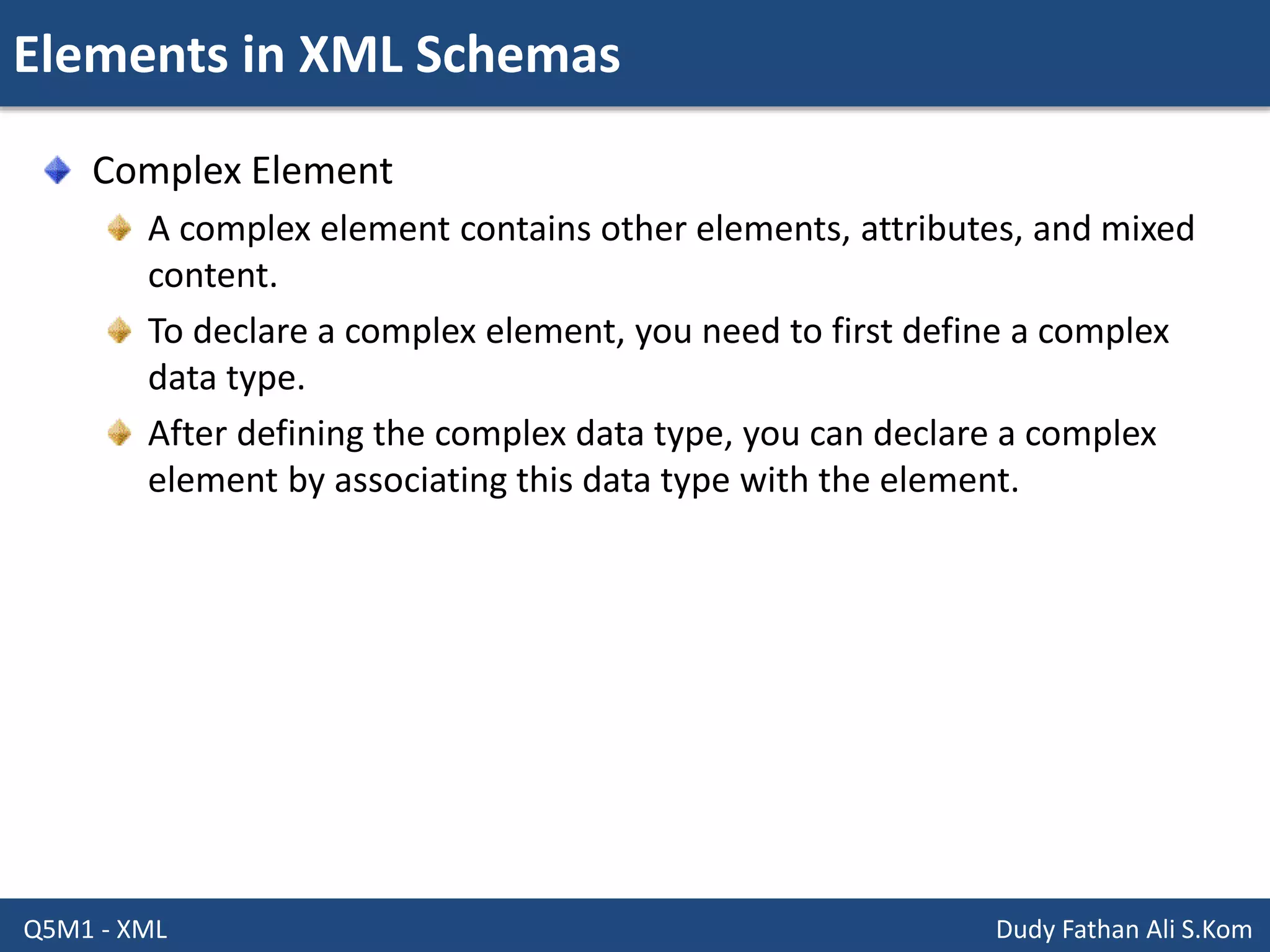
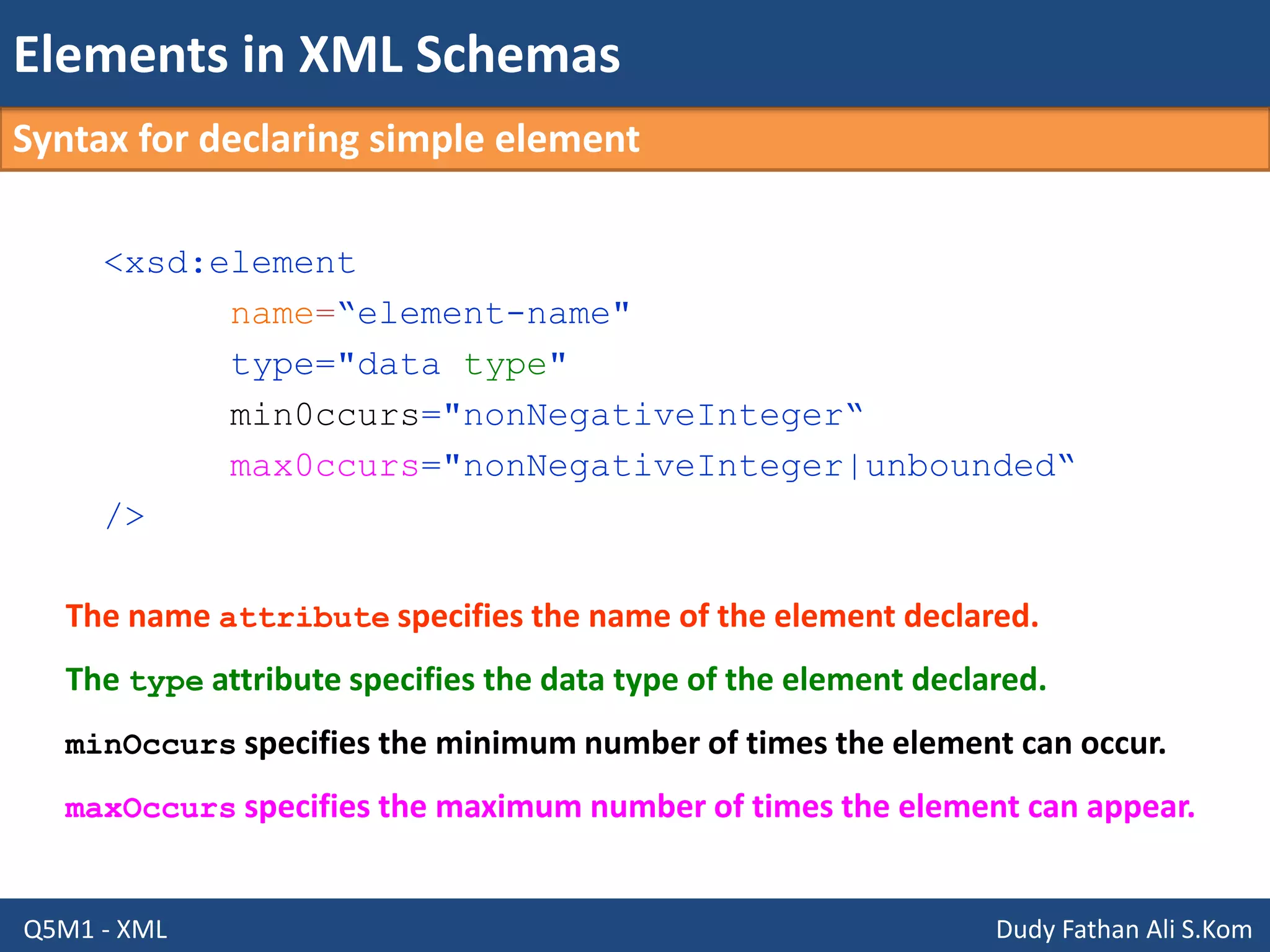
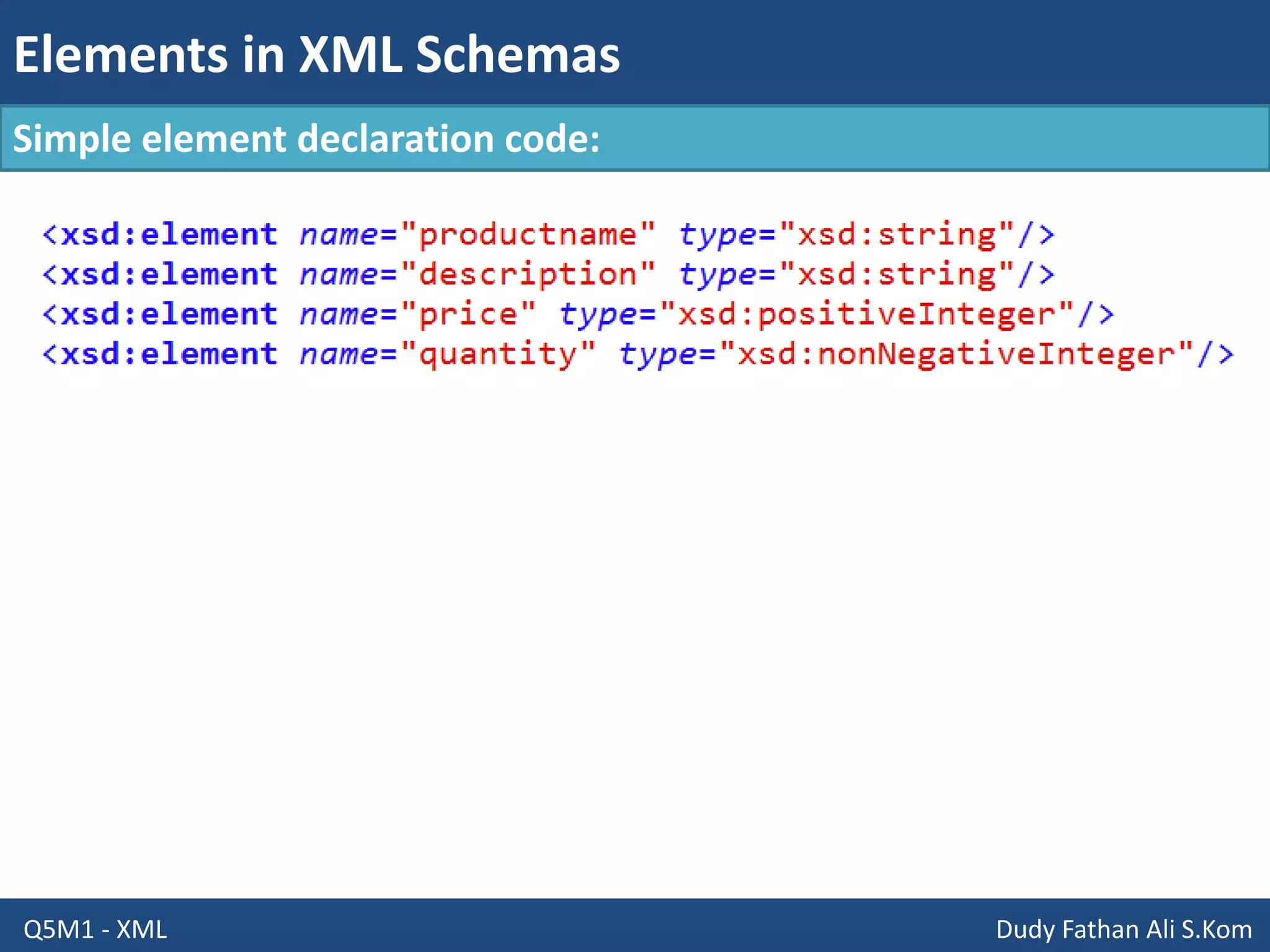
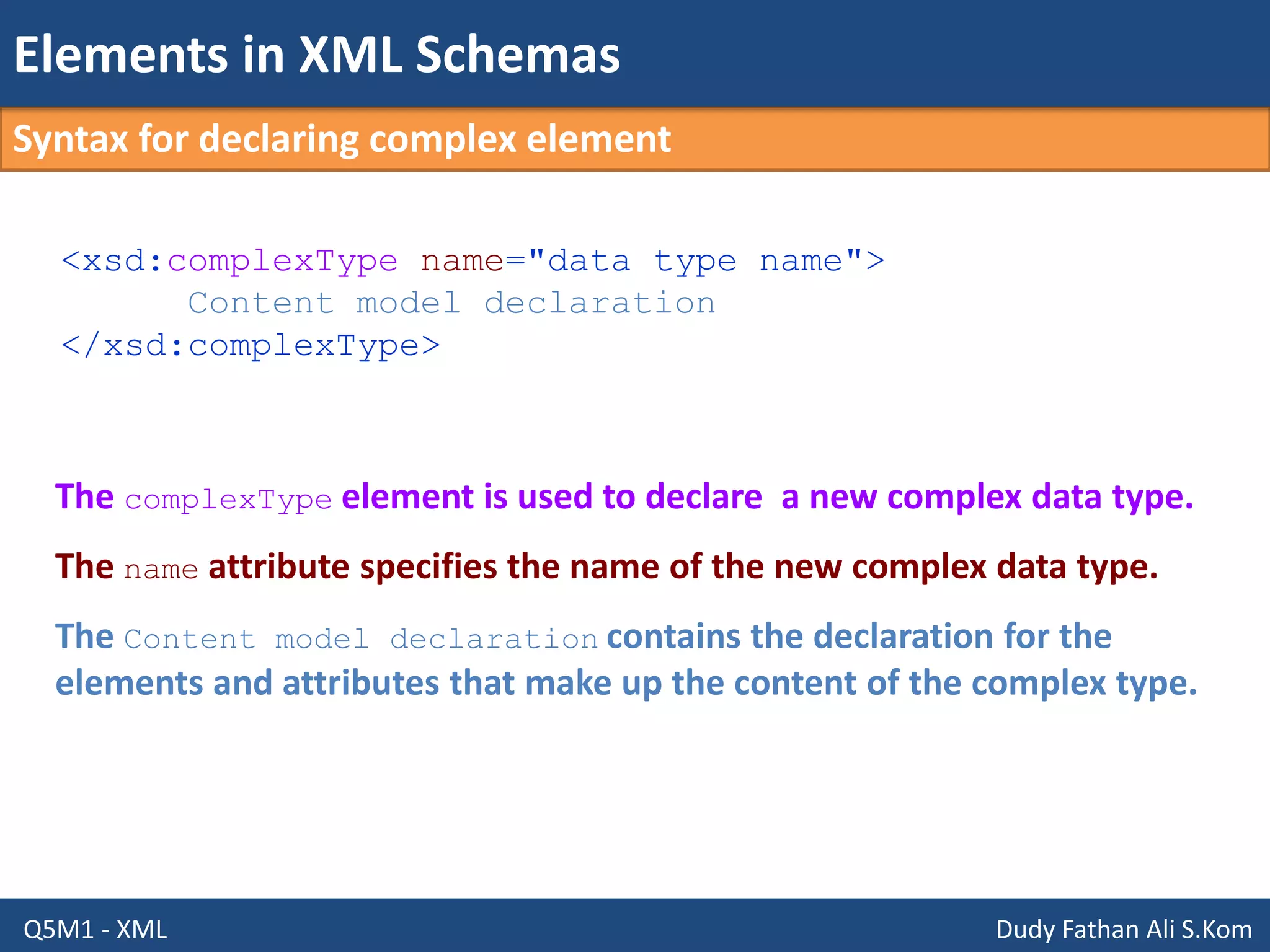
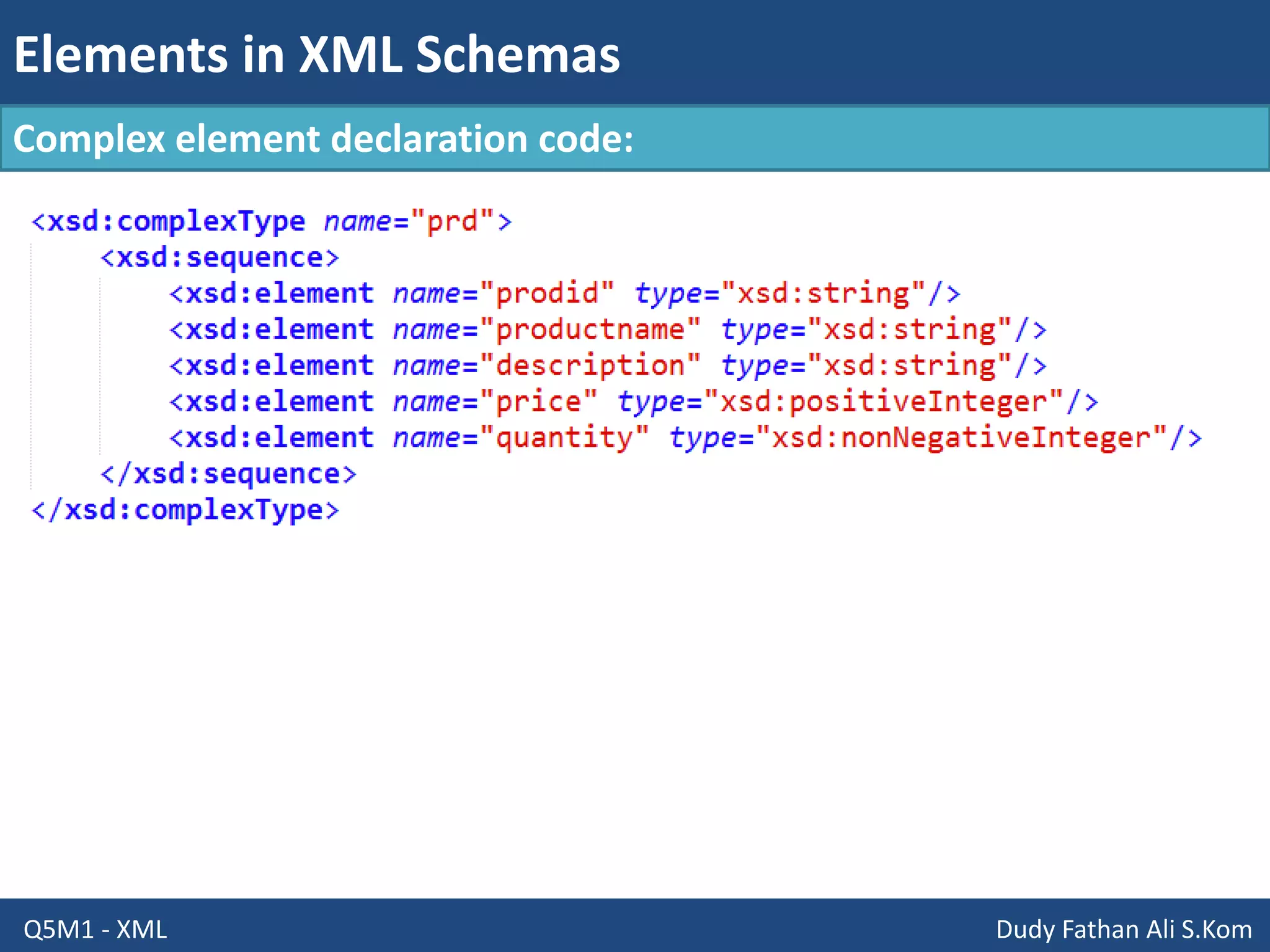
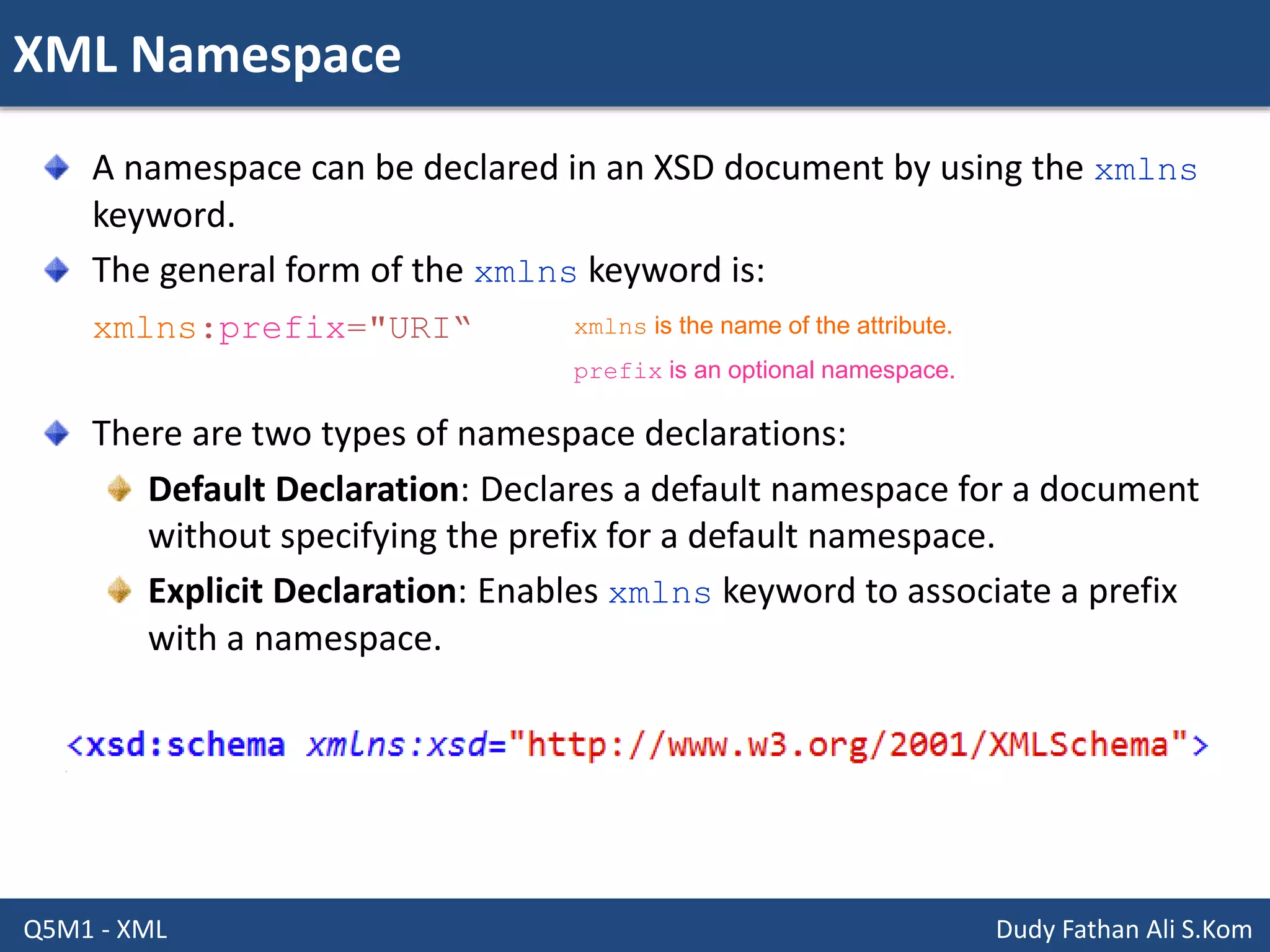
This document discusses XML schemas and their components. It begins by defining what an XML schema is and its purpose in specifying elements, attributes, and data types in an XML document. It then discusses the advantages of using XML Schema Definition (XSD) to define schemas and provides examples of parsers that support XML schemas. The document outlines the different data types in XSD like primitive, derived, atomic, list and union, as well as how to define simple and complex elements. It concludes with explanations of namespaces in XML and how they are declared in XSD.