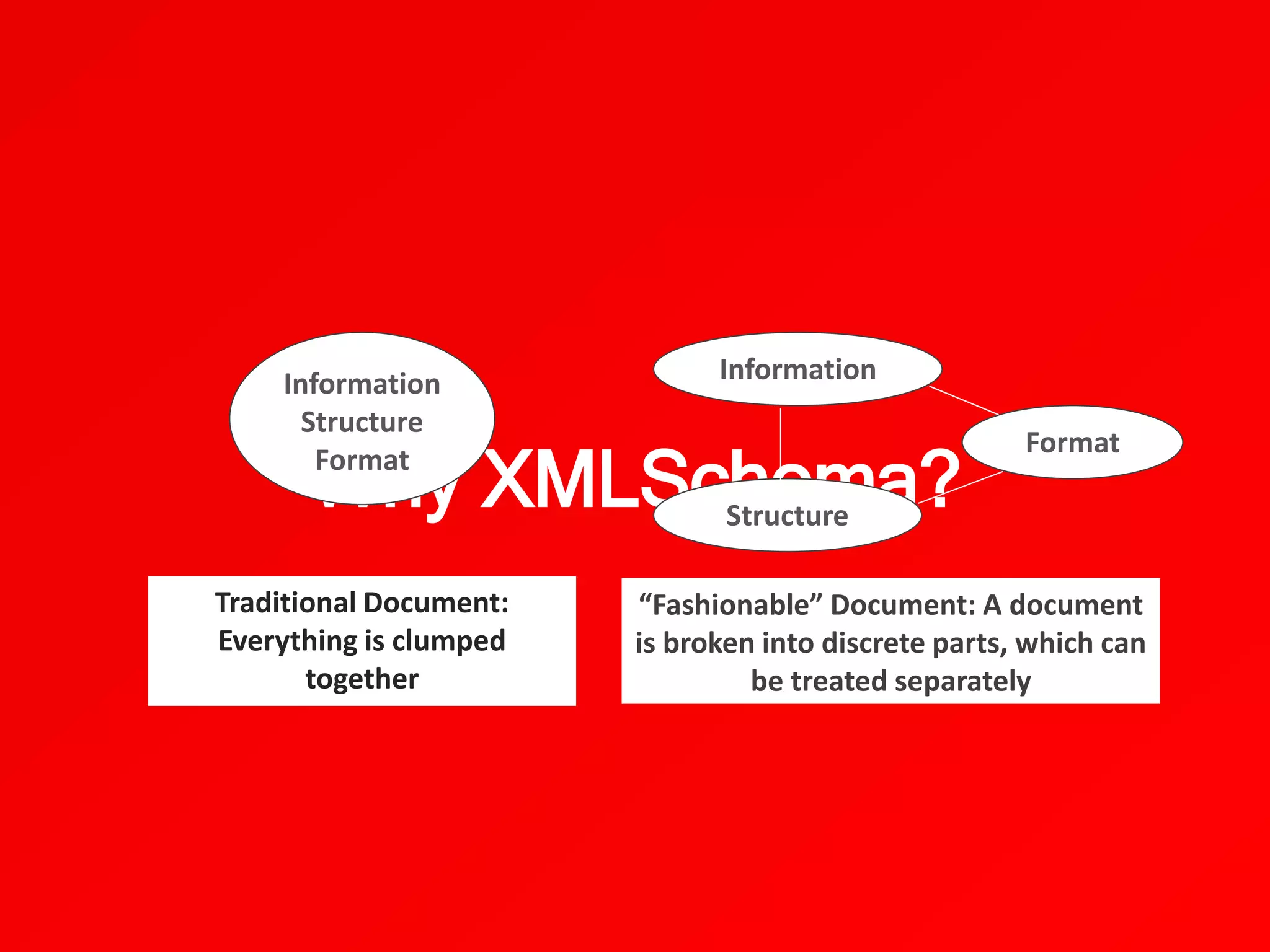
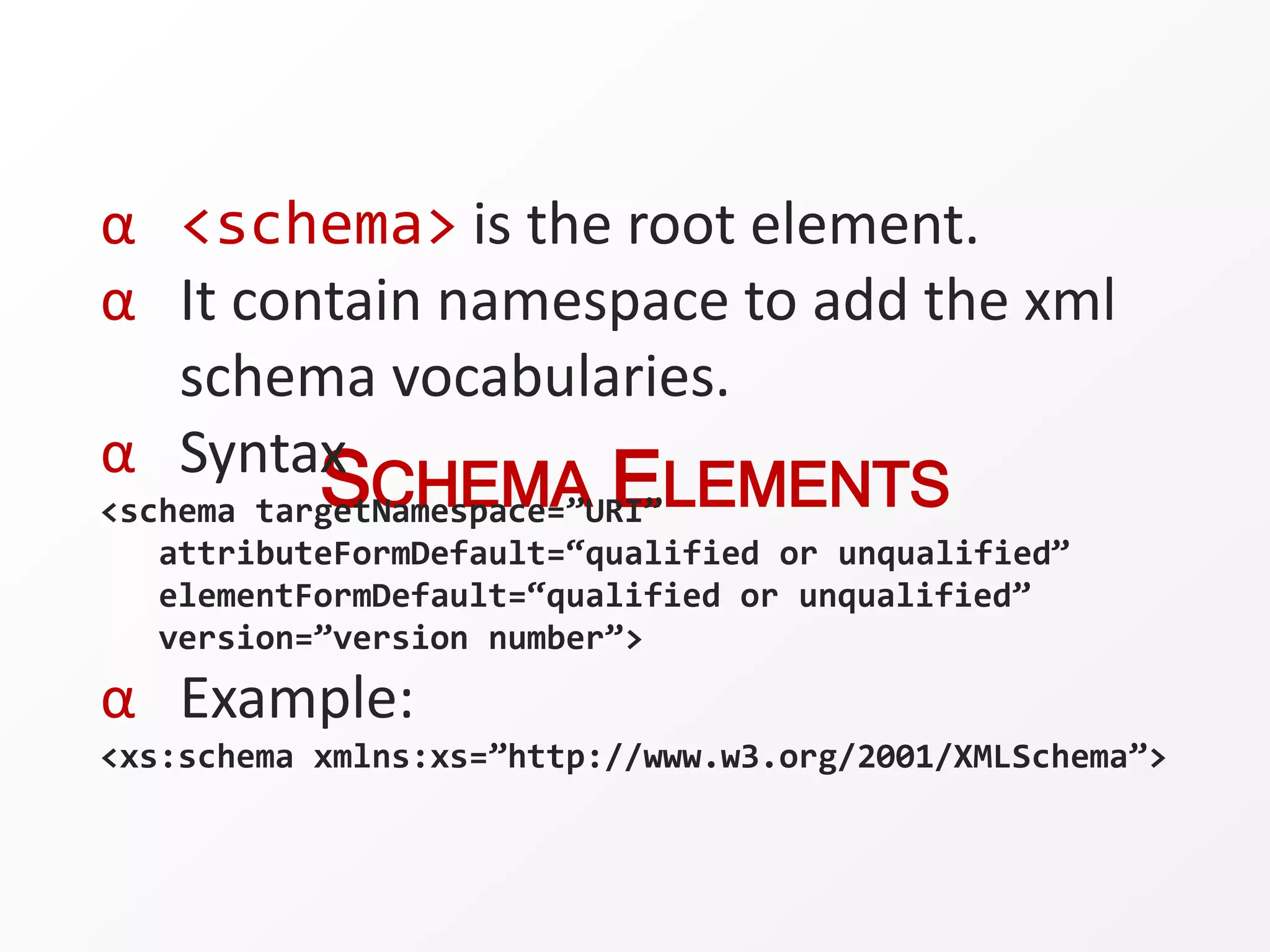
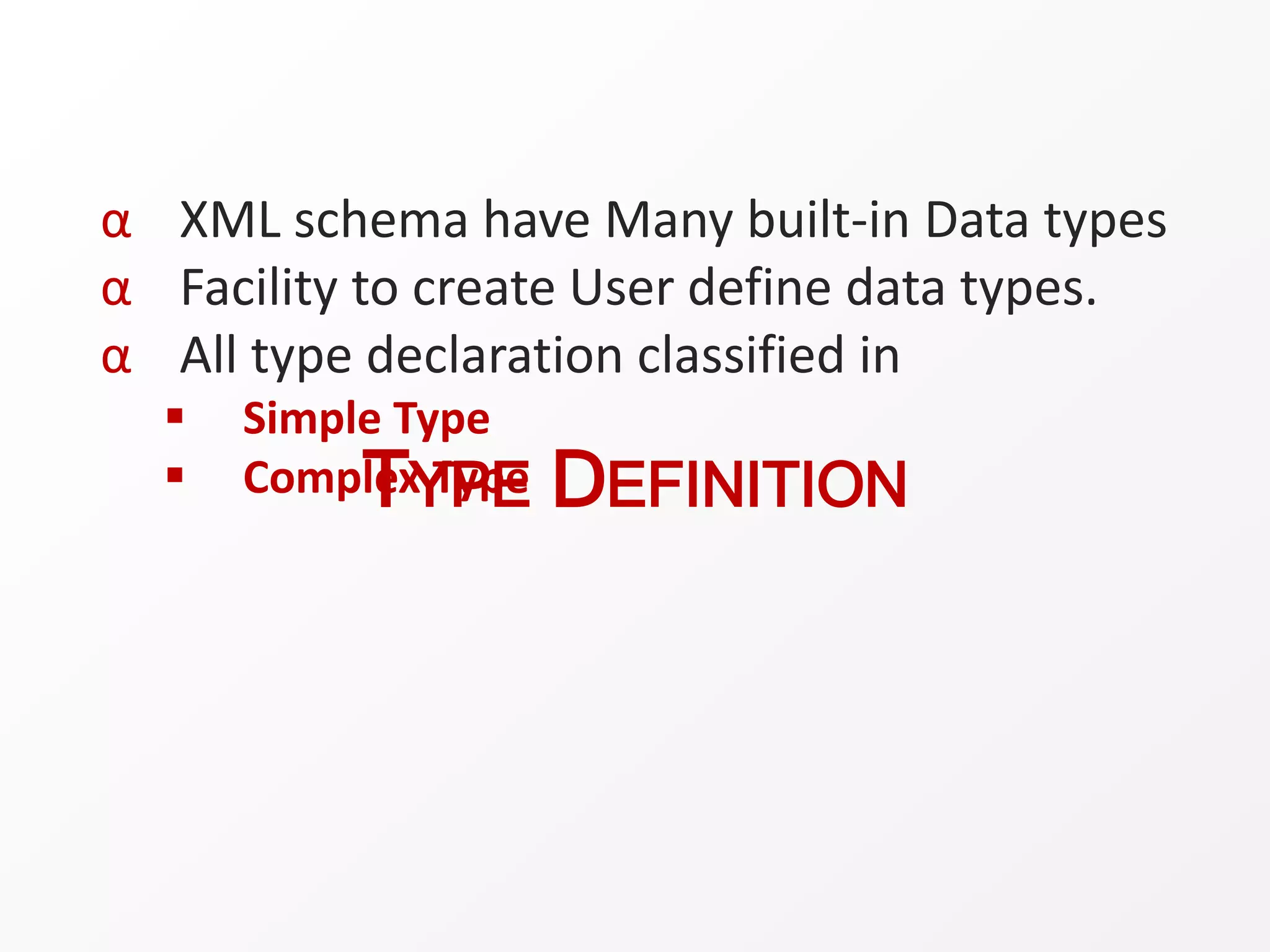
XML schemas define the structure and format of XML documents. They validate that an XML document complies with the specified structure and elements. Key components of an XML schema include element definitions, attribute definitions, annotations, and type definitions. Schemas use XML syntax to declare elements, attributes, and other components, unlike DTD syntax.











![SIMPLE TYPE
<xs:element name=“price”>
<xs:simpleType>
<xs:restriction base=“xs:string”>
<xs:pattern
value=”$[0-9]{1,4}.[0-9]{2}”/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:element>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wtxmlschema19augx-140819104424-phpapp02/75/XML_schema_Structure-15-2048.jpg)


