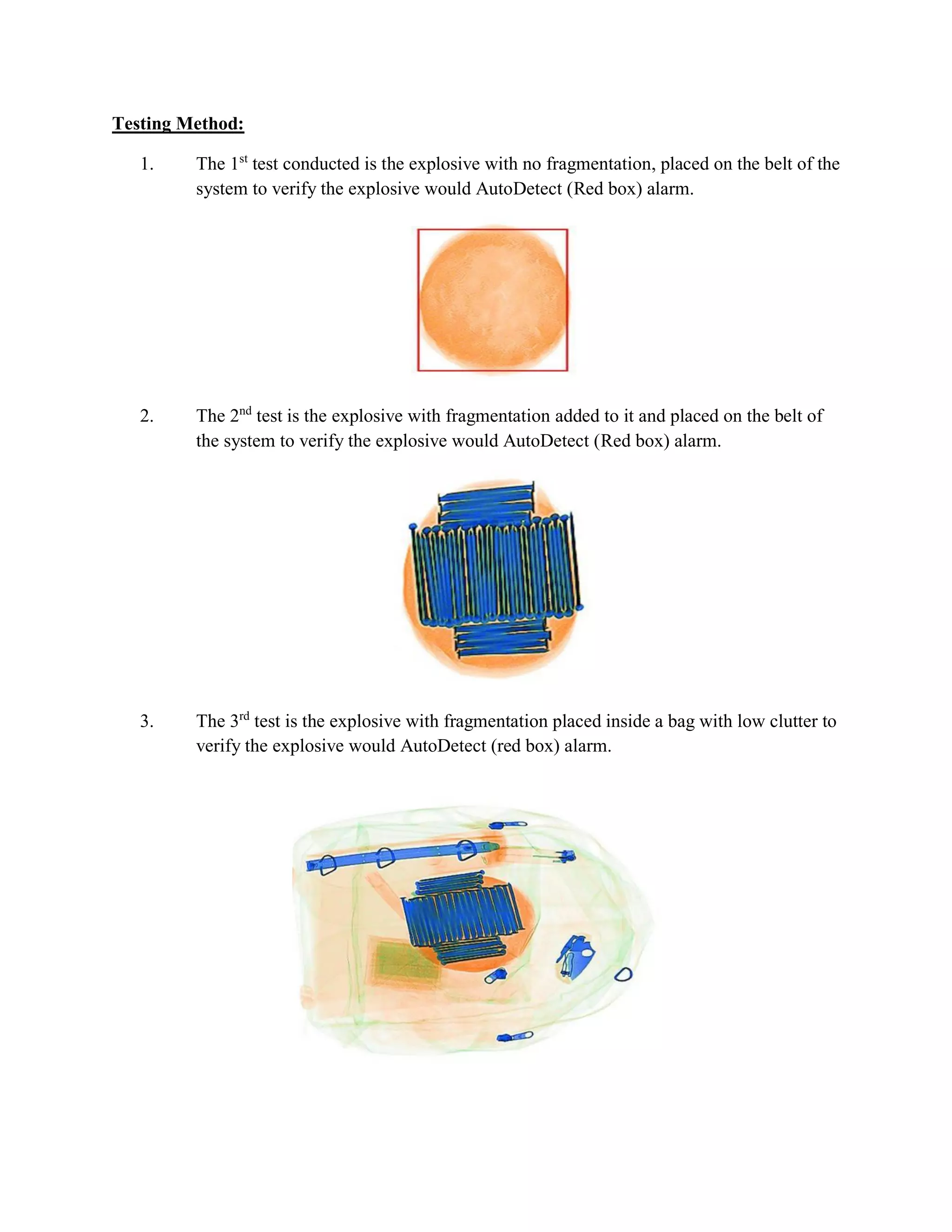
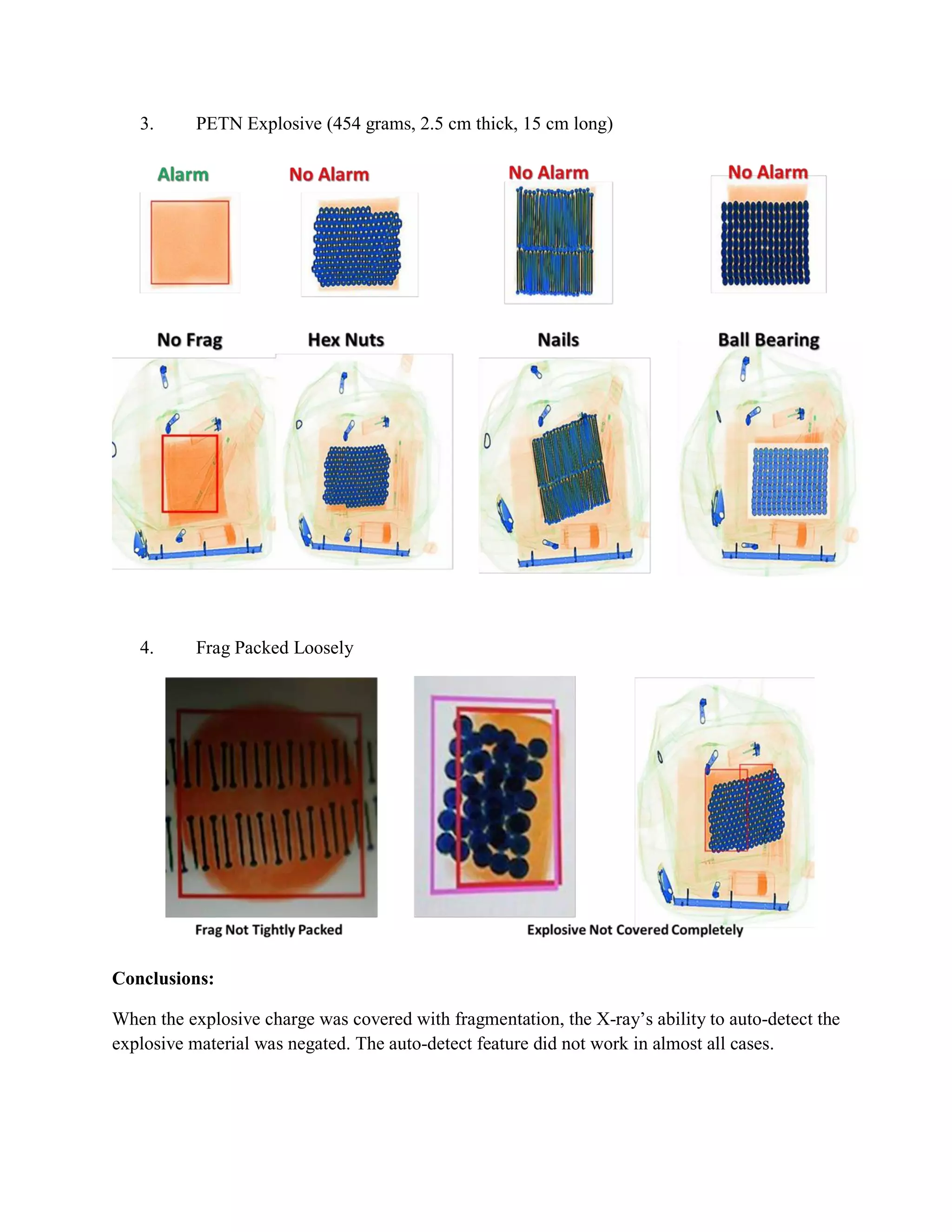
The document details testing of x-ray systems' capabilities to automatically detect explosives when fragmentation is added, reflecting current terrorist methods. Results showed that tight packing of fragmentation can significantly hinder detection, whereas loose packing or exposed explosives allow for better detection. Recommendations include enhanced training for x-ray operators and better evaluation of detection features to improve safety against IED threats incorporating fragmentation.