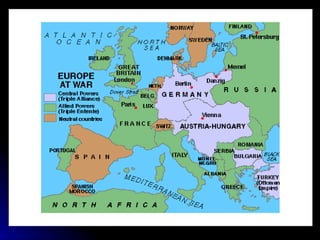
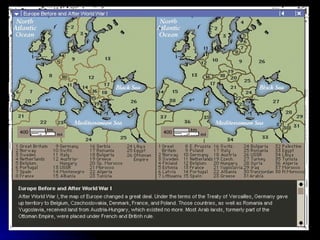
The document summarizes major events from World War I through World War II. WWI began in 1914 due to imperial competition and nationalism, and involved trench warfare between the Allied and Central powers. After US entry in 1917, an armistice was reached in 1918. The Treaty of Versailles in 1919 imposed punitive terms on Germany. Economic instability in the 1920s led to the Great Depression. Roosevelt responded with the New Deal in the 1930s. WWII began in 1939 with Germany invading Poland. The US entered in 1941 after Pearl Harbor. Key battles involved Stalingrad, Midway, and Hiroshima/Nagasaki. WWII ended in 1945 with the defeat of Germany, Italy and Japan, and the establishment of the United Nations