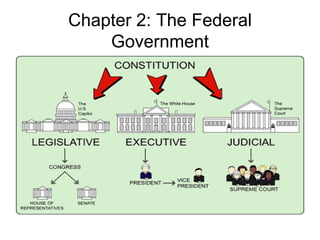
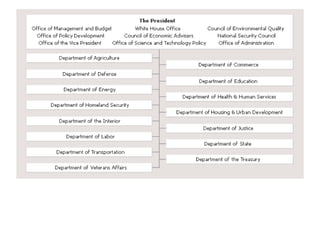
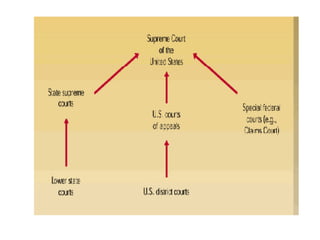
The US government is based on three main principles: federalism, separation of powers, and the Constitution. The national government is centered in Washington D.C. and consists of the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, with each branch having checks on the others to limit any one branch's power. The executive branch is headed by the President, the legislative branch consists of the two-house Congress, and the judicial branch's highest court is the Supreme Court, which has the sole power of judicial review.