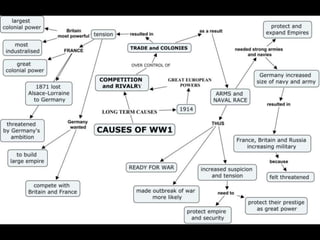
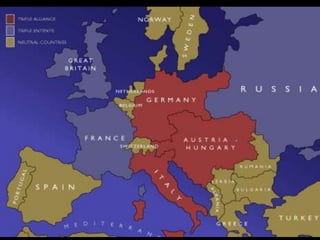
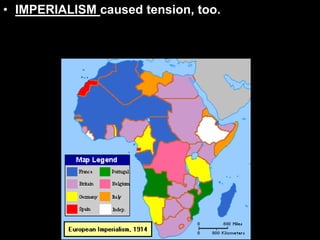
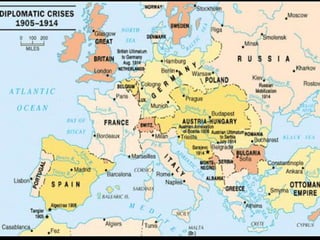
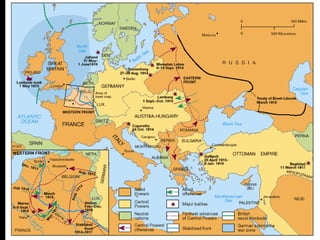
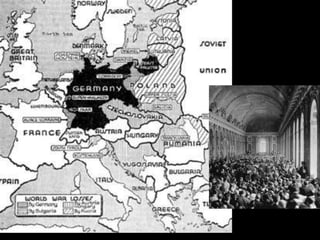
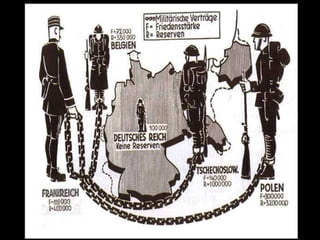
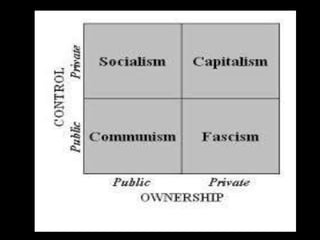
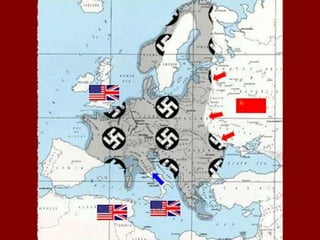
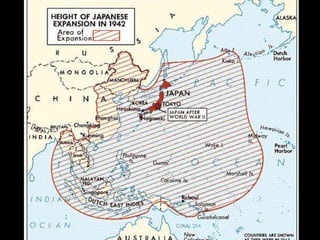
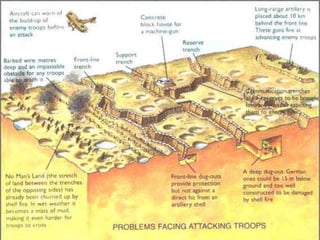
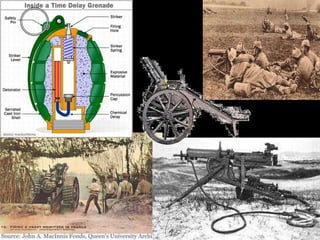
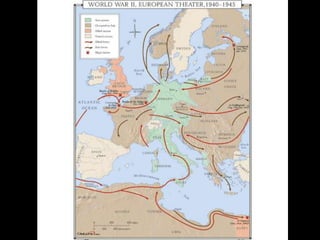
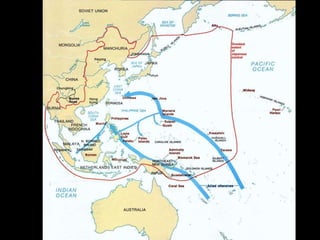
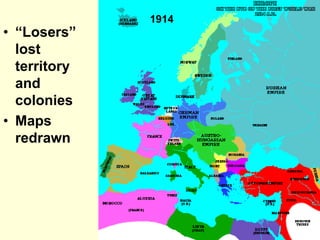
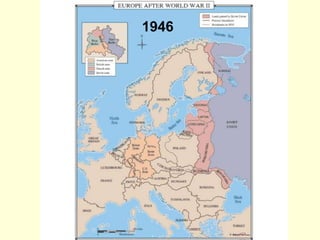
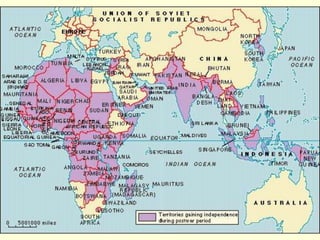
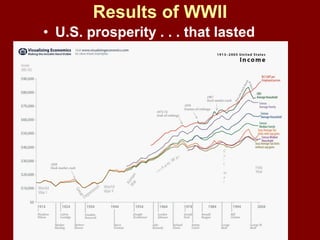
The document provides an overview of World War I and World War II, comparing their causes, warfare, and results. It notes that both wars were global conflicts caused by militarism, nationalism, and alliances that pulled nations in. World War I saw trench warfare while World War II featured mobile battle tactics and new weapons. Both wars redrew borders and led to the fall of old empires, though World War II also saw the rise of the United States as a superpower and the start of the Cold War between Western nations and the Soviet Union.