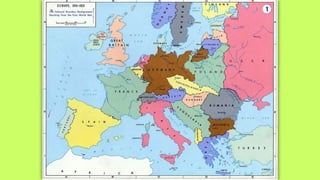
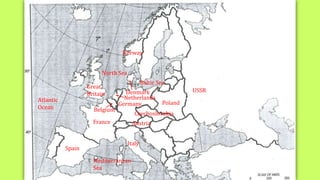
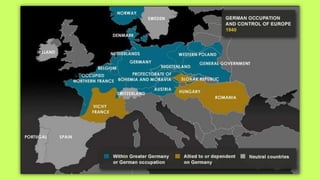
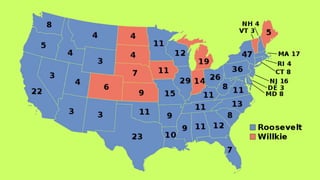
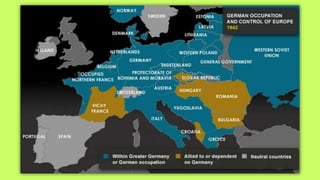
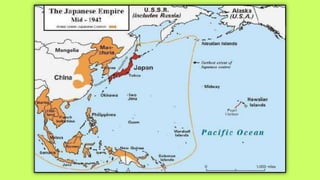
Roosevelt worked to improve foreign relations and adopt an isolationist stance in the 1930s as countries like Germany and Japan rose in power and aggression. As World War II began in Europe in 1939, Roosevelt provided some aid to Britain and France while maintaining official neutrality, though he recognized the threat posed by the Axis powers. By 1940, with Germany occupying much of Europe and threatening Britain, Roosevelt began abandoning the neutrality stance and provided more direct aid, seeing America's involvement as necessary to defend democracy.