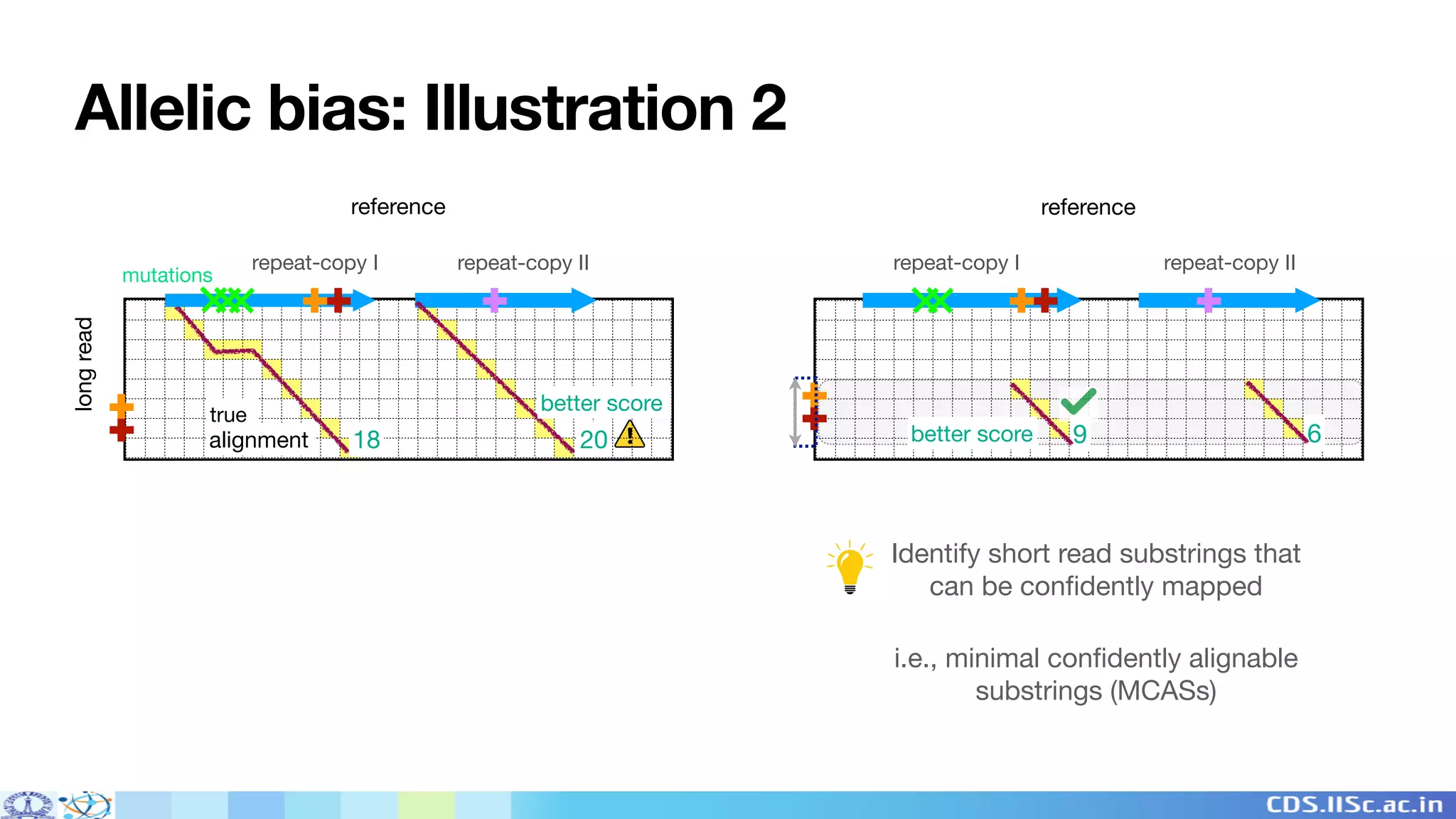
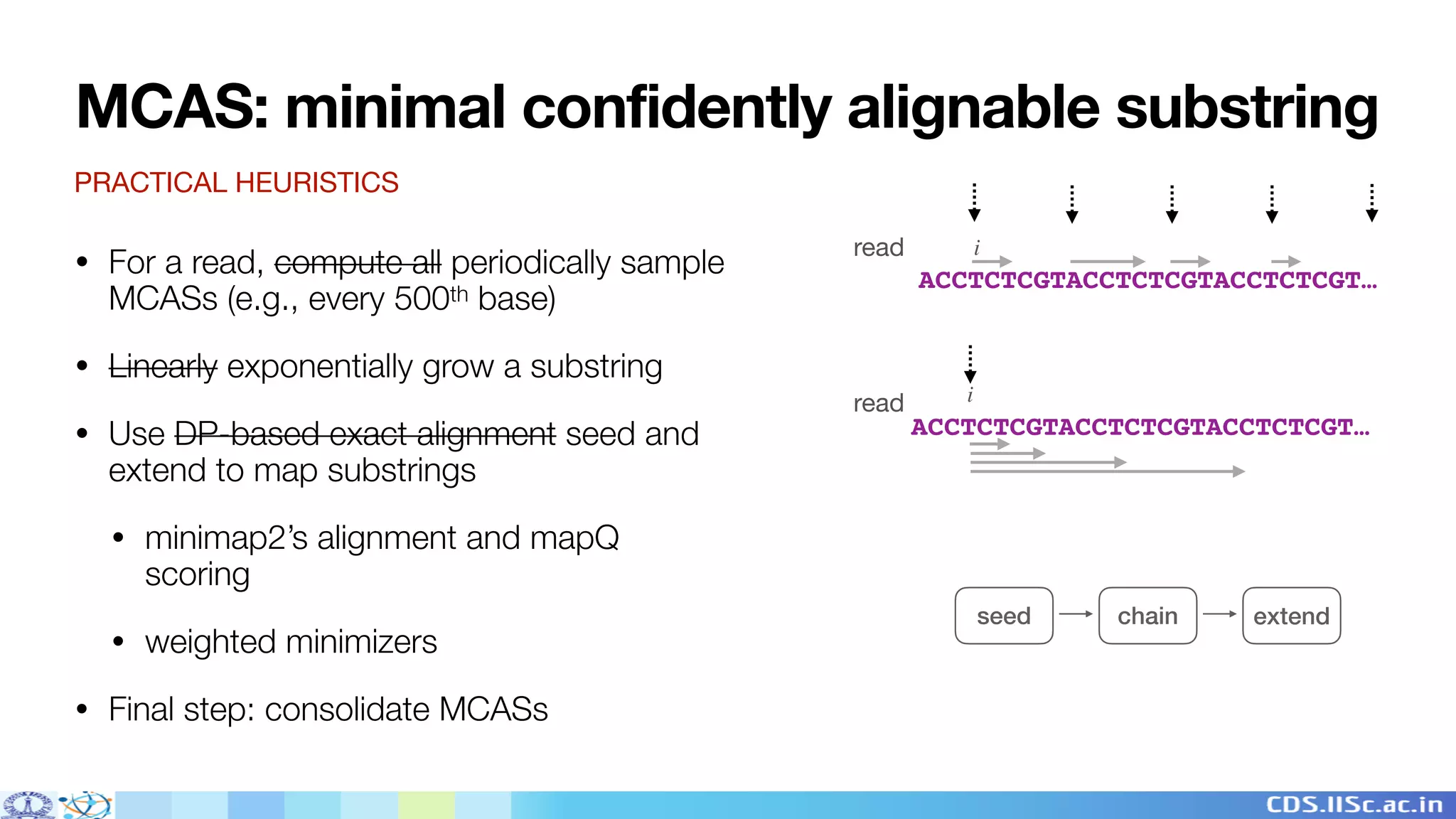
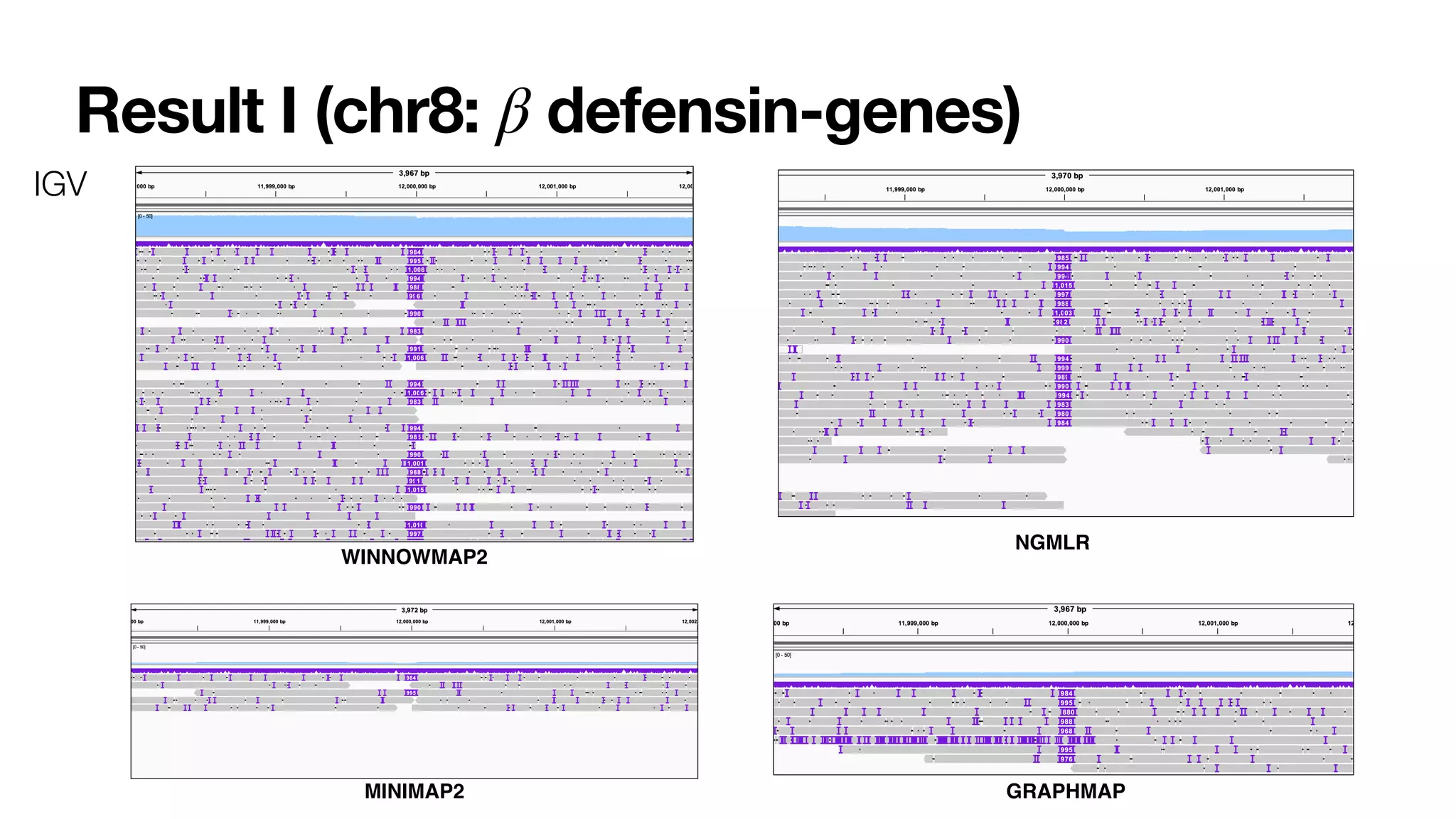
Winnowmap2 is a long read mapping method that improves on previous methods for mapping reads to highly repetitive reference sequences. It addresses issues like allelic bias by identifying minimal confidently alignable substrings (MCASs) within each read that can be mapped independently of non-reference bases. This allows MCASs to be more tolerant of structural variation and sensitive to paralog-specific variants. The method was shown to enable superior variant calling accuracy in repetitive regions compared to other mapping tools.


![EXACT PRACTICAL HEURISTICS
Smith-Waterman
seed
C G T C G C C T A A T C G C A C G T C C G T C G C C T A A T
chain
extend
Addressed in Winnowmap
using weighted minimizers
Improved in Winnowmap2
Repeat-aware read mapping
Is the highest scoring alignment always a
correct placement for a read?
Mask repetitive k-mers
[ISMB’20]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cshlbiodata2020-201105144319/75/Winnowmap2-A-long-read-mapping-method-for-highly-repetitive-reference-sequences-3-2048.jpg)