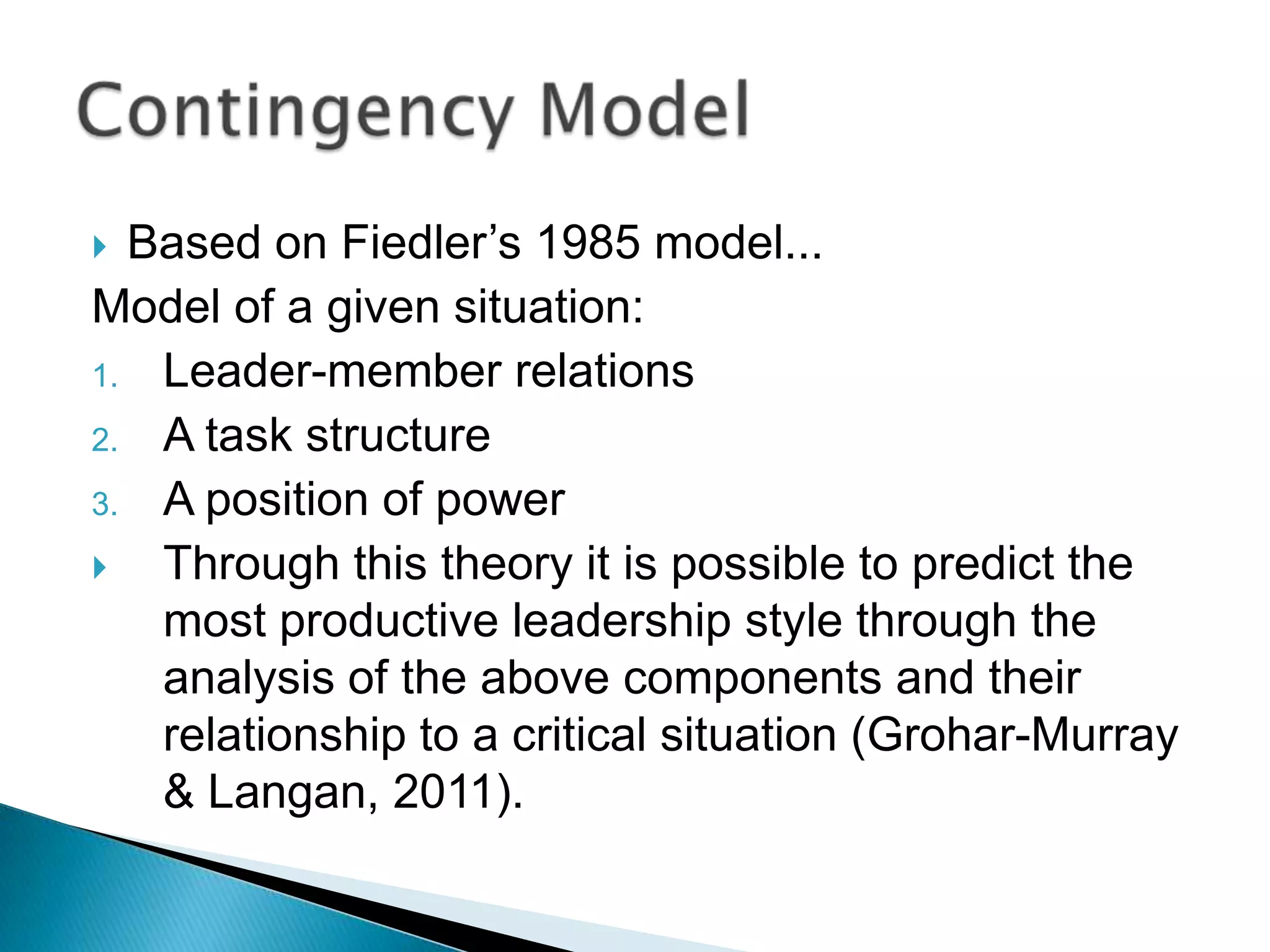
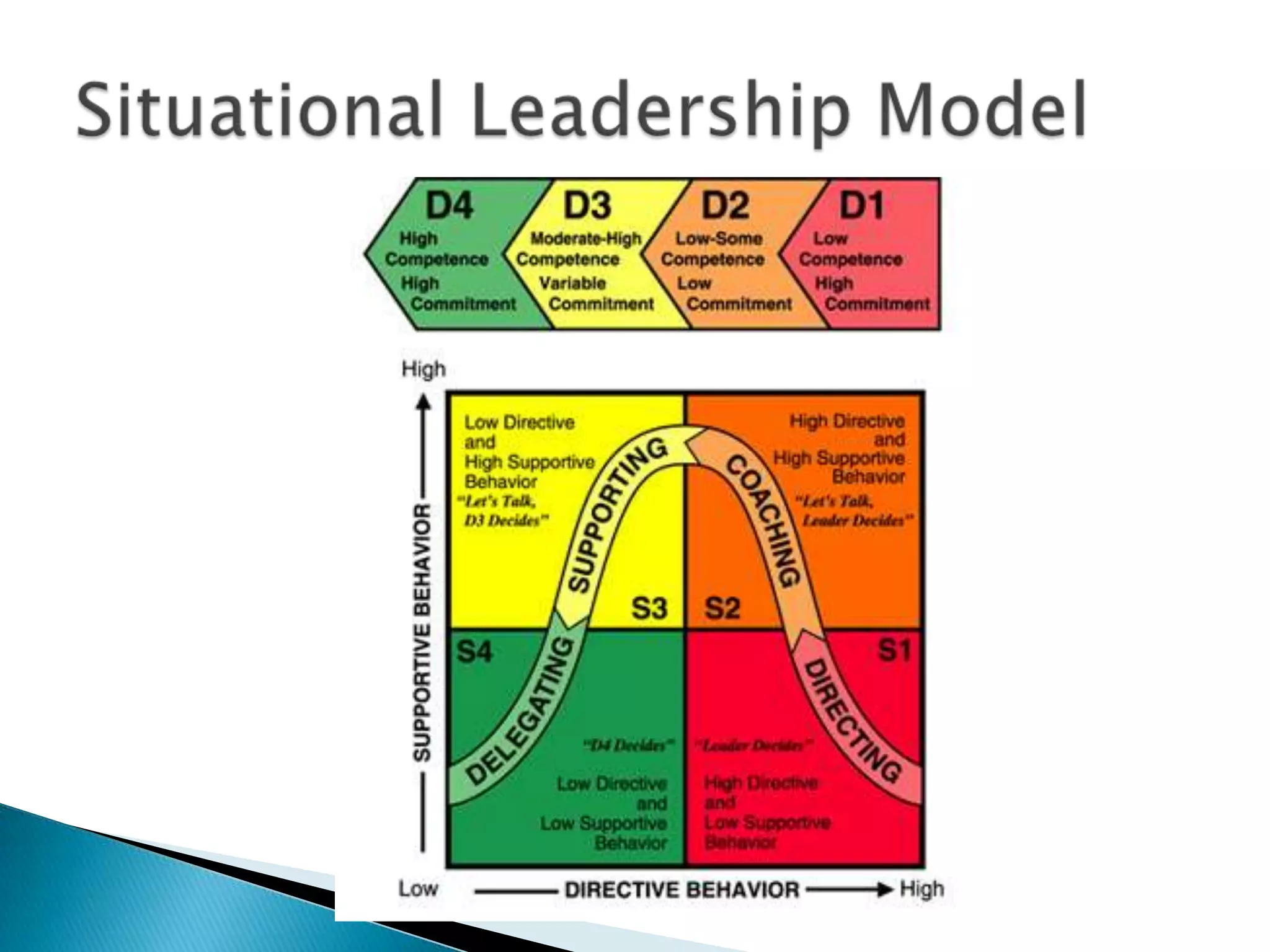
The document discusses several models and definitions of leadership. It describes leadership as a social influence process where a person enlists the aid of others to accomplish a common task. Several factors are seen as important in the leadership process, including the leader's traits, the situation, and the followers. The document also examines contingency models of leadership, which view the most effective leadership style as dependent on situational factors like the task structure and the leader-follower relationship. Transformational and transactional leadership styles are also defined.