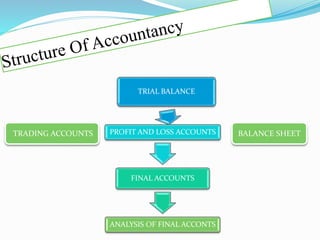
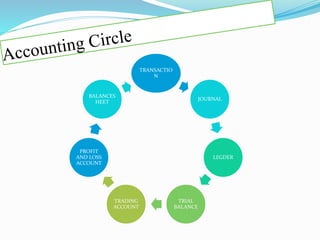
Accounting refers to collecting, summarizing, analyzing, and reporting financial information about a business in monetary terms. It allows businesses to track profit and loss, assets and liabilities, cash position, and other financial metrics. The accounting process involves recording economic transactions in journals and ledgers, then preparing final accounts like the trial balance, income statement, and balance sheet to analyze the business's financial condition.