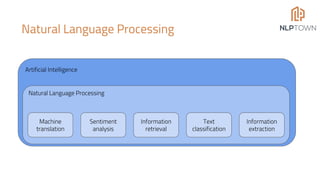
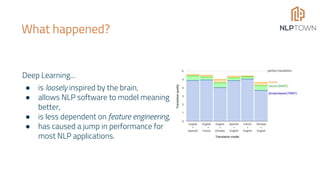
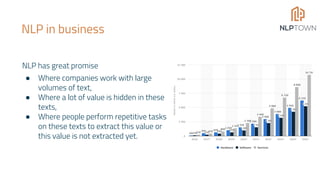
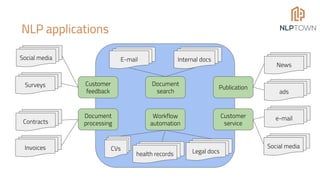
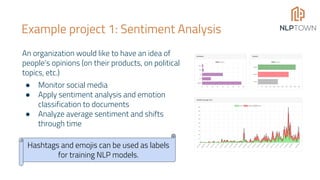
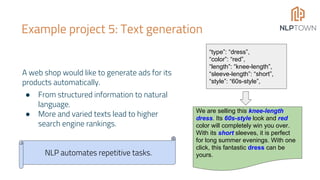
The document discusses the potential of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in business, highlighting applications like sentiment analysis, document processing, and customer service. It outlines steps for companies to implement NLP, emphasizing data readiness, project selection, and the need for customization in developing NLP solutions. The text also provides examples of specific NLP projects and offers guidance on maximizing the chances of success.