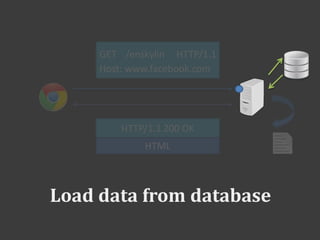
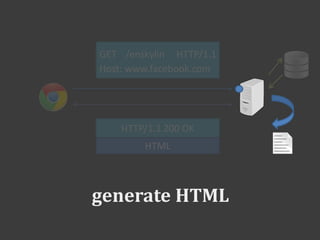
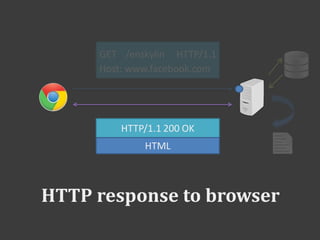
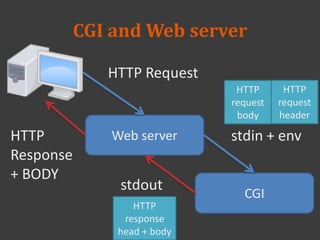
The document discusses PHP and how it works with HTML. PHP code is embedded within HTML code using opening and closing PHP tags. Variables and data from PHP can be outputted into the HTML. Forms allow sending data to PHP scripts via GET or POST requests. The PHP script receives the form data in the $_POST or $_GET superglobals. Sessions allow maintaining state across multiple requests by assigning a temporary ID stored in a cookie.









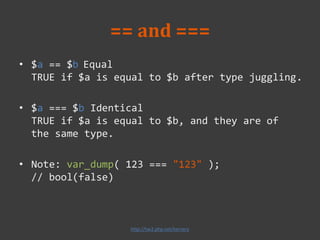
![Type verification
var_dump($variable)
// can print out the type
of $variable
var_dump(2147483647);
// int(2147483647)
var_dump(2147483648);
// float(2147483648)
var_dump(
array(1,2,3)
);
array(3) {
[0]=> int(1)
[1]=> int(2)
[2]=> int(3)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-14-320.jpg)


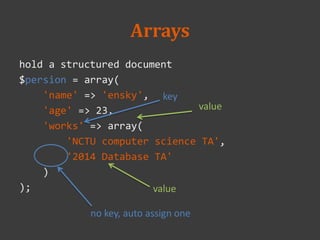
![Strings (cont'd)
There is no "char type"
$string = "this is a string!";
var_dump($string);
// string(17) "this is a string!"
var_dump($string[0]);
// string(1) "t"
$string[0] = 'T';
echo $string;
// This is a string!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-17-320.jpg)












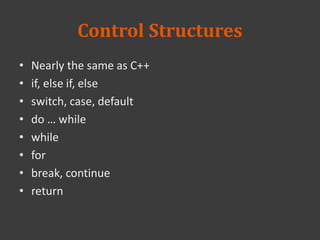
![Arrays
You can use like a simple C-style array
$scores = array(30, 35, 45, 25);
print_r($scores);
/* Array
(
[0] => 30
[1] => 35
[2] => 45
[3] => 25
) */
key
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-31-320.jpg)
![Arrays
Totally the same as
$scores = array(0 => 30, 1 => 35, 2 => 45, 3 => 25);
print_r($scores);
/* Array
(
[0] => 30
[1] => 35
[2] => 45
[3] => 25
) */
key
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-32-320.jpg)
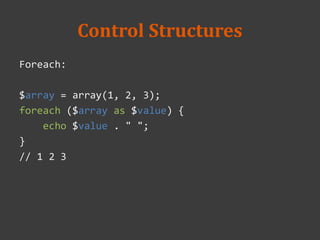
![Arrays
or a HashMap
$menu = array(
'beef noodles' => 260,
'noodles' => 60,
'beef' => 200
);
echo "price of beef is: $" . $menu['beef'];
// price of beef is: $200
key
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-33-320.jpg)
![Arrays
or act as an queue
$queue = array();
$queue[] = '1';
$queue[] = '2';
$queue[] = '3';
echo array_shift($queue);
// 1
print_r($queue);
/* Array
(
[0] => 2
[1] => 3
) */
auto key
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-34-320.jpg)
![Arrays
or act as an stack
$queue = array();
$queue[] = '1';
$queue[] = '2';
$queue[] = '3';
echo array_pop($queue);
// 3
print_r($queue);
/* Array
(
[0] => 1
[1] => 2
) */
auto key
value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-35-320.jpg)






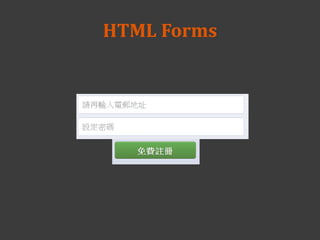

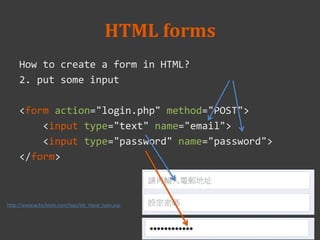


![email=enskylin@gmail.com&
password=nctu5566
/login.php
In login.php
-----
<?php
echo $_POST['email'];
echo $_POST['password'];
?>
POST /login.php HTTP/1.1
Host: your_hostname](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-50-320.jpg)









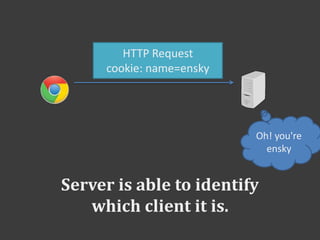


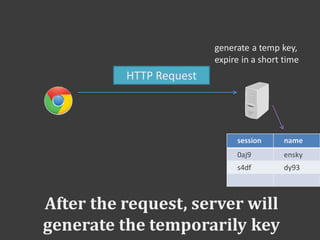
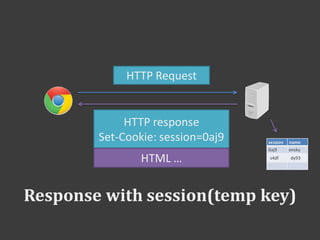
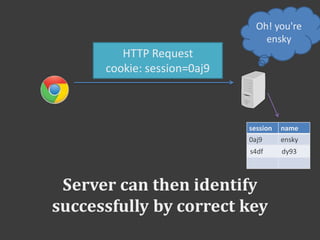
![Use session
Set
------
<?php
session_start();
$_SESSION['name'] = 'ensky';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-68-320.jpg)
![Use session
Get
------
<?php
session_start();
echo $_SESSION['name'];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/week2-20-20php-140312024517-phpapp01/85/2014-database-course-2-php-69-320.jpg)








