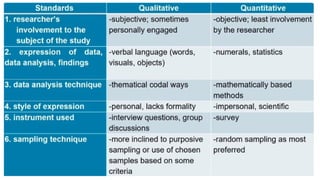
Nature of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation that focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data to explain, predict, or test relationships among variables. It relies on measurable evidence, statistical tools, and structured instruments such as surveys, tests, or experiments. In Practical Research 2, students explore how quantitative methods are used to answer research questions objectively, often through large samples and standardized procedures. This approach emphasizes precision, reliability, and replicability, making it ideal for studies that seek to quantify behaviors, opinions, or outcomes.
Quantitative research is often associated with experimental, descriptive, or correlational designs. It uses tools like graphs, tables, and statistical formulas to present findings clearly and concisely. Whether comparing groups, measuring change, or identifying patterns, this method helps researchers draw conclusions based on observable data.