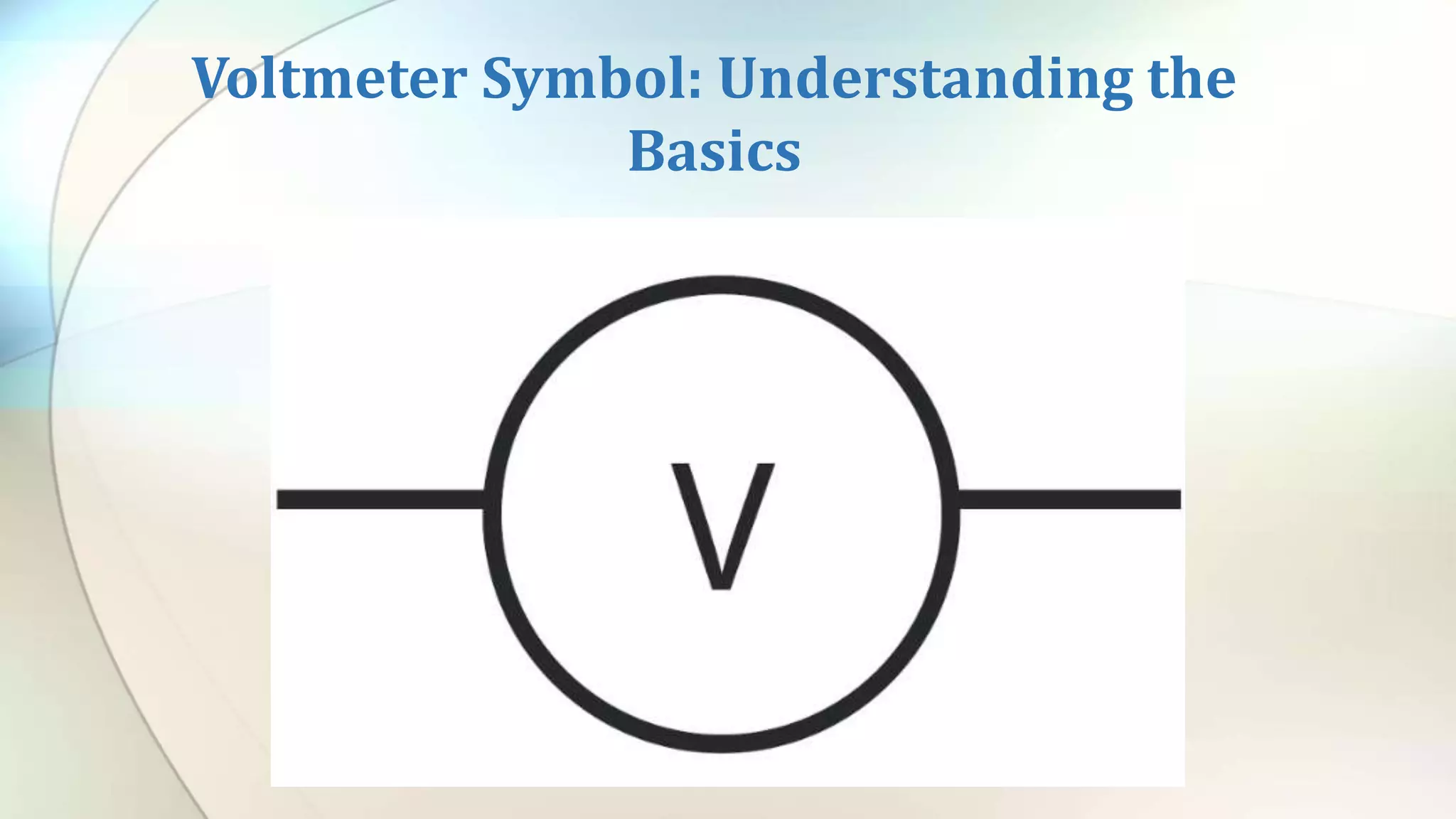
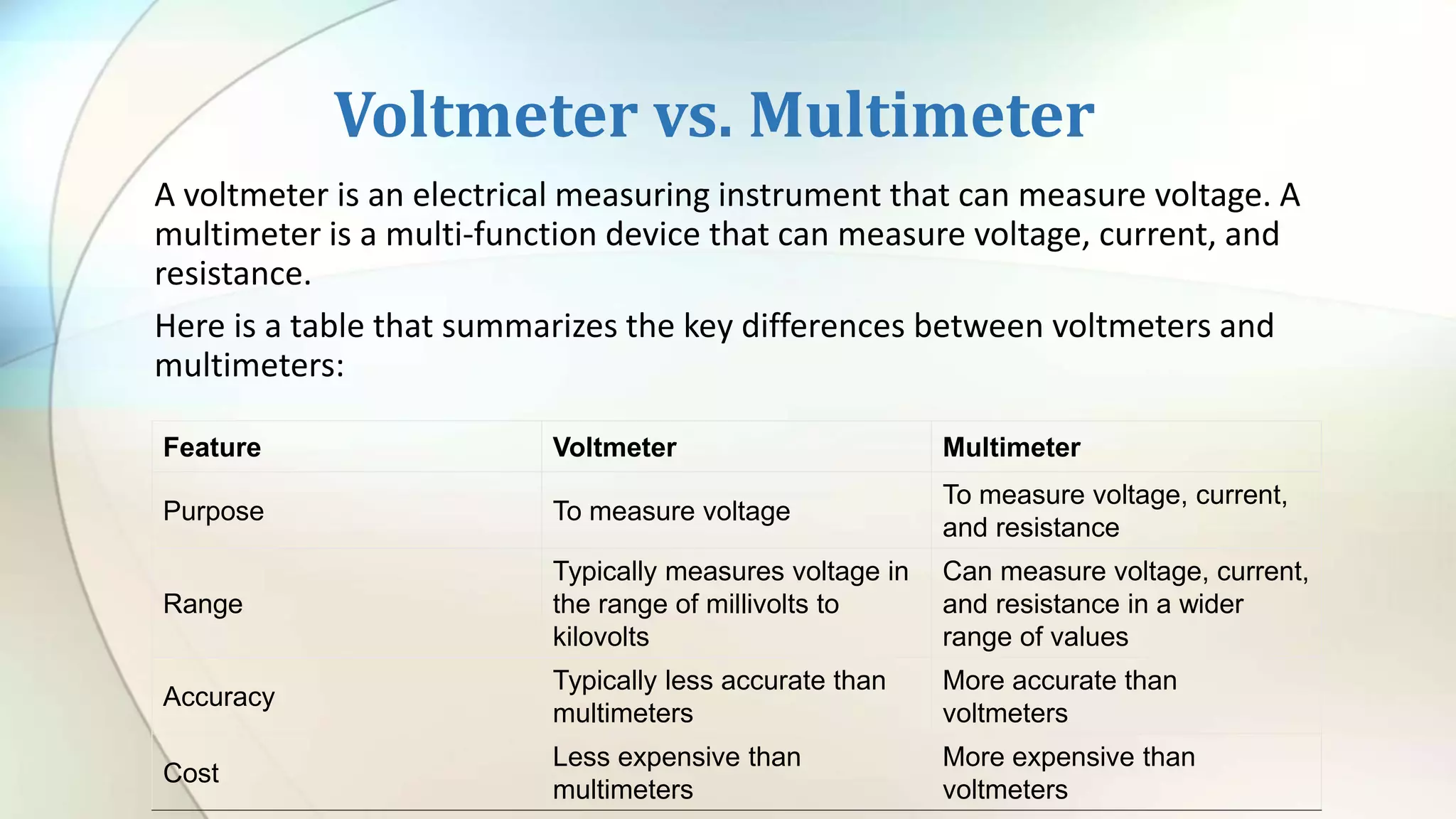
The voltmeter symbol is a crucial representation in electrical engineering, denoting the instrument that measures voltage between two points in a circuit. It is widely applied across various fields such as electronics, automotive diagnostics, and telecommunications, assisting technicians and engineers in understanding and monitoring voltage levels. Through different types of voltmeters, including analog and digital variations, users can ensure accurate voltage measurements for safe and efficient system operations.