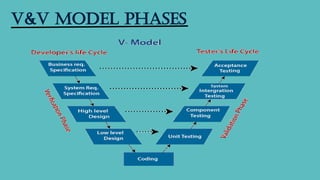
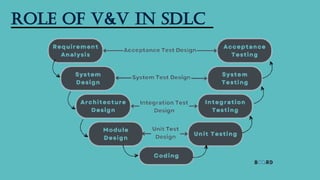
The verification and validation (V&V) model is a software engineering process that ensures a product meets its specifications and fulfills its intended purpose. It involves systematic checks throughout the software development life cycle (SDLC) to identify defects early, improve software quality, and enhance user satisfaction. Key phases of V&V include requirements analysis, design verification, code verification, and various testing phases, all integral to delivering reliable software solutions.