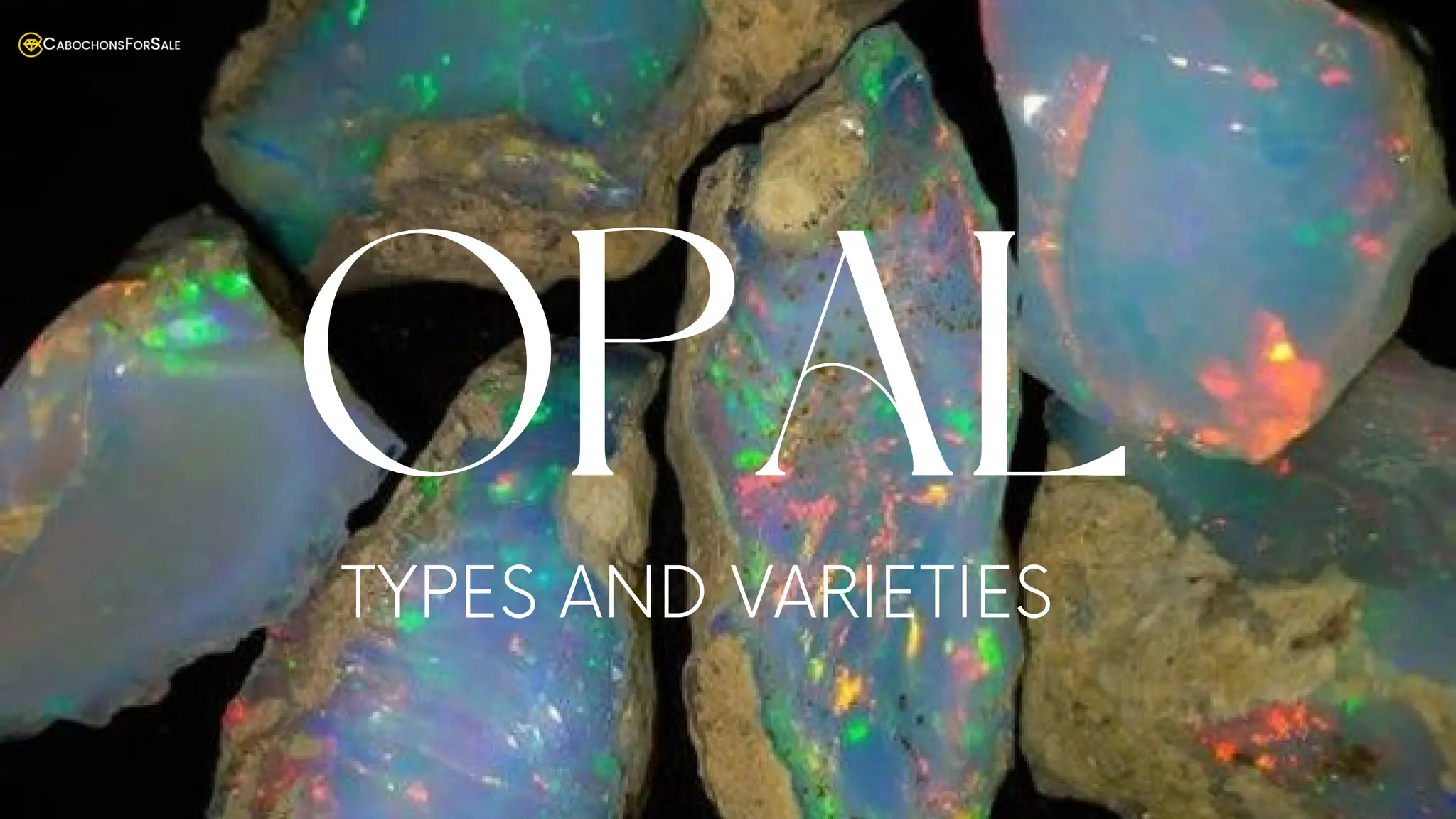
Opal is a captivating gemstone known for its iridescent play-of-color, with various types including precious opal, which can be further divided into black, white, crystal, and fire opals based on their characteristics. Common opal lacks play-of-color but features a range of colors, while doublets and triplets enhance opal's appearance and durability. Additional varieties include boulder opal, matrix opal, hydrophane opal, and synthetic opal, the latter being man-made and lacking the uniqueness of natural options.