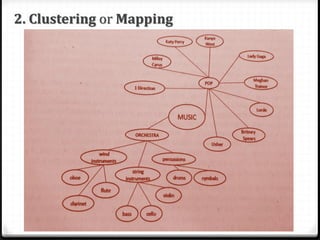
Here are 3 potential topics I came up with using the specified pre-writing strategies:
1. Social media (brainstorming): Effects of social media on relationships, Social media addiction, Benefits and drawbacks of social media
2. Summer vacation (mapping): Beach vacation, Road trip, Camping trip