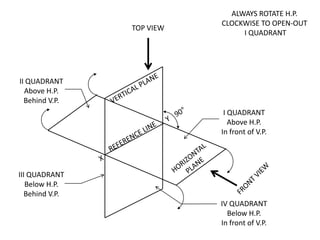
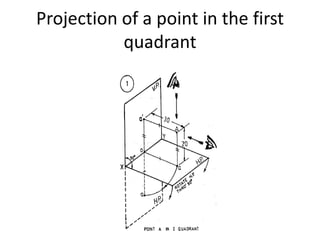
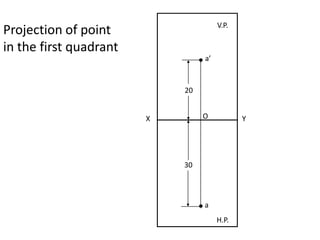
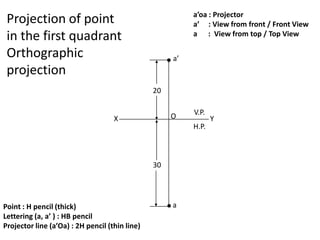
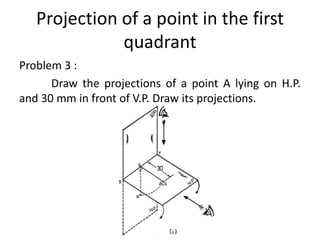
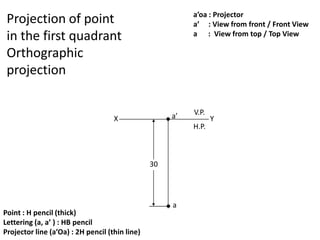
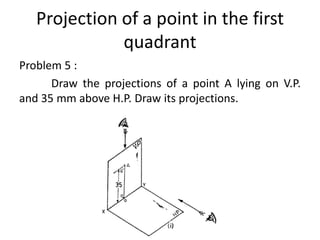
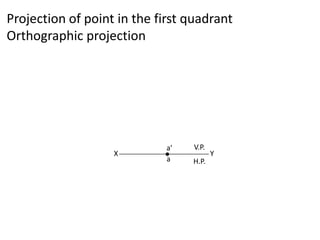
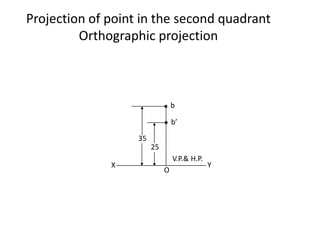
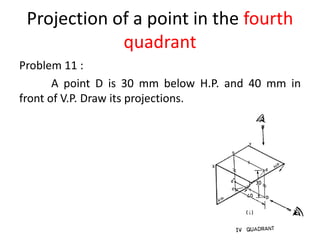
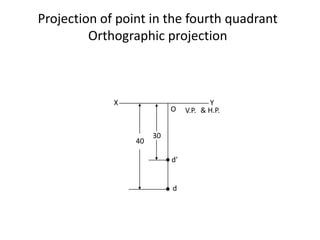
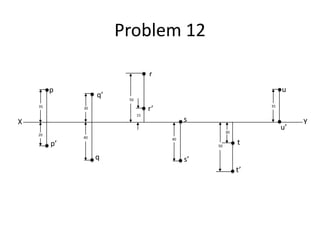
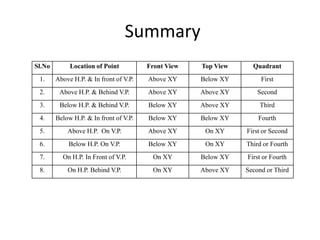
The document discusses the projection of points in 2D orthographic drawings. It defines a point as having no width, height or depth and being represented by the intersection of two lines. It then explains how to determine the front, top and quadrant location of a point based on its position relative to the horizontal and vertical planes. Numerous examples are given of drawing the front and top view projections of points located in different quadrants.