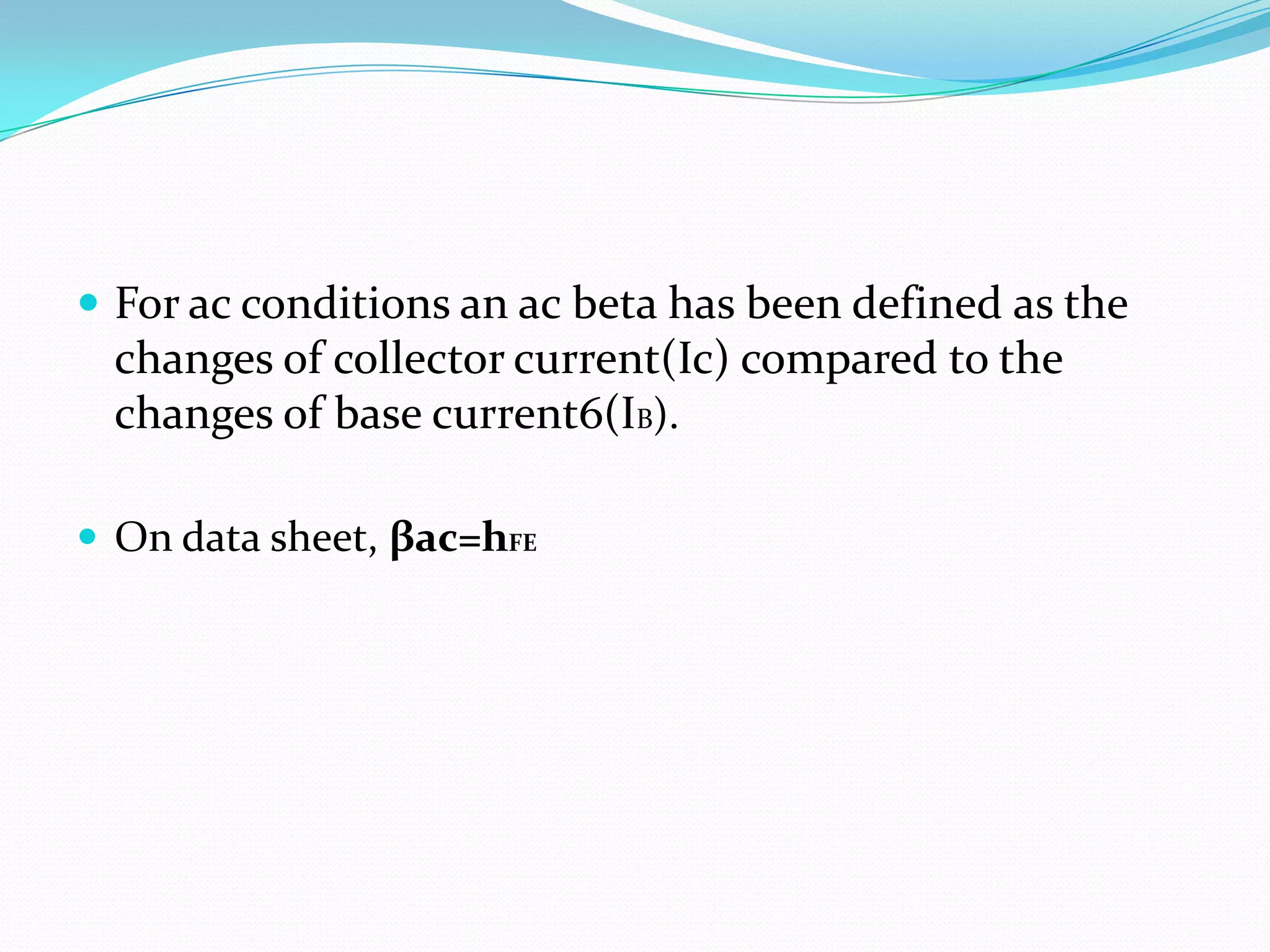
The document discusses bipolar junction transistors (BJTs). It covers:
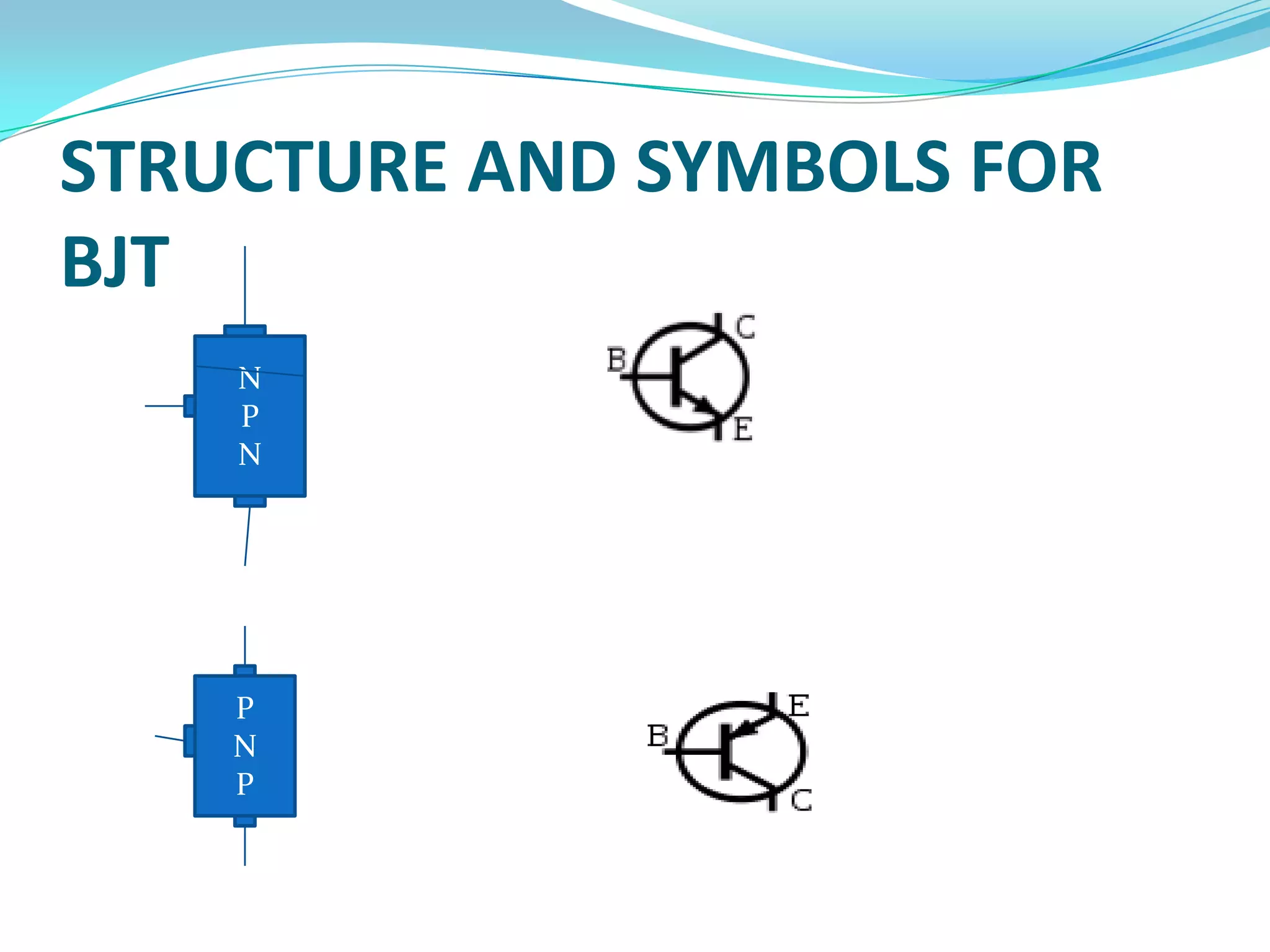
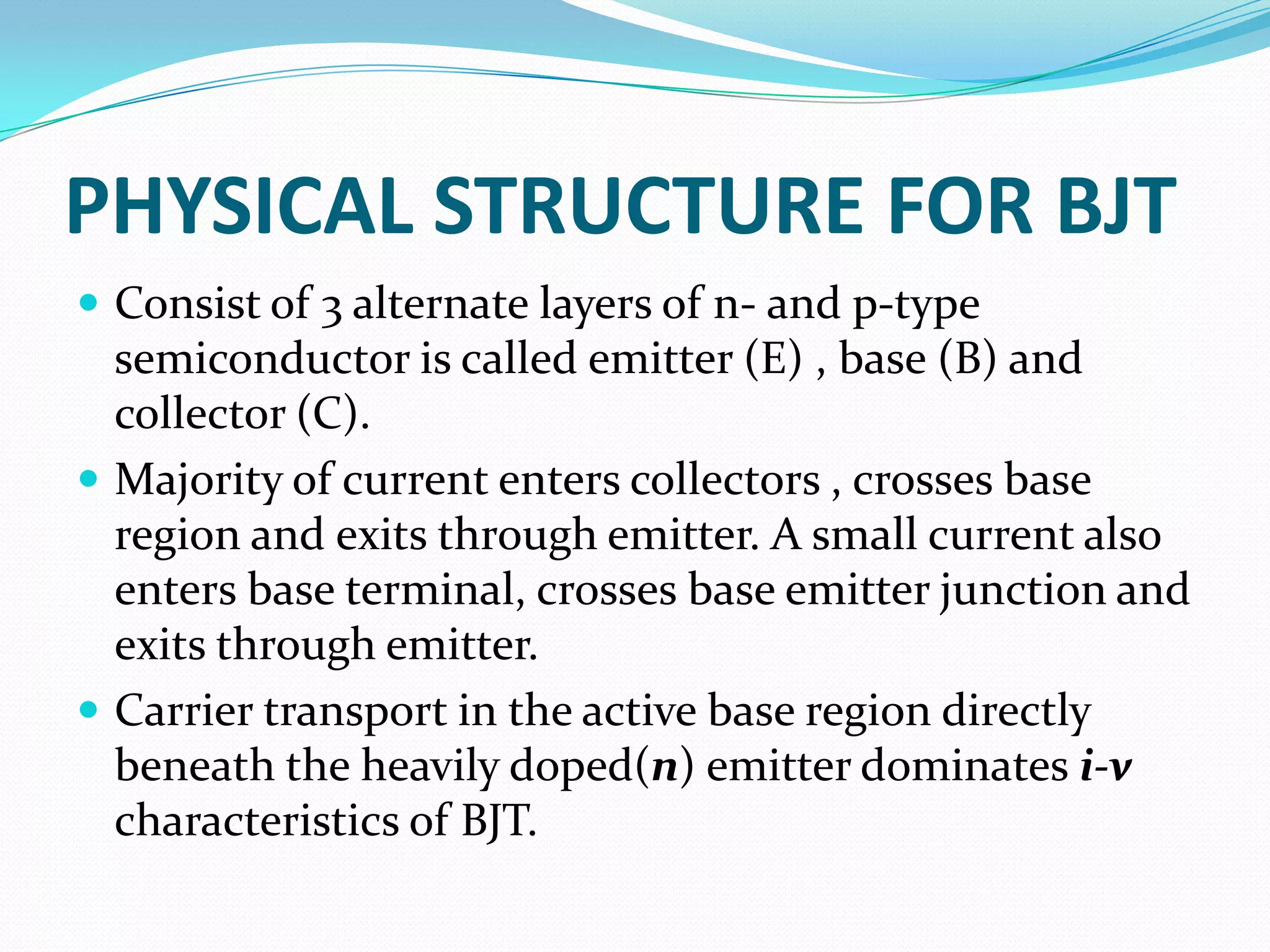
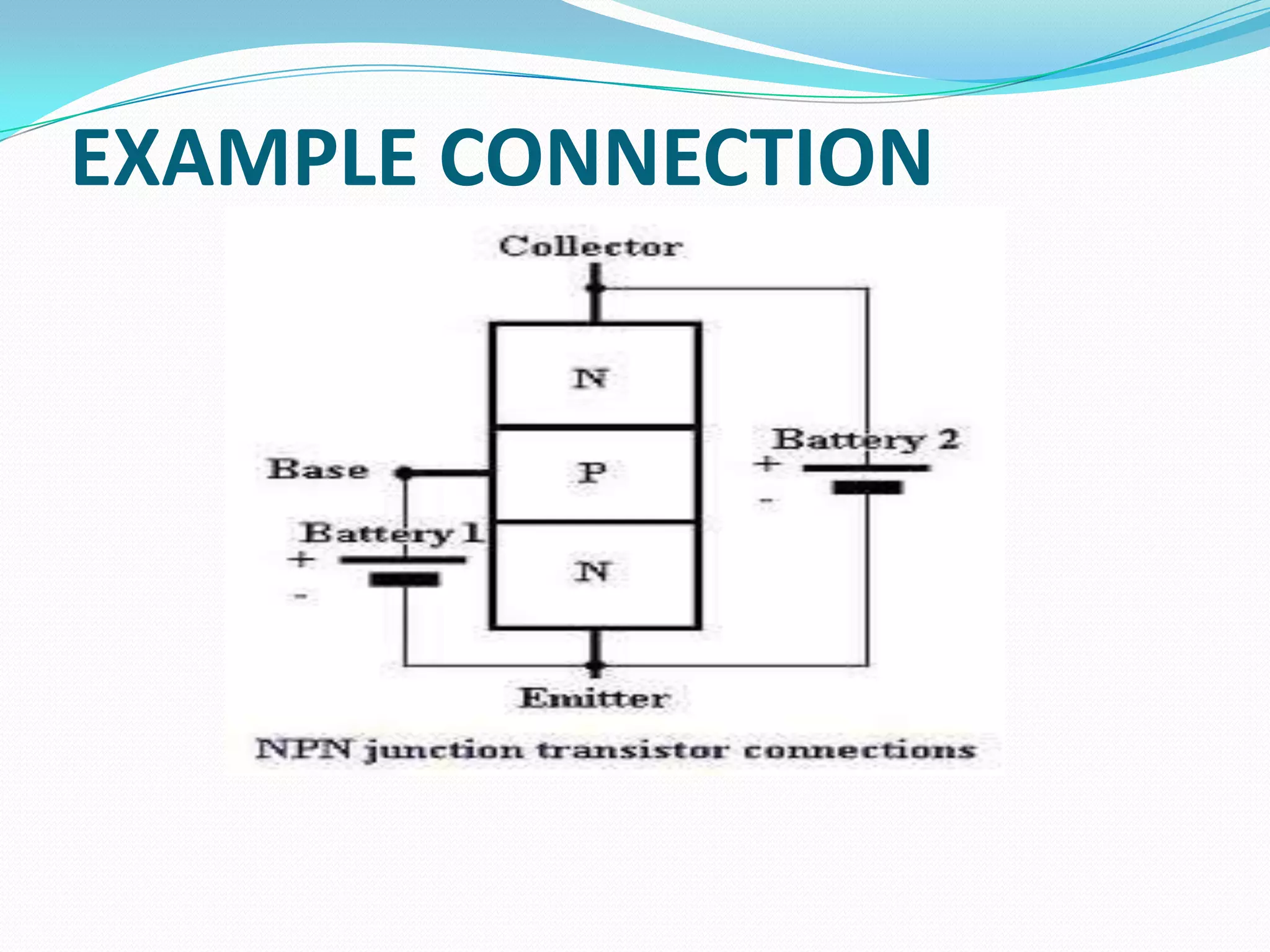
1) The basic structure of a BJT, which consists of three doped semiconductor regions forming two back-to-back PN junctions.
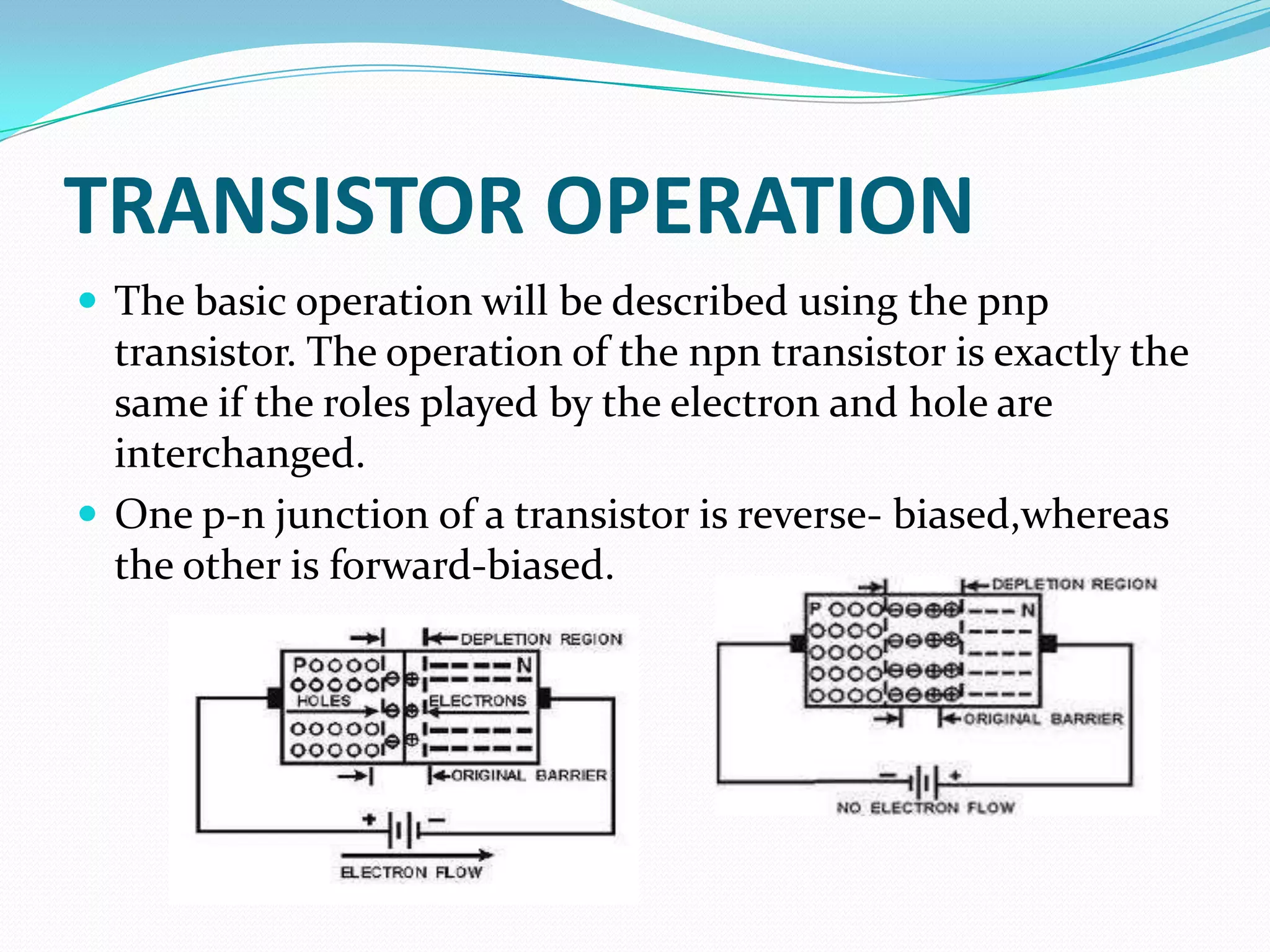
2) The common NPN and PNP transistor configurations and their symbols. BJTs operate by forward biasing one PN junction and reverse biasing the other.
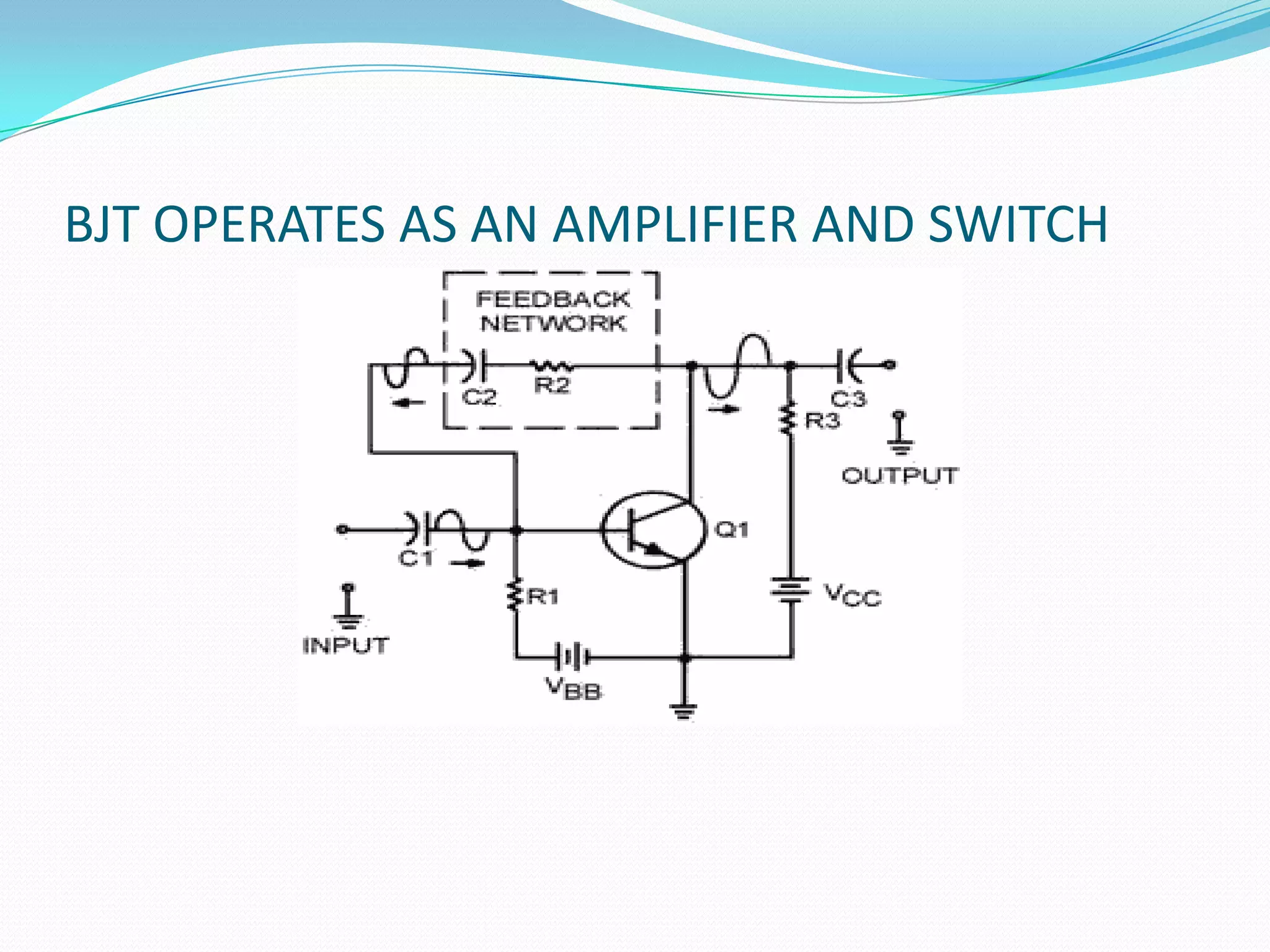
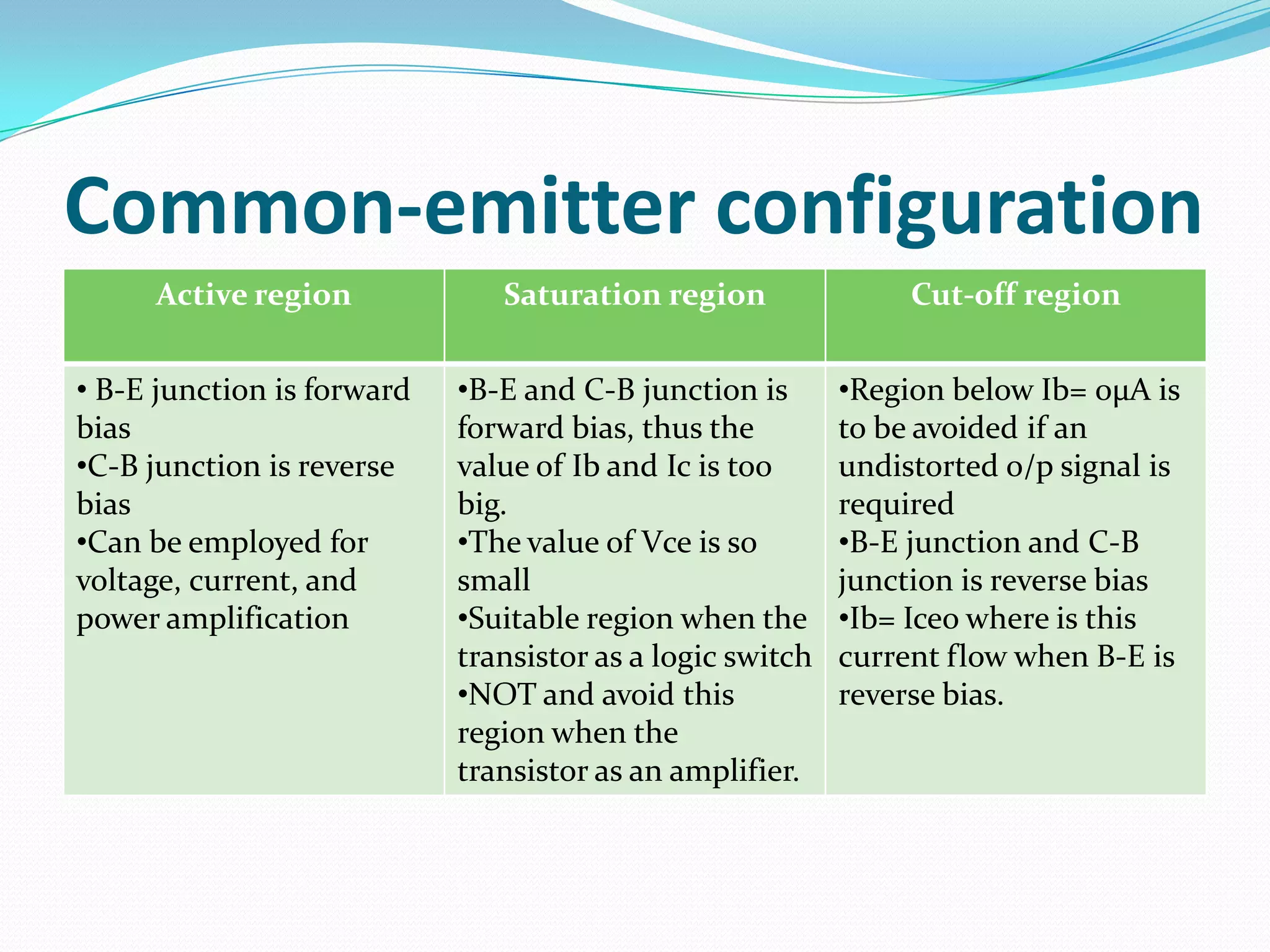
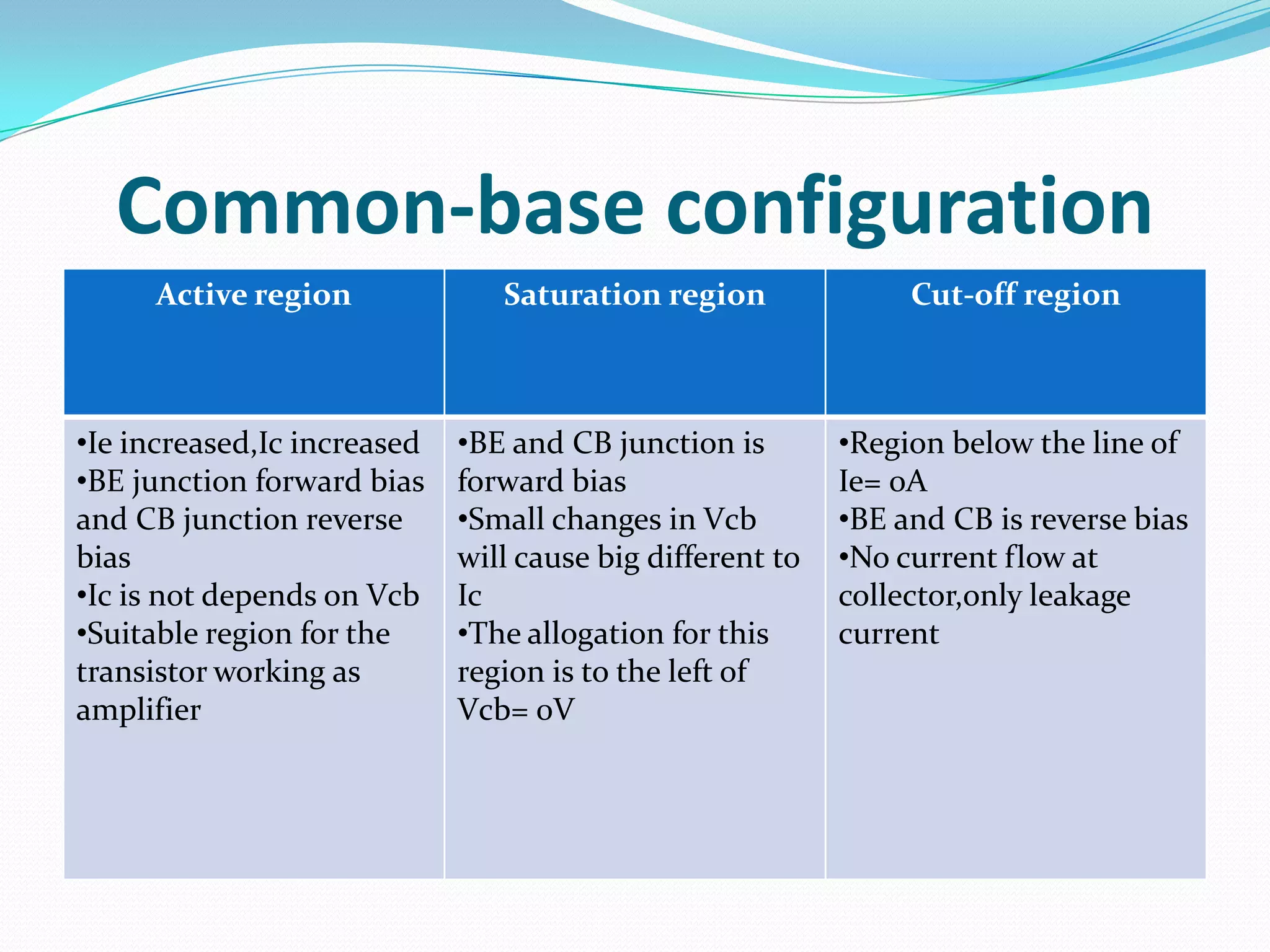
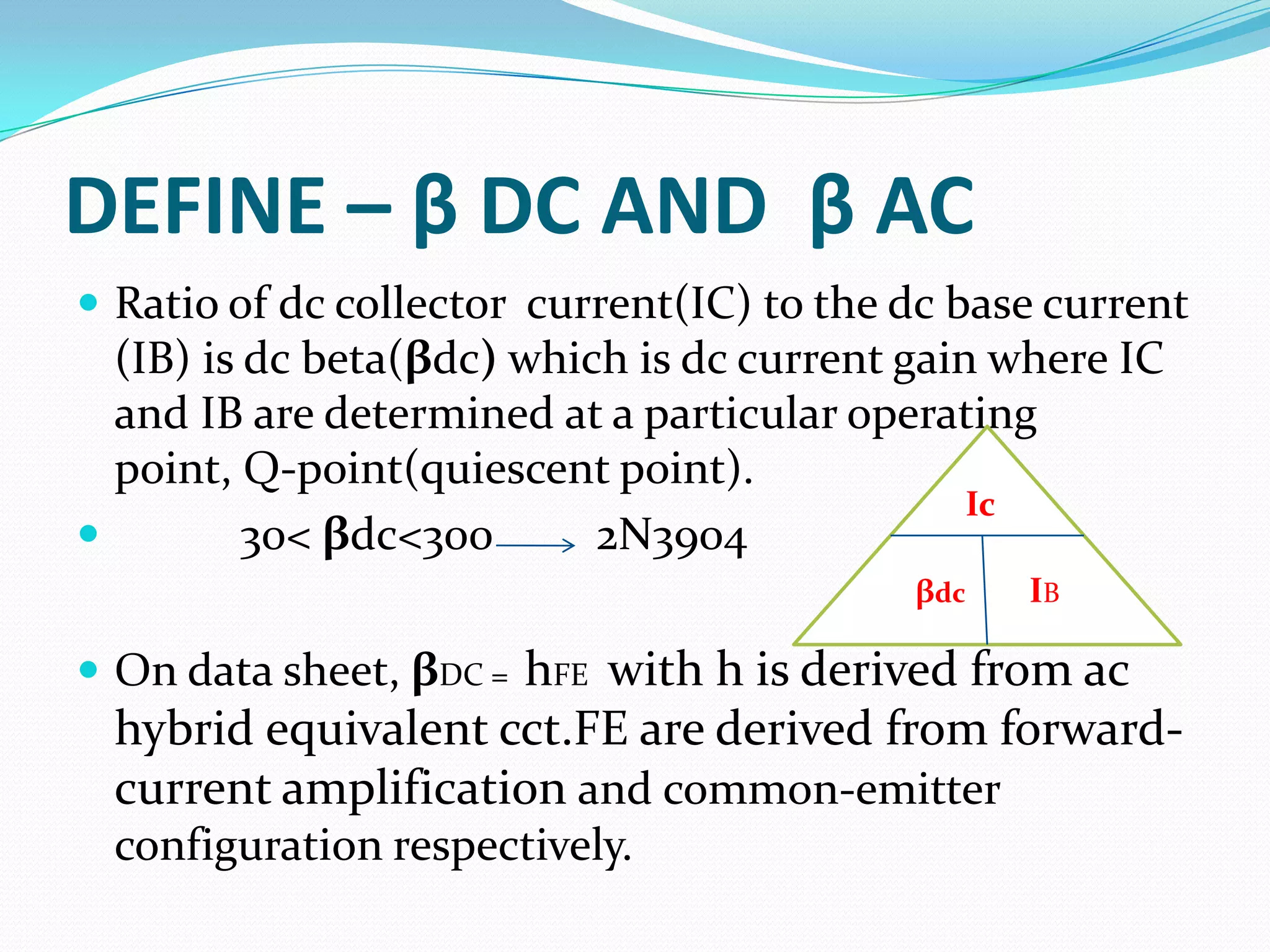
3) Key characteristics including current gain (beta) and the different regions of operation - cutoff, active, and saturation. BJTs are commonly used as linear amplifiers and switches.











![Voltage-divider bias
Because the base current is small, the approximatioon
V =[R2/R1+R2] Vcc is useful for calculating the base voltage.
B
After calculating VB, you can find VE by subtracting 0.7V for VBE.
Next, calculate IE by applying Ohm’s law to RE : IE=VE/RE
Then apply the approximation Ic=IE
Finally, you can find the collector voltage from Vc=Vcc-IcRc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit3-121031021149-phpapp01/75/Unit-3-25-2048.jpg)