A structure allows grouping of related data types together under one name. It can contain different data types as members. To define a structure, the struct keyword is used followed by the structure name and its members. Structures provide a way to organize data and pass it to functions by name rather than by index. Unions are similar to structures but allocate only enough memory for the largest member, so different members cannot coexist and overwrite each other's memory when accessed. Enumerations allow defining a set of named integer constants for clearer and safer code than #define.



![ struct person
{
char first[32]; //first field an array of chars
char last[32]; //second field an array of chars
int age; //third field an int
};
Note that the above code is only defining a
person structure. There are two ways
to declare a structure variable:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1adc-230519053825-06a319f3/85/Unit-1_ADC-pptx-5-320.jpg)



![ typedef struct
{
char first[32]; //first field an array of chars
char last[32]; //second field an array of chars
int age; //third field an int
}
person;
person student;
person teacher;
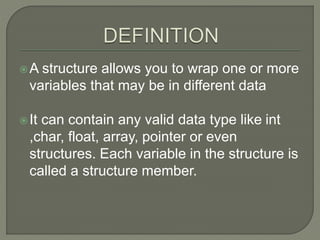
A structure allows you to wrap one or more
variables that may be in different data
It can contain any valid data type like int ,char,
float, array, pointer or](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1adc-230519053825-06a319f3/85/Unit-1_ADC-pptx-9-320.jpg)

![ person:
person student;
student.first = "Richard";
We can also use the dot operator to access a nested structure
and its members:
typedef struct
{
person teacher[0];
person students[50];
}
course;
course COMP2401;
COMP2401.students[0].first = "Richard";](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1adc-230519053825-06a319f3/85/Unit-1_ADC-pptx-11-320.jpg)






