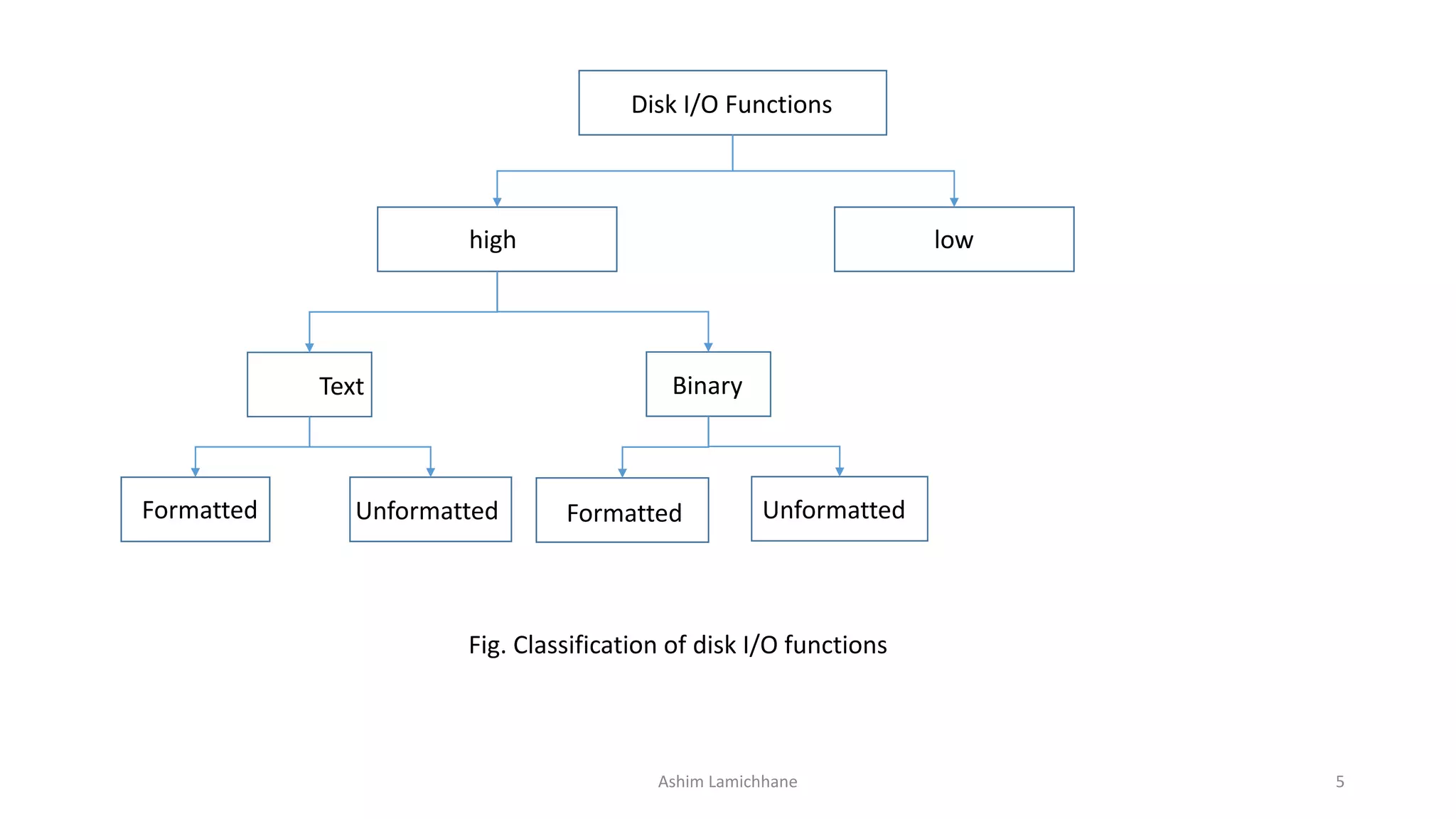
Unit 10 discusses files and file handling in C. It introduces the concept of data files, which allow data to be stored on disks and accessed whenever needed. There are two main types of data files: standard/high-level files and system/low-level files. Standard files are further divided into text and binary files.
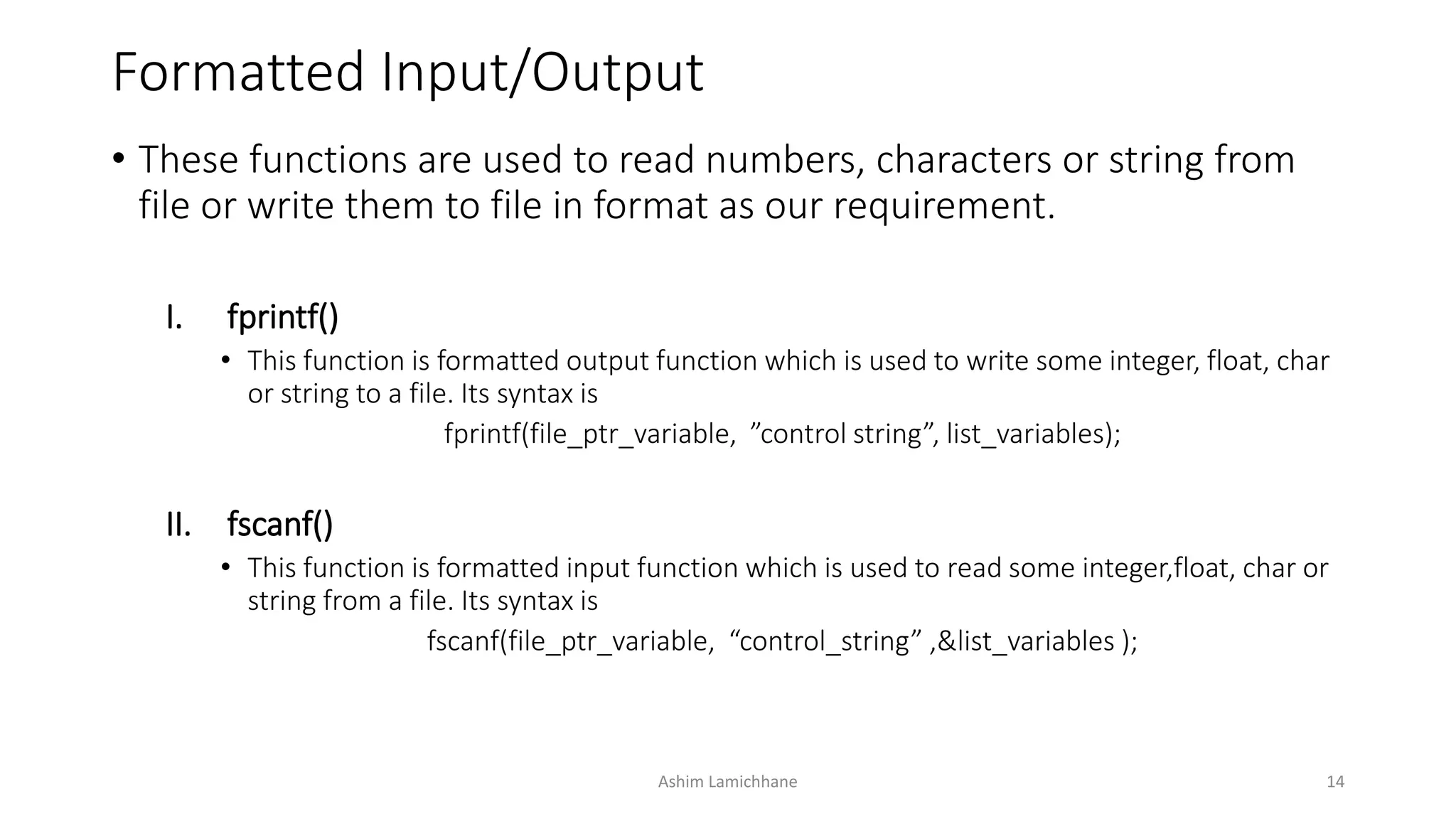
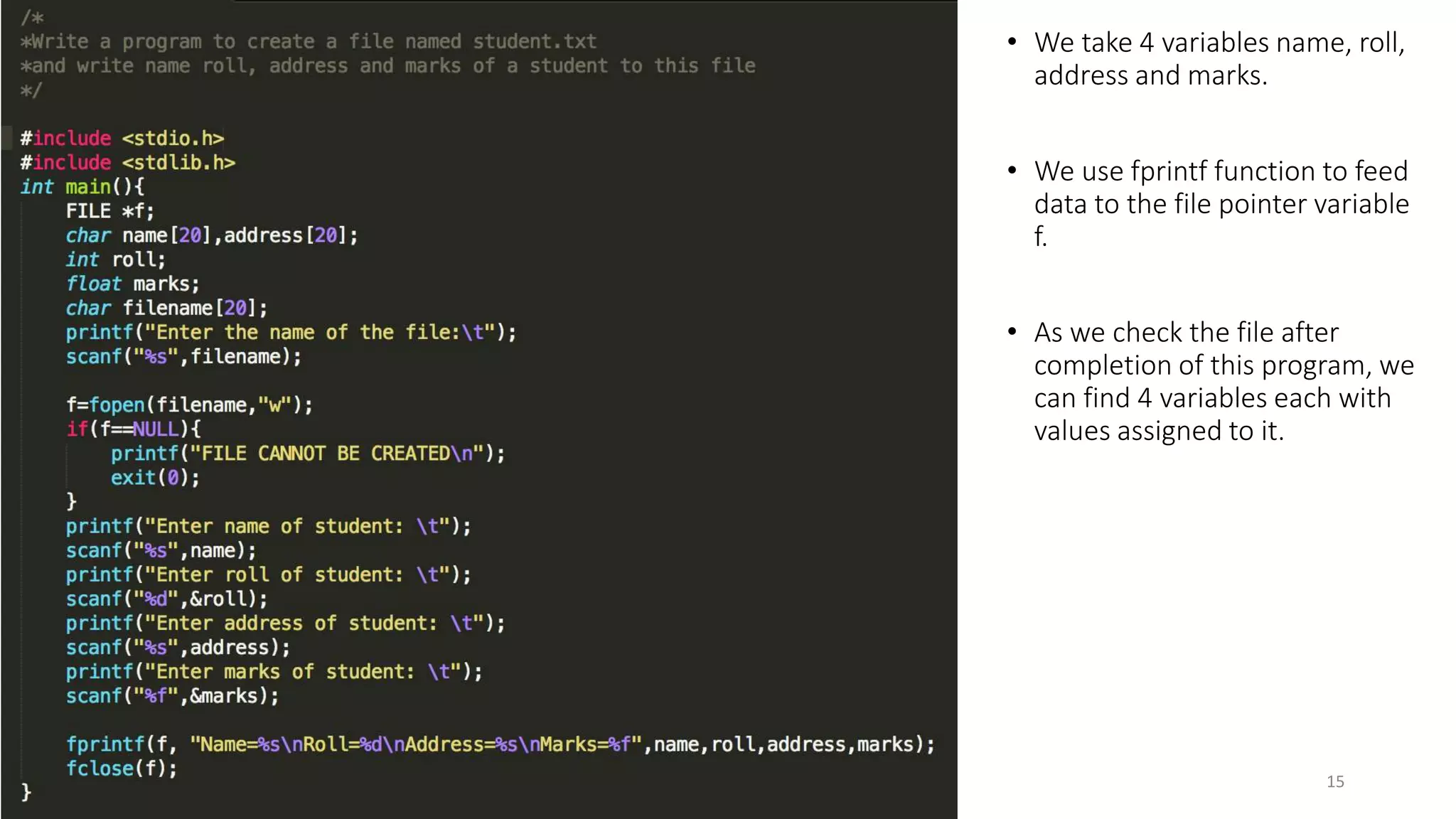
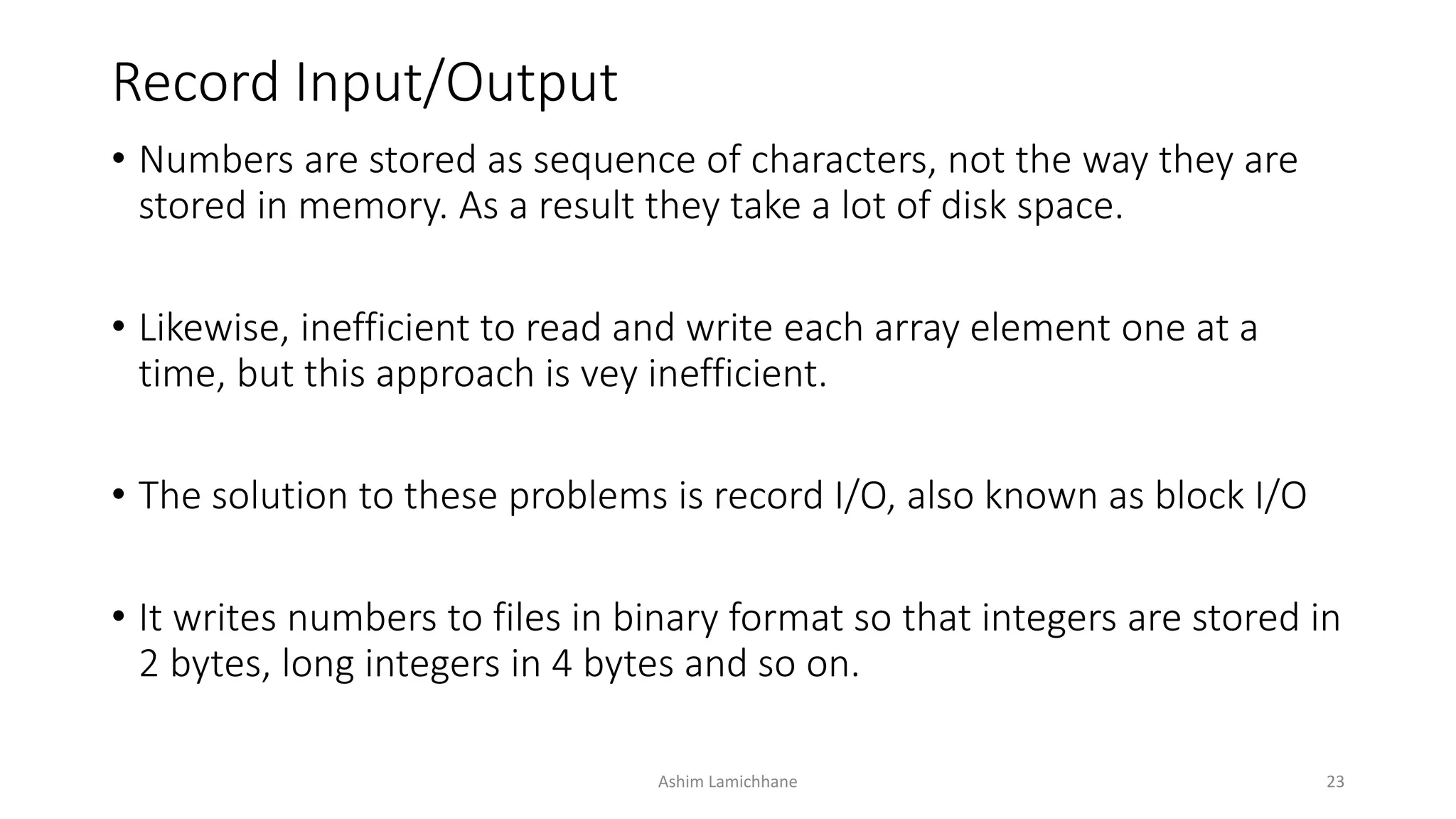
To read from or write to files, a program must first open the file. This establishes a link between the program and operating system. Various library functions allow reading, writing, and processing file contents, such as fopen() to open a file, fread() and fwrite() for record input/output, and fseek() to move the file pointer to different positions for direct access of














![Use of fwrite()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
FILE *f;
int num[10],i;
f=fopen("read","wb");
if(f==NULL){
printf("FILE CAN NOT BE CREATEDn");
exit(0);
}
printf("Enter 10 numbers:n");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&num[i]);
}
fwrite(&num,sizeof(num),1,f);
printf("n");
fclose(f);
}
Ashim Lamichhane 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandfilehandlinginc-160330191730/75/UNIT-10-Files-and-file-handling-in-C-26-2048.jpg)
![Use of fread()
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(){
FILE *f;
int num[10],i;
f=fopen("read",”rb");
if(f==NULL){
printf("FILE CAN NOT BE CREATEDn");
exit(0);
}
printf("Things read file:n");
fread(&num,sizeof(num),1,f);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%dt",num[i]);
}
printf("n");
fclose(f);
}
Ashim Lamichhane 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/filesandfilehandlinginc-160330191730/75/UNIT-10-Files-and-file-handling-in-C-27-2048.jpg)






