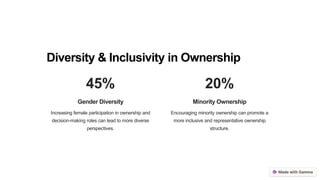
The document explains ownership structure, which refers to how a company's ownership is distributed among stakeholders, including various types of shareholders such as individuals and institutions. It highlights the importance of ownership structure for decision-making, corporate governance, and strategic planning while noting benefits like transparency and accountability. Challenges include conflicting interests and power struggles among stakeholders, with future trends indicating influences from technology and globalization.